Vitamin D has synergistic effect on the expression levels of SIRT1 and CYP24A1 in human breast cancer
Mandana Ameli Mojarad,Melika Ameli Mojarad,Mahnaz Noourbakhsh
Abstract—Vitamin D has found to have a critical regulatory role in genes expression by modifying cell proliferation,differentiation, and apoptosis. In this study, by using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the expression levels of SIRT1 and CYP24A1 genes and their correlation with clinical feature were evaluated before and after the vitamin D treatment in breast cancer (BC) cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) and in tissues. Our results indicated that the transcription of CYP24A1 and SIRT1 were affected by vitamin D treatment and,CYP24A1expression showed a significant correlation with tumor stages(P=0.02).Moreover, CYP24A1, SIRT1 showed a high diagnostic values based on the large area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, (0.85, 0.77) respectively, in conclusion,CYP24A1and SIRT1 can be used as potential biomarkers in the assessment of BC, and vitamin D treatment showed a regulatory role on the expression of CYP24A1 and SIRT1in BC cell lines.
Keywords—Breast cancer,CYP24A1,SIRT1,Biomarker
I.INTRODUCTION
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among women worldwide, especially in developing countries[1]. Despite the recent treatment approaches including surgery,endocrine therapy,and targeted therapy,the overall number of people diagnosed with cancer nearly doubled in the past two decades, therefore, understanding the molecular pathways in the progression and pathogenesis of breast cancer(BC)is crucial[2].
Silent mating-type information regulation 2 homolog 1(SIRT1),is one of the seven sirtuins family members(SIRT1–7)with different physiological functions such as metabolism,neurogenesis and cell survival, genomic stability [3,4].SIRT1has been studied more than other categories in humans’cancers,such as prostate and colon cancer[5,6].Stud-ies show thatSIRT1can be regulated by the vitamin D receptor (VDR),it also can be a mediator of anti-proliferative vitamin D signals by deacetylation of forkhead box protein O3a(FOXO3a) which is a transcription factor and a key player in apoptosis and cell cycle regulation which can be regulated by D pathway[7].
CYP24A1is a mitochondrial inner membrane cytochrome P450 enzyme,CYP24A1gene encodes a key enzyme 1,25-hydroxyvitamin-D3-24-hydroxylase, responsible for the inactivation of active vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3)(calcitriol) [4].CYP24A1may be an important player in dysregulation of cell growth through decreasing the local cellular 1,25(OH)2D concentration, therefore loss-of-function mutations inCYP24A1lead to increased levels of active vitamin D metabolites[8]. Active form of vitamin D can affect cell differentiation, and proliferation, by regulating the expression of genes in tissue homeostasis [9].CYP24A1was found as an oncogene in human breast cancer and affected the expression level of different signaling molecules related to carcinogenesis, therefore, understanding how vitamin D metabolism dysregulated in cancer will help to develop efficient therapeutic strategies by using vitamin D [10].
In the present study,we aimed to investigate the expression levels ofCYP24A1,SIRT1, and their clinical significance in BC tissues and paired normal adjacent tissues. We also assessed the expression levels of the mentioned genes in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines after vitamin D treatment to understand the effect of vitamin D onCYP24A1,SIRT1gene expression.
II.MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics,consent,and permissions
The present study was approved by the Medical Ethical Committee of TMUS, Tehran, Iran. All the samples were collected with written informed consent from the informed patients for scientific research studies by protecting their privacy. Data from patients who had received any therapy before surgery were not included in the current study.
Tissue and clinical data collection
A total of 30 breast cancer patients’ tissues were included in this study between 2019 and 2020. Tumor tissues and the paired normal adjacent tissues were assessed by two experienced pathologists and were immediately frozen after collection. Clinical data were collected retrospectively. the study was approved by Rasool Akram Hospital, all patients provided informed consent.
Cell lines and culture conditions
The human Breast cancer MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A cell (as control), were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 5%CO2at 37°C incubator.
In brief, (1×105/well) of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were seeded into six-well plates for vitamin D treatment, we treat cells with 1,25-(OH)2D3.
