Bushen Qiangjin capsule(补肾强筋胶囊)inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to ameliorate papain-induced knee osteoarthritis in rats
YAO Nan,CHEN Guocai,LU Yanyan,XU Xuemeng,ZHAO Chuanxi,HUANG Xuejun,LIU Wengang,PENG Sha,WU Huai
YAO Nan,HUANG Xuejun,PENG Sha,Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Guangdong Province Engineering Technology Research Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine),Guangzhou 510095,China;The Fifth Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510095,China;Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Research and Development in Traditional Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510095,China
CHEN Guocai,the Fifth Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou Guangdong,510095,China;Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Foshan 528000,China
LU Yanyan,the Fifth Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510095,China
XU Xuemeng,ZHAO Chuanxi,LIU Wengang,WU Huai,Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital(Guangdong Province Engineering Technology Research Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine),Guangzhou 510095,China;the Fifth Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine,Guangzhou 510095,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To evaluate the molecular mechanism underlying the beneficial effect of Bushen Qiangjin capsule (补肾强筋胶囊,BSQJ),a Traditional Chinese Medicine,on knee osteoarthritis(KOA).METHODS:In the present study,32 female Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups:control,KOA,high-dose BSQJ (H-BSQJ),and low-dose BSQJ (L-BSQJ).After successfully establishing the KOA model by intra-articular injection of papain,H-BSQJ and L-BSQJ groups were intragastrically administered 0.243and 0.122 g/kg BSQJ,respectively,daily for 6 weeks.At the end of the experiment,knee articular cartilage tissues of rats were collected for evaluation by hematoxylin and eosin staining,Safranin O-Fast Green staining,and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling assay.Serum interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α levels of rats were detected with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method.Gene expression of Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β),cysteinyl aspartate-specific proteinases 3 and 9(caspases 3 and 9),collagen type Ⅱ alpha 1(Col2a1),and matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 13(MMP-1 and MMP-3) of rat knee articular cartilage was quantified by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis.Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,GSK-3β,cleaved caspase-3,and cleaved caspase-9 protein expression in rat knee articular cartilage was determined by western blot analysis.RESULTS:BSQJ obviously reduced pathological damage and matrix degradation of articular cartilage in KOA rats.Compared with the KOA group,H-BSQJ rats exhibited downregulated mRNA and protein expression of Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,and caspase-3,as well as upregulated mRNA and protein expression of GSK-3β.In addition,H-BSQJ significantly increased mRNA expression of Col2a1 and decreased mRNA expression of MMP-1 and MMP-13.CONCLUSION:BSQJ exerted a beneficial effect on KOA by a mechanism involving downregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway,which inhibited both cartilage extracellular matrix degradation and chondrocyte apoptosis to ameliorate KOA in rats.
Keywords:papain;osteoarthritis;knee;Wnt signaling pathway;cartilage;Bushen Qiangjin capsule
INTRODUCTION
Osteoarthritis (OA),a common chronic degenerative disease in middle-aged and elderly individuals,is typically characterized by a series of pathological changes in the structure and function of joints-especially articular cartilage degeneration.1World Health Organization data indicate that the incidence of OA in people aged over 50 years is 50%,and the most common site of OA is the knee joint.2In China,the prevalence of knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is as high as 8.1%.Moreover,an increasingly aging population in China will impose a serious burden on patient families and society.3Articular cartilage is mainly composed of extracellular matrix(ECM),which contains type Ⅱcollagen,and chondrocytes responsible for the synthesis and catabolism of ECM.Both anabolic and catabolic disorders of chondrocyte ECM are closely related to the pathogenesis of OA.4Furthermore,cartilage degeneration may be associated with matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs),which can degrade type Ⅱcollagen.In the process of KOA,ECM degradation is mediated by MMPs in response to excess production of inflammatory cytokines,such as interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor α(TNF-α).5,6
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is composed of a series of proteins such as Wnts,β-catenin,Frizzled,glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β),and their downstream targets,which play an important regulatory role in the pathogenesis of various diseases including KOA.7,8Previous studies have shown that β-catenin plays a dual role in the pathogenesis of KOA.Overactivation or inhibition of β-catenin can cause abnormal changes in articular cartilage metabolism,leading to KOA.9,10Therefore,appropriate expression levels of Wnt/β-catenin pathway components are crucial to maintaining the homeostasis of articular cartilage.
