Matrix Effect in Direct Analysis of Raw Solid and Viscous Drugs by Solid-substrate Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
DI Dan-dan,YUAN Zi-cheng,WU Lin,YAO Ya-nan,HU Bin
(Institute of Mass Spectrometry and Atmospheric Environment,Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632,China)
Abstract:Solid and viscous auxiliaries are often used for manufacturing granules,tablets,capsules and ointments in pharmaceutical industry,which emerge in the promising forms to maintain the stability and activity of various drugs by a variety of matrices.Ambient mass spectrometry(MS) with wooden-tip electrospray ionization(ESI) has been successfully developed for direct analysis of raw drug samples.However,matrix effect in such an ambient ESI-MS analysis on solid and viscous drugs has not yet been well understood.In this work,ionization responses to several modes of drugs in various viscous and solid matrices were investigated using a typical wooden-tip ESI-MS.Ionization responses were found to be related to the solubility of solid matrices.Ionic suppression and interference were observed in soluble solid matrices,while significant ionic interference was not generated in insoluble matrices.However,by adding spray solvent,insoluble matrices were changed in a viscous state suppressing spray ionization process.Further investigation revealed that ionization responses to analytes were decreased as a power function(r2>0.95) with the increase of matrix viscosity from 1 cP to 500 cP in this study.Therefore,this study may provide a good understanding for matrix effect and signal response in substrate ESI-MS analysis on solid and viscous samples.
Key words:matrix effect;solid samples;viscous samples;solid-substrate electrospray ionization;ambient mass spectrometry
It is a fact that various formulated pharmaceuticals are made in solid and viscous forms to maintain the pharmaceutical stability in process,storage and usage,and many commercial drugs thus commonly contain complicated matrices[1-2].Commercially,various solid or viscous matrices such as talc powder,calcium carbonate(CaCO3),starch,dextrin,and liquid paraffin and polymers are commonly used in pharmaceutical industry[3-4].Various possibilities of active pharmaceutical ingredients can be significantly influenced by the chemical and physical properties of drug matrices[1,5].Therefore,characterization of drug molecules in complicated matrices is a routine task in pharmaceutical analysis in ensuring the quality and efficacy of drugs.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry(ESI-MS) is one of the most powerful analytical methods for characterization of drug molecules[6].Conventionally,sample pretreatment procedures such as extraction and separation,which are labor-intensive and time-consuming procedures,were usually required before ESI-MS characterization[6].Ambient MS techniques are hot topics for direct analysis of raw drug samples because the analytes can be analyzed with no or little sample pretreatment[7-8].Ambient MS with solid-substrate ESI has been successfully developed for direct drug analysis[9].Various substrates such as paper[10],wooden-tip[11],bamboo tip[12],metal probe[13]and others substrates[9]have been developed as ESI emitter[14-18].Particularly,wooden-tip ESI-MS has been successfully used for direct analysis of solid and viscous raw samples,including powders,tablets,capsules,ointment and cream[11,15,17-18].The wooden-tip(eg.toothpick) was used for loading raw sample,and extraction/spray solvent was loaded on the samples to extract analytes and to generate spray ionization under a strong electric field.The presence of matrices are parts of the raw samples and thus could be internal standards in quantitative analysis[19].Although good detection limits at ng/mL or lower level have been reported in the literatures for direct detection of target analytes in various raw samples,matrix effect and ion suppression were frequently found in direct ESI-MS detection of target analytes at low concentration[19-23].Matrix effect in direct ESI-MS analysis of raw samples has been conducted to investigate extraction/spray solvents and the sample position on the substrate[19,23].However,the intrinsic property of solid and viscous matrices affecting on the matrix effect in direct ESI-MS analysis of raw samples has not yet been well understood.Viscous and solid matrices that impact direct ESI-MS analysis of raw drugs are highly beneficial to further understand the matrix effect in direct drug analysis.
In this study,direct analysis of various raw solid and viscous drugs was demonstrated using a typical solid-substrate ESI-MS with wooden-tip.Model drugs and matrices were selected to investigate the matrix effect.The solubility and viscosity of matrices affecting on the ionization response of drugs were examined.Our results showed that solubility and viscosity of matrices were the key factors to cause matrix effect and ion suppression in direct analysis of raw drugs.This study extended the matrix effect investigations to solid and viscous forms where the sample behaved in a complicated manner in ambient MS analysis.
