气力式包衣杂交稻单粒排种器研制
臧 英,何思禹,王在满,刘顺财,王绪国,文智强
气力式包衣杂交稻单粒排种器研制
臧 英,何思禹,王在满※,刘顺财,王绪国,文智强
(1. 华南农业大学南方农业机械与装备关键技术教育部重点实验室,广州 510642;2. 华南农业大学工程学院,广州 510642)
为满足杂交稻单粒播种的作业需求,该研究结合包衣稻种设计了一种单粒气力式排种器,分析了吸种姿态对吸种精度的影响,利用稻种导流原理,设计了一种导流式吸种盘,对稻种在该吸种盘导流作用下的运动过程进行了分析,建立了吸附过程中稻种与吸种盘之间的运动模型。采用包衣稻种(杂交稻五优1179)为试验材料,采用三因素三水平全因素试验方法,在不同吸种盘转速、吸室负压和吸种盘结构情况进行试验分析。试验结果表明:在转速30 r/min、吸室负压1 400 Pa时,有导流槽和辅助吸种装置的吸种盘吸种效果最佳,单粒吸种率最高为81.58%,漏吸率为2.89%。试验结果验证了该吸种盘可有效提高单粒吸种率,满足杂交稻单粒播种的作业需求,为杂交稻单粒播种提供了一定理论基础。
农业机械;设计;试验;包衣稻种;气力式;单粒播种;导流槽;杂交稻;吸种姿态
0 引 言
精量穴直播技术是按水稻品种的种植农艺要求,精量定距成穴地将稻种均布于田间[1-2]。其直播稻的种类主要为常规稻和杂交稻。常规稻每穴播种量一般为5~10粒,而对于分蘖能力较强的杂交稻,直播时每穴播种量一般为2~4粒[3-4]。随着杂交稻种品质的提高,其用种量越来越低[5],因此,单粒播种技术尤为重要。
近年来,水稻机械直播技术得到快速发展[6-7]。机械式排种器主要适合中等或大播量要求,难以满足杂交稻精少播量播种的需要。气力式播种装置具有伤种率低、对种子形状适应性高等特点,是现在实现精少量播种的主要方式[8]。Karayel等[9-12]为实现玉米、棉花、大豆等作物种子的单粒播种,利用种子的物理特性建立数学模型,采用高速摄影等仪器观察记录整个播种过程,确定了气力式播种机的最佳负压值。Singh等[13]以棉花种子为研究对象,研究了气力式排种器吸种孔的结构,采用理论与试验相结合的方式分析了孔径与倒角对吸种效果的影响,确定最佳角度为120°。Yazgi等[14]为实现棉花和玉米种子的单粒播种,针对垂直圆盘式精密排种器,开展吸种盘不同吸孔数目和播种作业速度对排种性能影响的研究,试验结果表明,作业速度为1和1.5 m/s时,排种器对不同吸孔数目均有良好适应性。张国忠等[15-17]为实现杂交稻的精量穴播要求,采用群布吸孔的吸种盘设计,通过研究真空度、孔径和清种对平均播种量的影响,得到3~4粒/穴的合格率为81.87%。翟建波等[18]为解决杂交稻直播时因芽种流动性差和细长型状造成种箱中芽种架空或者堵塞的问题,设计了一种气力式杂交稻精量穴直播排种器,满足杂交稻2~4粒/穴的播种要求。邢赫等[19]设计了一种水稻播量可调气力式排种器,通过设置不同流道,采用全因素的试验方法,实现杂交稻的播量可调,且当吸孔组数为12、吸种负压为1 600 Pa和吸种盘排转速为20r/min时,1孔播种达到最佳效果,1~2粒率为82.41%,对实现单粒播种有一定的参考价值。王宝龙等[20]为提高杂交稻气力滚筒集排式精量排种器的排种精度,设计了一种楔形搅种装置,在吸种负压为1 600 Pa、滚筒转速为10 r/min、清种距离为1.94 mm时,1~3粒的吸种合格率为86.00%。上述研究在一定程度上实现了水稻的小播量播种要求,但未涉及单粒播种技术。
