烟草胚胎发育晚期丰富蛋白家族的全基因组鉴定与分析
吴辉 耿伟博 宗浩 刘文涛 高强 徐后娟 侯欣 唐恒
摘要 在烟草中鉴定了45个LEA家族成员与7个亚组。系统发育分析表明,NtLEA家族成员之间具有较高的同源性,染色体分析显示,NtLEA家族成员在染色体分布上偏好性较小;NtLEA家族成员结构上具有相似性。通过对烟草LEA基因家族进行全基因组的鉴定与分析,为进一步阐明NtLEA作用和提高烟草在非生物胁迫下的抗性提供基础。
关键词 LEA基因家族;烟草;抗逆性;生物信息学
中图分类号 Q-943.2 文献标识码 A
文章编号 0517-6611(2021)13-0098-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.13.024
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Genome Wide Identification and Analysis of Abundant Protein Family in Late Embryonic Development of Tobacco
WU Hui1,GENG Wei bo1,ZONG Hao2 et al
(1.College of Plant Protection,Shandong Agricultural University,Taian,Shandong 271018; 2.Linyi Tobacco Limited Conpany of Shandong Province,Linyi,Shandong 276000)
Abstract In this study,45 LEA gene family members and 7 subgroups were identified in tobacco.Phylogenetic analysis showed that the members of the NtLEA family had high homology.Chromosome analysis showed that the members of NtLEA gene family had less preference in chromosome distribution.In addition,NtLEA family members are similar in structure.In this study,we conducted a bioinformatics analysis of the tobacco LEA gene family,which is helpful in understanding its resistance and genetic breeding in tobacco.
