油菜Oleosin基因启动子的克隆、分析及瞬时表达
王伟权 李树俊 朱欣琪 丘志慧 施力汛 张哲
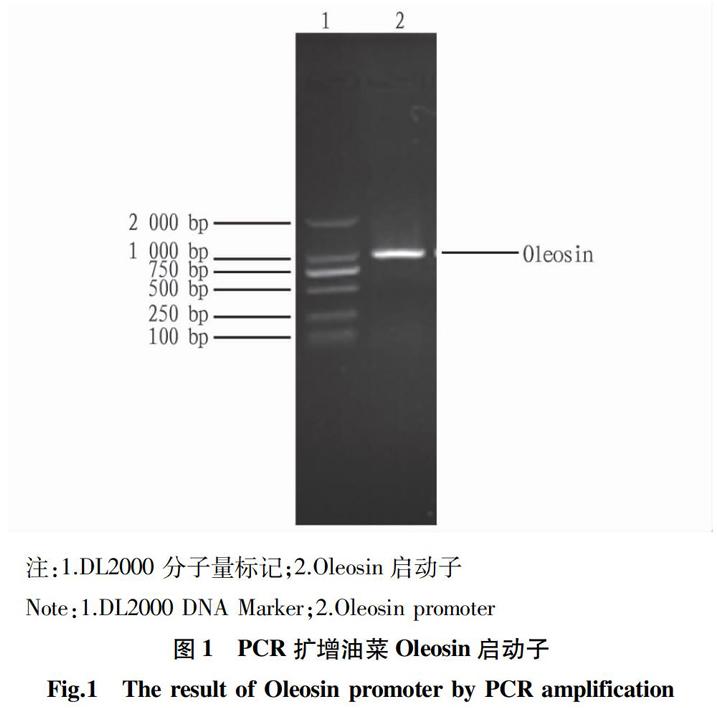


摘要 以甘藍型油菜幼苗为材料,根据油脂蛋白Oleosin(O20)基因的启动子序列设计引物,PCR扩增了长度为935 bp的片段,把该片段连接到pBI101载体,GUS瞬时染色结果表明,该片段可以驱动GUS基因在油菜幼苗根部特异性表达。油菜油脂蛋白是一个蛋白质家族,为进一步鉴别扩增到的935 bp油脂蛋白启动子,该研究利用油菜基因组信息进行序列对比,结果表明935 bp的启动子和Oleosin(O20)的启动子序列之间有较多的变异,但和油菜1号染色体上的序列完全一致;1号染色体上紧跟的编码框序列和油脂蛋白Oleosin(O20)的编码框序列也完全一致,但油脂蛋白Oleosin(O20)的基因组序列要比油菜1号染色体的基因组序列短。通过PLACE和PlantCARE软件对935 bp启动子进行了扫描预测,结果表明该启动子中含有许多顺式作用元件,尤其是脱落酸、茉莉酸甲酯和水杨酸这3个与激素有关的元件;将该研究扩增到的另一个928 bp长度的启动子与935 bp的启动子相比,前者启动子区域水杨酸顺式作用元件缺少了1个碱基,同时也缺失了1个碱基的片段,这些序列的变化可能是该启动子丧失活力的原因。
关键词 启动子;油菜;瞬时表达;Oleosin
中图分类号 S188文献标识码 A
文章编号 0517-6611(2020)22-0115-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.22.030
Cloning,Analysing and Transient Expressing Oleosin Gene Promoter in Brassica napus
WANG Wei-quan,LI Shu-jun,ZHU Xin-qi et al (College of Agriculture and Biology,Zhongkai University of Agricultural and Engineering,Guangzhou,Guangdong 510225)
Abstract According to the young seedlings of Brassica napus as materials,Oleosin promoters designed by the oil protein Oleosin (O20) sequence with length of 935 bp and 928 bp were amplified by PCR.GUS staining showed that 935 bp lipid protein Oleosin promoter can drive the specific expression of GUS gene in B.napus seedlings root.Comparing 935 bp with Oleosin (O20) promoter sequences,we found that there is a lot of variation between them.Because B.napus oil protein is a protein family,when utilizing B.napus genome sequencing information to be compared to confirm the oil protein promoter,we found that the promoter sequence amplified with length of 935 bp and the sequence of B.napus chromosome 1 were completely consistent.Then comparing coding sequences predicted behind chromosome 1,we found that the coding sequences behind the 1 chromosome is exactly the same with that of the Oleosin(O20) oil protein.While there are differences in their genome sequence,the 935 bp promoter sequence on chromosome 1 is much larger than that of the Oleosin (O20).There is no comparison of their genome sequence in this paper.Studying thoroughly the promoter amplified of 935 bp through the PLACE and the PlantCARE website,we have found many cis-acting elements.Three components related to abscisic acid,methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid are notable.Because we also amplified a promoter with length of 928 bp,the promoter can not drive the expression of the GUS gene.Analysing and comparing the sequence of 935 bp and 928 bp,we found that a base lacked in the promoter TCA motif of 928 bp.The loss of these sequential changes may cause the loss of the vitality of the promoter.