已有研究在一定程度上提高了播种精度,对实现单粒播种有一定指导意义,相较于多粒播种的吸种精度,单粒播种对吸种要求更高。本文从气力式排种器的吸种过程出发,以稻种的吸附姿态为研究基础,进行吸种盘的结构设计,以杂交稻五优1179为研究对象,采用三因素三水平的全因素试验方法,分析了吸种盘转速、吸室负压和吸种盘的结构对排种器吸种性能的影响,并进行了排种性能试验,以期为实现杂交稻的单粒播种提供依据。
1 单粒排种器总体结构与稻种吸附姿态分析
1.1 总体结构
水稻单粒气力式排种器整体结构如图1所示,主要包括种箱1,种箱连接件2,吸室壳体3,排种壳体4,法兰5,排种轴6,种刷7,吸种盘8,导种管9和卸种装置10。
排种器工作时,稻种由种箱1经种箱连接件2流入排种壳体4中的吸种室内,受吸室壳体3的负压流道内流场作用,在吸种室内被吸附在吸种盘8的吸孔上,吸种盘通过螺栓固定在法兰5上,法兰与排种轴6通过键连接同步转动,被吸附的稻种随吸种盘转动到投种区,在吸室壳体3的正压流场作用下离开吸种盘8经导种管9落在播种沟内,吸种盘8上的吸孔被种刷7清理干净后继续吸种过程。播种作业结束后,卸种装置10将剩余稻种回收。
1.2 稻种吸附姿态分析
由于稻种的球形度低,与吸孔配合方式难以固定,采用气力式排种器吸种时,经常出现重吸与漏吸现象,根据文献[21]与前期高速摄影观察可知,稻种的吸附姿态是影响稻种与吸孔精准配合的主要因素。通过高速摄影机拍摄排种器工作过程发现,单粒稻种的吸附姿态可大致分3种:1)种子中部被吸孔吸附,且长轴方向与吸种盘转动切向方向一致;2)种子中部被吸孔吸附,且长轴方向不与吸种盘转动切向方向重合;3)种子一端被吸孔吸附,如图2所示。
稻种的吸附过程就是稻种由静止加速到匀速转动的过程[22],在吸种盘完成吸种前,稻种与吸孔在吸种盘运动方向上存在相对速度,会产生相对位移,若稻种在被吸孔吸附前,脱离了吸附范围,会造成漏吸,图3为稻种相对于吸孔的运动示意图。
当稻种长轴方向相对于吸种盘转动为切向姿态时,吸种有效距离长,有利于被吸孔吸附。因此,通过对稻种吸附过程的稻种运动分析,可为实现对吸孔附近的稻种姿态调整、提高排种器的吸种性能、进行吸种盘结构设计提供理论基础。
2 关键结构设计
2.1 吸种盘
通过上述分析可知,稻种的吸附姿态将对稻种的吸附精度产生影响。吸种盘是排种器的核心部件,直接与稻种接触,其结构参数与尺寸参数将直接影响稻种的吸附姿态,如图4所示,吸种盘由吸孔、导流槽和辅助吸种装置构成。吸种盘直径165 mm,厚度2 mm,盘面均布16个吸孔,吸孔孔径为1.8 mm(根据经验公式,=(0.64~0.66)[23]计算,为吸孔直径,为稻种平均宽度,为2.85 mm)。吸种盘上设有16个导流槽,导流槽由内侧和外侧导流槽构成,分别位于吸孔两侧,整个导流槽长33 mm,宽16 mm。辅助吸种装置紧靠吸孔外侧,为长条状,与外侧导流槽平行,长5 mm,宽2 mm,高2 mm。