Considering the shortcomings of anti-inflammatory drugs,hyaluronic acid,and surgical treatments,an increasing number of individuals are seeking Traditional Chinese Medicine(TCM)to alleviate OA.11,12Based on the TCM principles of tonifying kidney and promoting blood circulation,Bushen Qiangjin capsule (补肾强筋胶囊,BSQJ)is composed of six TCMs:Duzhong(Cortex Eucommiae),Buguzhi (Fructus Psoraleae),Gusuibu (Rhizoma Drynariae),Shudihuang (Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata),Xuejie (Sanguis Draconis) and Quanxie (Scorpio).Although previous clinical experiments reported a good treatment effect of BSQJ on KOA,13,14the underlying mechanism is far from fully elucidated.Therefore,the purpose of this study was to investigate whether BSQJ regulates the Wnt pathway in KOA rat cartilage.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals
Thirty-two specific-pathogen-free (SPF) female Sprague-Dawley rats,each weighing 180-220 g,were purchased from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center (Guangdong,China).All rats were kept in an SPF animal laboratory of Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Guangdong,China) under standard laboratory conditions.A 12-h light-dark cycle was maintained,with lights on between 6:00 a.m.and 6:00 p.m.The temperature was maintained at 21-25 ℃and relative humidity was maintained at 40%-70%.Rats were provided standard laboratory food and water ad libitum.
Establishment of papain-induced KOA and drug treatment
All rats were divided randomly into control (n=8)and treatment(n=24)groups after adaptive feeding in the SPF animal laboratory of our organization for 1 week.Rats in the treatment group underwent KOA modeling according to a previous report.15,16Prior to modeling,all rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% pentobarbital sodium solution(0.1 mL/100 g).To model KOA,50 μL of a mixture(v∶v=2∶1) of 4% papain (Sigma-Aldrich,St.Louis,MO,USA) and 0.03 mol/L L-cysteine (Sigma-Aldrich) was injected into the right knee joint of the rat,and intra-articular injections were repeated on days 1,4,and 7.Rats in the control group were injected with the same amount of normal saline in the right knee joint.Two weeks after the final injection,rats in the treatment group were randomly divided into three groups according to body weight (n=8 per group):KOA,high-dose BSQJ (H-BSQJ),and low-dose BSQJ(L-BSQJ).H-BSQJ and L-BSQJ groups were intragastrically administered 243 and 122 mg/kg BSQJ daily,respectively,provided by the preparation room of Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Guangdong,China).Control and KOA groups were given the same volume of saline.BSQJ-administered groups were administered drugs and maintained for 42 d.
Experimental sampling
After 6 weeks,all rats were anesthetized as described above,blood was obtainedviacardiac puncture,and serum was stored in a refrigerator at-80℃for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA).After anesthesia and blood collection,rats were euthanized by cervical dislocation.A portion of knee articular cartilage from each rat was harvested and fixed in 4% formaldehyde for hematoxylin and eosin(HE)staining,and Safranin O-Fast Green staining.Additional knee articular cartilage from each rat was stored at-80℃for reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction(RT-qPCR)and Western blot analyses.The care and experimental treatment of rats were approved by the Ethical Committee of Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Guangdong,China;Approval No.048650).
Histological analysis
Articular cartilage fixed in 4% formaldehyde was observed following staining with hematoxylin-eosin (HE)and Safranin O-Fast Green.Images of all groups were acquired with a BX51 fluorescence microscope (Olympus,Tokyo,Japan).In addition,modified Mankin scores were assigned according to the results of cartilage appearance,HE staining,and Safranin O-Fast Green staining,as we previously reported.17
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling(TUNEL)assay
Apoptotic chondrocytes in tissue sections were detected by TUNEL assay with an In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit (Roche,Basel,Switzerland) according to the manufacturer's instructions.Apoptotic rat chondrocytes were stained by kit reagents and subsequently counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole(DAPI;Servicebio,Wuhan,Hubei,China).Images of all groups were observed with a BX51 fluorescence microscope.
ELISA detection
Serum levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in rats were detected with ELISA kits(Anoric,Tianjin,Hebei,China)according to the manufacturer's instructions.
