注射用质子泵抑制剂在某院住院患者中的应用分析
张纯洁 王素梅
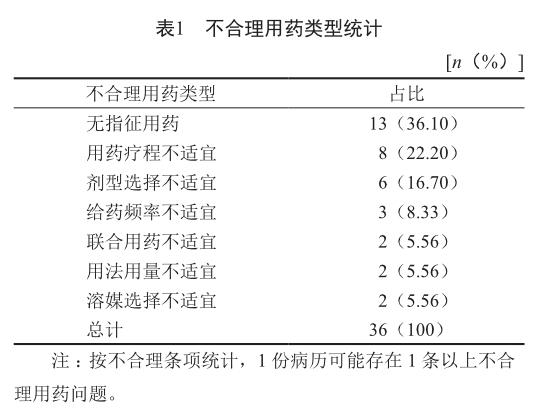
摘 要 目的:分析某院注射用质子泵抑制剂在住院患者中应用的合理性,为质子泵抑制剂合理应用提供参考。方法:在某院随机抽取应用注射用质子泵抑制剂的住院患者200例,对医嘱用药合理性进行评价及分析。结果:200例病例中,总不合格率为10.5%(21/200),不合理例次共计36例次,其中无指征用药36.10%(13/36),用药疗程不适宜22.20%(8/36),联合用药不适宜5.56%(2/36),用法用量不适宜5.56%(2/36),给药频次不适宜8.33%(3/36),剂型选择不适宜16.67%(6/36),溶媒选择不适宜5.56%(2/36)。结论:该院注射用质子泵抑制剂在临床应用中存在不合理现象,应进行有效干预,提高临床合理用药水平。
关键词 质子泵抑制剂 住院患者 合理用药
中图分类号:R975.2; R969.3 文献标志码:C 文章编号:1006-1533(2021)13-0035-04
Analysis of the application of proton pump inhibitor for injection in a hospital
ZHANG Chunjie, WANG Sumei
(Qingpu Branch of Zhongshan Hospital affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai 201700, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To analyze the rationality of the application of proton pump inhibitors for injection in a hospital so as to provide references for their reasonable clinical application. Methods: Two hundred cases of inpatients using proton pump inhibitor for injection in the hospital were randomly selected and the rationality of medication prescribed by Doctors order was evaluated and analyzed. Results: Total failure rate accounted for 10.5% (21/200) in 200 cases, and there were a total of 36 unreasonable cases, in which the unindicated drug use, the unsuitable course of medication, the unsuitable combination medication, the unsuitable usage and dosage, the inappropriate frequency of administration, the inappropriate selection of dosage form and the unsuitable solvent selection accounted for 36.10% (13/36), 22.20% (8/36), 5.56% (2/36), 5.56% (2/36) , 8.33% (3/36), 16.67%(6/36) and 5.56% (2/36), respectively. Conclusion: The clinical application of proton pump inhibitors for injection in this hospital is unreasonable, and the effective intervention should be carried out to improve the level of clinical rational drug use.
KEy WORDS proton pump inhibitor; inpatient; reasonable use of drugs
質子泵抑制剂(proton pump inhibitors,PPIs)是胃酸分泌的高特异性抑制剂,通过与H+/K+-ATP酶不可逆地结合而作用于胃酸分泌循环的终末阶段,几乎可以完全抑制基础胃酸和刺激后的胃酸分泌。PPIs疗效好、安全性高,临床使用非常广泛[1],是目前临床治疗和预防酸相关性疾病的首选药物[2]。近年来,PPIs不合理应用问题日益突出,特别是注射剂型。有研究报道,中国PPIs临床使用超过25%存在不合理问题,处于较高水平,形势严峻,不仅增加了患者的经济负担,也加大了用药风险,因而评估其临床应用的合理性显得至关重要[3]。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料来源
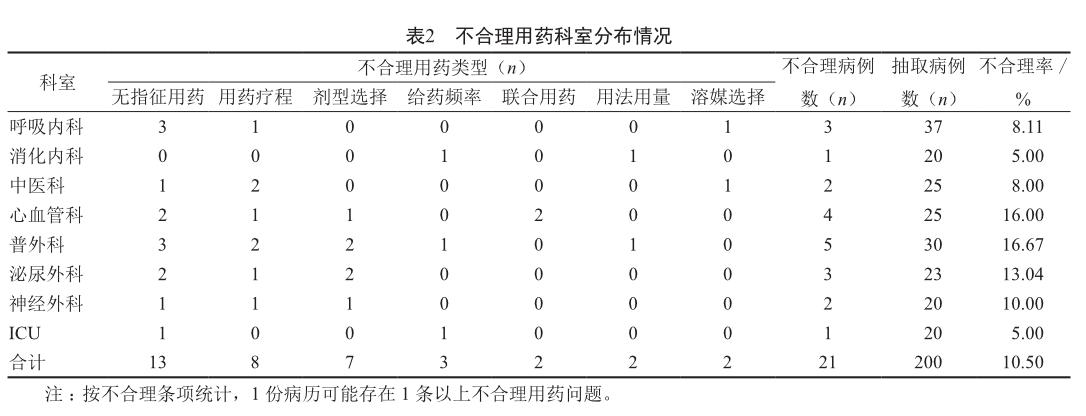
通过该院HIS系统随机抽取2020年1—6月期间使用注射用PPIs的住院患者有效病例200例为本次研究对象。主要涉及科室:呼吸内科、消化内科、中医科、心血管科、普外科、泌尿外科、神经外科、ICU。
1.2 方法
采用回顾性调查分析法,制定“PPIs临床应用统计表”,收集患者的基本信息(病历号、年龄、性别、出入院时间,出院诊断)、应激性溃疡(stress ulcer,SU)风险因素、预防用药指征、手术情况(手术名称、手术持续时间、术间出血情况)、PPIs使用情况(剂型选择、给药剂量、给药频次、给药时机、用药疗程、溶媒选择)。依据《质子泵抑制剂预防性应用专家共识(2018版)》《应激性溃疡防治专家建议(2018版)》《湖南省质子泵抑制剂临床应用指导原则》及相关文献和药品说明书等,对患者使用PPIs的用药指征、品种选择、用法用量、给药频次、用药疗程等进行评价分析。

