MicroRNA expression in inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal cancer
Thais Gagno Grillo,Ana Elisa Valencise Quaglio,Rodrigo Fedatto Beraldo,Talles Bazeia Lima,Julio Pinheiro Baima,Luiz Claudio Di Stasi,Ligia Yukie Sassaki
Thais Gagno Grillo,Rodrigo Fedatto Beraldo,Talles Bazeia Lima,Julio Pinheiro Baima,Ligia Yukie Sassaki,Department of Internal Medicine,São Paulo State University(Unesp),Medical School,Botucatu 18618-686,São Paulo,Brazil
Ana Elisa Valencise Quaglio,Luiz Claudio Di Stasi,Department of Biophysics and Pharmacology,São Paulo State University(Unesp),Institute of Biosciences,Botucatu 18618-689,São Paulo,Brazil
Abstract MicroRNAs(miRNAs)are non-coding RNA molecules composed of 19–25 nucleotides that regulate gene expression and play a central role in the regulation of several immune-mediated disorders,including inflammatory bowel diseases(IBD).IBD,represented by ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease,is characterized by chronic intestinal inflammation associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer(CRC).CRC is one of the most prevalent tumors in the world,and its main risk factors are obesity,physical inactivity,smoking,alcoholism,advanced age,and some eating habits,in addition to chronic intestinal inflammatory processes and the use of immunosuppressants administered to IBD patients.Recent studies have identified miRNAs associated with an increased risk of developing CRC in this population.The identification of miRNAs involved in this tumorigenic process could be useful to stratify cancer risk development for patients with IBD and to monitor and assess prognosis.Thus,the present review aimed to summarize the role of miRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of IBD-associated CRC.In the future,therapies based on miRNA modulation could be used both in clinical practice to achieve remission of the disease and restore the quality of life for patients with IBD,and to identify the patients with IBD at high risk for tumor development.
Key Words:MicroRNA;Colorectal cancer;Inflammatory bowel disease;Crohn's disease;Ulcerative colitis;Cancer;Diagnosis;Prognosis;Targets
INTRODUCTION
MicroRNAs(miRNAs)are non-coding RNA molecules composed of approximately 19–25 nucleotides that are capable of regulating gene expression[1].MiRNAs are involved in biological functions such as embryonic development,proliferation,cell differentiation,metabolism,apoptosis,and stress response[2,3].The isolation of miRNAs is possible using various biological materials such as tissues,cells,and body fluids(tears,urine,serum,and plasma)[4].Polymerase chain reaction,in situhybridization,microarrays,and RNA sequencing are the main methods used to detect miRNA expression[1].
MiRNAs can downregulate mRNA[5]by binding to the 3′ untranslated region of the target mRNAs[6].As only one miRNA can regulate many mRNA targets,any minimal structural change can lead to major changes in cell homeostasis[7],disease evolution[8],and predisposition to neoplastic and inflammatory conditions[9-11].Alterations in miRNA expression have been described in several tumors,including colorectal cancer(CRC)acting as oncogenes or tumor suppressors[12].This expression is specific according to the tumor type and the surrounding tissue;thus,the study of tumor miRNAs helps to differentiate normal and tumor tissues and,in addition,reflects the degree of tumor differentiation[13].
Inflammatory bowel diseases(IBD),such as ulcerative colitis(UC)and Crohn’s disease(CD),are characterized by chronic intestinal inflammation associated with an increased risk of CRC.Tumor development is one of the most feared long-term disease complications,accounting for 15% of deaths in patients with IBD[14].UC patients are approximately 30 times more likely to develop CRC than the general population[15],the main risk factors being the extension and duration of the disease[16],family history of CRC[17],and the presence of primary sclerosing cholangitis(PSC)[18].Likewise,patients with CD are at a higher risk of small bowel cancer[19].
In IBD studies,miRNAs have been found to be involved in pathogenesis and can serve as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Recent studies have identified miRNAs associated with an increased risk of developing CRC in this population.The identification of miRNAs involved in this tumorigenic process could be useful to stratify cancer risk development for patients with IBD and to monitor and assess prognosis.Thus,this review article aimed to characterize the miRNAs expressed in IBD,CRC,and IBD-related CRC to better understand their role in the diagnosis and prognosis of these diseases,in addition to analyzing their potential as therapeutic targets.
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND MICRORNA EXPRESSION
IBD is a chronic disease involving the gastrointestinal tract,the pathophysiology of which is complex,encompassing environmental,genetic factors and the immune response[20],and comprises two specific diseases,UC and CD[20-22].There is no specific examination to establish the diagnosis of CD and UC,which requires the association of clinical,biochemical,endoscopic,radiological,and histologic data[23].Thus,a distinction between these two diseases can be challenging when inflammation is limited to the colon,and 10%–15% of IBD patients are classified as having indeterminate colitis[24].