RNA isolation and reverse transcription
Total RNA was extracted from fresh frozen tissues and cell lines by using a GeneAll Hybrid-RTMRNA purification kit (Geneall, Korea). The qualification and quantification of RNA were evaluated according to the A260/A280 ratio. Complementary DNA was synthesized from 1 μg of RNA using a Revert Aid First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit according to manufacturer-provided instruction(Qiagen GmbH,Hilden,Germany),
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction(q RTPCR)
For qRT-PCR we used SYBR Green method using SYBR Premix Ex Taq(TaKaRa,China)on ABI Step One Plus System(Applied Biosystems,Foster, CA) Primer sets for all transcripts were designed by the primer3 software are described onTable 1.Each reaction consisted of 10 μl 2×Real qPCR Master Mix,1 μl cDNA,1 μl of each primer(10 pmol), and 7 μl of nuclease-free water to conduct amplification in 20 μl of the reaction mixture.PCR condition was based on,one cycle at 95°C for 15 min,45 cycles of 95°C for 15 s,and 60°C for 60 s,and Beta-2 micro globulin(β2M)was used as reference gene.
Statistical analysis
We analyzed the experimental data as the mean±SD,with two independent experiments and ANOVA by using GraphPad Prism 8.0(GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA) and for evaluation of the diagnostic power of the selected genes,Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used. (P-value less than 0.05 were considered Statistically significant.
III RESULTS
Evaluating the CYP24A1 and SIRT1 levels, in patients’tissues,and cell lines
qRT-PCR. was used to discover the vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3) function onCYP24A1andSIRT1expressions, both in tissues and cell lines after and before the vitamin D treatment.CYP24A1,SIRT1expression were significantly upregulated in Breast cancer tissues and cell lines compared with paired normal adjacent tissues (P<0.0001)Figure 1. and (P< 0.05)FIGURE2, compare to normal cell line MCF-10A before and after the vitamin D treatment.
Gene expression level and clinicopathological characteristics Correlation