Key words LEA gene family;Tobacco;Stress resistance;Bioinformatics
胚胎发育晚期丰富蛋白(late embryogenesis abundant,LEA)是在高等植物胚胎发育后期、伴随着脱水干燥过程形成的一类低分子量(大部分为10~30 kD)的蛋白质[1-2]。LEA蛋白最早在棉花的胚胎发育后期分离得到[3],进一步研究表明,LEA蛋白在其他植物组织(根、幼苗、芽)也具有丰富的表达[4-5]。LEA蛋白基因家族成员是具有重复的氨基酸基序和倾向于α螺旋结构的亲水性蛋白[6],同时亚细胞定位分析表明,LEA蛋白主要位于细胞核和细胞质[7]。根据LEA蛋白质序列的同源性与特异性将其划分为7个不同的组,分别为LEA1、LEA2、LEA3、LEA4、LEA5、dehydrin和SMP(种子成熟蛋白),但目前缺乏明确的LEA蛋白的通用分类标准[1,8]。
LEA蛋白在植物正常生长以及在干旱、盐碱、寒冷等非生物胁迫下保护过程中发挥着重要作用[9],同时也可以作为分子伴侣来抵抗细胞损伤[10]。前人研究表明,LEA基因家族是ABA依赖和非依赖信号通路的主要下游基因,其中大多数在小麦幼苗的抗冻性中起到协同调控的作用[11]。将松树LEA基因导入大肠杆菌,大肠杆菌表现出更强的耐盐性、耐热性和活力,说明LEA蛋白在胁迫下对细胞起保护作用[12]。另外,谷子中的LEA_1亚家族中的5种LEA蛋白在干旱胁迫过程中发挥着重要作用[13]。将小麦LEA(WCOR410)基因在草莓中表达,转基因草莓叶片的抗寒性得到显著提高[14],而将大麦的LEA(HVA1)转入水稻与小麦后能显著提高其耐盐性和抗寒性[15-16]。
目前,已有大量关于LEA基因结构与功能的报道,同时在多种植物中LEA基因家族得到鉴定,如欧洲油菜[17]、毛果杨[18]、小麦[19]、玉米[20]、黄瓜[21]等。然而,目前仍缺乏对烟草LEA基因家族进行全基因组分析与鉴定。烟草是世界上重要的经济作物,也是科研中重要的模式作物。随着测序技术和比较基因组学的发展,大量植物基因组被释放、大量植物基因功能被鉴定,对利用模式信息进行作物改良奠定了良好的基础[22]。