In recent years,new biomarkers associated with easy application have been identified,such as miRNAs,to facilitate disease diagnosis and prognosis[25].However,the real role of miRNAs in IBD is not fully understood,and it is believed that some miRNAs might be common to both diseases,whereas others are unique to each,depending on the severity of disease activity and the tissue analyzed[26].Changes in miRNA expression in patients with IBD were first described by Wuet al[27]in 2008.The authors showed an increase in the expression of eight miRNAs(Let-7f,miR-16,miR-21,miR-23a,miR-24,miR-29a,miR-126,and miR-195)and a decrease in the expression of three miRNAs(miR-192,miR-375,and miR-422b)in colonic tissue samples from patients with active UC.In 2010,the same group[28]observed increased expression of miR-23b,miR106a,and miR-191 and decreased expression of miR-19b and miR-629 in colonic samples of patients with colonic CD and increased expression of miR-16,miR-21,miR-223,and miR-594 in terminal ileum samples of CD patients with active disease.In UC patients,miR-19a,miR-21,miR-31,miR-146a and miR-375 levels were found increased when compared with CD patients indicating these miRNAs as potential differential biomarkers for CD and UC[29,30].In addition to these studies,others studies have demonstrated changes in miRNA expression in the colonic tissue of patients with IBD[31,32].
Guoet al[31]evaluated the differential expression of miRNA in inflamed or noninflamed ileum mucosa of patients with CD and found decreased expression of miR-192-5p in those with inflammation.Among the alterations in the expression of miRNAs already observed,miR-10a,miR-192,and miR-320 seem to negatively regulate the inflammatory response by inhibiting the expression ofNOD2mRNA(domain 2 of nucleotide-binding oligomerization)[33-35].In contrast,miR-155,by activating the nuclear factor kappa B(NF-κB)signaling pathway,plays an important role in the progression of intestinal inflammation[36].Besides that,Luet al[37]showed that miR-155 was capable to decrease SH-2 containing inositol 5’ polyphosphatase 1(SHIP-1),an important phosphatase correlated with membrane trafficking,contributing to inflammation pathogenesis.
Shiet al[38]demonstrated that the miR-31/interleukin(IL)-25 signaling axis can regulate the Th1/Th17 IL-12/23-mediated inflammatory response in experimental colitis,indicating that a decrease in miR-31 expression with a consequent increase in IL-25 levels could be an alternative treatment for IBD.This pathway is also intricately linked to miR-155 and miR-223[39,40].
Pre-clinical studies have also been performed to evaluate the role of miRNAs in intestinal inflammation.Nataet al[41]administered miR-146b intraperitoneally to mice with dextran sodium sulfate(DSS)-induced intestinal inflammation and observed an improvement in the inflammatory process and intestinal barrier,demonstrating a potential use of miRNAs for IBD treatment[41].Additionally,Huanget al[42]observed the regulation of leukocyte infiltration and consequently a reduction in the inflammatory process with a intracolonic injection of miR-141 in mice[42].On the other hand,the use of an antagomir for miR-155,a small synthetic RNA complementary to miR-155 used to silence this miRNA,in the DSS-induced intestinal inflammation model improved intestinal inflammation indicating miR-155 as a possible target for IBD treatment[37].Jinet al[43]using miRNA mimics,namely miR-133a to target UCP2(mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2)observed a reduction in the severity of DSSinduced intestinal inflammation,suggesting that miRNA mimics are another therapeutic option for IBD patients[43].In another study with the DSS-model of intestinal inflammation,Tianet al[44]found a super expression of miR-31,results similar to what was found in inflamed mucosa from patients with CD or UC.
Besides that,levels of miR-301a were also increased in intestinal epithelial cells from patients with active IBD reducing the expression of BTG anti-proliferation factor 1(BTG1)and promoting Th17 cell differentiation through downregulation of Smad Nuclear Interacting Protein 1(SNIP1).BTG1 reduces epithelial integrity and promote inflammation in mouse colon and leading to tumorigenesis.This way,blockade of miR-301ain vivomay serve as a novel therapeutic approach in the treatment of IBD and colitis associated-CRC[45,46].
Some miRNAs act on the same inflammatory pathways as drugs currently used to treat IBD.MiR-29 has been described to comprise a family of miRNAs with the ability to decrease IL-23 levels[47,48],effects similar to ustekinumab and others antiinterleukin 12/23 used for the treatment of moderate to severe IBD.The blockade of integrin α4β7 in T helper lymphocytes has anti-inflammatory activity through the inhibition of leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells.Harriset al[49]observed that endogenous miR-126 could inhibit this adhesion through the regulation of VCAM-1 adherence[49,50],effects similar to those found with the use of vedolizumab,a monoclonal antibody that blocks integrin α4β7.Likewise,Pathaket al[51]demonstrated that miR-155 targets suppressor of cytokine signaling 1(SOCS1),a regulatory protein of the JAK signaling pathway[51],mimicking the use of JAK inhibitors currently available for UC treatment.
In addition to their possible application in clinical practice,some miRNAs can be used as predictors of the response to clinical treatment.Morillaet al[52]evaluated patients with severe UC and their response to corticosteroids,or infliximab and cyclosporine in those corticosteroid-refractory UC patients.The authors identified 15 miRNAs associated with the response to corticosteroids,six with the response to infliximab,and four with the response to cyclosporine,indicating that miRNAs can be used to screen patients according to the probability of responding to a specific medication.Cordeset al[53]evaluated the potential of miR-320a to monitor disease activity and predict the course of disease in patients with IBD,and found that blood levels of miR-320a were significantly increased in patients with active CD and UC when compared to healthy controls assessing the role of miRNA in monitoring inflammatory activity.Moreover,miR-320a levels were strongly correlated with endoscopic disease activity in both CD and UC patients,highlighting the use of miRNA as a noninvasive tool useful in monitoring disease activity in these patients.