RT-qPCR analysis
Total RNA from articular cartilage was extracted with Trizol Reagent (Dingguo Changsheng,Beijing,China)and subsequently reverse-transcribed into cDNA with a 5× PrimeScript ™RT Master Mix (Takara,Dalian,China).RNase-free ddH2O,specific primers,cDNA,and SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™Ⅱ(Tli RNaseH Plus,2×;Takara) were mixed,and 25 μL were evaluated by an IQTM5 Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad,Hercules,CA,USA) for PCR amplification.After the amplification reaction,the melting curve of each product was analyzed.Finally,gene expression levels were normalized to that of 18S in the same sample,as calculated by the 2-△△Ctmethod.
Western blot analysis
Total protein from articular cartilage was extracted with radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer and protease/phosphatase inhibitor mixture (BestBio,Shanghai,China),then separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.After separation,protein samples were electrically transferred into a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane and blocked with 5%skimmed milk for 1 h.Subsequently,membranes were incubated overnight at 4 ℃with the following primary antibodies:Wnt-4 (BA3160-2,1∶1000;Boster,Wuhan,China),β-catenin (51067,1∶1000;Proteintech,Chicago,IL,USA),Frizzled-2 (24272,1∶1000;Proteintech),GSK-3β (22104,1∶1000;Proteintech),cleaved-cysteinyl aspartate-specific proteinase-3 (caspase-3) [9661S,1∶1000;Cell Signaling Technology(CST),Danvers,MA,USA],cleaved-cysteinyl aspartate-specific proteinase-9 (caspase-9) (20750S,1∶1000;CST),β-actin (20536,1∶1000;Proteintech).Following incubation,membranes were washed four times (5 min each) with Tris-buffered saline containing Tween (Beyotime,Beijing,China).Next,horseradish peroxidase-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG(SA00001-2,1∶2000;Proteintech) was added to membranes for incubation at 37 ℃for 60 min.After washing four times(5 min each)with buffer solution,membranes were incubated with 1 mL of SuperSignal West Pico PLUS Chemiluminescent Substrate (ThermoFisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA) for 2 min.X-ray film (FujiFilm,Tokyo,Japan) was applied for developing in a dark room.Finally,bands in the film were scanned and quantified with ImageJ software (https://imagej.nih.gov),and protein expression levels were normalized to that of β-actin in the same sample.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed by SPSS22.0 software(SPSS,Armonk,NY,USA)and are expressed as mean±standard deviation(±s).One-way analysis of variance was applied to analyze differences in data for all parameters among the different groups.The Student-Newman-Keuls method was used when the parameter had equal variance,while Dunnett's T3 method was used when the parameter had unequal variance.Differences were considered statistically significant whenP<0.05.
RESULTS
Effect of BSQJ on histologic evaluation of articular cartilage in KOA rats
The general morphology of articular cartilage was assessed using HE staining,while cartilage proteoglycan content was determined by Safranin O-Fast Green staining.Compared with the Control group,cartilage lesions in the papain-induced KOA group were significantly more severe and had significantly higher Mankin scores (P <0.01).BSQJ significantly ameliorated cartilage lesions and matrix degradation,and obviously decreased Mankin scores(P<0.01)(Figure 1).
Effect of BSQJ on chondrocyte apoptosis in articular cartilage of KOA rats
As presented in Figure 2,TUNEL staining was performed to detect apoptotic chondrocytes in articular cartilage.Papain induction significantly increased numbers of TUNEL-positive apoptotic chondrocytes in rats.Furthermore,BSQJ obviously reversed the apoptosis-inducing effect of papain in KOA rats.
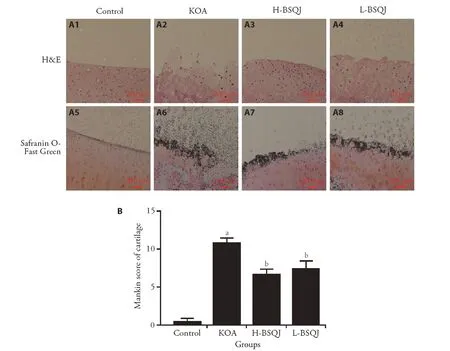
Figure 1 Pathological examination of articular cartilage in each group
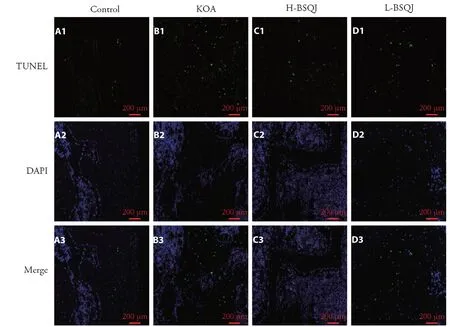
Figure 2 TUNEL assay of articular cartilage in each group(×200 magnification)
Effect of BSQJ on serum IL-1β and TNF-α levels in KOA rats
Table 1 shows that serum IL-1β and TNF-α levels were significantly enhanced in the KOA group compared with the control group(P<0.01).However,BSQJ obviously decreased levels of IL-1β and TNF-α production(P<0.01).
