Shumian capsule(舒眠胶囊)improves symptoms of sleep mood disorder in convalescent patients of Corona Virus Disease 2019
LI Li,AN Xuedong,ZHANG Qing,TAO Junxiu,HE Jing,CHEN Yun,LI Kejian,LIU Ru,GUO Juan,ZHANG Hao,TONG Xiaolin,BA Yuanming
LI Li,ZHANG Qing,TAO Junxiu,HE Jing,CHEN Yun,LI Kejian,LIU Ru,GUO Juan,ZHANG Hao,BA Yuanming,Department of Psychiatry,Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Wuhan 430061,China;Department of Psychiatry,Hubei Province Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Wuhan 430074,China;Department of Psychiatry,the Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine,Wuhan 430065,China
AN Xuedong,TONG Xiaolin,Department of Endocrinology,Guang'anmen Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences,Beijing 100053,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To evaluate the clinical effectiveness of Shumian capsule (舒眠胶囊) in improving the symptoms of insomnia,anxiety,depression,and other symptoms of convalescent patients of COVID-19.METHODS:Totally 200 patients were collected and randomly divided into experiment group (n= 100)and control group(n=100).The control group was treated with Shumian capsule simulator,and the experiment group was treated with Shumian capsule.The improvement of TCM symptom score,the total effective rate and symptom disappearance rate of TCM symptoms in the two groups before and after treatment were observed,and the clinical effect was evaluated.RESULTS:One week after treatment,the scores of anxiety symptoms in the experiment group were significantly different from those in the control group(P<0.05),but there was no significant difference in the scores of insomnia and depression between the experiment group and the control group(P>0.05).There was no significant difference in the total effective rate and disappearance rate of TCM symptoms of insomnia,anxiety and depression between the experiment group and the control group(P>0.05).After 2 weeks of treatment,the scores of insomnia,anxiety,depression and the total effective rate of TCM symptoms in the experiment group were significantly different from those in the control group (P < 0.05).There was no significant difference in the disappearance rate of insomnia,anxiety and depression between the experiment group and the control group(P>0.05).There were no significant differences in heart rate,respiration,systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure between the experiment group and the control group(P>0.05).CONCLUSION:Shumian capsule can significantly improve the symptoms of insomnia,anxiety and depression in COVID-19's convalescent patients with sleep and mood disorders.
Keywords:COVID-19;convalescence;sleep wake disorders;mood disorders;Shumian capsule
INTRODUCTION
Most patients with Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19),mainly in Hubei,have entered the convalescent period after treatment.Although all the discharged patients have met the discharge criteria of improvement in lung inflammation and negative nucleic acid tests,a considerable number of patients still suffer from clinical discomfort and organ damage,such as cough,chest tightness,shortness of breath,increased heart rate,and fibrotic lesion changes in the lungs,as well as insomnia,anxiety,depression,and other symptoms of sleep disorders.
To utilize the advantage of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in "healing and prevention of recurrence,"appropriate TCM treatment modalities can be selected and recommended to patients recovering from COVID-19 to help them recover as soon as possible and reduce the risk of recurrent COVID-19 infection.In this study,combined with symptoms related to sleep mood disorders in patients with COVID-19 in the convalescence period,a randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled,multicenter design was used to evaluate the therapeutic effects of using the TCM Shumian capsule(舒眠胶囊)as an intervention drug to improve insomnia,anxiety,depression,and other clinical symptoms of sleep disorders.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Clinical characteristics
Between April and May 2020,200 patients with convalescent COVID-19 with symptoms of insomnia,anxiety,depression,and other sleep disorders were collected from three sites,and were divided into group A(experiment group,100 cases) and group B (control group,100 cases)using a random number table.Two hundred patients were enrolled in the three sites,6 cases were eliminated,and 12 cases were dropped.As a result,197 patients were included in the FAS (Full Analysis Set,FAS),and 182 patients were included in the PPS(Per-Protocol Set,PPS) for statistical analysis.All enrolled patients completed 2 weeks of treatment and follow-up(Table 1).
There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of sex,age,body mass index,smoking,drinking,temperature,systolic blood pressure,diastolic blood pressure,respiration,pulse,waiting time for admission,length of stay,length of discharge,condition classification,CT (Pulmonary Computed Tomography),blood routine,comorbidity,and concomitant medication.Obvious differences were observed between the two groups in terms of length of intervention and history of allergies (P=0.023;P=0.032).The average length of intervention was longer in group A than in group B,and more patients in group B had a history of allergies than those in group A(Table 2).