New studies have evaluated the role miRNAs in fecal samples of IBD patients.Verdieret al[54]analyzed more than 800 miRNAs in fecal samples from control individuals and patients with IBD with levels of miR-223 and miR-1246 significantly increased in fecal samples from patients with active IBD.Furthermore,the miRNAs were correlated with clinical disease activity scores,such as the Mayo score,and fecal calprotectin levels in these patients,indicating that miRNAs from fecal samples might be a new noninvasive and easy fecal biomarker for monitoring IBD activity.MiR-223 was also identified as a fecal marker in a study by Schönauenet al[25],in addition to miR-155 and miR-16.A summary of miRNAs found altered in each disease is shown in Table 1[55-61]and Table 2[62-69].

Table 1 Expression of altered miRNAs in colonic tissue in patients with Crohn's disease

let-7b Decreased[59]miR-10a Decreased[33]miR-18a Decreased[59]miR-19b Decreased[28]miR-26a Decreased[32]miR-140-3p Decreased[59]miR-143 Decreased[60]miR-192-5p Decreased[31]miR-194b Decreased[58]miR-203 Decreased[61]miR-216b Decreased[58]miR-320a Decreased[34]miR-320b Decreased[34]miR-320c Decreased[34]miR-375 Decreased[27]miR-548e Decreased[58]miR-559 Decreased[58]miR-629 Decreased[28]
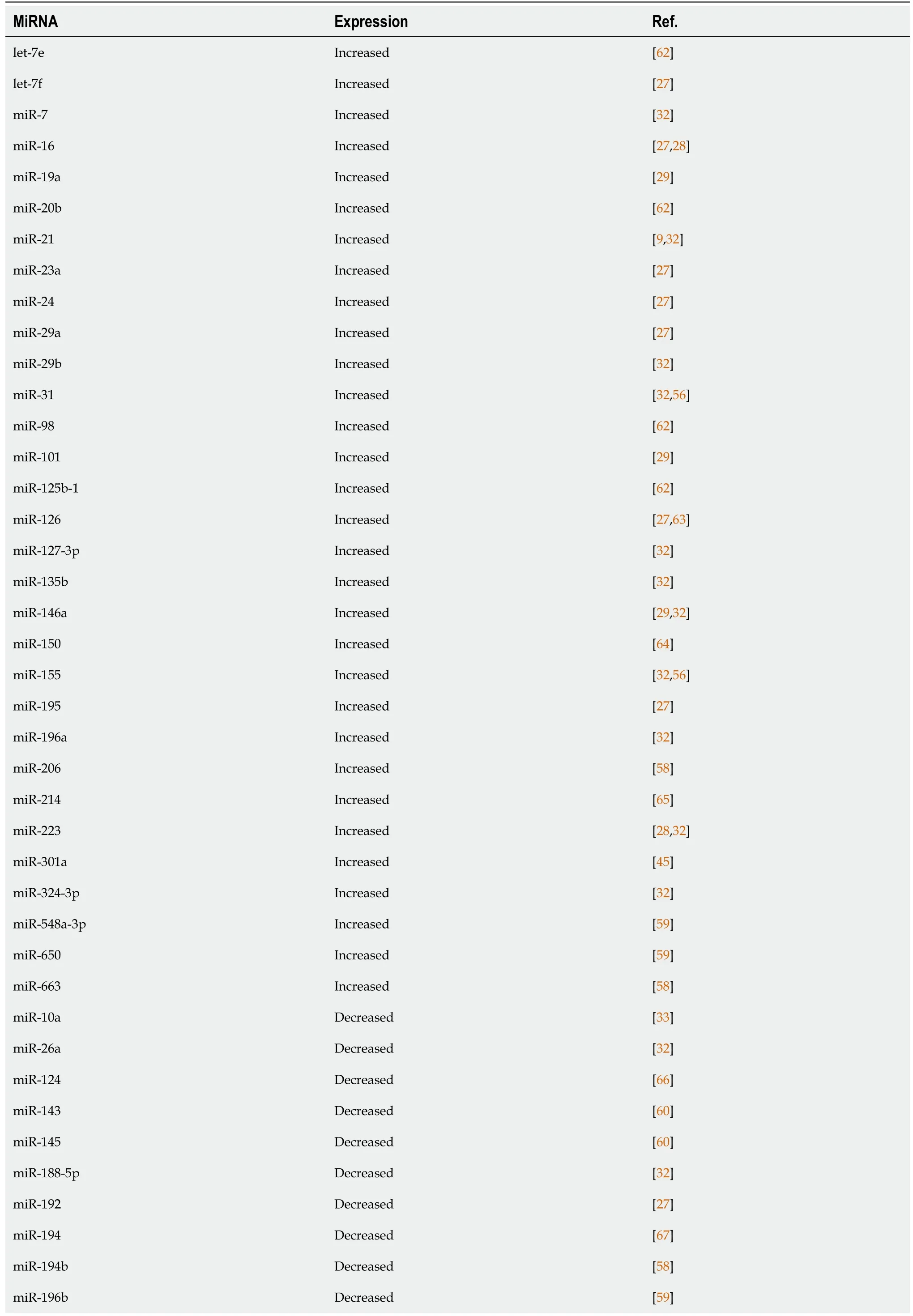