该研究基于烟草K326基因组信息,对烟草LEA基因家族进行理化性质分析、染色体定位、系统进化与基因结构分析,以期为烟草LEA基因家族调控和功能研究奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 數据来源 烟草K326数据(基因组序列文件、基因组注释文件与蛋白质序列文件)下载于茄科基因组数据库(ftp://ftp.solgenomics.net/)。拟南芥LEA基因家族蛋白质序列文件下载于拟南芥信息资源数据库(http://www.arabidopsis.org/)。
1.2 烟草LEA基因家族的鉴定及理化性质分析
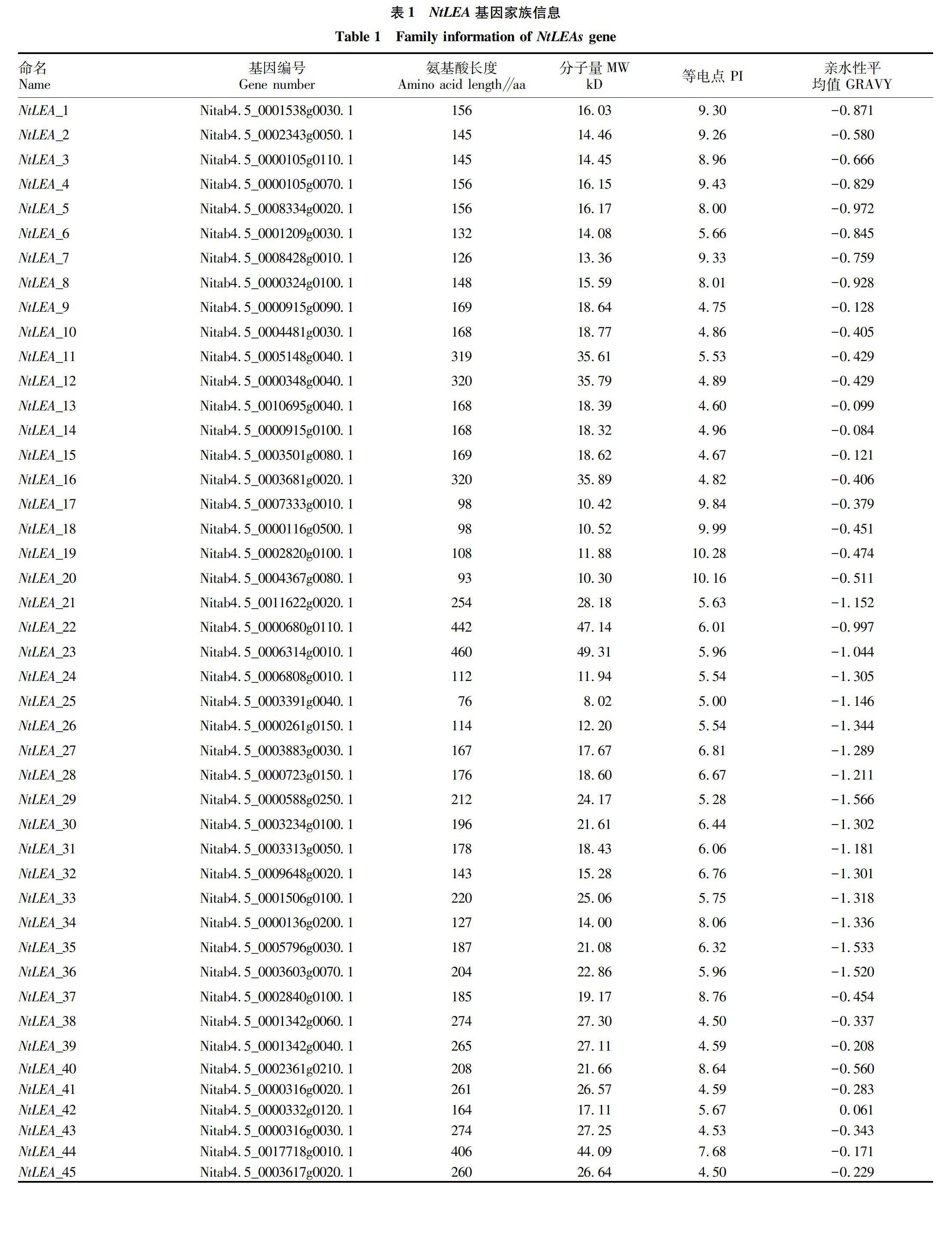
以拟南芥LEA基因家族为模板,利用BLASTp(设置(E-value<1e-5)进行多重序列比对,得到候选烟草LEA基因家族成员(NtLEA)候选成员。利用NCBI数据库 CD-Search(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi)工具对NtFBA候选成员进行保守域鉴定,最终确定NtLEA基因家族成员。利用蛋白质分析工具ExPASy (http://cn.expasy.org/tools)对NtLEA家族成员进行蛋白质长度(aa)、分子量(MW)、等电点(pI)和亲水性的均值(GRAVY)预测。
1.3 煙草LEA基因家族染色体定位
利用烟草K326基因组注释文件确定NtLEA染色体位置,利用Mapchart 2.3.2进行染色体定位作图。
1.4 烟草LEA基因家族系统进化及基因结构分析 利用ClustalW 软件对NtLEA基因家族成员进行序列联配。将联配结果导入MEGA X[23]中,利用邻位相接法(NJ)构建NtLEA进化树。默认的自举值(Bootstrap analysis)设置为1 000个重复,其他参数均设置为默认值。利用在线工具GSDS 2.0(http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn /)进行基因结构分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 烟草基因组LEA的鉴定及系统发育
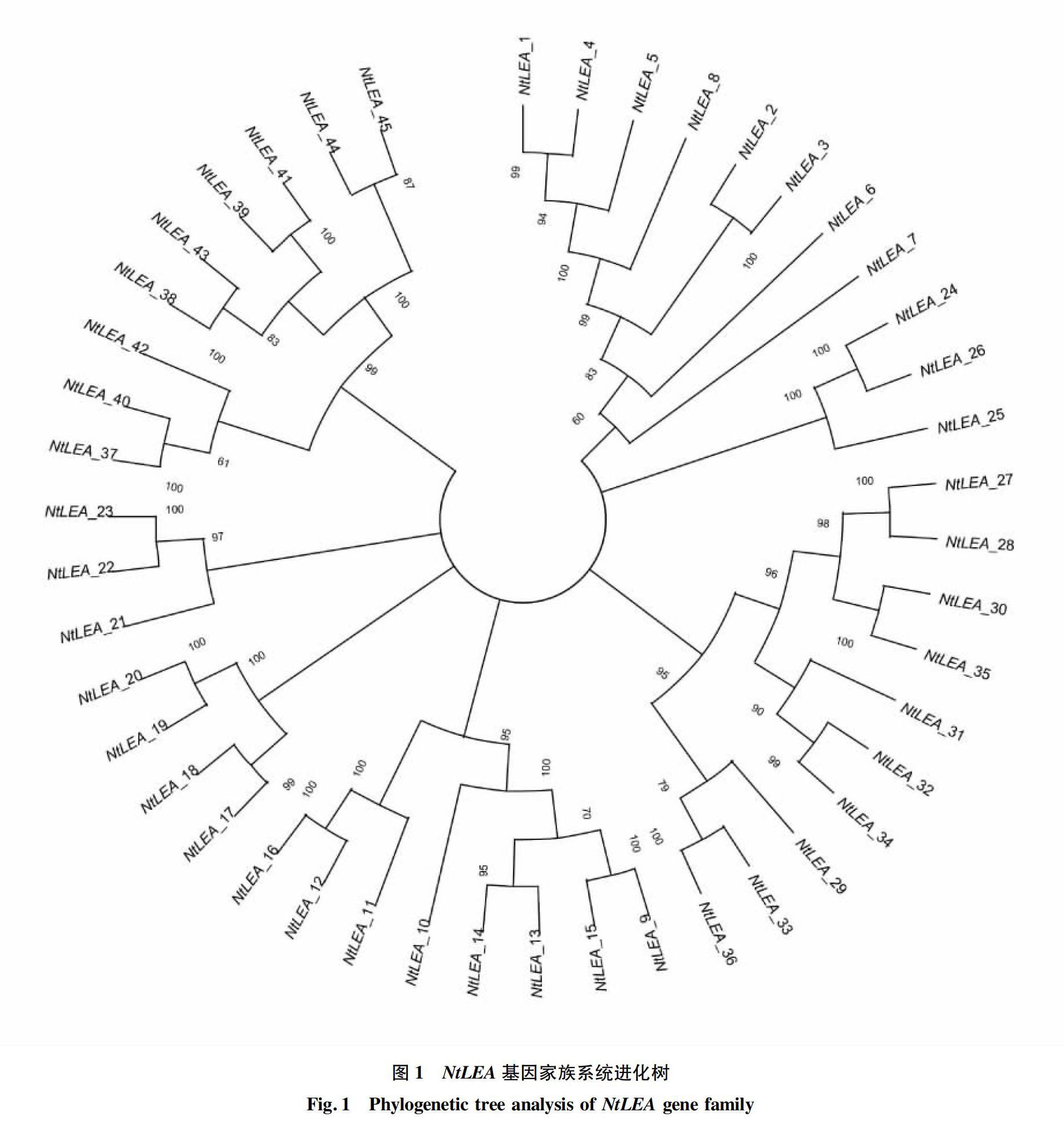