当吸种盘转动时,吸种室内的稻种在外侧导流槽1和内侧导流槽2共同作用下,向吸孔3处汇聚。在这个过程中,由于稻种为纺锤状,当吸种盘转动时,稻种受导流槽和种群的作用,为通过两侧导流槽形成的隘口,稻种将长轴方向与吸种盘转动的切线方向重合。通过导流槽的稻种在吸孔3处受辅助吸种装置4和吸孔处负压的作用而不断加速,最终被吸附在吸孔3上,完成吸种过程。
1.外侧导流槽 2.内侧导流槽 3.吸孔 4.辅助吸种装置
1.Outside guide groove 2.Inner guide groove 3.Suction hole 4.Auxiliary seed suction device
注:为吸种盘转动角速度,rad·s-1。
Note:is the rotation angular velocity of the seed sucking plate, rad·s-1.
图4 吸种盘结构示意图
Fig.4 Structure diagram of seed sucking plate
2.2 导流槽
2.2.1 导流槽深度
通过对稻种吸附姿态分析可知,稻种长轴方向与吸种盘转动方向切向一致时有利于吸种。为实现稻种吸附姿态的调整,利用导流槽的凹槽结构对一端靠近吸种盘的稻种进行翻转。如图5所示,当吸种盘转动时,导流槽带动一端靠近吸种盘的稻种翻转,稻种由姿态1变为姿态2。为分析导流槽深度对稻种翻转的影响,建立导流槽深度对稻种吸附姿态的影响模型。
根据稻种与吸种盘之间的受力分析,以稻种翻转前的质心位置为坐标原点轴方向与吸种盘盘面垂直,轴方向与吸种盘转动的切向方向一致,建立稻种在轴方向的受力方程:
式中f2=μF,为吸种盘与稻种间的摩擦系数,取0.36; F1=Ftan,为种子的自然休止角,通过试验求得=31.87°。
为使目标稻种通过导流槽后,在种群作用力下实现姿态调整,对目标稻种与底层稻种的接触点′点的力矩进行分析,目标稻种在吸种盘作用下转动时,应满足:
将式(1)代入式(2)求得≥50°,根据图5中稻种转动力学模型可知:
根据前期不同稻种的三轴尺寸测量结果,稻种的长轴尺寸一般在6~9 mm之间,为提高吸种盘的适应性,取为9 mm,代入式(3)求得导流槽深度为1.5 mm。根据文献[24],结合包衣稻种的物理特性,导流槽斜面倾角取45°。
2.2.2 内侧导流槽
为了驱使吸孔内侧的稻种向吸孔处靠近,并将吸孔处稻种姿态调整为长轴方向与吸种盘运动的切向方向一致。根据文献[25]设计内侧导流槽,使吸孔内侧的稻种沿导流槽向吸孔处运动。在吸种盘转动时,稻种一边随吸种盘转动,一边沿着导流曲线从点运动至点,在吸孔上方汇聚,在该曲线上,稻种运动的绝对轨迹为点所在基圆切线方向的线段,如图6所示。
内侧导流槽曲线表达式为
式中x为稻种在轴坐标值,mm;y为稻种在轴坐标值,mm;0为导流槽曲线基圆半径,mm;为稻种由点运动至点时,吸种盘转过的角度,(°);为稻种转角速率系数,取0.1~0.9。
根据图6几何关系有:
式中1=0/cos,化简式(5)得:
当稻种随导流槽向吸孔处运动时,为使稻种长轴方向与吸孔切向方向保持一致,的值应大于45°。为保证导流槽离开堆积的稻种前,带动吸种室内侧稻种从点运动至吸孔上方点,依据所使用的气力式排种器排种壳体结构[26],取0为45 mm,依据吸种室内的种层高度,取为0°~50°。将上述参数代入式(6)中,求得转角速率系数为0.1。
2.2.3 外侧导流槽
为使吸孔外侧的稻种向吸孔处靠近,对外侧导流槽上的稻种受力进行分析,如图7所示。