Table 2 Expression of altered miRNAs in the colonic tissue of patients with ulcerative colitis
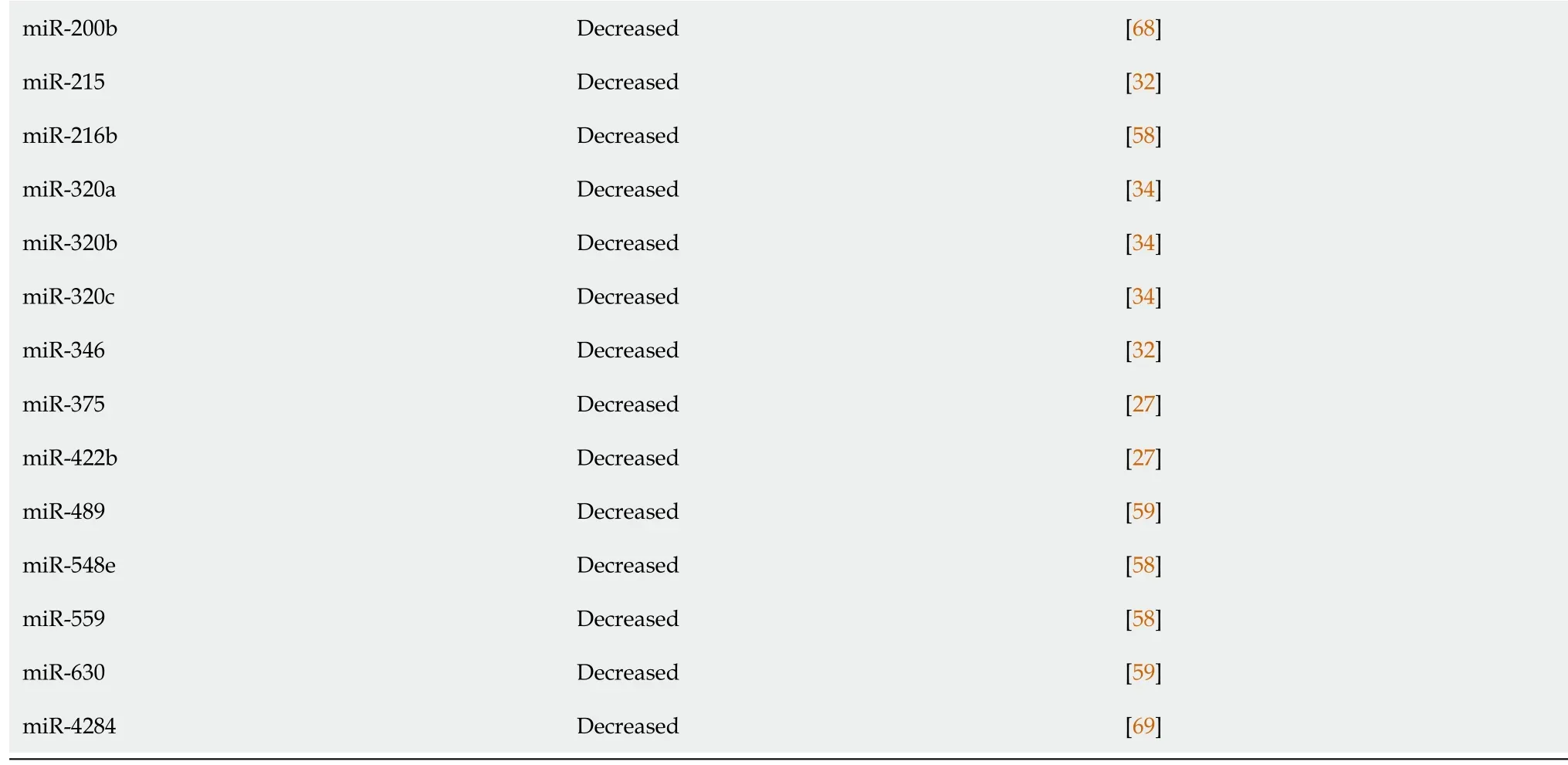
miR-200b Decreased[68]miR-215 Decreased[32]miR-216b Decreased[58]miR-320a Decreased[34]miR-320b Decreased[34]miR-320c Decreased[34]miR-346 Decreased[32]miR-375 Decreased[27]miR-422b Decreased[27]miR-489 Decreased[59]miR-548e Decreased[58]miR-559 Decreased[58]miR-630 Decreased[59]miR-4284 Decreased[69]
The future treatment of IBD involves the application of pharmacological strategies to control or even stop the progression of inflammation and to improve sensitivity to the therapy.This could occur,for example,through anti-miRNA oligonucleotides to inactivate miRNAs association with increased expression in the inflammatory process or increase the expression of suppressor miRNAs[70].The alteration of immune system cells by miRNAs is also a factor for inflammation[71].Thus,tracking the immune status in IBD based on miRNA alterations may be powerful for designing individualized therapies[72].
Taken together,these differences in the expression of miRNAs in UC and CD patients are relevant from the moment they lead to the emergence of biomarkers for diagnosis and therapeutic targets,aiming to improve the management of IBD;however,larger and more consistent studies are necessary for their implementation in clinical practice[60,72].