以拟南芥的全部LEA基因家族成员为模板,利用BLASTP与NCBI的CD-Search功能确定烟草中45个NtLEA家族成员,并根据系统发育分析命名为NtLEA_1~NtLEA_45。利用NJ法对45个NtLEA基因家族成员进行系统进化树的构建(图1),并根据NtLEA家族的结构域将NtLEA家族成员分成7个亚组:LEA_1(NtLEA_1~NtLEA_8)、LEA_2(NtLEA_9~NtLEA16)、LEA_3(NtLEA-17~NtLEA-20)、LEA_4(NtLEA_21~NtLEA23)、LEA_5(NtLEA_24~NtLEA_26)、Dehydrin(NtLEA_27~NtLEA_36)、SMP(NtLEA_37~NtLEA_45),并且7亚组的数量分别是8、8、4、3、3、10、9个,其中NtLEA_37和NtLEA_40同源性最高,共同位于SMP亚组中。
2.2 NtLEA基因家族的分子特征
利用ExPASy,对NtLEA家族成员进行基本信息和理化性质进行分析,结果见表1。45个NtLEA家族成员平均长度为198 aa(76~460 aa);平均分子量为21.24 kD(8.02~49.31 kD);LEA 1~7个亚组的平均等电点分为8.49、4.89、10.07、5.87、5.36、6.41、5.94。亲水性最大值为0.061,其余均为负值,说明大部分NtLEA家族蛋白质大部分为亲水性蛋白质。
2.3 NtLEA基因家族染色体信息
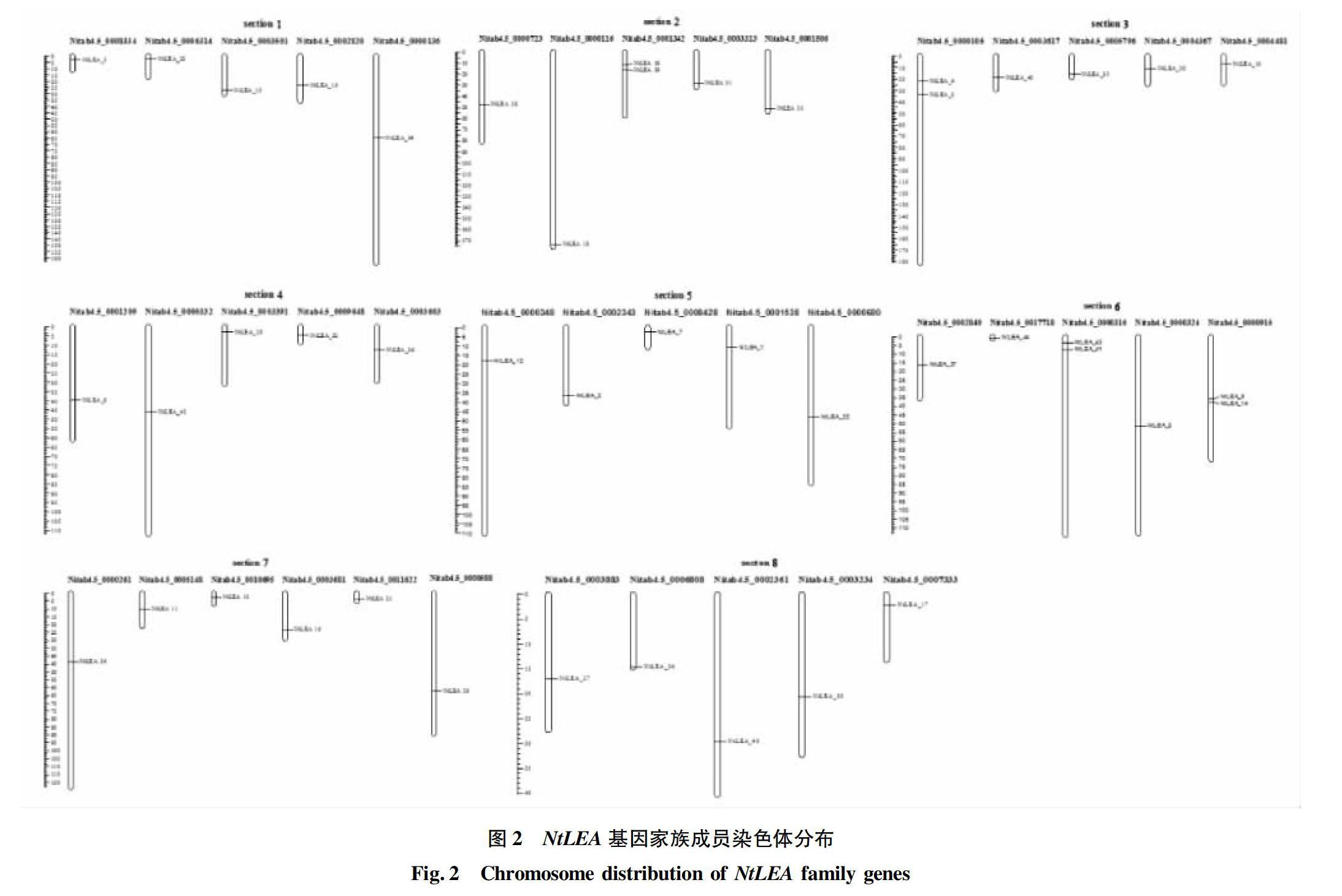
根据NtLEA基因家族鉴定结果信息,利用Mapchart 2.3.2进行染色体定位作图。经软件分析可知,45个NtLEA基因家族成员分布在41条染色体区段上(图2)。
2.4 NtLEA基因家族的基因结构 为了研究NtLEA基因家族的进化分组以及结构的特异性,利用GSDS在线软件对NtLEA基因的CDS、内含子等进行可视化展示(图3)。结果显示,45个NtLEAs基因家族成员具有结构的相似性,同时7个亚组具有差异性。45个NtLEAs基因家族的CDS结构具有1~3个,内含子数量为0~2个。LEA_1、LEA_2、LEA_3、LEA_4、LEA_5、dehydrin中CDS的数量大都为2个,其中NtLEA_11与NtLEA_16含1个CDS。SMP亚家族CDS数量均为3个。
3 讨论
越来越多的证据证明基因家族在植物的代谢、发育中起着不可或缺的作用。LEA蛋白在植物界中广泛存在,其编码基因在被子植物、裸子植物、苔藓植物、蕨类植物、藻类中均有克隆,甚至在部分动物、酵母、细菌及真菌中也有发现[24]。