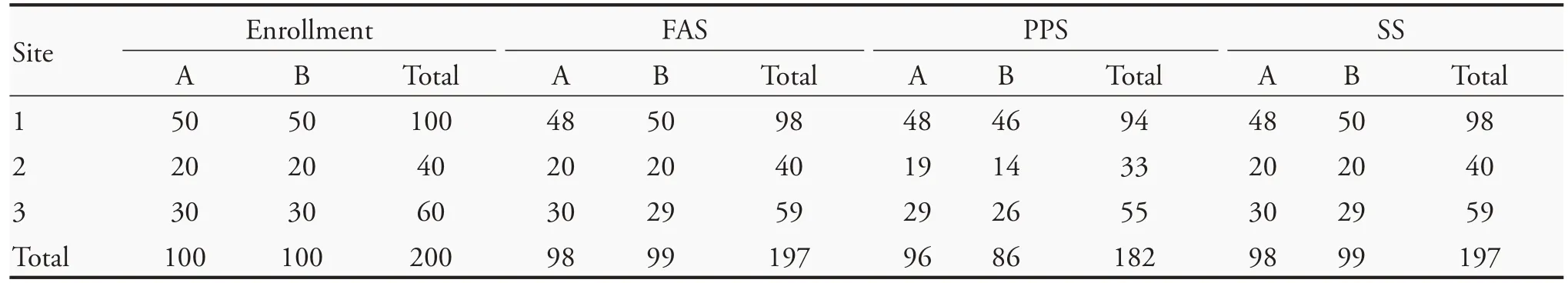
Table 1 Enrollment status(n)

Table 2 Demographic baseline data
Diagnostic criteria
The diagnostic criteria adopted were the criteria for release from isolation and discharge in the "COVID-19 Diagnostic and Treatment Protocol (Trial Version 6)":1body temperature returns to normal for more than 3 d;respiratory symptoms improve significantly;lung imaging shows significant absorption of inflammation;and two consecutive negative nucleic acid tests for respiratory pathogens (with a sampling interval of at least 1 d),then the patient can be released from isolation or discharged and enter the convalescence period.
Inclusion criteria
Patients who meet the diagnostic criteria for recovery from COVID-19;patients who have been cured and discharged from the hospital for >2 weeks;patients who are aged between 18 and 70 years;patients who have irritability,anxiety,poor sleep,and other sleep mood disorders as main clinical manifestations;patients who have two of these symptoms at the same time;patients who have a score of ≥4 on the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) for a single symptom;and patients who have signed the informed consent form.
Exclusion criteria
Patients who have difficulty taking oral medications due to underlying diseases;patients with serious underlying diseases that affect survival,including uncontrolled,clinically significant cardiac,pulmonary,renal,digestive,hematologic,neuropsychiatric,immunologic,metabolic diseases,malignant tumors,and severe malnutrition;patients with allergies to medications in-volved in the treatment regimen;women who are pregnant or lactating;patients whose mental status does not allow them to cooperate and who have psychiatric disorders,who are unconscious,and who are unable to express themselves clearly;patients who are participating in other clinical trials;and patients who,in the judgment of the investigator,may have complications in enrollment or poor compliance that may affect the evaluation of efficacy and safety.
Treatment methods
Subjects were randomized in a 1∶1 ratio into two groups,with 100 patients in each group.The study drug was dispensed according to the drug number obtained from the central randomization system.The drug number remained unchanged throughout the trial.
Experiment group (group A):The intervention drug for all subjects in the observation group was Shumian capsule.The duration of intervention was 2 weeks;approval number:NMPA20 050543;drug specification:1 capsule=0.4 g;and the route of administration:oral,3 capsules at a time,2 times a day.
Control group (group B):The intervention drug was a mock-up of Shumian capsule.The duration of intervention was 2 weeks;drug specification:1 capsule=0.4 g;and the route of administration:oral,3 capsules at a time,2 times a day.
Observational indicators
Clinical symptoms:VAS was used to observe the changes in clinical symptoms of the two groups at weeks 0,1,and 2,and the worst symptom score and the mean score were recorded within 24 h.
Efficacy evaluation indicators and criteria
The severity of clinical symptoms such as irritability,anxiety,and poor sleep caused by the decline in pulmonary and cardiac function was evaluated in two groups using VAS.Scores "0" and "10" were set on both ends of the vernier caliper,with "0" representing no symptoms and "10" representing the most severe symptoms.The patients were asked to move the vernier caliper to mark the severity of their own symptoms from 0 to 10 points,with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms.