CRC AND MICRORNA EXPRESSION
CRC is the second most common cancer in women and the third in men,with higher rates in developed countries,and is responsible for approximately 900000 deaths each year[73].An increase in the global incidence to 2.5 million new cases is expected in 2035[74,75],mainly due to an increase in exposure to risk factors.Obesity,physical inactivity,smoking,alcoholism,aging,and eating habits are some of the main risk factors for the appearance of tumors[73].Genetic factors are also involved,such as the presence of a positive family history in 10%–20% of the cases[76]and hereditary syndromes in 5%–7% of the cases[77].Patients with long-standing IBD constitute a risk group due to the presence of the inflammatory processes and the use of immunosuppressive drugs,with CRC being responsible for 15% of deaths in this population[14].
The development of CRC results from an evolutionary period of approximately 10–15 years and originates,in most cases,from alterations to the crypt pattern thatevolves to a pre-neoplastic lesion(polyp)and later to a tumor[78,79].Precursor lesions appear in two ways.The first isviaadenoma-carcinoma,responsible for 70%–90% of tumors and related to an adenomatous polyposis coli(APC)gene mutation with the subsequent activation of RAS and loss of tumor suppressor p53(TP53)function;the second is through a serrated neoplasia,which is responsible for 10%–20% of cases[73,80]and is mainly related to RAS and RAF mutations[73].
It has also been noted that changes in cell homeostasis due to genetic changes lead to the activation of oncogenes and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes[78,79].WNT signaling pathways,epidermal growth factor(EGFR),the TP53 complex,and transforming growth factor beta(TGF-β)are implicated in the carcinogenesis of CRC[81].The WNT pathway is related to the regulation of stem cell activity in intestinal crypts,and inadvertent signaling by this pathway leads to the inhibition of cell differentiation and death,leading to the development of polyps and consequently carcinoma[82,83].
It was noted that marked expression of miR-135b,which activates the WNT pathway is involved in sporadic and inflammatory CRC and is related to the tumor stage and a worse prognosis[84].The EGFR signaling pathway is also responsible for cellular activities and is related to certain oncogenes,predominantly Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog(KRAS),for which mutations are present in approximately 30%–40% of CRC cases,resulting in worse prognosis[85].It is also important to note that KRAS seems to be regulated by isoforms of the let-7 family,such as let-7a,which when deregulated,contributes to colorectal carcinogenesis[86].
Senescence,cell cycle arrest,apoptosis,invasion,and metastasis are related to TP53 when cells are subjected to stress[87].Some of the miRNAs that participate in the TP53 pathway include let-7i,miR-20a,miR-21,miR-25,miR-34a/b/c,miR-145,miR-181b,miR183,miR-195,miR-215,and miR-451 with a special attention with miR-34 family.Activation of TP53 by miR-34a has already been observed in several types of cancer,especially CRC,with a overexpression of this miRNA in those patients[88].Finally,the TGF-β pathway regulates activities such as proliferation,differentiation,and apoptosis,and miRNAs that regulate the TGF- β receptor 2(TGFBR2)have been identified,including miR-17-5p,miR-20a,miR-21,miR-23b,miR-106a,and miR-301a[89].
There are specific molecular expression profiles in CRC cells compared to those in non-tumor cells.Among the overexpressed miRNAs,miR-106,miR-31,miR-21,miR-25,miR-20a,miR-93,miR-183,and miR-203 have been identified,whereas those with reduced expression include miR-1,miR-126,miR-30a,miR-143,miR-145,miR-191,and miR-192[81].A reduced expression of miR-192 seems to be related to an increase intumor size[90],and a reduced expression of miR-145 was determined to be related to invasion,metastasis,degree of differentiation,and tumor size[91],demonstrating the relationship between specific miRNAs and tumor behavior.
It is believed that there is a difference in miRNA expression based on the stage of the tumor.For example,overexpression of miR-92a can be a biomarker for the early diagnosis of CRC[92],whereas the overexpression of miR-21 and miR-31 is associated with advanced CRC[93,94].According to that,Tsukamotoet al[95],demonstrated that the overexpression of exosomal miR-21 showed a significant association with liver metastasis and TNM stage in CRC patients being associated with a decrease in the overall survival and disease-free survival rates.Besides that,as a proangiogenic miRNA,miR-21 targets the programmed cell death protein 4(PDCD4)gene enhancing invasion,intravasation and metastasis[96].
Giráldezet al[97],in turn,showed a positive correlation of appearance of distant metastasis in advanced CRC patients and miR-103 overexpression.Besides that,miR-29a also presented overexpressed in metastatic CRC patients when compared to nonmetastatic ones[98],and plasmatic expression of miR-203 and miR-141 could help in the differentiation of early and advanced CRC as demonstrated by Sunet al[99]In addition to these alterations correlated with stage of the tumor,there are also changes related to the response to treatment.MiR-1914-3p and miR-1915-3p were found downregulated in plasma samples from patients with chemo resistant CRC.This way,up-regulation of miR-1914-3p and -1915-3p reduces the chemoresistance abilities of chemo resistant CRC cells and may represent a possible therapy and diagnosis tool in CRC[100].
Alteration in angiogenesis is a contributing factor to tumor development,supporting proliferation,growth,dissemination,and metastasis[101,102].MiRNAs are thought to participate as regulators of angiogenesis,acting both as antiangiogenic and proangiogenic[103,104],directly influencing endothelial cells or indirectly modulating protein expression[104],which makes them an interesting pathway in antiangiogenic therapies[105].Non-responding bevacizumab(antibody anti-vascular endothelial growth factor A(VEGF-A)patients had increased levels of miR-126 correlated with an increase in tumor size[106].On the other hand,miR-140-5p showed a tumor suppression role in CRC,targeting VEGF-A/MMP-2 pathway,and leading to inhibition of tumor progression and angiogenesis[107].Additionally,miR-497 also blocks VEGF-A/ERK/MMP-9 pathway with reduction on angiogenesis,invasion,and metastasis in CRC[108].