根据稻种在外侧导流槽上的受力分析可知,稻种在、方向上的受力方程为
解方程,化简后可得:
根据前期试验结果,稻种在不锈钢板上的滑动摩擦系数=0.36,吸孔所在圆的半径=70 mm。根据田间作业效率要求,水田作业机具的行走速度一般在0.5~1 m/s,对应排种器转速在20~40 r/min之间[19]。故的取值范围为2.09~4.19 rad/s,求得的范围为31.15°~55.87°。取值越小,越有利于提高稻种的流动,同时为了便于加工,设计为35°。
2.3 辅助吸种装置
在吸种盘转速高的情况下,仅靠负压作用吸种精度难以保证。为此,本文设计了辅助吸种装置带动吸孔处的稻种,以提高吸种精度[27-30]。
如图8所示,通过前期试验研究,辅助吸种装置设计为长条状,长5 mm,宽2 mm,高2 mm,粘附在吸孔外侧,长轴方向与吸孔相切,且与外侧导流槽平行。
为研究辅助吸种装置对吸孔处稻种的带动作用,对吸孔处的稻种进行受力分析(由于吸种盘上的导流槽对稻种的姿态进行调整,故以长轴方向与吸种盘转动方向的切向一致的稻种为研究目标)。稻种的加速度=2/,式中为稻种随盘转动的线速度,为稻种的长轴长度,吸孔处稻种的受力如图9所示。
参考袁月明[31]对稻种充种区的受力分析,稻种在吸力作用下紧贴吸种盘,受吸种盘的摩擦力和辅助吸种装置的摩擦力作用加速运动,目标稻种由静止状态加速至随盘转动。由图9可知,吸孔处稻种在轴上的受力关系为
式中f2=Fμ,为吸种盘与稻种间的摩擦系数。
吸力与真空度之间的关系为
式中为吸孔面积,m2,πd/4,为吸孔直径,mm;H为吸室临界真空度,Pa。
联立式(9)~(10)有:
由式(11)可知,在吸种盘转速一定的情况下,辅助吸种装置提供的作用力f1能减少稻种吸附所需负压值,有利于降低吸种盘转速和吸室负压对吸种精度的影响,提高吸种性能。
3 播种性能试验
3.1 试验材料
根据上述理论分析进行吸种盘结构设计,为了验证所设计吸种盘的单粒吸种性能,对该排种器进行了台架试验。
由于水稻裸种存在形状不规则、流动性差和脆性大等特性[32],影响吸种精度,故试验选用华南农业大学培育、广东农科院包衣处理的五优1179。分别测量未包衣和包衣处理后的稻种物理参数(尺寸、千粒质量、休止角),其含水率分别为13.8%、18.0%,物理特性如表1所示。
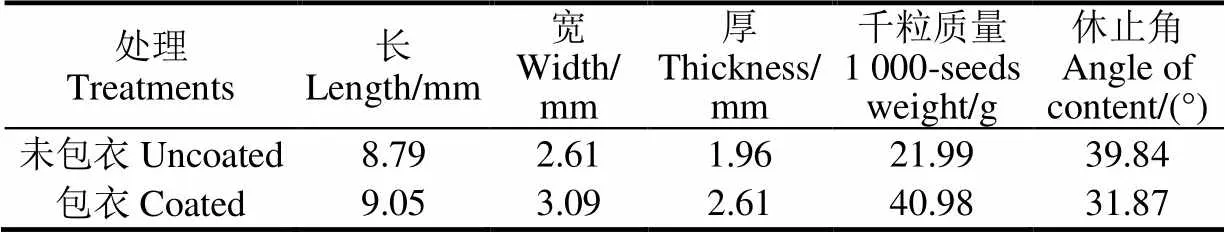
表1 稻种物理参数
由表1可知,包衣处理后的稻种三轴尺寸更大,气流作用有效面大,休止角小,稻种流动性好,相较于裸种更易于吸附。
试验装置如图10所示,主要包括排种器、驱动电机、风机、电子气压计和高速摄影机。试验采用微差压变电子气压计进行气压监测,采用美国PHOTRON公司生产的FASTCAMSUPER 10K型高速摄像机对排种器的吸种情况进行连续拍摄记录。
3.2 试验设计
吸种盘转速是影响播种精度的因素之一[33]。根据田间作业速度要求,气力式排种器吸种盘的转速一般为20~40 r/min。为提高排种器适应性,研究高速作业状态下不同吸种盘的吸种情况,排种器转速设置为30、40和50 r/min。