Criteria for determining the efficacy were as follows:(a) Symptoms disappeared:symptoms and signs disappeared,and the symptom score was 0;(b) markedly effective:symptoms and signs improved significantly,and the symptom score decreased by ≥70%;(c) effective:symptoms and signs improved,and the symptom score decreased by ≥30%;(d) ineffective:symptoms and signs did not improve significantly,or even worsened,and the symptom score decreased by<30%.The calculation formula (nimodipine method) was:[(pretreatment points-posttreatment points) ÷ pretreatment points]× 100%.Safety measures were general physical examination items:temperature,blood pressure,respiration,pulse,and heart rate.There was no significant difference(P>0.05)between the two groups regarding insomnia,anxiety,and depression before treatment(Table 3).
Statistical analysis
SPSS 25.0 (IBM Corp.Released 2017.IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows,Version 25.0.Armonk,NY,USA)statistical software was used to analyze all the data in this study.Missing data were filled using last carryover.Quantitative data were expressed as mean,standard deviation,median,upper quartile,and lower quartile.A two-samplet-test was used for normally distributed quantitative data,and Mann-WhitneyUtest was used for non-normally distributed quantitative data.The qualitative data described the number of cases and percentages for each category.Other qualitative variables were subjected to the χ2test,and Fisher's exact test was used when the conditions for χ2test were not met.The statistical tests were two-tailed,andP≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hubei Provincial Hospital of TCM (No.HBZY2020-C27-01) and registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry under registration number ChiCTR2000032214.
RESULTS
Comparison of TCM symptom scores
The scores for insomnia,anxiety,and depression werecompared.After 1 week of treatment,no difference was observed between the two groups in insomnia and depression(P>0.05),but there was a significant difference in anxiety (P=0.05);after 2 weeks of treatment,there was a significant difference between the two groups in these symptoms(P<0.01)(Table 4).
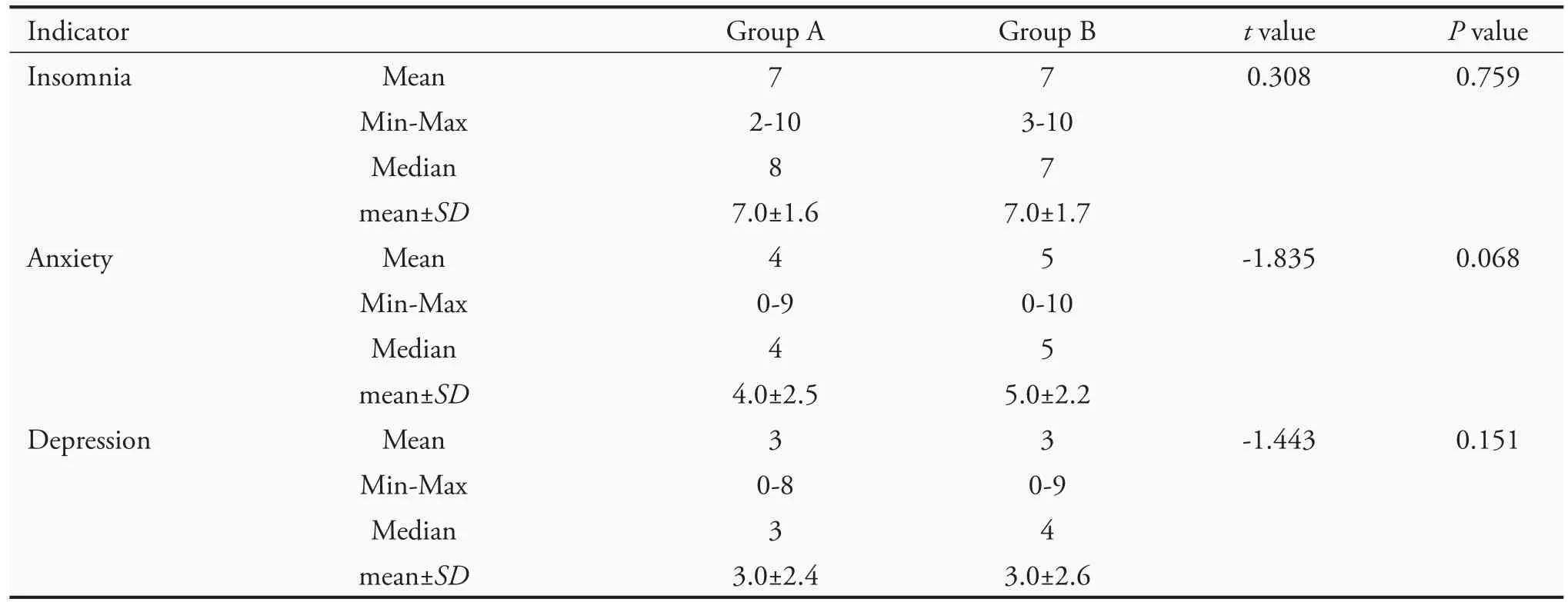
Table 3 Scores for insomnia,anxiety,and depression of the subjects before treatment
Comparison of the efficacy of TCM symptoms
Analysis of covariance revealed no significant difference between the two groups after 1 week of treatment (P >0.05) in insomnia,anxiety,and depression.After 2 weeks of treatment,there was a significant difference between the two groups in these symptoms (P <0.05)(Table 5).