该研究采用生物信息学方法对烟草LEA基因家族进行家族成员的鉴定、系统发育分析、分子特征的鉴定、染色体定位和基因结构分析。结果表明,在烟草中共鉴定出45个NtLEA基因家族成员,分布在LEA所有的亚组当中,共7个亚组。相同亚组中NtLEA成员具有进化的相近性,其中NtLEA_37和NtLEA_40进化关系最近。同时,相同的LEA亚组成员具有高同源性与相似的分子特征(等电点、分子量等)。NtLEA基因家族在染色体上分布广泛、偏好性较小,同时具有相似的基因结构,说明NtLEA基因家族具有功能的特异性与相似性。LEA蛋白在植物正常生长以及在干旱、盐碱、寒冷等非生物胁迫下保护过程中发挥着重要作用[9]。NtLEA家族蛋白具有亲水性的特点,可能与烟草对干旱等胁迫的应答有关。烟草胚胎发育晚期丰富蛋白家族基因可能是重要的抗性基因,研究烟草胚胎发育晚期丰富蛋白及相关基因,对烟草抗性育种具有重要意义。
参考文献
[1]
DURE L,CROUCH M,HARADA J,et al.Common amino acid sequence domains among the LEA proteins of higher plants[J].Plant Mol Biol,1989,12(5):475-486.
[2] GALAU G A,HUGHES D W,DURE L.Abscisic acid induction of cloned cotton late embryogenesis abundant (Lea)mRNAs[J].Plant Mol Biol,1986,7(3):155-170.
[3] DURE L,GREENWAY S C,GALAU G A.Developmental biochemistry of cottonseed embryogenesis and germination:Changing messenger ribonucleic acid populations as shown by in vitro and in vivo protein synthesis[J].Biochemistry,1981,20(14):4162-4168.
[4] GEORGE S,USHA B,PARIDA A.Isolation and characterization of an atypical LEA protein coding cDNA and its promoter from drought tolerant plant Prosopis juliflora[J].Appl Biochem Biotechnol,2009,157(2):244-253.