Tumor growth depends on angiogenesis and the formation of new blood vessels,to ensure a continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients.This way,antiangiogenic agents are used to treat cancers,either alone or in combination[109].However,the mechanistic details of how these combination therapies work are far from clear,and the lack of validated prognostic and predictive biomarkers represents one of the greatest obstacles in determining treatment outcomes and optimal response[109,110].Based on that,miRNAs could serve as new predictive biomarker,therapeutic targets as an antiangiogenic therapy,or screening tools for immune-based therapies[111].
MiRNAs stability and predictive property make them ideal serum and plasma biomarkers in cancer patients,and they may be useful in predicting patterns of sensitivity and resistance to anti-cancer drugs[112].This has brought attention to future personalized treatment strategies targeting miRNA expression in these patients.Thus,the identification of miRNAs as a tool for the early detection,prognostic evaluation,and treatment of CRC has gained clinical importance in recent years[81].
A summary of miRNAs found altered in CRC is shown in Table 3[113-141].
IBD,CRC,AND MICRORNA EXPRESSION
Chronic inflammation is a contributing factor to carcinogenesis;therefore,patients with IBD,and especially those with colonic involvement,are at an increased risk for CRC,which is responsible for approximately 15% of deaths in this population[14].However,the exact mechanisms underlying this relationship have not yet been fully elucidated[20,142].Among the risk factors involved,we can emphasize a positive family history of CRC,long disease duration,colonic involvement,the presence of PSC,and the presence of disease activity[142].For this reason,screening colonoscopy should be performed 8 years after the onset of symptoms in all patients with IBD to detect dysplasia in the early stages,with subsequent surveillance ranging from 1–5 years according to individual risk stratification[16].Patients with IBD-associated PSC must undergo annual endoscopic surveillance after the diagnosis of PSC because of the increased risk of developing CRC[16].
The accumulation of reactive oxidative species from continuous cycles of inflammation and tissue repair results in damage to DNA,proteins,and lipids,leading to tumor development in patients with UC[143].The progression of colitis-associated CRC occurs through processes that are perpetuated by the absence of dysplasia,undefined dysplasia,and low-and high-grade dysplasia until it progresses definitively to cancer[144].Therefore,despite adequate surveillance,detecting dysplasia in these patients is difficult owing to difficulties in distinguishing lesions from the adjacent inflamed mucosa and foci of constant tissue regeneration and repair caused by the inflammatory process[145].In 2010,O’ Connoret al[146]observed that chronic inflammation in these patients exposed them to tumorigenic traits based on the NF-κB pathways and inflammatory mediators such IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha(TNF-α).Oxidative stress,the activation of survival pathways,apoptosis,and the formation of a tumorigenic environment have been found to be involved in carcinogenesis.Changes in P53 gene occur early and can be detected before the onset of dysplasia,being identified in 47–85% of patients with colitis-associated CRC[146,147].
The release of cytokines resulting from chronic inflammation is related to the development of all stages of cancer,such as initiation,promotion,angiogenesis,and metastasis,and the transcription factor NF-κB is a primary factor in the inflammation/cancer cascade[146].In addition to the involvement of molecular mediators in the inflammation/cancer relationship,such as cytokines,growth factors,Toll-like receptors(TLRs),Pl3K/MAPK signaling,and transcription factors(NF-κB/STAT3,P53,c-Myc,and Wnt/β-catenin),among others[148],it is worth noting that cellular changes caused by a chronic inflammatory status in patients with IBD also contribute to the development of the tumor[149].
MiRNAs are believed to participate in the intestinal inflammation of IBD patients and contribute to the inflammation/tumor process.The identification of miRNAs involved in this tumorigenic process could be useful to stratify the risk of tumor development in patients with IBD and monitor and assess the prognosis of cases.Figure 1 and Table 4 shows the miRNAs found altered in UC,CD,CRC,and IBDassociated CRC summarizing the alterations described for each condition and the relationship between them.
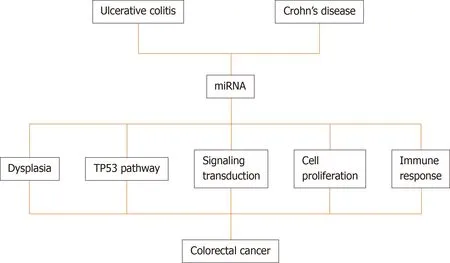
Figure 2 A schematic diagram showing the pathways modulated by miRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease-related colorectal cancer progression.