1 Experimental
1.1 Chemicals and materials
High performance liquid chromatography -grade methanol was purchased from J&K Scientific Ltd.(Beijing,China).Ethanol was purchased from Guangzhou Samhoo Trading Co.,Ltd.(Guangzhou,China).Diazepam and oxazepam were purchased from the National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products(Beijing,China).Vaseline was purchased from Meryer(Shanghai) Chemical Technology Co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).Wooden-tip(common toothpick) was purchased from local store.Reserpine and cellulose were purchased from Sigma(St.Louis,MO,U.S.A).Starch was purchased from Jindingsheng Seasoning Food Co.,Ltd.(Foshan,China).Liquid paraffin,dextrin,talcum,calcium carbonate and sucrose were purchased from Macklin(Shanghai Macklin Bio-Technology Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai,China).Polyvinyl pyrrolidone was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Biological Technology Co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).Polyethylene glycol was purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).Paracetamol-caffeine tablets and mupirocin ointment were purchased from SK & F(Tianjin Smith Kline & French Laboratories Ltd.,Tianjin,China).The weight of each paracetamol-caffeine tablet is 0.7 g,which contains 65 mg of caffeine and 500 mg of acetaminophen and 135 mg of other solid matrices such as corn starch,pregelatinized starch,polyvinylpyrrolidone,potassium sorbate,croscarmellose sodium,stearic acid,talc,glyceryl triacetate and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose.Arginine-ibuprofen tablets were purchased from Hainan Zanbang Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.(Haikou,China).Each arginine-ibuprofen tablet is 1.18 g that contains 0.34 g of arginine and 0.4 g of ibuprofen,and sodium bicarbonate,crospovidone,magnesium stearate,hypromellose,sucrose,titanium dioxide and polyethylene glycol 4000.Triamcinolone acetonide-econazole nitrate cream was purchased from Fujian Pacific Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.(Quanzhou,China),which contains mono- and di-glyceryl stearate,isopropyl myristate,light liquid paraffin,acetyl alcohol,stearyl sorbitan,glycerin,polysorbate 80,hydroxy phenethyl,and econazole(10 mg/g).
1.2 Sample preparation
To prepare viscous matrix systems,different amounts of liquid paraffin(25 cP) were mixed with ethanol(1.083 cP) or vaseline(2 200 cP).The viscosities of the mixed matrix systems were calculated by the Kendal-Monroe model[24]in the binary system:μ1/3=VAVBμA1/3μB1/3,whereμ,μAandμBare the viscosity of mixed matrices,matrix A and matrix B,respectively;VAandVBare the volume ratio of matrix A and matrix B,respectively.To prepare the spiked matrices,drug solution was pipetted into solid matrix and dried in the air to form solid sample and was then further prepared to be homogeneous powders in this work.
1.3 Ambient MS with Wooden-tip ESI-MS
As shown in Fig.1,wooden-tip was mounted onto the capillary holder of a commercial nano electrospray ionization (nanoESI) ion source of Orbitrap mass spectrometer(Q-Exactive,Thermo Fisher Scientific,Bremen,Germany) as described previously[18,25].Viscous or solid drug(1.0 mg) was directly deposited on the surface of wooden-tip.Subsequently,5.0 μL of pure methanol and a high voltage of 3.5 kV were applied to wooden-tip for generating spray ionization.All the samples were analyzed at least three times.Mass spectra were recorded at least 1 minute.Target ions were selected with an insolation window at 0.4 Da under optimized collision energy in MS/MS experiments.
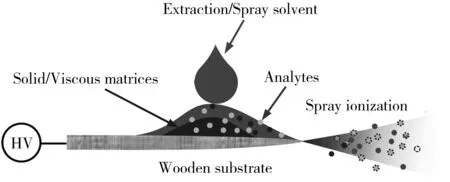
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of wooden-tip ESI-MS for direct analysis of drugs in solid and viscous matrices
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Direct analysis of drugs in raw forms
Being a powerful analytical tool for direct drug analysis,wooden-tip ESI-MS was demonstrated for directly analyzing various raw solid tablets.For example,Fenbid tablet was made with two major active pharmaceuticals(acetaminophen and caffeine) and other solid matrices,including corn starch,pregelatinized starch,polyvinylpyrrolidone,potassium sorbate,croscarmellose sodium,glyceryl triacetate,stearic acid,talc,and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as listed in the packing box.Protonated acetaminophen atm/z152.07 and protonated caffeine atm/z195.08 were dominated with high signal-to-noise in the mass spectrum(Fig.2A).Upon MS/MS experiments,acetaminophen and caffeine were identified by their major characteristic fragments(insert of Fig.2A).Fragment ions atm/z110.06 were obtained from protonated acetaminophen(m/z152.07) by loss of CH2CHO,while fragments atm/z138.06 andm/z110.07 were obtained from protonated caffeine(m/z195.08) by loss of CH3NCO and by loss of CH3NCO and a subsequent loss of CO,respectively.Arginine(0.34 g per tablet) had a lower concentration than ibuprofen(0.40 g per tablet) in a compound tablet(Fig.2B),but arginine atm/z175.12 was dominated as base peak while ibuprofen(m/z207.06) was not observed.These data implied that ibuprofen was suppressed by the complex matrices.