In summary,we have successfully obtained a tissue specific promoter of B.napus that can be used for scientific research and production.
Key words Promoter;Brassica napus;Transient expression;Oleosin
作者简介 王伟权(1968—),男,江苏宜兴人,副教授,博士,从事分子生物学研究。
李树俊(1998—),男,广东广州人,从事分子生物学研究。王伟权与李树俊为共同第一作者。
收稿日期 2019-09-26;修回日期 2020-04-13
植物作为生产药用蛋白或其他具有重要价值蛋白的生物反应器,为人类提供一个更加安全和廉价的生产系统,是植物基因工程的发展方向,从而使传统农业生产和现代生物技术紧密结合,大幅度地提高农产品对人类的服务功效及市场竞争力,增加农民收入,促進农业的可持续发展。用各种农作物为载体的植物生物反应器产品可通过种子、果实或块茎表达,便于贮藏、运输和利用[1]。
油脂蛋白Oleosin是依附于油体表面的属于碱性高度疏水的小分子嵌入蛋白,在植物种子成长或后熟过程中可大量特异性表达,是一个蛋白质家族,最早在芥菜中被发现,随后不同油料作物(大豆、芝麻、油菜等)、不同树木(油棕、可可、柑橘等)以及其他植物如玉米、水稻、拟南芥等的Oleosin基因序列和氨基酸序列被陆续报道[2-3]。油脂蛋白受到广泛关注,其原因有三个方面,一是通过融合外源营养价值高的肽链,改善种子的营养成分,提高种子食用或作为饲料的品质,如利用该技术成功表达有生物活性的鱼生长激素;二是生产回收获得外源蛋白,需在Oleosin与外源蛋白间加上合适的蛋白酶酶切位点,目前已通过该系统成功获得有生物活性的GUS[4]、木聚糖酶[5]和水蛙素[6],在加拿大利用油菜生产水蛙素已进入商业化阶段[7];三是不通过切割回收过程,直接生产固定化酶[8]。此外,油质蛋白具有稳定油体的生物学特性,它们可以对食品、化妆品、油漆等产品中的乳液起到稳定作用[9]。更有研究初步确定Oleosin基因是调控谷子干旱胁迫的候选基因,可能受干旱或脱落酸(ABA)、茉莉酸甲酯(MeJA)诱导表达[10]。
瞬时表达(transient expression)是一种快速地研究不同启动子在特定基因表达、蛋白质亚细胞定位及基因互作的一种重要手段,对比传统转基因技术中的转化周期长、效率低及不稳定性,其外源DNA不需要整合到宿主细胞染色体上,因此转化更容易、更快速,转化效率更高。植物细胞几天内可进行多个基因的表达及高效传递[11],尤其是合成生物学的发展使瞬时表达有了更大的应用前景。
该研究根据网上已经克隆的Oleosin基因的启动子序列设计引物,并扩增Oleosin基因的启动子,然后连接到pBI101载体上,对油菜幼苗进行瞬时表达,为油脂蛋白的生产应用奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 菌株和载体
大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)菌株为 DH5α;根癌农杆菌(Agrobacterium tumefaciens)菌株为 LBA4404,抗性标记为利福平 (Rif r)和卡那霉素 (kan);植物表达载体为 pBI101,抗性标记为卡那霉素 (kan)。
1.2 试剂
限制性内切酶、T4 DNA 连接酶、PMD-T Easy Vector及DNA 凝胶回收试剂盒等购自TaKaRa公司。抗生素为 Sigma 产品,其他生化试剂为国产分析纯。
1.3 油菜总DNA的提取 以甘蓝型油菜幼苗为材料,用CTAB法提取油菜总DNA。
1.4 Oleosin启动子的扩增与相关载体的构建