参考现有垂直圆盘式排种器的研究,吸附1~3粒稻种的最佳工作负压为1 600 Pa[34],由于本文所设计的排种器只吸附1粒稻种,负压要比多粒吸附的负压值小。根据预试验(如表2所示),当负压值过大时,吸种合格率下降,重吸率增大,因此负压真空度取1 200~1 600 Pa。
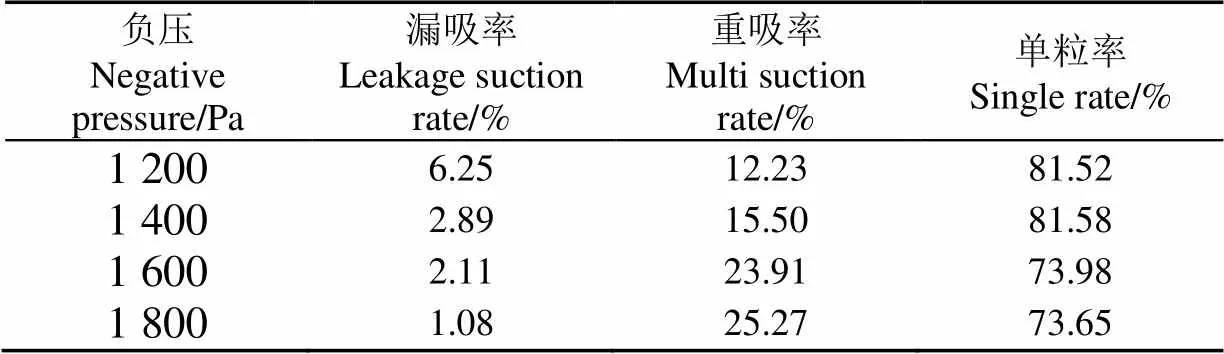
表2 吸种盘转速30 r·min-1时的吸种效果
为明确吸种盘结构对排种器吸种性能的影响,选取3种吸种盘结构进行试验,分别为仅有导流槽的吸种盘(a盘)、仅有辅助吸种装置的吸种盘(b盘)和导流槽加辅助吸种装置的吸种盘(c盘),如图11所示。结合吸种盘转速、吸室负压进行单粒排种全因素试验。
试验因素水平如表3所示。
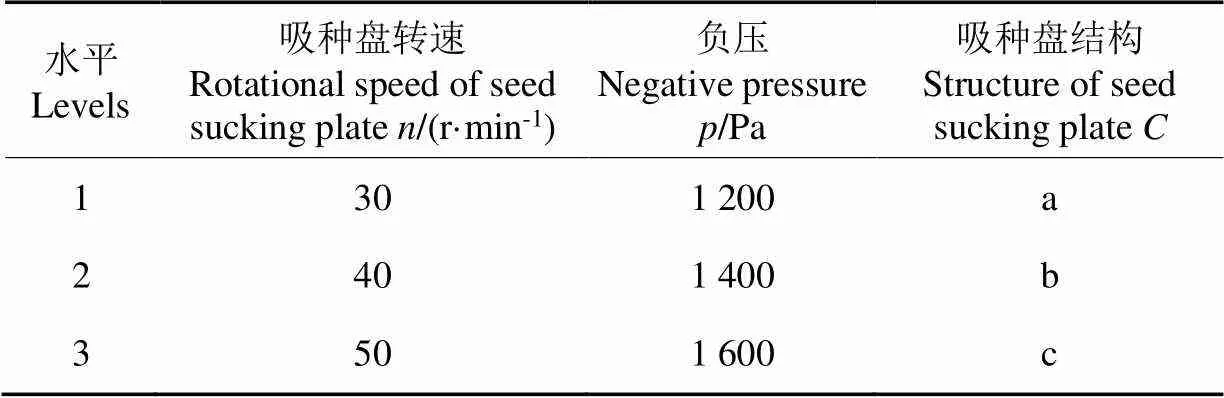
表3 试验因素与水平
3.3 评价指标
根据GB/T6973-2005《单粒(精密)播种机试验方法》[35]进行试验设计,定义每组吸孔吸附1粒稻种为单粒指标,≥2粒为重吸,0粒为漏吸,每组试验统计250粒种子,重复3次。
4 结果与分析
其试验结果如表4所示。由表4可知,a盘的平均单粒率为63.16%,b盘的平均单粒率为74.81%,c盘的平均单粒率为78.63%。c盘的吸种单粒率最高,其原因在于,b盘和c盘利用辅助吸种装置对稻种吸附位置进行限制,提高了吸种单粒率,a盘只有导流槽,吸种单粒率受转速和负压的影响较大。
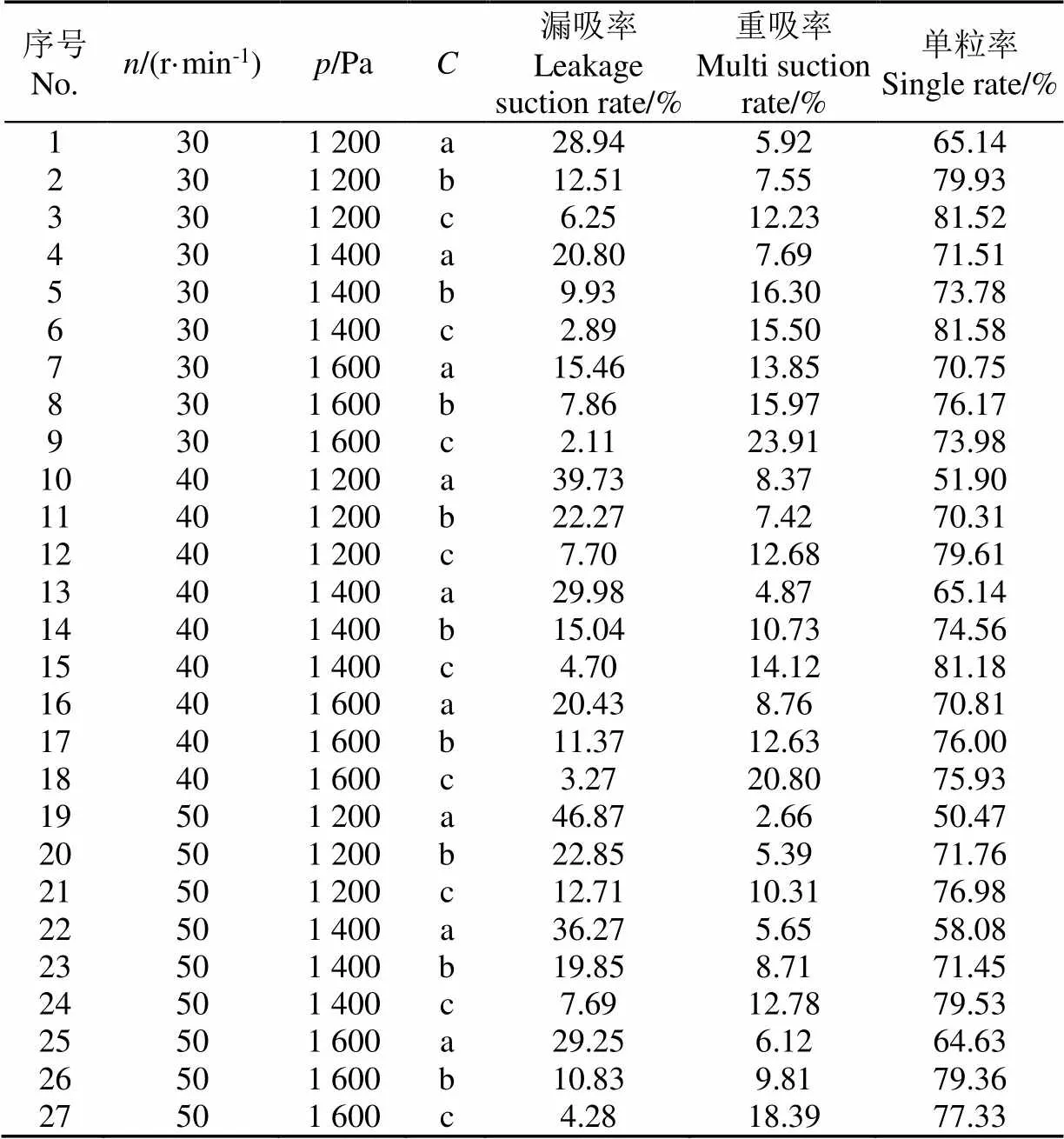
表4 全因素试验统计结果
由表4的漏吸率可知,各吸种盘的漏吸情况均随负压的增大而减少,随转速的增大而增大,符合气力式排种器的吸种特点。其中a盘受转速和负压的影响最大,在试验参数条件下,漏吸率为15.46%~46.87%;b盘的漏吸率为7.86%~22.85%;c盘的漏吸率为2.11%~12.71%。在相同条件下,c盘的漏吸率受转速和负压的影响最小,漏吸率最低,在转速为30 r/min、负压为1 600 Pa时,最低漏吸率为2.11%。其原因在于,c盘通过导流槽实现稻种吸附姿态的调整,辅助吸种装置带动吸孔处的稻种,降低了漏吸率。a盘没有辅助吸种装置,稻种的吸附仅靠负压流场的作用来实现,在负压较低和吸种盘转速过快时,稻种很难被吸附;b盘由缺少导流槽对稻种吸附姿态的调整,漏吸率高。
对上述试验结果进行方差分析,结果如表5所示,由方差结果可知,在高速作业速度范围和所选负压范围内,吸种盘的结构对漏吸率、重吸率和单粒率有极显著的影响(<0.01),吸种盘转速和吸室负压对漏吸率以及重吸率的影响极为显著(<0.01)。3个试验因素对单粒率的影响显著性从大到小的顺序为、、,其中吸种盘的结构对单粒率的影响极为显著(<0.01),吸种盘转速和吸室负压对单粒率的影响不显著(>0.05)。本文通过预试验与理论分析,已基本确定了适宜的工作负压范围,在进行试验分析时,负压与转速的水平范围控制在适宜的范围内。
由图12高速摄影照片可以看出,导流槽加辅助吸种装置的吸种盘结构能对吸孔处稻种吸附姿态调整,使得吸附稻种的长轴方向均与吸种盘切向方向保持一致,实现对稻种吸附姿态的调整。
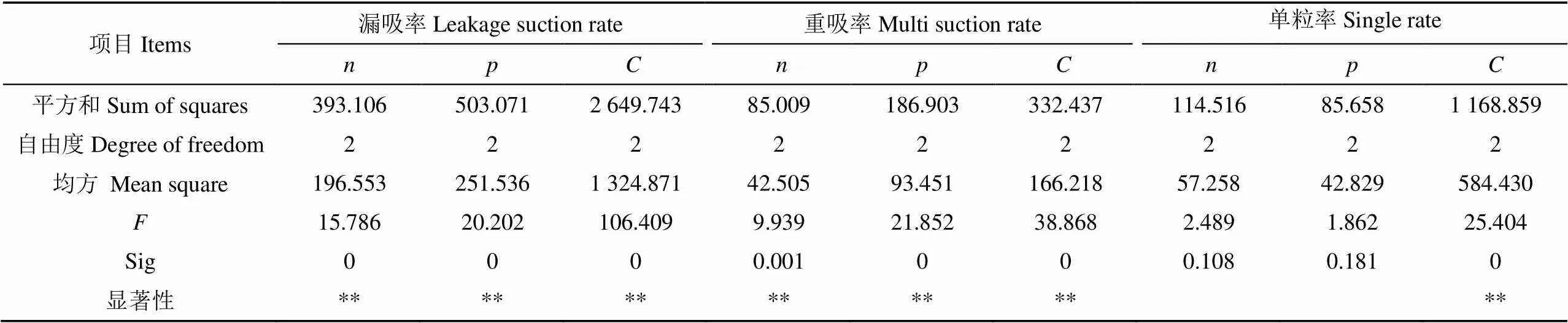
表5 方差分析
注:**表示极显著(<0.01)。
Note: ** is extremely significant (<0.01).