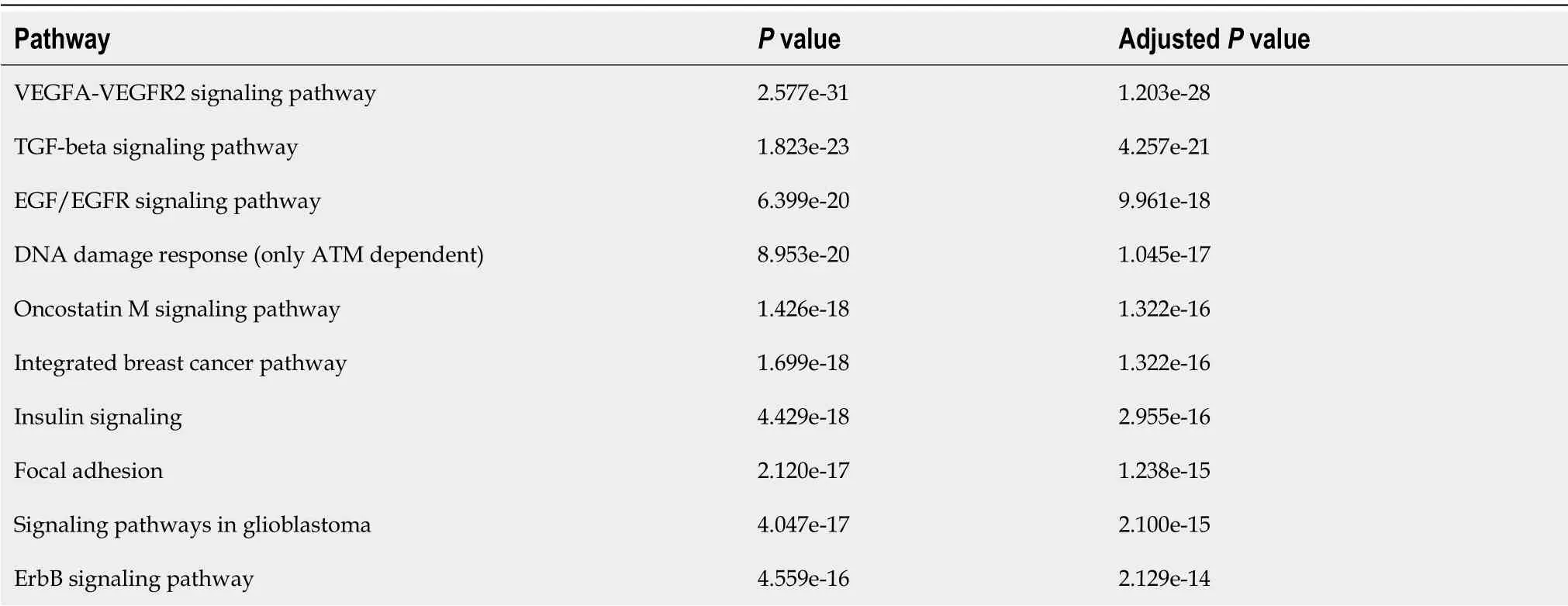
Table 5 Enrichment analysis of the target genes of the altered microRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal cancer
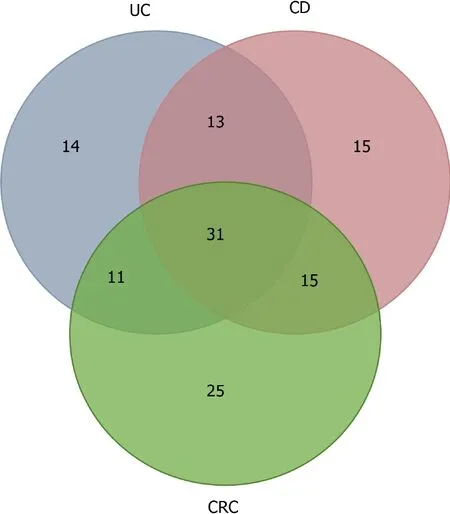
Figure 1 Venn diagram showing microRNAs differentially expressed in patients with ulcerative colitis(14),Crohn’s disease(15),colorectal cancer(25),and,in the intersections,shared microRNA by ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease(13),ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer(11),Crohn’s disease and colorectal cancer(15)and inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal cancer(31).UC:Ulcerative colitis;CD:Crohn’s disease;CRC:Colorectal cancer.

Table 3 Expression of altered miRNAs in the colonic tissue of patients with colorectal cancer
miR-20a[113,119,131]miR-21[9,32,132]miR-210[133]miR-212[133]miR-214[65,123]miR-215[32,90,121]miR-218[115]miR-222[117]miR-223[28,32,120,121]miR-224[117,121]miR-23b[28,114]miR-25[117,124]miR-27a[117]miR-27b[115]miR-29a[27,114,117]miR-29b[29,114]miR-30a[32,115]miR-30c[32,115,120]miR-31[32,56,128]miR-32[120,134]miR-320a[34,135]miR-328[59,134]miR-34a[136]miR-375[27,137]miR-422a[59,113,116]miR-422b[27,138]miR-424[118,123]miR-451[114,116]miR-490-3p[115,121,125]miR-497[115]miR-506[139]miR-552[121,134,140]miR-650[59]miR-7[32,123,140]miR-885-5p[59]miR-892b[115,121]miR-92a[119,141]miR-93[113,124]miR-95[117,123]miR-96[121]miR-98[62,113,117]

Table 4 MicroRNAs differentially expressed in ulcerative colitis,Crohn’s disease and colorectal cancer,and shared by ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease,ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer,Crohn’s disease and colorectal cancer and inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer
The first study on the differential expression of miRNAs in IBD and CRCprogression from non-neoplastic mucosa to dysplasia and invasive cancer was published in 2012[150].Using naïve immunotherapy patients from CD or UC and tree types of tissue(non-neoplastic,dysplastic and neoplastic)from each patient,the authors observed that five miRNAs(miR-193b,miR-373,let-7e,miR-15b,and miR-372)were significantly downregulated in both diseases,correlated with the progression from non-neoplastic tissue to dysplasia and from dysplasia to cancer[150].In CD patients,during non-neoplastic to dysplasia progression,miR-181a,miR-146b-5p,let-7e,and miR-17 were found to be upregulated,on the other hand,during the progression from dysplasia to cancer,let-7e,miR-17,and miR-143 were downregulated.From the deregulated miRNAs,let-7e,miR-15b,miR-17,miR-122,miR-124,andmiR-372 had a tumorigenic effect on the TP53 pathway[150].