The correlations between theCYP24A1andSIRT1expression levels and clinicopathological features in 30 BC patients are shown inTables 2 and 3respectively. Based on our data, onlyCYP24A1expression was significantly correlated with tumor staging(P=0.02).
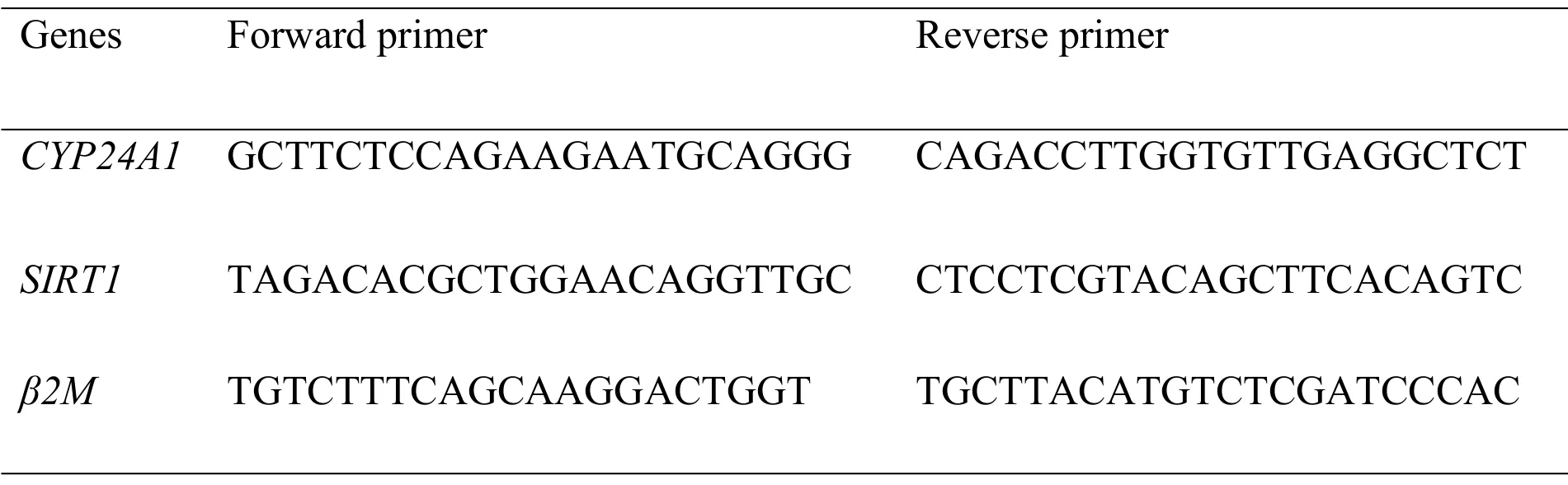
Table 1 Primer pairs for q RT-PCR1
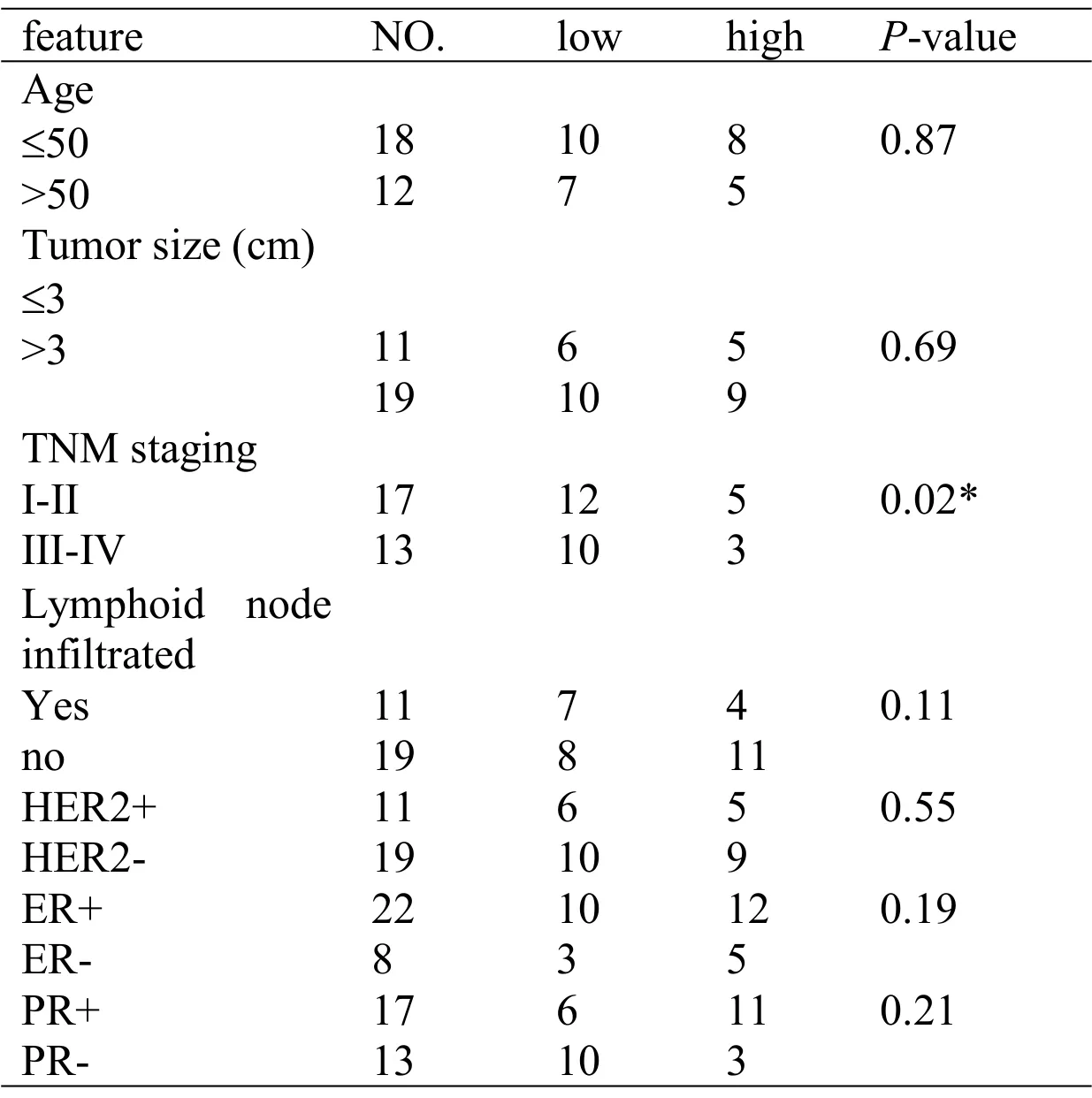
Table 2 The relationship between CYP24A1 expression level(as divided into two groups based on the median of ΔCt)in BC tissues with clinic pathological parameters
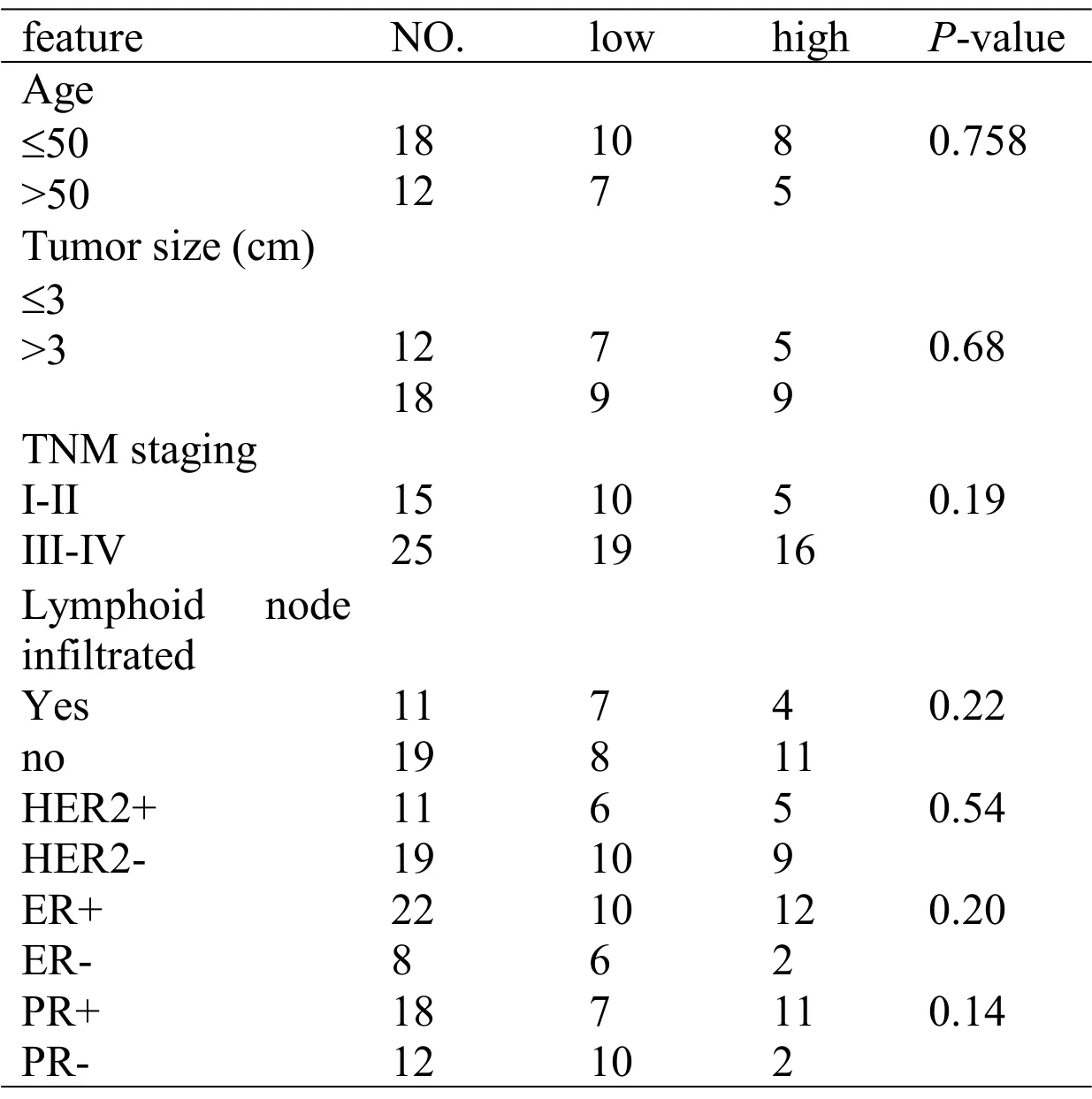
Table 3 The relationship between SIRT1 expression level(as divided into two groups based on the median of ΔCt)in BC tissues with clinic pathological parameters
The theraputic value of SIRT1 and CYP24A1,in BC
diagnostic values ofCYP24A1,SIRT1were evaluated by performing the ROC curve .The larger the area under the ROC curve (AUC), the higher the diagnostic value. ROC expression, The area under the ROC curve forSIRT1was 0.77 (Pvalue<0.0001)with the sensitivity and specificityof(0.63 and 0.77)and AUC ofCYP24A1was 0.85(Pvalue =0.0002)with the sensitivity and specificity of(0.83 and 0.73)respectively,shown inFigure3.