5 讨 论
本文以包衣杂交稻种为试验材料,进行了单粒吸种试验。试验结果表明,本文所设计的吸种盘可有效的提高单粒吸种率。其原因为:吸种盘上的导流槽通过对吸孔处稻种的姿态进行改变,提高了吸种率,所以带导流槽加辅助吸种装置的吸种盘其空穴率要低于只有辅助吸种装置的吸种盘;辅助吸种装置位于吸孔外侧,能对吸孔处的稻种进行提速和对吸种位置进行限制,提高了稻种的吸附精度,所以带辅助吸种装置的吸种盘其单粒率要高于仅有导流槽的吸种盘。
试验材料选用的杂交稻五优1179的包衣稻种,相较于裸种,其三轴尺寸有所增大,流动性更好,有利于提高吸种精度。本文仅对包衣稻种的吸种精度进行研究,没有分析排种器结构对包衣破损率的影响,对于包衣材料和包衣厚度等对稻种破损率的影响还需进一步研究。
本文对试验结果进行方差分析发现,吸种盘转速和吸室负压对漏吸率和重吸率的影响显著,但对合格率的影响不显著,这与现有研究有差异。其原因在于,本文试验所选取的负压和转速通过理论分析与预试验确定,在此范围内,合格率受转速和负压的影响不显著,但超过该范围内,吸种负压与转速将对合格率产生一定影响[19]。
6 结 论
1)为满足杂交稻的单粒播种要求,本文对气力式排种器的吸种原理进行研究,通过理论分析、高速摄影技术与试验台试验相结合发现,当吸孔处的稻种其长轴方向与吸孔切向方向一致时,有利于提高排种器的吸种性能。因此,设计了一种导流槽加辅助吸种装置的吸种盘结构,并通过理论分析,确定了吸种盘参数。
2)选取杂交稻五优1179的包衣稻种为试验材料,在不同吸种负压、吸种盘转速和吸种盘结构条件下进行三因素三水平全因素试验,试验结果表明:导流槽加辅助吸种装置的吸种盘结构单粒吸种率高,吸种精度受转速和气压的影响小,在转速30 r/min、吸室负压1 400 Pa时,单粒吸种率最高为81.58%,相较于另外2种吸种盘结构,漏吸率较低,为2.89%,满足杂交稻单粒播种的技术要求。
[1]Xing H, Luo X W, Zang Y, et al. General structure design and field experiment of pneumatic rice direct-seeder[J]. Int J Agric & Biol Eng, 2017, 10(6): 31-42.
[2]Fu W, Zhang Z, Zang Y, et al. Development and experiment of rice hill-drop drilling machine for dry land based on proportional speed regulation[J]. Int J Agric & Biol Eng, 2017, 10(4): 77-86.
[3]Zhang M H, Wang Z M, Luo X W, et al. Review of precisionrice hill-drop drilling technology and machine for paddy[J].Int J Agric & Biol Eng, 2018, 11(3): 1-11.
[4]郑天翔,唐湘如,罗锡文,等. 不同灌溉方式对精量穴直播超级稻生产的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(8):52-55.
Zheng Tianxiang, Tang Xiangru, Luo Xiwen, et al. Effects of different irrigation methods on production of precision hill-direct-seeding super rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(8): 52-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5]吴明亮,汤楚宙,李明,等. 水稻精密播种机排种器研究的现状与对策[J]. 中国农机化,2003(3):30-31.
Wu Mingliang, Tang Chuzhou, Li Ming, et al. The present situation and countermeasures about seeding apparatus of paddy precision seeder[J]. China Agricultural Mechanization, 2003(3): 30-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6]罗锡文,蒋恩臣,王在满,等. 开沟起垄式水稻精量穴直播机的研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(12):52-56.
Luo Xiwen, Jiang Enchen, Wang Zaiman, et al. Precision rice hill-drop drilling machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(12): 52-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7]曾山,汤海涛,罗锡文,等. 同步开沟起垄施肥水稻精量旱穴直播机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程报,2012,28(20):12-19.
Zeng Shan, Tang Haitao, Luo Xiwen, et al. Design and experiment of precision rice hill-drop drilling machine for dry land with synchronous fertilizing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(20): 12-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8]梅婷,李仲恺,王小龙,等. 国内气力式精密播种器的研究综述[J]. 农业装备与车辆工程,2013,51(4):17-21.
