呼吸功能锻炼联合膳食干预对COPD稳定期患者的影响分析
祝冲
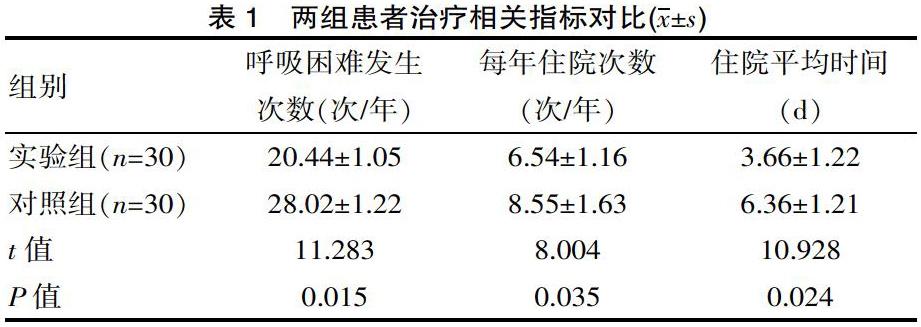
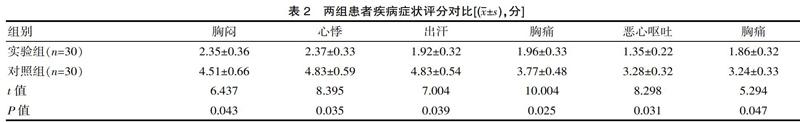
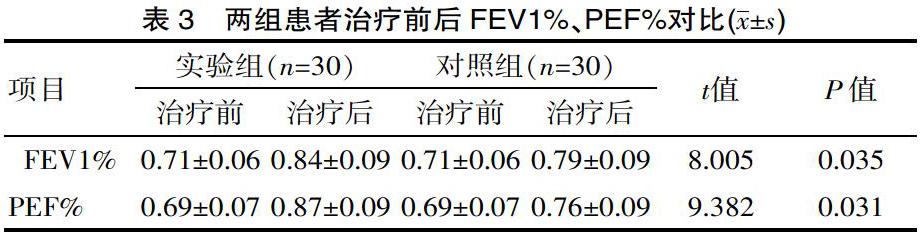
[摘要] 目的 分析呼吸功能锻炼结合膳食干预对COPD患者的影响。方法 方便选取2018年6月—2019年6月该院稳定期COPD患者60例。随机分组,对照组常规护理,实验组联合应用饮食护理及呼吸功能锻炼干预,比较两组症状评分,肺功能及生活质量。结果 实验组患者呼吸困难发生次数、每年住院次数、住院平均时间分别为(20.44±1.05)次/年、(6.54±1.16)次/年、(3.66±1.22)d,均显著优于对照组(t=11.283、8.004、10.928,P<0.05);干预后,实验组各项症状评分、生活质量显著优于对照组(P<0.05);干预后实验组FEV1%、PEF%分别为(0.84±0.09)、(0.87±0.09),显著优于对照组(t=8.005、9.382,P<0.05)。 结论 对稳定期COPD患者进行饮食干预联合呼吸功能的锻炼,效果显著,可显著改善患者的生活质量,善患者肺功能。
[关键词] COPD;稳定期;膳食干预;呼吸功能锻炼
[中图分类号] R505 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2020)10(b)-0118-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the effects of breathing exercise combined with dietary intervention on COPD patients. Methods Sixty patients with stable COPD in our hospital from June 2018 to June 2019 were convenient selected. Randomized groups, the control group with routine nursing care, and the experimental group combined application of diet nursing and respiratory function exercise intervention, compared the two groups' symptom scores, lung function and quality of life. Results The number of occurrences of dyspnea, the number of times per hospitalization, and the average length of stay in the experimental group were (20.44±1.05)times/year, (6.54±1.16)times/year, (3.66±1.22)d, respectively, which were significantly better than those in the control group (t=11.283, 8.004, 10.928, P<0.05); After intervention, the symptom scores and quality of life of the experimental group were significantly better than those of the control group(P<0.05); FEV1% and PEF% of the experimental group after intervention were (0.84±0.09) and (0.87±0.09), respectively , Significantly better than the control group (t=8.005, 9.382, P<0.05).Conclusion The effect of dietary intervention combined with respiratory function exercises for patients with stable COPD can significantly improve the quality of life of patients and improve their lung function.
[Key words] COPD; Stable period; Dietary intervention; Respiratory function exercise
COPD在中老年群體中属于多发病,可以引起阻塞性通气障碍,易导致慢性缺氧。现今的主流治疗手段是进行雾化吸入治疗,该方法痛苦小,且效果好,在临床工作中越来越普遍[1]。以往常规的护理方法忽视了患者呼吸功能的训练,及饮食习惯的改善,部分患者的治疗依从性较低,有研究者提出,可以采用膳食干预理联合呼吸功能训练的方法对患者进行治疗,取得了一定的临床疗效,可减少患者的住院次数,进一步改善患者的治疗体验,为了促进越来越多COPD患者护理工作的进一步发展[2],该院方便选取该院2018年6月—2019年6月60例稳定期COPD患者进行研究,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
经过患者同意以及医院伦理委员会的批准,方便选取在该院治疗COPD的患者60例。随机分为两组。对照组有男17例,女13例;患者的年龄在55~78岁之间,平均(65.61±3.57)岁;病程约在0.5~8年之间,平均(3.32±0.26)年。实验组有男16例,女14例;患者的年龄在56~79岁之间,平均(66.79±3.51)岁;病程在0.7~8年之间,平均(1.25±0.89)年。所有患者中,合并糖尿病患者有12例,合并冠心病有11例,合并慢性肝病有10例。两组患者年龄、性别以及病程构成等基线资料对比,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。纳入标准:①在该院就诊并长期复查随访;②均需要进行相应药物治疗干预者。排除标准:①对沙丁胺醇等药物有严重过敏史,不能遵从医嘱用药;②有严重的器官衰竭等需其他药物干预史;③治疗过程中转院或者失去随访;④患者有明显的精神障碍不能正常的沟通。