1.4.1 Oleosin启动子的扩增。引物设计根据O20(GenBank: M63985.2)Oleosin启动子核苷酸序列,其中上游引物:5′-GATAAAGCAATCACCTGG-3′,下游引物:5′-TTTGCTTCTTGTGAATTGAG-3′。以油菜总DNA 为模板,通过PCR扩增得到Oleosin启动子,送上海英骏生物技术有限公司测序。
1.4.2 重组表达载体的构建。将测序正确的菌体扩大培养,按《分子克隆实验指南》用碱裂解法提取质粒。用Hind Ⅲ与BamH Ⅰ 酶切Oleosin启动子和PBI101质粒,于1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,凝胶回收试剂盒分别回收Oleosin启动子片段和PBI101载体片段。用T4连接酶连接两片段,构建重组表达载体。
1.5 重组质粒的筛选和转化
将构建好的载体用热激法转化农杆菌,并将转化产物涂布于含50 mg/L卡那霉素(kan)和25 mg/L利福平(Rifr)的LB培养基平板,28 ℃培养48 h。挑取阳性克隆并扩大培养36 h备用。
1.6 农杆菌介导油菜愈伤组织的转化
用菌悬浮培养基(MS+6-BA 0.5 mg/L+NAA 0.1 mg/L+100 μmol/L乙酰丁香酮)28 ℃振荡培养农杆菌,至最终浓度为OD600=0.6 ,备用。将已培养好的带有愈伤的80棵油菜幼苗随机分为2组,一组幼苗设为对照,另一组幼苗浸泡在农杆菌菌液中10 min。将幼苗转移至共培养基(MS+6-BA 0.5 mg/L+NAA 0.1 mg/L+100 μmol/L乙酰丁香酮)中,暗培养3 d。
1.7 GUS染色与瞬时表达
将油菜幼苗转移至固定液(50 mmol/L PBS+1%甲醛+0.5% Triton-100)中固定45 min,用蒸馏水洗涤3次。然后油菜幼苗被转移至染色液[100 mmol/L PBS+0.5% Triton-100+X-Gluc+1 mmol/L K3Fe(CN)6+1 mmol/L K4Fe(CN)6]中,37 ℃过夜。用70%乙醇进行脱色,观察油菜幼苗染色情况,同时拍照记录。
參考文献
[1] 庞俊峰,黄东光,吴燕民.植物生物反应器研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2011(1):21-25.
[2] CAO H P.Genome-wide analysis of oleosin gene family in 22 tree species:An accelerator for metabolic engineering of BioFuel crops and agrigenomics industrial applications?[J].OMICS:A journal of integrative biology,2015,19(9):521-541.
[3] 刘昱辉,贾士荣.植物油体表达体系的研究进展[J].农业生物技术学报,2003,11(5):531-537.
[4] VAN ROOIJEN G J H,MOLONEY M M.Plant seed oil-bodies as carriers for foreign proteins[J].Bio/Technology,1995,13(1):72-77.
[5] LIU J H,SELINGER L B,CHENG K J,et al.Plant seed oil-bodies as an immobilization matrix for a recombinant xylanase from the rumen fungus Neocallimastix patriciarum[J].Mol Breed,1997,3:463-470.
[6] PARMENTER D L,BOOTHE J G,VAN ROOIJEN G J H,et al.Production of biologically active hirudin in plant seeds using oleosin partitioning[J].Plant molecular biology,1995,29:1167-1180.