Mei Ting, Li Zhongkai, Wang Xiaolong, et al. Study on pneumatic precision seeder in china[J]. Agricultural Equipment and Vehicle Engineering, 2013, 51(4): 17-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9]Karayel D. Performance of a modified precision vacuum seeder for no-till sowing of maize and soybean[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 2009, 104(2): 121-125.
[10]Karayel D, Barut Z B, ÖZmerzi A. Mathematical modelling of vacuum pressure on a precision seeder[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2004, 87(4): 437-444.
[11]Karayel D, Wiesehoff M, ÖZmerzi A, et al. Laboratory measurement of seed drill seed spacing and velocity of fall of seeds using high-speed camera system[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2006, 50(2): 89-96.
[12]Karayel D, ÖZmerzi A. Effect of forward speed on hill dropping uniformity of a precision vacuum seeder[J]. Hort Technology, 2004, 14(3): 364-367.
[13]Singh R C, Singh G, Saraswat D C. Optimization of design and operational parameters of a pneumatic seed metering device for planting cottonseeds[J]. Biosystems Engineering 2005; 92(4): 429-438.
[14]Yazgi A, Degirmencioglu A. Measurement of seed spacing uniformity performance of a precision metering unit as function of the number of holes on vacuum plate[J]. Measurement, 2014, 56(10): 128-135.
[15]张国忠,罗锡文,臧英,等. 水稻气力式排种器群布吸孔吸种盘吸种精度试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(6):13-20.
Zhang Guozhong, Luo Xiwen, Zang Ying, et al. Experiment of sucking precision of sucking plate with group holes on rice pneumatic metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(6): 13-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16]张国忠,臧英,罗锡文,等. 粳稻穴播排种器直线型搅种装置设计及排种精度试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(17):1-9.
Zhang Guozhong, Zang Ying, Luo Xiwen, et al. Line-churning tooth design and metering accuracy experiment of rice pneumatic precision hill-drop seed metering device on pregnant japonica rice seed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(17): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17]张国忠,臧英,罗锡文,等. 水稻气力式排种器导向型搅种装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(12):1-8.
Zhang Guozhong, Zang Ying, Luo Xiwen, et al. Design and experiment of oriented seed churning device on pneumatic seed metering device foe rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(12): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18]翟建波,夏俊芳,周勇. 气力式杂交稻精量穴直播排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(1):75-82.
Zhai Jianbo, Xia Junfang, Zhou Yong. Design and experiment of precision hill-drop drilling seed metering device for hybrid rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(1): 75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19]邢赫,臧英,王在满,等. 水稻气力式播量可调排种器设计与参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(4):20-28.
Xing He, Zang Ying, Wang Zaiman, et al. Design and parameter optimization of rice pneumatic seeding metering device with adjustable seeding rate[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(4): 20-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20]王宝龙,王在满,罗锡文,等. 杂交稻气力滚筒集排式排种器楔形搅种装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(23):1-8.
Wang Baolong, Wang Zaiman, Luo Xiwen, et al. Design and experiment of wedge churning device for pneumatic cylindertype seed metering device for hybrid rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(23): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21]李凤丽,陈江辉,刘飞,等. 基于高速摄像技术种子吸附姿态对排种性能的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2018,23(4):128-136.
Li Fengli, Chen Jianghui, Liu Fei, et al. Influence of seed adsorption posture on seeding performance based on high speed camera technology[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2018, 23(4): 128-136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22]杨宛章,孙学军,康秀生. 气吸式播种机种子吸附过程研究[J]. 新疆农业大学学报,2001(4):49-53.
Yang Wanzhang, Sun Xuejun, Kang Xiusheng. A study on suction seed course of pneumatic seeder[T]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2001(4): 49-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23]中国农业机械化科学研究院. 农业机械设计手册:上册[M]. 北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2007.
[24]史嵩,刘虎,位国建,等. 基于DEM-CFD的驱导辅助吸种气吸式排种器优化与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2020,51(5):54-66.
Shi Song, Liu Hu, Wei Guojian, et al. Optimization and experiment of pneumatic seed metering device with guided assistant filling based on EDEM-CFD[J]. Transcations of the Chinese Society for Agriculural Machinery, 2020, 51(5): 54-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25]史嵩,周纪磊,刘虎,等. 驱导辅助吸种气吸式精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2019,50(5):61-70.
Shi Song, Zhou Jilei, Liu Hu, et al. Design and experiment of pneumatic precision seed-metering device with guided assistant seed-filling[J]. Transcations of the Chinese Society for Agriculural Machinery, 2019, 50(5): 61-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26]罗锡文. 一种气力穴播排种器:102349376A[P]. 2012-02-15.
[27]李成华,马成林,于海业,等. 倾斜圆盘勺式玉米精密排种器的试验研究[J]. 农业机械学报,1999(2):3-5.
Li Chenghua, Ma Chenglin, Yu Haiye, et al. An experimental study on the precision metering device with declined scoop-type disc for maize[J]. Transcations of the Chinese Society for Agriculural Machinery, 1999(2): 3-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28]马成林,王十周,张守勤,等. 气力轮式排种器试验研究[J]. 农业机械学报,1990(3):28-34.
Ma Chenglin, Wang Shizhou, Zhang Shouqin, et al. The study and design of pneumatic wheel-type seed-metering device[J]. Transcations of the Chinese Society for Agriculural Machinery, 1990(3): 28-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29]丁力,杨丽,刘守荣,等. 辅助充种种盘玉米气吸式高速精量排种器设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(22):1-11.