Efficacy evaluation of TCM symptoms
According to the rank-sum test,after 1 week of treatment,the differences in insomnia,anxiety,and depression symptoms were not statistically significant (P >0.05);after 2 weeks of treatment,the differences in these symptoms between the two groups were statistically significant(P≤0.001),and group A had better improvements in these symptoms than group B(Table 6).
Comparison of the overall effective rate of TCM symptom improvement
The overall effective rate of improvement in insomnia,anxiety,and depression were compared.After 1 week of treatment,there was no significant difference between the two groups(P>0.05);after 2 weeks of treatment,there was a significant difference between the two groups(P<0.05)(Table 7).
Comparison of TCM symptom disappearance rates
The disappearance rates of insomnia,anxiety,and depression were compared,which showed no significant difference (P >0.05) across the two groups after 1 and 2 weeks of treatment(Table 8).
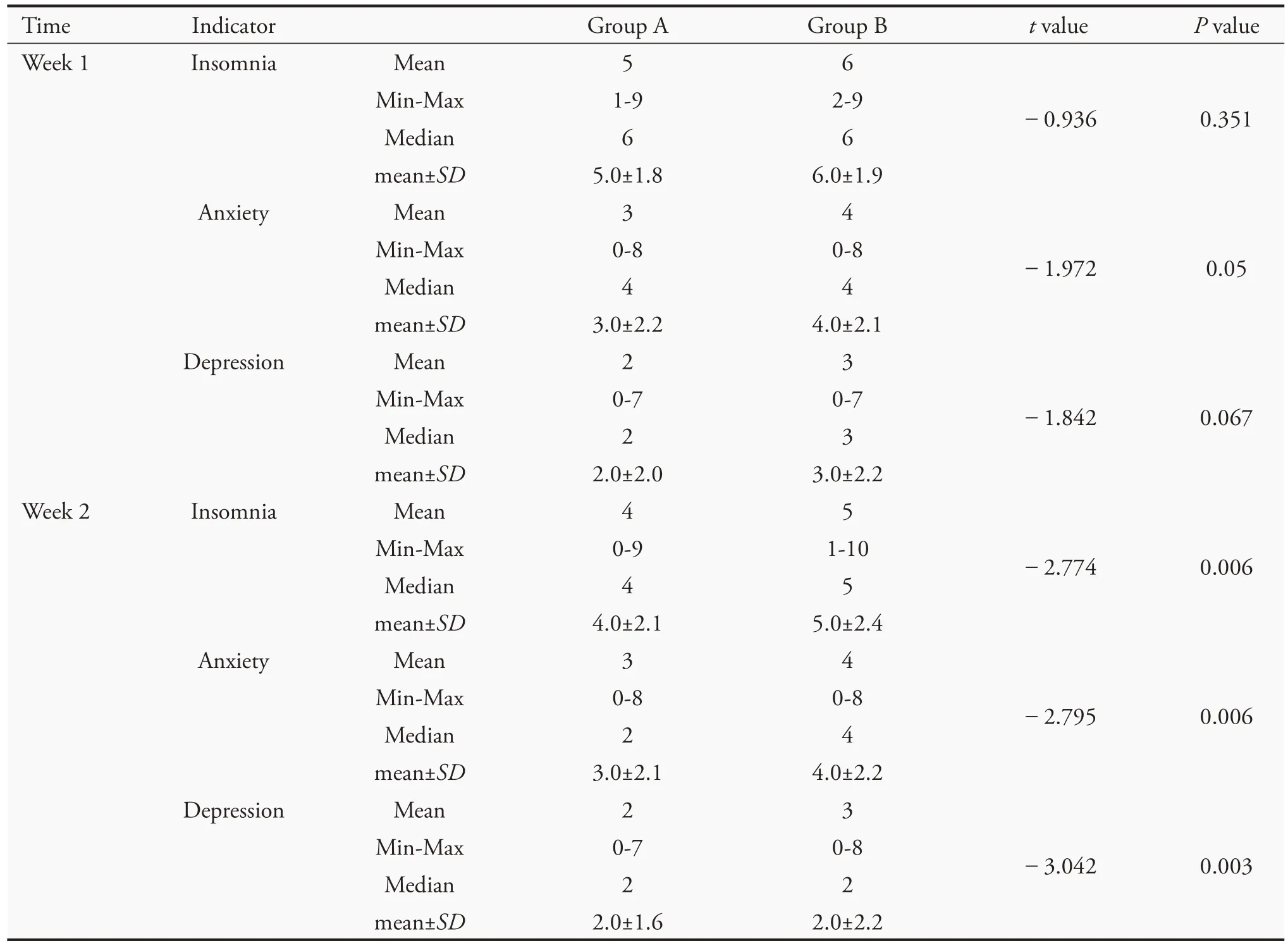