Direct analysis of raw viscous drugs using wooden-tip ESI-MS was also demonstrated in this study.As shown in Fig.2C,mass spectrum of mupirocin cream(common medicine for fungal infections on human skin) was directly obtained using wooden-tip ESI-MS under negative ion detection mode.Deprotonated mupirocin atm/z499.29 was observed and was further confirmed by MS/MS experiment(insert of Fig.2C).Other abundant peaks of cluster ions ranging fromm/z100 tom/z600 were mainly due to viscous matrices.Similarly,direct analysis of other viscous drugs such as econazole cream from viscous matrices was also successfully performed(Fig.2D).These results showed that like solid drugs,analytes could be rapidly extracted and ionized from viscous matrices.
It is a fact that major active pharmaceuticals in complicated matrices commonly are at high concentration(mg/g level or higher) for most of the solid and viscous commercial drugs,relative to the sensitivity of mass spectrometer.The different ionization responses of analytes were mainly depended on their intrinsic properties such as proton affinity[19]and concentration.In general,background noises depend on the matrices in drug samples.Therefore,ion suppression could be significantly made for detecting target analytes in the soluble and ionizable matrices.
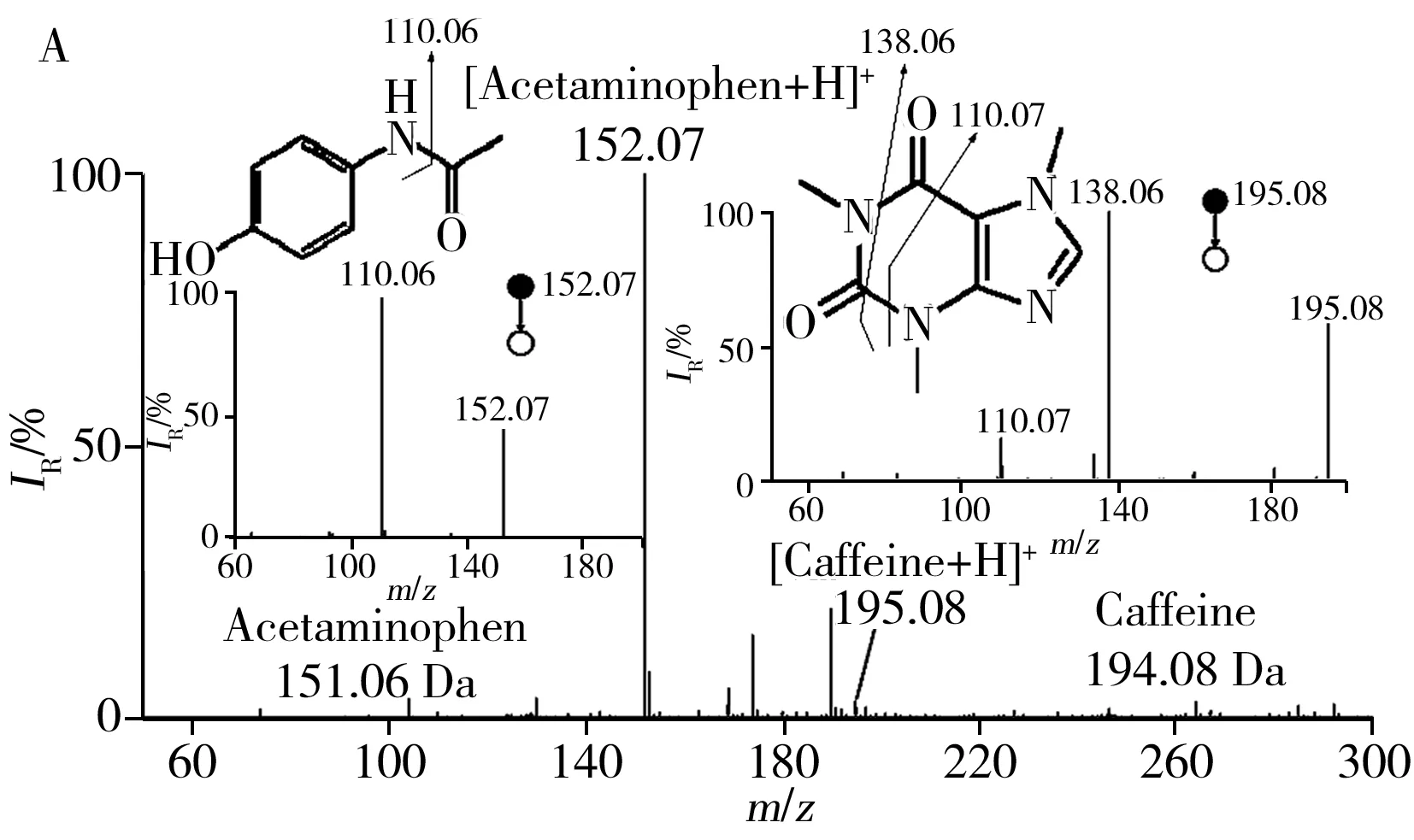
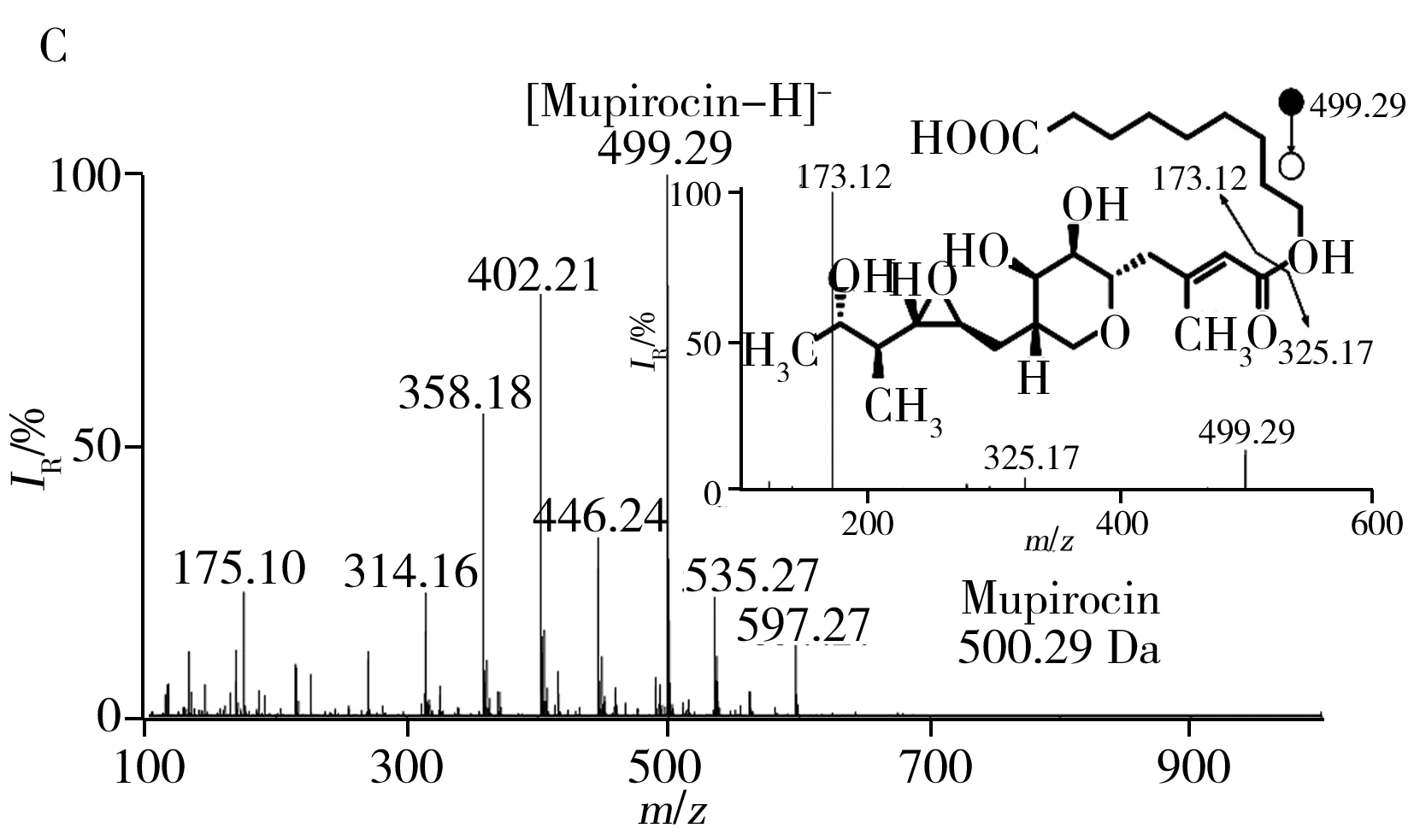
2.2 Matrix effect in solid matrices
Ionization responses of spiked drugs in pure solvent and in different solid matrices were compared in this work.Soluble matrices,including polyvinyl pyrrolidone(PVP) and polyethylene glycol(PEG),and insoluble matrices such as talc powder,calcium carbonate(CaCO3),and starch,were compared.Diazepam and oxazepam were chosen as model drugs in this work,because they were frequently spiked into powder and tablet in illegal food and drug samples,and thus requiring a rapid screening method in food safety and forensic applications[15,26].The characteristic mass peaks atm/z285.08(diazepam) and atm/z287.06(oxazepam) were used to investigate their responses in complex matrices.