Ding Li, Yang Li, Liu Shourong, et al. Design of air suction high speed precision maize seed metering device with assistant seed filling plate[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 34(22): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30]Xing H, Zang Y, Wang M Z, et al. Design and experimental analysis of astirring device for a pneumatic precision rice seed metering device[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2020, 63(4): 799-808.
[31]袁月明. 气吸式水稻芽种直播排种器的理论及试验研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2005.
Yuan Yueming. Research of Theory and Experiment on Air Suction Seed-metering Device for Direct Direct Drilling of Rice Bud-sowing[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32]张顺,杨继涛,李勇,等. 水稻内充气力式精量穴直播排种器吸种性能试验[J]. 浙江农业学报,2019,31(8):1379-1387.
Zhang Shun, Yang Jitao, Li Yong, et al. Experiment of sucking performance of inside-filling pneumatic type precision hill-drop drilling seed-metering device for rice[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2019, 31(8): 1379-1387. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33]万霖,王洪超,李海龙,等. 水稻旱直播气吸式精量穴播机的设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2018,40(11):64-68.
Wan Lin, Wang Hongchao, Li Hailong, et al. Design and test on the precision hill-drop drill of dry direct seeding rice type[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2012, 40(11): 64-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34]邢赫,臧英,王在满,等. 水稻气力式排种器分层充种室设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(4):42-48.
Xing He, Zang Ying, Wang Zaiman, et al. Design and experiment of stratified seed-filling room on rice pneumatic metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(4): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35]全国农业机械标准化技术委员会. 单粒(精密)播种机试验方法:GB-T 6973-2005[S]. 北京:中国国家标准化管理委员会,2005.
Design of pneumatic single seed metering device for coated hybrid rice
Zang Ying, He Siyu, Wang Zaiman※, Liu Shuncai, Wang Xuguo, Wen Zhiqiang
(1.,,510642,;2.,,510642,)
Direct seeding of rice is widely expected as one of the most important technology in mechanized rice planting. At present, two ways were mainly divided into the transplanting and direct seeding. The direct seeding can reduce the input of procedures and costs, while the growth cycle. In the complex field environment, direct-seeded rice seeds are easily affected by diseases, pests, weeds, and flooding, leading to greatly reduce the emergence rate and the yield. Alternatively, the seed coating technology can be used to provide micro-fertilizers, growth regulators and pesticides for the germination of seeds and the growth of seedlings. Specifically, the film-forming agents, adhesives, and other ingredients are generally used to uniformly bond the active ingredients on the surface of seeds. Since its convenient application, low cost, as well as resistance to pests and diseases, the seed coating technology can greatly contribute to enhance the seedling rate in the field, and the growth potential of seedlings. Particularly, small environmental pollution can meet the harsh requirement of ecological agriculture. In recent years, the mechanical direct seeding technology of rice has been commonly used in a large area in China, one of which the precision hole direct seeding technology of rice has good ventilation and permeability in the paddy field. The rice seeds are distributed evenly in the field, according to the agronomic requirements of rice varieties. The main types of direct seeding rice are the conventional rice and hybrid rice. The sowing rate is normally 5-10 per hole of conventional rice, while the sowing rate is generally 2-4 grains per hole for the hybrid rice with strong tillering ability. With the emergence of super hybrid rice and some high-quality rice varieties, the single-grain sowing has become particularly important, due to it meets the requirements of agronomic planting. In this study, a single-grain pneumatic seed metering device was designed for the coated rice to meet the demand of single-grain sowing of super rice. The physical parameters of coated rice seeds were measured. A movement model was established between rice seed and diversion suction plate during adsorption, according to the movement process of rice seed under the action of suction tray. The optimal negative pressure was calculated under the ideal condition of seed suction disk. Taking the coated rice variety (Super Rice Wuyou 1179) as the experimental object, the three-factor and three-level all-factor test was used to analyze the seed absorption of rice varieties at the speed of suction tray, negative pressure of suction chamber, and structure of seed suction tray. The experimental results show that the seed suction effect was the best, when the rotating speed of diversion suction tray was 30 r/min, and the negative pressure of suction chamber was 1 400 Pa. The seed sucking effect was best in the seed sucker structure with diversion groove and auxiliary seed sucking device, where the maximum of single seed sucking rate was 81.58%, and the leakage rate was 2.89%. Therefore, the suction tray can effectively improve the seed absorption rate per grain, suitable for the needs of single-grain sowing of super rice. The finding can provide a theoretical basis for the rapid development of single-grain sowing of rice.
agricultural machinery;design; test; coated rice seed; pneumatic; single seed seeding;diversion groove; hybrid rice; sucking posture
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.01.002
S223.2
A
1002-6819(2021)-01-0010-09
臧英,何思禹,王在满,等. 气力式包衣杂交稻单粒排种器研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(1):10-18.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.01.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Zang Ying, He Siyu, Wang Zaiman, et al. Design of pneumatic single seed metering device for coated hybrid rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(1): 10-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.01.002 http://www.tcsae.org
2020-09-28
2020-12-20
国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFD0100800);国家自然科学基金(31871529);现代农业产业技术体系建设专项基金(CARS-01-41)
臧英,博士,教授,研究方向为水稻生产机械关键技术与装备。
王在满,博士,副研究员,研究方向为水稻生产机械化关键技术与装备。
中国农业工程学会高级会员:臧英(E041200443S)