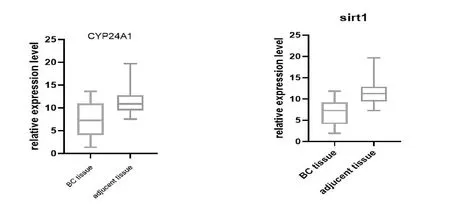
Figure 1:The Relative expression of CYP24A1,SIRT1,in BC samples compared with paired adjucent controls.The figure shows the the overall pregulation of candidate genes in BC samples compared with controls(P<0.0001)
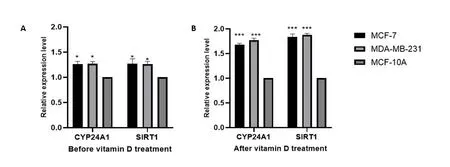
Figure 2.Effect of vitamin D(1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) on the expression of CYP24A1 and SIRT1.Expression of CYP24A1 and SIRT1 was upregulated in BC cell lines before vitamin D treatment (P<0.05)(A)expression of CYP24A1 and SIRT1 in breast cancer cell lines(MC7-MDA-MB-231)significantly induced compare to normal cell line MCF-10A after vitamin D treatment(p<0.0001)(B) *P<0.05,**P<0.0001
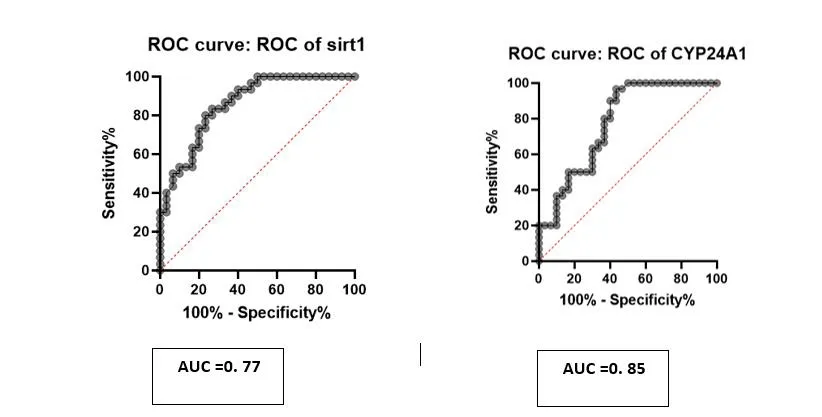
Figure 3: Potential diagnostic values of, SIRT1and CYP24A1 in Breast cancer. AUCs of ROCs 0.85 and 0.77 respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of CYP24A1,and SIRT1 were (0.83 and 0.73) and (0.63 and 0.77)respectively.
IV DISCUSSION
Breast cancer is the first common cancer among women worldwide. Due to the lack of proper biomarkers for early de- tection and screening, most patients are diagnosed at advanced stages so, it is crucial to diagnose BC in the early stages by discovering new effective biomarkers[2].
SIRT1a Type III histone deacetylase interacts with different signaling pathways, Many studies have shown thatSIRT1plays an active regulatory role in cell proliferation,differen- tiation, metabolism, and apoptosis, moreover overexpression ofSIRT1is related to ER-positive breast cancer cases[4,11].SIRT1is considered to have a vital role in tumor initiation,progression,and drug resistance by blocking senescence and apoptosis or promoting cell growth [12].