Fig.3A shows signal response of diazepam in different solid matrices and pure methanol.As expected,diazepam signal obtained in solid matrices were generally lower than in pure solvent,mainly due to the matrix effects of solid matrices.It was also found that soluble solid matrices had a higher impact on ionization response of diazepam than in insoluble matrices,indicating that solubility of matrix plays a key role in ionization suppression.Similar results were obtained for detecting oxazepam obtained in different solid matrices,confirming matrix effects of soluble matrices and insoluble matrices(Fig.3B).The major reason for insoluble matrices can be described as the effect of the extraction process of analytes.
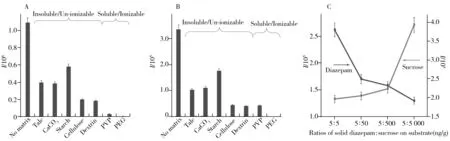
Fig.3 Ionization responses of drugs(5.0 ng) in different solid matricesA: diazepam;B:oxazepam;C:diazepam
Sucrose,a typical soluble matrix in solid drugs,was further used to investigate the matrix effect of soluble matrices.Different amounts of solid sucrose(5,50,500,5 000 ng) were mixed with a fixed amount of diazepam(5.0 ng).Fig.3C displays that diazepam signal was scientifically reduced with the increases of sucrose whereas sucrose single was significantly increased with amounts.These results indicated that competitive ionization of soluble and ionizable matrices was similar to a typical matrix effect and ion suppression in conventional capillary ESI-MS analysis of analytes at high concentration[27].
2.3 Matrix effect in viscous matrices
It was noted that many insoluble matrices such as starch could change to be a viscous form when some solvents were added.Therefore,further investigation of viscosity of matrices to matrix effect is highly needed.In this work,reserpine(m/z609.23),a typical model drug,was used as a model drug.Liquid paraffin(a common un-ionizable viscous matrix) in ethanol solution was used to prepare viscous matrices.As shown in Fig.4A,the signal response of reserpine(0.1 ng) was significantly reduced with the increased viscosity of viscous system(1 mg) ranging from 1 cP to 25 cP.Interestingly,the plot shows a power function relation(r2=0.952 6) between reserpine signal against viscosity of matrix system.
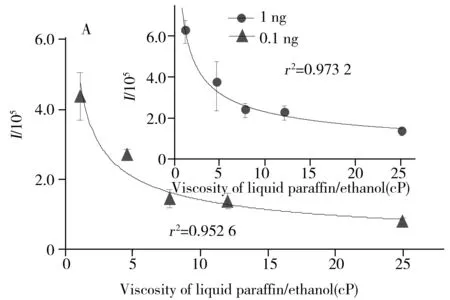
To further investigate the power function relation at higher viscous matrix systems,similar power function relation(r2=0.974 2) was also found in the higher viscous liquid paraffin/Vaseline system from 25 cP to 500 cP(Fig.4B).Moreover,it was also found that there were power function relations when higher concentration(1 ng) of reserpine was added in the same viscous systems(inserts of Fig.4).These results indicated that viscosity of matrices significantly impacted the extraction of drugs in viscous matrices.Early investigations indicated that the sample flow was significantly changed when highly viscous liquids were sprayed out under ESI conditions[28-30].Therefore,it was believed that the matrix effects of viscous matrices impact on not only the extraction process,but also the spray process in direct ESI-MS with a solid substrate.
3 Conclusions
Direct detections of drug molecules in solid and viscous forms were demonstrated using wooden-tip ESI-MS.Matrix effects of soluble/ionizable matrices were mainly generated from extraction/ionization processes,while matrix effects of insoluble/un-ionizable matrices were mainly generated from the extraction processes.These findings might give some considerable improvements in aspects of extraction and spray ionization of raw samples.To minizine the matrix effects of solid and viscous samples,new ambient MS method that integrated fast extraction and direct ionization is being investigated.