Effect of BSQJ on mRNA expression of articular cartilage in KOA rats
mRNA expression levels of Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,GSK-3β,collagen type Ⅱalpha 1 (Col2a1),matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1),matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13),caspase-3,and caspase-9 were detected by RT-qPCR (Table 2).Compared with the control group,papain obviously increased mRNA expression of Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,MMP-1,MMP-13,caspase-3,and caspase-9,and remarkably decreased mRNA expression of GSK-3β and Col2a1 in the KOA group (P <0.01).In addition,H-BSQJ rats exhibited significantly decreased mRNA expression of Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,MMP-1,MMP-13,and Caspase-3,and notably increased mRNA expression of GSK-3β and Col2a1 (P <0.05 orP <0.01).In addition,L-BSQJ rats exhibited significantly decreased mRNA expression of MMP-1,MMP-13,and Caspase-3,and notably increased GSK-3β mRNA expression(P<0.05 orP<0.01).
Table 1 Effect of BSQJ on serum IL-1β and TNF-α levels of each group(pg/mL,±s)

Table 1 Effect of BSQJ on serum IL-1β and TNF-α levels of each group(pg/mL,±s)
Notes:control:normal group:receive intra-articular injection of normal saline;KOA:knee osteoarthritis group:receive intra-articular injection of papain;H-BSQJ:high-dose Bushen Qiangjin capsule group (per rat:243 mg·kg-1·d-1 × 42 d);L-BSQJ:low-dose Bushen Qiangjin capsule group(per rat:122 mg·kg-1·d-1 × 42 d).IC:inflammatory cytokine;IL-1β:interleukin-1β;TNF-α:tumor necrosis factor-α.The results are represented as mean ± standard deviation obtained from 8 rats in each group.aP <0.01,compared with the control group;bP <0.01,compared with the KOA group.
Table 2 Effect of BSQJ on mRNA expression of articular cartilage in each group(±s)
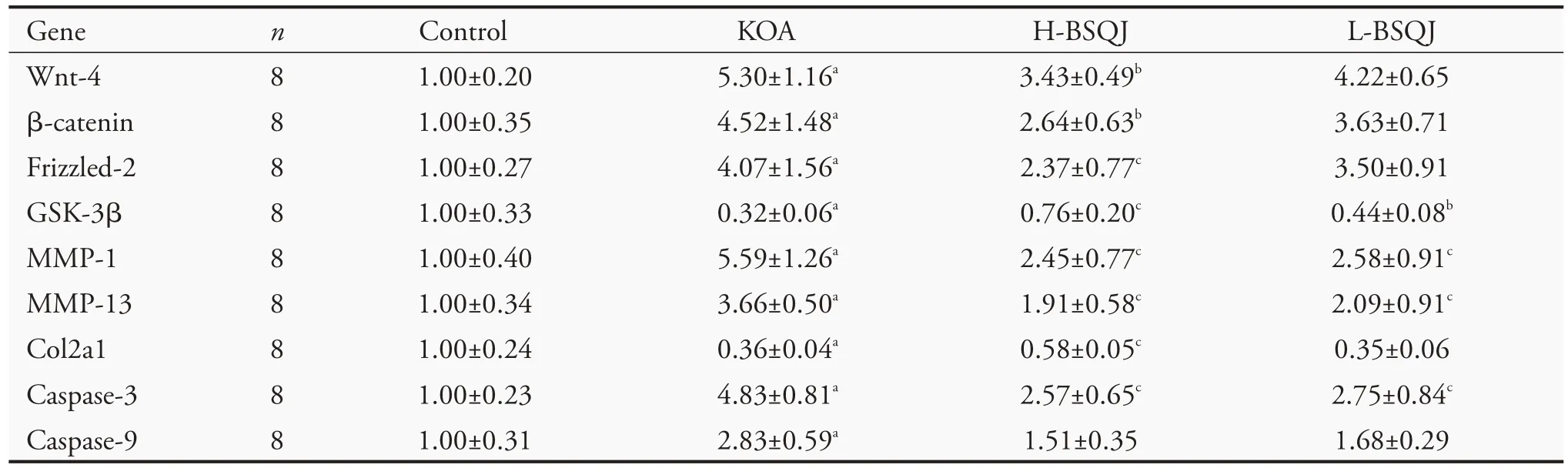
Table 2 Effect of BSQJ on mRNA expression of articular cartilage in each group(±s)
Notes:control:normal group:receive intra-articular injection of normal saline;KOA:knee osteoarthritis group:receive intra-articular injection of papain;H-BSQJ:high-dose Bushen Qiangjin capsule group (per rat:243 mg·kg-1·d-1 × 42 d);L-BSQJ:low-dose Bushen Qiangjin capsule group(per rat:122 mg·kg-1·d-1×42 d).18S was used as an internal control for normalization.18S:ribosomal protein S18;caspase-3:cysteinyl aspartate-specific proteinase-3;caspase-9:cysteinyl aspartate-specific proteinase-9;Col2a1:collagen type Ⅱalpha 1;GSK-3β:glycogen synthase kinase-3β;MMP:matrix metalloproteinase.The results are represented as mean ± standard deviation obtained from 8 rats in each group.aP<0.01,compared with the control group;bP<0.05,cP<0.01,compared with the KOA group.
Effect of BSQJ on protein expression of articular cartilage in KOA rats