Baiet al[151],integrated genome-wide gene expression profiles and biological pathway information to explore the associations among UC,CD and CRC at function and gene level,and found 34,20 and 47 risk pathways for UC,CD and CRC,respectively.Furthermore,the authors found that UC and CD share 16 pathways,indicating that the two inflammatory diseases are strikingly linked with each other at the biological pathway level.On the other hand,more pathways were shared between CRC and UC compared to CRC and CD,which might suggest that UC has a potential functional link with CRC.Pathways for UC and CRC were mainly related to the immune system and metabolism like the Intestinal immune network for IgA production[151].
When analyzing the correlation between miRNA and the risk pathways,four miRNAs participate in all three diseases(miR-146a,miR-335,miR-26b and miR-124).Targets of these four miRNAs were mainly associated with “signaling transduction”,“cell proliferation” and “immune responses”.The authors concluded that miRNAs,genes and pathways are connected and there is a crosstalk between different pathways,and the miRNAs might mediate pathway crosstalkviaregulating the corresponding gene[151].
A study conducted by Olaruet al[123]evaluated fragments of colon tissue from healthy people and compared with fragments of non-inflamed mucosa,inflamed mucosa of patients with IBD,IBD-dysplasia tissue and IBD-associated cancer tissue.The authors identified five upregulated miRNAs in IBD-related cancer,namely,miR-31,miR-135b,miR-200a,miR-224,and miR-552.MiR-224 was expressed at the highestlevel during differentiation between IBD patients with tumors and patients with IBD without tumors.
Several miRNAs are being correlated with the transition of normal tissue to dysplasia or neoplasia.In CD,miR-196 is a marker of dysplasia[57].Further,miR-124a,a tumor-suppressive miRNA,undergoes methylation during exposure to chronic inflammation leading to the emergence of dysplasia and then neoplastic tissues in UC patients[152].Wanet al[153]revealed that miR-155 is related to the involvement of cancer cells and worse prognosis.Additionally,Fanget al[154]analyzed patients with colorectal disease and healthy controls and determined that miR-24,miR-320a,and miR-423-5p,which were aberrantly expressed,were associated with high sensitivity for the detection of early CRC and could be promising biomarkers for IBD.In a recent study,Al-Mustanjidet al[155]used a system biology approach to identify common molecular signatures and pathways that interact between IBD and CRC and found that mir-335-5p,mir-26b-5p,mir-124-3p,mir-16-5p,mir-192-5p,mir-548c-3p,mir-29b-3p,mir-155-5p,mir-21-5p,mir-15a-5p are related with the 177 common differentially expressed genes between IBD and CRC.A schematic diagram showing the pathways modulated by miRNAs in IBD-related CRC progression is shown in Figure 2.
Due to the role of inflammation in CRC carcinogenesis,prevention methods targeting pro-inflammatory pathways have been studied.Among these pathways are the NF-κB pathway,which regulates innate and adaptive immune functions[156],and the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase pathways(Pl3K),TLR,Janus kinase,and the activating factor transcript 3(JAK/STAT3),which are also involved in the inflammation/cancer cascade[157-159].Thus,the development of drugs that regulate miRNAs and these pro-inflammatory pathways has become an important field to prevent the development of CRC in these patients[20].
After predicting the target genes for the IBD-associated CRC miRNAs[160]were found 8939 possible targets for the selected miRNAs(Supporting material).The enrichment analysis performed showed large modulation of signaling pathways that participate in the pathophysiology of both IBD and CRC,pathways such as the VEGFA,TGF- β and EGFR pathways that have already been discussed in this review[161-163](Table 5).The participation of these pathways in both diseases could help to explain the correlation between these two conditions and why IBD patients are more likely to develop CRC.
CONCLUSION
Inflammatory processes and immunosuppressive drugs are the main risk factors for the development of tumors in patients with IBD.The identification of miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers can revolutionize the screening of high-risk patients,allowing for personalized surveillance according to individual risk and the early diagnosis of lesions,directly affecting the treatment and prognosis of the patient.Further studies are needed to clarify the role of miRNAs in disease pathogenesis and evolution in patients with IBD,in addition to the identification of miRNAs related to the therapeutic response and disease prognosis.In the future,therapies based on miRNA modulation could be used in clinical practice to achieve remission of the disease and restore the quality of life for patients with IBD.
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2021年9期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2021年9期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology的其它文章
- Use of liquid biopsies in gastrointestinal cancers
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy without radiation as a potential alternative treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer:A metaanalysis
- Prognostic value of modified Lauren classification in gastric cancer
- Scoparone inhibits pancreatic cancer through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- Effect of oncometabolic surgery on gastric cancer:The remission of hypertension,type 2 diabetes mellitus,and beyond
- Characterization of metabolic landscape in hepatocellular carcinoma
