联合电刺激对脑外伤后昏迷患者促醒的临床疗效观察
陈琴 余晴 谢徐勇 程毛锋 梅卉子 杨珊 余鸿斌

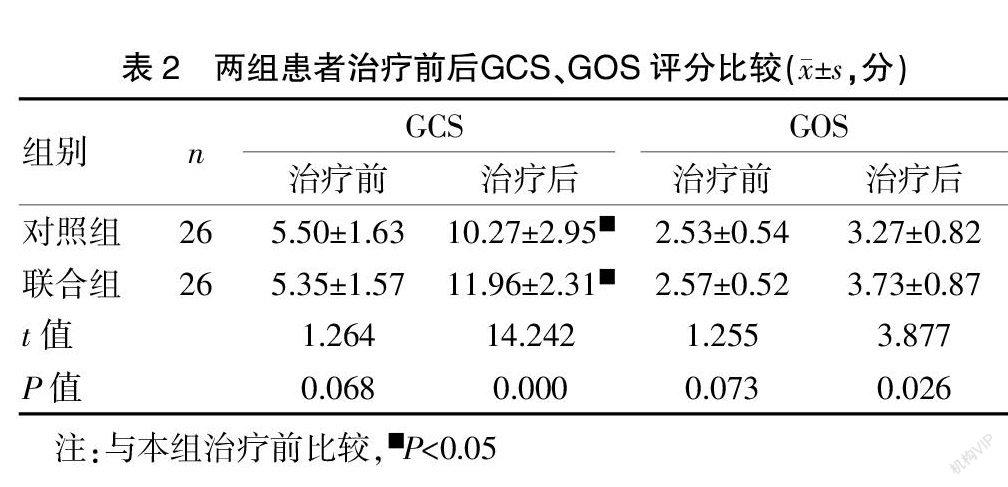
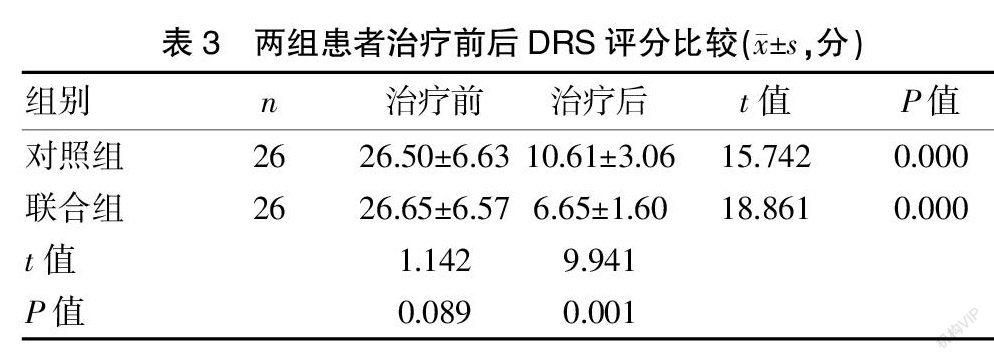
[摘要] 目的 探討正中神经电刺激(MNES)联合经颅直流电刺激(tDCS)治疗颅脑外伤(TBI)后昏迷患者的促醒疗效。 方法 选取2017年6月至2019年6月九江市第一人民医院康复医学科和神经外科脑外伤后昏迷患者52例,按照随机数字表法随机分为联合组和对照组,每组各26例。对照组患者接受常规康复治疗方法,联合组在对照组的基础上给予MNES和tDCS,共治疗4周。采用格拉斯哥昏迷量表(GCS)、格拉斯哥预后量表(GOS)、残疾评定量表(DRS)、脑干听觉诱发电位(BAEP)和上肢体感诱发电位(USEP)评估,并对两组临床疗效进行分析比较。 结果 治疗后,两组患者GCS评分均高于治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);且联合组GCS评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);治疗后,联合组GOS评分明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);治疗后,两组患者DRS评分均较治疗前降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),且联合组治疗后DRS评分低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);治疗后,两组患者BAEP、USEP评分均高于治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),且联合组治疗后BAEP、USEP评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);治疗后,联合组总有效率为88.46%,显著高于对照组的65.38%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 常规康复治疗能提高TBI后昏迷患者的意识水平,改善预后,在此基础上,增加MNES联合tDCS的干预方案治疗效果更显著,具有一定的临床推广价值。
[关键词] 经颅直流电刺激;正中神经电刺激;颅脑外伤;昏迷;促醒
[中图分类号] R742 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)24-0117-05
Observation on the clinical efficacy of combined electrical stimulation on awakening promotion of coma patients after traumatic brain injury
CHEN Qin1 YU Qing1 XIE Xuyong1 CHENG Maofeng2 MEI Huizi1 YANG Shan1 YU Hongbin1
1.Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Jiujiang No.1 People′s Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Jiujiang 332000, China; 2.Department of Neurosurgery,Jiujiang No.1 People′s Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Jiujiang 332000, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the therapeutic efficacy of median nerve electrical stimulation(MNES) combined with transcranial direct current stimulation(tDCS) on awakening promotion of coma patients after traumatic brain injury(TBI). Methods A total of 52 coma patients after TBI admitted to the department of rehabilitation and neurosurgery, Jiujiang first people′s Hospital, from June 2017 to June 2019 were selected and divided into the combined group(n=26) and the control group(n=26) according to the random number table method. Patients in the control group were treated with conventional rehabilitation therapy, while those in the combined group were treated with MNES and tDCS on the basis of the control group for totally 4 weeks. Glasgow coma scale(GCS), Glasgow outcome scale(GOS), disability rating scale(DRS), brainstem auditory evoked potential(BAEP) and upper limb somatosensory evoked potential(USEP) were adopted and evaluated, and the clinical efficacy of the two groups were analyzed and compared. Results After treatment, the GCS scores of patients in both groups were higher than before treatment, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). Meanwhile, the GCS score of the combined group was higher than that of the control group, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). After treatment, the GOS score of the combined group was significantly higher than that of the control group, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). After treatment, the DRS scores of patients in both groups were lower than those before treatment,with statistically significant difference(P<0.05), and the DRS score of the combined group was lower than that of the control group,with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). After treatment, BAEP and USEP scores of patients in the two groups were higher than before treatment, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05), and BAEP and USEP scores of the combined group were higher than those of the control group,with statistically significant differences(P<0.05). After treatment, the overall response rate of the combined group was 88.46%, which was significantly higher than that of 65.38% of the control group, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). Conclusion Conventional rehabilitation treatment can boost the consciousness level of coma patients after TBI and improve the prognosis. On this basis, the intervention scheme of MNES combined with tDCS has more significant therapeutic efficacy, which is worthy of clinical promotion to a certain extent.