CYP24A1a mitochondrial inner membrane cytochrome enzyme is nominated as a candidate oncogene in cancer progression.Upregulation ofCYP24A1expression was found in different cancers, upregulation ofCYP24A1modulating variety of signaling molecules expression which is contributing with carcinogenesis, [13,14]. Data from previous studies reported two vitamin D-responsive elements(VDREs) upstream of theCYP24A1promoter. These VDRE sites are synergisti- cally involved in the regulation ofCYP24A1expression and play a critical role in the vitamin D metabolism pathway[15]. vitamin D (calcitriol), performs a different biological function by inducing apoptosis,modifying the calcium and phosphate homeostasis,regulating hormone-dependent genes, and inhibiting proliferation [16]. While Inhibitory role of vitamin D on cell proliferation may change to a stimulating role depending on the concentration and cell differentiation degree and the type of vitamin D metabolites[17]. In addition, vitamin D can upregulate the expression of a different growth factor such as Keratinocyte (KGF) to enhance the proliferation of cancer cells, However, the effect of vitamin D on modifying other genes is not investigated widely yet[18,19].
Previous studies, reported the overexpression ofCYP24A1andSIRT1in different malignancies including cancers. A study by Nour-LoueTant.et.al,reported the over expression ofCYP24A1gene in prostate cancer especially in advanced stages, and showed thatCYP24A1suppression promoted the antiproliferative effect of 1,25(OH)2D3in prostate cancer(20).
In another study overexpression ofCYP24A1was promoted after vitamin D treatment in colon cancer cell lines after 6 hrs.[21].In addition, overexpression ofCYP24A1was reported in colon cancer especially in carcinogenesis[22].SIRT1over expression was increased with Vitamin D supplementation treatment in vitamin D deficient type 2 diabetes patients ,and affects glucose metabolism in adipose tissue[23].
In the present research, for the first time we, demonstrated the effect of vitamin D treatment on the expression levels ofCYP24A1andSIRT1Compared with the normal adjacent tissues by using q-RT PCR, and emphasizingCYP24A1andSIRT1as a potential biomarker in BC.
Our results showed that the mRNA expression levels ofCYP24A1andSIRT1was significantly higher, compared with the normal adjacent tissue. the correlation analysis between gene expression levels and clinic pathological characteristics showed that onlyCYP24A1gene was correlated significantly with tumor stage (P= 0.02). AUCs results of ROC curve analysis was (0.83 and 0.77 respectively), which suggest thatCYP24A1,SIRT1have the potential role as a distinguish marker in BC. Therefore, combination ofCYP24A1, SIRTS,could be used for differentiate BC tissue from normal adjacent tissues. We also investigate the role of vitamin D treatment on the expression levels of these gens in BC cell lines(MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) compared with MCF-10A.Data showed vitamin D treatments significantly induced expression ofCYP24A1,SIRT1in cells.
In conclusion up-regulation ofCYP24A1,SIRT1expression in tissues may play important roles in BC progression and have the potential to be used as a diagnostic biomarker in distinguishing BC tissues from normal tissues and vitamin Dtreatment showed the modulator role on gene expression ofCYP24A1,SIRT1,despite the limitation of the sample size , therefore , further studies are needed to elucidate the role of vitamin D on other genes expression profile and its role in cell growth and cell differentiation in breast cancer.
Acknowledgments:
This project has been supported in part by a research grant from the Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Nos:TUM81224517)
Competing interests:
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Data availability statement:
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.
Author’s contributions:
MA and MA Authors contributed similarly to data collection.MN conceived and developed the idea for the paper and revised the manuscript. authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate:
This trial was approved by the ethics committee of the Tehran University of Medical Sciences A written informed consent form (in Persian) was obtained from all the patients.Participation was free, and a patient could withdraw at whatever point the person feels he/she was unable to continue.There was no bar for the patients to receiving the other health care services of the center. The personal information of patients was kept secret before, during, and after the study.
Citation:
Mojarad MA,Mojarad MA, Noourbakhsh M. Vitamin D has synergistic effect on the expression levels ofSIRT1andCYP24A1in human breast cancer.Prec Med Res.2021;3(3):11.doi:10.53388/PMR2021090801.
Executive editor:Na Liu.
Submitted:08 July 2021,Accepted:30 July 2021,Online:09 August 2021
©2021 By Authors.Published by TMR Publishing Group Limited.This is an open access article under the CC-BY license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/BY/4.0/).