Table 4 TCM symptom scores(VAS)of the two groups
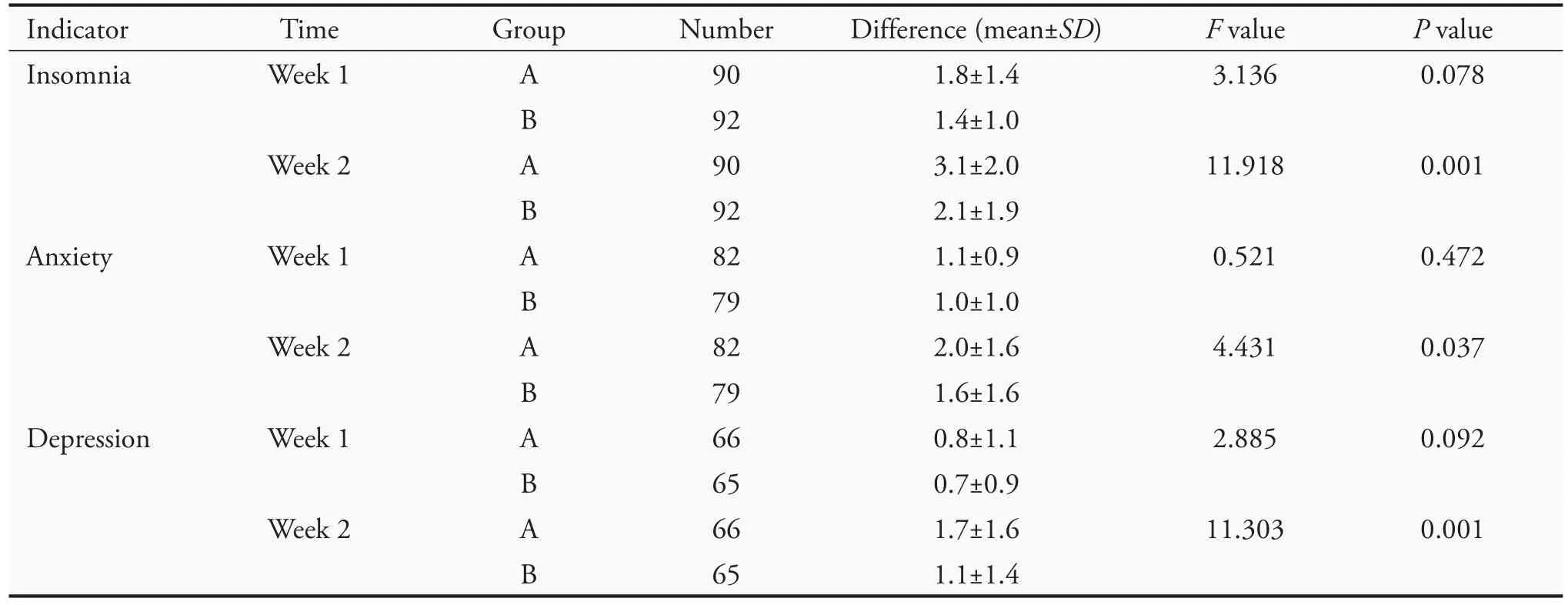
Table 5 Results of analysis of covariance for the difference in TCM symptom scores(VAS)

Table 6 Efficacy evaluation of TCM symptoms after treatment in groups A and B

Table 7 Comparison of the overall effective rate across the two groups

Table 8 Comparison of symptom disappearance rates across the two groups
DISCUSSION
Studies have shown that patients with COVID-19 suffer from the disease and also experience psychological distress such as insomnia,anxiety,and depression due to the threat of the virus,life changes,and isolation restrictions.The TCM theory indicates that the onset of COVID-19 is usually caused by "cold and dampness,"which invades the body with hostility (COVID-19)and obstructs the body'sQiflow.In the convalescent period,positiveQiis weak,remaining pathogenic factors are still present,liverQiis not drained,and the mind is restless,resulting in symptoms of sleep mood disorders such as insomnia,anxiety,and depression.