[7] GIDDINGS G,ALLISON G,BROOKS D,et al.Transgenic plants as factories for biopharmaceuticals[J].Nature biotechnology,2000,18:1151-1155.
[8] LEE K H,ISENHART T M,SCHULTZ R C,et al.Nutrient and sediment removal by switchgrass and cool-season grass filter strips in Central Iowa,USA[J].Agroforest Syst,1999,44:121-132.
[9] 孙静,姜宇,陶俊.植物油质蛋白的结构、功能及应用[J].植物生理学报,2018,54(3):363-369.
[10] 蒋茂双,元香梅,刘晓东,等.谷子Oleosin基因家族及其对干旱响应的分析[J].山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,38(1):16-20.
[11] SAINSBURY F,LOMONOSSOFF G P.Transient expressions of synthetic biology in plants[J].Current opinion in plant biology,2014,19:1-7.
[12] HIGO K,UGAWA Y,IWAMOTO M,et al.PLACE:A database of plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements[J].Nucleic Acids Res,1998,26(1): 358-359.
[13] LESCOT M,DHAIS P,THIJS G,et al.PlantCARE,a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2002,30(1):325-327.
[14] GUTIERREZ L,VAN WUYTSWINKEL O,CASTELAIN M,et al.Combined networks regulating seed maturation[J].Trends Plant Sci,2007,12(7): 294-300.
[15] SKRIVER K,MUNDY J.Gene expression in response to abscisic acid and osmotic stress[J].Plant cell,1990,2:503-512.
[16] NORASTEHNIA A,SAJEDI R,NOJAVAN-ASGHARI M.Inhibitory effects of methyl jasmonate on seed germination in maize(Zea mays):Effect on α-amylase activity and ethylene production[J].Gen Appl Plant Physiology,2007,33(1/2):13-23.
[17] NOJAVAN-ASGHARI M,ISHIZAWA K.Inhibitory effects of methyl jasmonate on the germination and ethylene production in cocklebur seeds[J].J Plant Growth Regul,1998,17(1):13-18.
[18] MAITI S,PATRO S,PAL A,et al.Identification of a novel salicylic acid inducible endogenous plant promoter regulating expression of CYR1,a CC-NB-LRR type candidate disease resistance gene in Vigna mungo[J].Plant cell,tissue and organ culture,2015,120(2):489-505.
[19] ALI E,MAODZEKA A,HUSSAIN N,et al.The alleviation of cadmium toxicity in oilseed rape (Brassica napus) by the application of salicylic acid[J].Plant Growth Regul,2015,75(3):641-655.
[20] KEDDIE J S,TSIANTIS M,PIFFANELLI P,et al.A seed-specific Brassica napus oleosin promoter interacts with a G-box-specific protein and may be bi-directional[J].Plant Mol Biol,1994,24(2):327-340.
[21] CHE N Y,YANG Y,LI Y D,et al.Efficient LEC2 activation of OLEOSIN expression requires two neighboring RY elements on its promoter[J].Sci China Ser C,2009,52(9):854-863.
[22] SUN C X,PALMQVIST S,OLSSON H,et al.A novel WRKY transcription factor,SUSIBA2,participates in sugar signaling in barley by binding to the sugar-responsive elements of the iso1 promoter[J].Plant cell,2003,15(9): 2076-2092.
[23]BUROW M D,SEN P,CHLAN C A,et al.Developmental control of the β-phaseolin gene requires positive,negative and temporal seed-specific transcriptional regulatory elements and a negative element for stem and root expression[J].Plant J,1992,2(4):537-548.
[24] KAWAGOE Y,MURAI N.A novel basic region/helix-loop-helix protein binds to a G-box motif CACGTG of the bean seed storage protein β-phaseolin gene[J].Plant Sci,1996,116(1):47-57.
[25] 劉昱辉.植物油体表达体系的建立及Profilin2维管束特异表达启动子的区段缺失分析[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2001.
[26] 张冉.利用油菜油体系统表达重组人胰岛素原的研究[D].上海:上海师范大学,2010.

