基于微信平台信息共享对颈动脉易损斑块患者预后的影响
陈薇 应君芳 寻华音 王凤

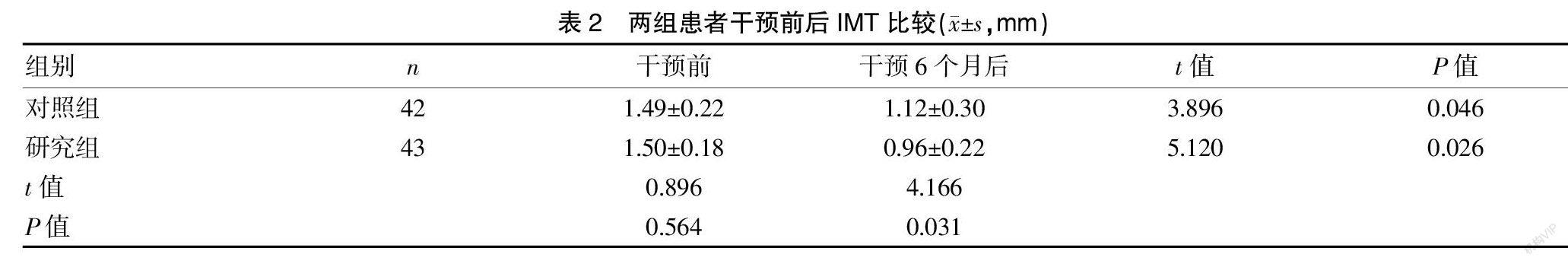
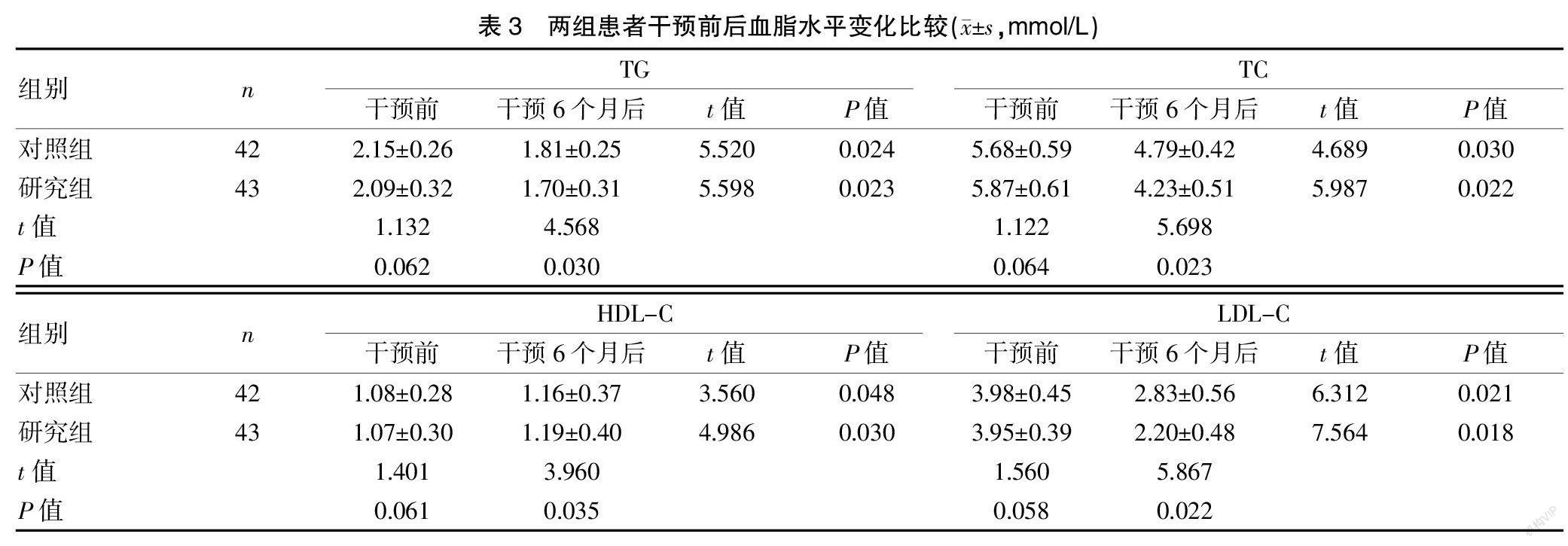
[摘要] 目的 探讨基于微信平台信息共享对颈动脉易损斑块患者预后的影响。 方法 选取2018年6月至2020年6月我院收治的颈动脉易损斑块患者85例作为本研究对象。采用随机数字表法将本研究对象分为研究组43例与对照组42例。对照组患者采用他汀类药物进行治疗,研究组在对照组药物治疗的基础上,给予基于微信信息共享的干预措施,统计比较干预前后各组的易损斑块的面积大小及斑块数量的变化情况,比較组间干预前后颈总动脉平均内中膜厚度(IMT),比较各组干预前后的血脂变化情况。 结果 干预6个月后,两组易损斑块面积大小均较干预前变小,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组易损斑块面积比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),干预6个月后,研究组易损斑块面积小于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后6个月,研究组斑块消失数量多于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。干预6个月后,两组IMT均较干预前降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组IMT比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),干预6个月后,研究组IMT低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。干预后6个月,两组三酰甘油(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)均较干预前降低,高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)较干预前升高,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组TG、TC、LDL-C、HDL-C比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后6个月,研究组TG、TC、HDL-C低于对照组,HDL-C高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 针对颈动脉易损斑块患者,在药物治疗的基础上给予基于微信信息共享的干预措施,可以改善治疗效果,降低不良心血管事件的发生,值得在临床上推广应用。
[关键词] 颈动脉易损斑块;颈动脉粥样斑块;脑梗死;微信平台;信息共享
[中图分类号] R743.3 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)24-0122-04
The impact of information sharing based on WeChat platform on the prognosis of patients with vulnerable carotid plaques
CHEN Wei1 YING Junfang2 XUN Huayin3 WANG Feng4
1.Service Center, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University, Taizhou 317000, China; 2.Department of Neurosurgery, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University, Taizhou 317000, China; 3.Department of Blood Purification, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University, Taizhou 317000, China; 4.Department of Neurology, Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University, Taizhou 317000, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the impact of information sharing based on WeChat platform on the prognosis of patients with vulnerable carotid plaques. Methods Ninety-five patients with vulnerable carotid plaques admitted to our hospital from June 2018 to June 2020 were selected as the study objects and divided into two groups by random number table method, namely 43 cases in the study group and 42 cases in the control group. The control group was treated with statins, while the study group was given WeChat information