Studies have shown that,compared with western medicine in the treatment of insomnia,TCM treatment of insomnia is economical,simple,effective,no side effects and no addiction,and has a broader development prospect.2
Shumian capsule,as a Traditional Chinese Medicine product that has been on the market for more than 10 years,has been widely used in patients with insomnia.3The Shumian capsule is composed of the seed of Suanzaoren (Semen Zizyphi Spinosae),Chaihu (Radix Bupleuri),Baishao (Radix Albus Paeoniae Lactiflorae),Hehuanhua(Flos Albiziae),Hehuanpi(Cortex Albizziae Ju-librissinis),Jiangcan (Stiff Silkworm),Chantui (Ps Cicadae),Dengxincao (Juncaceae Juss).Suanzaoren (Semen Zizyphi Spinosae) has the effect of tonifying the liver and tranquilizing the heart,astringing sweat,and promoting the secretion of saliva.Chaihu (Radix Bupleuri)is responsible for the liver and gallbladder meridians,and has the effect of relieving fever,soothing the liver,and elevatingYang Qi.Baishao (Radix Albus Paeoniae Lactiflorae) is combined with Hehuanhua (Flos Albiziae) and Hehuanpi (Cortex Albizziae Julibrissinis) to soothe the liver,relieve depression,and calm the mind.The Jiangcan (Stiff Silkworm) and Chantui (Ps Cicadae) sooth the liver and relieve spasms;Dengxincao(Juncaceae Juss)draws all the herbs to the heart to soothe the liver,relieve depression,and calm the mind.3,4
Relevant studies have shown that Shumian capsule combined with psychological intervention can improve the sleep quality and anxiety and depression of patients.5Lianget al6found that the mechanism of the sedative and hypnotic effects of capsules may be related to an increase in brain tissue GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) levels,a decrease in Glu (glutamic acid) content,and an up-regulation of hippocampal 5-HT1AR(5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor) protein expression.Xiaet al7and Lianget al8also showed that the treatment of insomnia with Shumian capsules has few adverse effects,is well tolerated,and has a high safety profile.
This study showed that the scores for TCM symptoms of insomnia,anxiety,and depression,as well as the overall effective rate of TCM symptoms in the test group treated with Shumian capsule were significantly different from those in the control group (P <0.05),indicating that Shumian capsule had obvious improvement effect on sleep mood disorders in the COVID-19 convalescent period.
In summary,the impact of COVID-19 on patients'sleep quality and mood is common,and some patients still have symptoms of insomnia,anxiety,and depression in the convalescent period.TCM diagnosis and treatment should continue to play an advantageous role in consolidating treatment and improving patients'quality of life.
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2021年6期
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2021年6期
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Editorial Board Listing
- In vivo anti-diarrheal activity of jujube honey on castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice
- Chemical characters and protective effect of Baqi Lingmao formula(巴芪灵猫方)on experimental liver injury
- Effectiveness of herb-partitioned moxibustion combined with electroacupuncture on polycystic ovary syndrome in patients with symptom pattern of kidney deficiency and phlegm-dampness
- Traditional Chinese Medicine enhances absorption of lung lesions in corona virus disease 2019 patients
- Efficacy on rabbits with arrhythmia:needling acupoint of Neiguan(PC6)at shallow or deep depth,and retaining needles for 10,20,or 30 min