[5] OLVERA CARRILLO Y,CAMPOS F,REYES J L,et al.Functional analysis of the group 4 late embryogenesis abundant proteins reveals their relevance in the adaptive response during water deficit in Arabidopsis[J].Plant Physiol,2010,154(1):373-390.
[6] TUNNACLIFFE A,HINCHA D K,LEPRINCE O,et al.LEA Proteins:Versatility of form and function[M]//LUBZENS E,CERDA J,CLARK M.Sleeping beauties dormancy and resistance in harsh environments.Berlin:Springer,2010:91-108.
[7] CANDAT A,PASZKIEWICZ G,NEVEU M,et al.The ubiquitous distribution of late embryogenesis abundant proteins across cell compartments in Arabidopsis offers tailored protection against abiotic stress[J].Plant Cell,2014,26(7):3148-3166.
[8] HUNAULT G,JASPARD E.LEAPdb:A database for the late embryogenesis abundant proteins[J].BMC Genom,2010,11:1-9.
[9] ALTUNOGLU Y C,BALOGLU P,YER E N,et al.Identification and expression analysis of LEA gene family members in cucumber genome[J].Plant Growth Regul,2016,80(2):225-241.
[10] UMEZAWA T,FUJITA M,FUJITA Y,et al.Engineering drought tolerance in plants:Discovering and tailoring genes to unlock the future[J].Curr Opin Biotechnol,2006,17(2):113-122.
[11] KOBAYASHI F,TAKUMI S,NAKATA M,et al.Comparative study of the expression profiles of the Cor/Lea gene family in two wheat cultivars with contrasting levels of freezing tolerance[J].Physiol Plant,2004,120(4):585-594.
[12] GAO J,LAN T.Functional characterization of the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) protein gene family from Pinus tabuliformis (Pinaceae) in Escherichia coli[J].Sci Rep,2016,6:1-10.
[13] WANG Y J,HE L,HOU R,et al.Identification and the response to osmotic stress of LEA_1 gene family in Setaria italica[J].Mol Plant Breed,2018,16(12):3801-3807.
[14] HOUDE M,DALLAIRE S,N′DONG D,et al.Overexpression of the acidic dehydrin WCOR 410 improves freezing tolerance in transgenic strawberry leaves[J].Plant Biotechnol J,2004,2(5):381-387.
[15] SIVAMANI E,BAHIELDIN A,WRAITH J M,et al.Improved biomass productivity and water use efficiency under water deficit conditions in transgenic wheat constitutively expressing the barley HVA1 gene[J].Plant Sci,2000,155(1):1-9.
[16] XU D P,DUAN X L,WANG B Y,et al.Expression of a late embryogenesis abundant protein gene,HVA1,from barley confers tolerance to water deficit and salt stress in transgenic rice[J].Plant Physiol,1996,110(1):249-257.
[17] LIANG Y,XIONG Z Y,ZHENG J X,et al.Genome wide identification,structural analysis and new insights into late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) gene family formation pattern in Brassica napus[J].Sci Rep,2016,6:1-17.
[18] LAN T,GAO J,ZENG Q Y.Genome wide analysis of the LEA (late embryogenesis abundant) protein gene family in Populus trichocarpa[J].Tree Genet Genomes,2013,9(1):253-264.
[19] LIU H,XING M Y,YANG W B,et al.Genome wide identification of and functional insights into the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) gene family in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum)[J].Sci Rep,2019,9(1):1-11.
[20] LI X,CAO J.Late Embryogenesis Abundant (LEA) gene family in maize:Identification,evolution,and expression profiles[J].Plant Mol Biol Report,2016,34(1):15-28.
[21] ALTUNOGLU Y C,BALOGLU P,YER E N,et al.Identification and expression analysis of LEA gene family members in cucumber genome[J].Plant Growth Regul,2016,80(2):225-241.
[22] SUNARPI,HORIE T,MOTODA J,et al.Enhanced salt tolerance mediated by AtHKT1 transporter induced Na+ unloading from xylem vessels to xylem parenchyma cells[J].Plant J,2005,44(6):928-938.
[23] KUMAR S,TAMURA K,NEI M.MEGA:Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software for microcomputers[J].Comput Appl Biosci,1994,10(2):189-191.
[24] BATTAGLIA M,OLVERA CARRILLO Y,GARCIARRUBIO A,et al.The enigmatic LEA proteins and other hydrophilins[J].Plant Physiol,2008,148(1):6-24.

