Spinal Osteoid Osteoma 脊柱骨样骨瘤
医学词汇注释与简要讲解
Key Facts
Definition:benign osteoblastic tumor with central core of vascular osteoid tissue,peripheral sclerosis.
Osteoid osteoma (OO)=tumor of children,young adults.
10% in spine (most common cause of painful scoliosis in adolescents).
Classic presentation=night pain relieved by salicylates/NSAIDS.
Imaging findings:less than 1.5 cm round low density and surrounding sclerosis.
osteoid osteoma 骨样骨瘤
scoliosis 脊柱侧凸
salicylates 水杨酸盐
NSAIDS,nonsteroidal antiinflamma
tory drugs 非甾体抗炎药
Imaging Findings
General features
Best imaging clue:hypodense nidus with calcification,surrounding sclerosis;neural arch>>vertebral body.
neural arch 椎弓
CT finding
NECT:lesion less than 1.5 cm (larger=osteoblastoma); well-defined low density nidus,and/or calcification; variable surrounding sclerosis.
nidus (瘤)巢
CECT:variable enhancement.
MR findings
T1WI:hypo-or iso-intense (compared to marrow).
T2WI:hyperintense or intermediate signal; variable calcification (very hypointense); surrounding hyperintensity may reflect inflammation.
Variable enhancement (minimal to intense).
Other modality findings
Radiography:(1)Classic appearance:discrete round or oval nidus with surrounding sclerosis; lesion at or near apex (concave aspect) of scoliotic curve.
(2)Common appearance:normal,subtle sclerosis,sometimes only scoliosis.Radionuclide scans:(1)Nidus shows marked radiotracer accumulation.
(2)“Double density sign”=small central high uptake (nidus) with surrounding less intense zone of uptake (osseous reaction).
concave aspect (椎弓)凹面
Imaging recommendations
Radionuclide scan and NECT.
MR if radiculopathy or myelopathy.
Differential Diagnosis
Osteoblastoma:Larger (>1.5 cm); expansile lesion of neural arch or pedicle;neurologic deficits more common.
Sclerotic metastasis,Lymphoma:Older patients; often involves pedicle,
鉴别诊断包括:
osteoblastoma 骨母细胞瘤
sclerotic metastasis 成骨转移
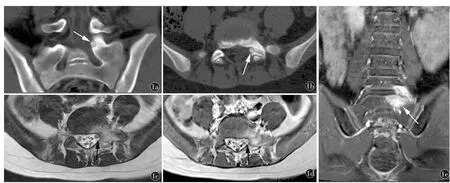
Fig1 A 12-year-old male with low back pain relieved by salicylates.a)Coronal and b)axial non-enhanced CT shows a discrete lucent mass with a calcified nidus in the left pedicle of the S1 vertebra.Note the surrounding reactive sclerosis and small size (<1.5 cm),characteristic for osteoid osteoma.c)Axial T2WI,d)enhanced axial T1WI and e)coronal enhanced T1WI shows edema around the mass with enhancement.
destroys posterior body cortex; associated soft-tissue mass common.
Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC):Larger,expansile; often multicystic with hemorrhagic fluid-fluid levels.
Benign (Nonneoplastic) reactive sclerosis:Facet sclerosis (spondylolysis;contralateral to absent pedicle); unusual or chronic infection (rare).
lymphoma 淋巴瘤
aneurysmal bone cyst 动脉瘤样骨囊肿
benign (nonneoplastic) reactive sclerosis 良性(非肿瘤性)反应性骨硬化
Pathology
General path commentsLocation:femur>tibia>hands/feet>vertebral; Lumbar>cervical>thoracic>sacrum;posterior element(lamina,facet,pedicle);vertebral body<10%.
Epidemiology:(1)12% of all benign skeletal neoplasms.(2)10% in axial skeleton.(3)59% lumbar,27 cervical,12% thoracic,2% sacrum.(4)Majority of patients between 10-20 years.(5)M:F=2-3:1
Gross pathologic-surgical features
Sharply-demarcated,round,pink-red mass (nidus).
Microscopic features:(1)Nidus:well-organized interconnecting trabecular bone in various stages of maturity within a highly vascular fibrous connective tissue stroma.(2)Similar to osteoblastoma.(3)No malignant degeneration.
Clinical Issues
Presentation
Night pain with relief from salicylates/NSAIDS.
Symptoms:painful scoliosis,focal or radicular pain,gait disturbance,muscle
典型临床症状:
(1)可为非甾体抗炎药控制的夜间痛;(2)痛性脊柱侧弯;局部或放射痛;(3)70%脊柱侧弯伴有肌肉
atrophy.
Scoliosis (70%) related to muscle spasm.
In pediatric patients,torticollis,spinal stiffness,scoliosis may occur.
痉挛;(4)儿童患者可出现斜颈(torticollis)、脊柱僵直或侧弯。
Natural history
Surgical resection is curative in most cases.Spontaneous healing has been reported.
Treatment
Complete excision:(1)New:CT-guided percutaneous excision.(2)Thermo-/photocoagulation.
Conservative observation (patients with well controlled symptoms).
percutaneous excision 经皮切除
thermocoagulation 热消融
photocoagulation 激光消融
Prognosis
Recurrence extremely rare after surgical excision.