Protein expression levels of Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,GSK-3β,cleaved caspase-3,and cleaved caspase-9 were detected by western blot(Figure 3).The results demonstrated that protein expression of Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,cleaved caspase-3,and cleaved caspase-9 in the KOA group was significantly higher compared with the control group (P <0.05 orP <0.01).Additionally,protein expression of GSK-3β was significantly lower in the KOA group compared with the control group (P <0.01).H-BSQJ rats exhibited significantly lower protein expression of Wnt-4,β-catenin,Frizzled-2,and cleaved caspase-3 compared with the KOA group (P <0.05 orP <0.01).L-BSQJ rats exhibited significantly decreased protein expression of β-catenin and cleaved caspase-3 compared with the KOA group(P<0.05 orP<0.01).Both H-BSQJ and L-BSQJ groups exhibited obviously elevated GSK-3β protein expression(P<0.05 orP<0.01).
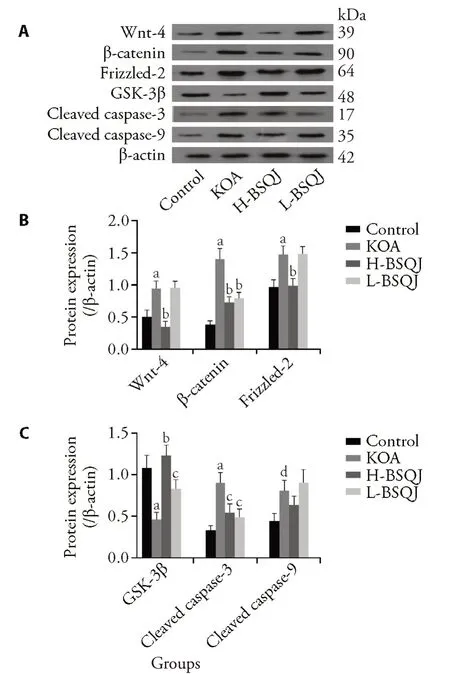
Figure 3 Effect of BSQJ on protein expression of articular cartilage in each group
DISCUSSION
KOA is a frequently occurring disease among middle-aged and elderly people across the world,and its incidence is increasing annually.Articular cartilage degeneration,which is closely related to increased chondrocyte apoptosis and metabolic disorders of ECM,plays an important role in the pathogenesis of KOA.18Chondrocytes are the most important cell type in articular cartilage because they secrete both ECM and the proteinases that degrade redundant cartilage matrix to maintain the metabolic balance of ECM,thus participating in the maintenance of articular cartilage homeostasis.MMPs,such as MMP-1 and MMP-13,are the main proteinases responsible for the degradation of type Ⅱcollagen,one of the primary ECM macromolecules in cartilage;therefore,MMPs are considered to be key factors of KOA.19
This study demonstrated that BSQJ had a protective effect against papain-induced damage to articular cartilage.Specifically,morphological and histological examinations showed that the superficial layer of articular cartilage in rats administered BSQJ was smooth and flat on the whole,and surface chondrocytes were uniformly present,suggesting that BSQJ could improvepathological changes of articular cartilage in KOA rats.The abnormal production of inflammatory cytokines that occurs during the pathogenesis of KOA is the main inducer of KOA inflammatory responses;two typical inflammatory cytokines,IL-1β and TNF-α,are regarded to have key roles in the pathogenesis of KOA.5,6We found that BSQJ could reduce serum levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in KOA rats,which inhibited KOA inflammatory reactions to a certain degree.On the basis of the pathological improvement and anti-inflammatory effect of BSQJ on KOA,we evaluated mechanisms related to the Wnt pathway.