sharing based intervention measures on the basis of the same drug treatment as the control group. The changes in the area of vulnerable plaques and the number of plaques in each group before and after the intervention were statistically compared. Meanwhile, the mean intima-media thickness (IMT) in the common carotid artery and the changes in blood lipid before and after the intervention were compared between the two groups. Results After 6 months of intervention, the areas of vulnerable plaques in the two groups were smaller than those before the intervention, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). Before the intervention, there was no statistically significant difference in the areas of vulnerable plaques between the two groups(P>0.05). After 6 months of intervention, the areas of vulnerable plaques in the study group were smaller than those in the control group, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). During 6 months after the intervention, the number of plaques in the study group disappeared more than that in the control group, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). The IMT in the two groups after 6 months of intervention was lower than that before the intervention, with statistically significant difference (P<0.05). The IMT difference between the two groups was not statistically significant before the intervention(P>0.05). The IMT of the study group after 6 months of intervention was lower than that of the control group, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). The levels of triacylglycerol (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in the two groups during 6 months after the intervention were lower than those before the intervention, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) was higher than that before the intervention, all with statistically significant differences(P<0.05).There were no statistically significant differences in TG,TC,LDL-C, and HDL-C between the two groups before the intervention(P>0.05). During 6 months after the intervention, TG, TC, and HDL-C in the study group were lower than those in the control group, and HDL-C was higher than that in the control group,with statistically significant differences(P<0.05). Conclusion For patients with vulnerable carotid plaques, WeChat information sharing based intervention based on drug therapy can improve the treatment effect and reduce the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events. Therefore, it is worthy of clinical application.