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway represents a canonical Wnt pathway.20-22Wnt,β-catenin,GSK-3β,and Frizzled are key regulatory proteins in this pathway.Normally,most intracellular β-catenin is combined with cadherin on the cell membrane,which allows it to adhere to cytoskeletal actin and mediate homotypic intercellular adhesion.However,in the absence of Wnt signal conduction,activated GSK-3β phosphorylates β-catenin,resulting in its ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.23,24When Wnt signaling is activated,Wnt combines with Frizzled to inhibit GSK-3β activity through signal conduction,thus inhibiting phosphorylation-mediated degradation of β-catenin by GSK-3β.Finally,unphosphorylated β-catenin aggregates in the cytoplasm (up to a certain concentration)and enters the nucleus,whereby it promotes the expression of many target genes,such as MMPs.25,26Wnt-4,an important member of the Wnt family,has been shown to possess many activities,including triggering the overexpression of downstream β-catenin to promote overmaturation,differentiation,and apoptosis of articular chondrocytes,which increases articular cartilage degeneration.27,28Similar to other studies involving rat KOA models,29-32we found that the Wnt/β-catenin pathway was activated in the papain-induced rat KOA model,as characterized by significant increases in Wnt-4,β-catenin,and Frizzled-2 mRNA and protein expression,and significant decreases in GSK-3β mRNA and protein expression.After intervention with H-BSQJ,expression of Wnt-4,β-catenin,and Frizzled-2 in articular cartilage of KOA rats was significantly decreased,and GSK-3β expression was significantly increased.Accordingly,mRNA expression of downstream targets MMP-1 and MMP-13 was downregulated,resulting in inhibited degradation of ECM by MMPs.
Previous cell and animal studies found that the rate of apoptotic chondrocytes in KOA was much higher than that of normal chondrocytes.33-35Increased apoptosis of KOA chondrocytes can reduce ECM synthesis and accelerate articular cartilage degeneration.36Upregulated expression of caspases 3 and 9,two important effector caspases involved in many apoptosis signaling pathways,is one of the mechanisms driving excessive apoptosis of chondrocytes in KOA.Therefore,expression of caspases 3 and 9 largely reflects the occurrence of apoptosis.37TUNEL assay results of the present study indicate that BSQJ intervention significantly decreased the number of apoptotic chondrocytes by downregulating expression of caspase 3 mRNA and cleaved caspase 3 protein in articular cartilage of KOA rats,leading to inhibition of chondrocyte apoptosis.
At present,there are no drugs on the market that target the Wnt pathway for KOA.It is worth seeking new agents for KOA treatment that target the Wnt pathway from TCM.20In summary,our experimental results showed that BSQJ could inhibit abnormal Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation during the pathogenesis of KOA,thereby reducing degradation of ECM by MMPs and inhibiting excessive chondrocyte apoptosis.Our findings explain the treatment effect and mechanism of BSQJ on articular cartilage to some extent,and provide a theoretical and experimental basis for its clinical application.Remarkably,identification of Wnt pathway inhibitors is a current trend,20,21so isolating the active ingredient of BSQJ is worth further study in the future.
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2021年6期
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2021年6期
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Editorial Board Listing
- In vivo anti-diarrheal activity of jujube honey on castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice
- Chemical characters and protective effect of Baqi Lingmao formula(巴芪灵猫方)on experimental liver injury
- Effectiveness of herb-partitioned moxibustion combined with electroacupuncture on polycystic ovary syndrome in patients with symptom pattern of kidney deficiency and phlegm-dampness
- Traditional Chinese Medicine enhances absorption of lung lesions in corona virus disease 2019 patients
- Shumian capsule(舒眠胶囊)improves symptoms of sleep mood disorder in convalescent patients of Corona Virus Disease 2019
