miRNA-29c在喉癌组织中的表达及对喉癌Hep-2细胞增殖、侵袭的影响
张朝晖 金巧智 马志超

[摘要] 目的 觀察miRNA-29c在喉癌组织和喉癌Hep-2细胞株中的表达情况,研究其与肿瘤临床分期、淋巴转移及预后等临床病理参数的关系,并探讨miRNA-29c对喉癌Hep-2细胞增殖、侵袭的影响。 方法 选取2006年1月~2016年12月在我院确诊的86例喉癌患者的蜡块标本,利用实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应检测喉癌组织和癌旁正常喉黏膜上皮组织中miRNA-29c的表达,并分析其与临床病理学特征的关系;通过Q-RT-PCR检测转染后每组细胞中miRNA-29c的表达;CCK-8检测细胞增殖能力变化情况;Transwell实验检测跨膜细胞数量的变化。 结果 miRNA-29c在喉癌组织中相对表达量明显低于癌旁组织(P<0.01),其表达量与不同临床分型、TNM分期、淋巴转移密切相关(P<0.05);转染miRNA-29c模拟物组细胞中的miRNA-29c表达水平显著高于无关序列组和空白对照组(P<0.01),并可抑制喉癌Hep-2细胞的增殖和侵袭力(P<0.01)。 结论 在喉癌中,miRNA-29c是一个抑制性miRNA,miRNA-29c低表达可能是影响喉癌预后的重要因素;过表达miRNA-29c可显著降低喉癌Hep-2细胞的增殖和侵袭能力,miRNA表达水平的下调可能参与了喉癌的发生发展及侵袭转移过程。
[关键词] miRNA-29c;喉癌;预后;增殖;侵袭
[Abstract] Objective To observe the expression of miRNA-29c in the tissue of laryngeal carcinoma and laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cell line, to study its relationship with clinical pathological parameters such as clinical staging, lymphatic metastasis and prognosis, and to investigate the effect of miRNA-29c on proliferation and invasion of laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cells. Methods Paraffin-embedded specimens of a total of 86 patients with laryngeal cancer who were diagnosed in our hospital from January 2006 to December 2016 were selected. Real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to detect the expression of miRNA-29c in laryngeal carcinoma tissues and adjacent normal laryngeal mucosa epithelial tissues, and its relationship with clinical pathological characteristics was analyzed; the expression of miRNA-29c in each group of cells after transfection was detected by Q-RT-PCR; CCK-8 was used to detect changes in cell proliferation ability; Transwell assays were used to detect changes in the number of transmembrane cells. Results The relative expression level of miRNA-29c in the tissue of laryngeal carcinoma was significantly lower than that in adjacent cancer tissues (P<0.01). The expression level was closely related to different clinical stages, TNM stages and lymphatic metastasis (P<0.05); the expression level of miRNA-29c in the cells of transfected miRNA-29c mimic group was significantly higher than that in the unrelated sequence group and the blank control group(P<0.01), and it can inhibit the proliferation and invasiveness of laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cells (P<0.01). Conclusion In laryngeal cancer, miRNA-29c is an inhibitory miRNA. Low expression of miRNA-29c may be an important factor affecting the prognosis of laryngeal cancer; overexpression of miRNA-29c can significantly reduce the proliferation and invasiveness of laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cells. Down-regulation of miRNA expression level may be involved in the occurrence, development, invasion and metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma.
[Key words] miRNA-29c; Laryngeal carcinoma; Prognosis; Proliferation; Invasion
喉癌是頭颈部肿瘤中常见的恶性肿瘤,相当一部分晚期喉癌的5年生存率仅有大概51%[1]。微小RNA(MicroRNA,miRNA)是当前研究热点和前沿之一[2]。miRNA可通过调节下游基因的表达和功能参与生命活动的调节,如凋亡、增殖及分化,发挥类似癌基因或抑癌基因的作用[3-5]。最新研究显示,miRNA-29c表达异常减少是导致一些恶性肿瘤细胞无限增殖及肿瘤发生、发展的重要因素[6-8]。但暂时未见与喉癌的相关的报道。本研究检测miRNA-29c在喉癌及癌旁组织中的表达,并探讨其与临床病理特征的关系及对肿瘤预后的影响。此外以喉癌细胞系Hep-2为研究对象,瞬时转染技术提高了Hep-2细胞中miRNA-29c的表达水平,观察miRNA-29c对喉癌Hep-2细胞增殖和侵袭的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料来源
选取2006年1月~2016年12月在我院耳鼻喉科经手术切除的喉癌患者的蜡块标本86例作为喉癌实验组,同时,将42例石蜡包埋的癌旁正常喉黏膜上皮组织作为对照组。86例喉癌患者中,男79例,女7例,年龄47~82岁,平均(62.3±5.5)岁,所有患者在手术前均未接受放化疗或其他治疗。
1.2 细胞及试剂
人喉鳞Hep-2细胞株购买于中国科学院上海细胞研究所。RPMI-1640培养基及胎牛血清(Gibco公司),CCK-8试剂盒(Bryotime公司),核糖核酸试剂盒Trizol及细胞转染试剂Lipofectamine2000(Invitrogen公司);Real MasterMix(SYBR Green)荧光定量PCR试剂盒(Tiangen公司);Transwell小室(Corning公司);Matrigel Basement Membrane Matrix(BD公司);miRNA-29c模拟物(miRNA-29c mimics)及无关序列(negetive control,NC)由Ribobio合成。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 Hep-2细胞培养 将人喉癌Hep-2细胞接种于6孔板,用含有10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养基进行培养,条件是37℃、含5% CO2。实验分为三组: miNRA-29c mimics组(miRNA-29c模拟物+Lipo2000);NC组(NC+ Lipo2000);mock组(正常空白对照)。
1.3.2 细胞转染并检测转染效率 待Hep-2细胞株的生长密度达到约80%时,根据LipofectamineTM 2000的操作说明书,使用Lipo 2000分别将miRNA-29c模拟物和无关序列NC转染至Hep-2细胞。转染Cy3-NC 24 h后,利用荧光显微镜观察转染效率并拍照。
1.3.3 Q-RT-PCR用于检测喉癌标本及癌旁组织中mRNA-29c的表达量 将每个蜡块样品切成10 μm 厚的切片,并取5个切片提取总RNA。根据Trizol说明书的方法,进行细胞的总RNA的提取,并利用紫外分光光度计测A260/A280。通过逆转录合成cDNA,并将合成的cDNA稀释10倍。按如下条件进行PCR反应:预变性95℃ 30 s,变形95℃ 5 s,退火延伸60℃ 30 s, 扩增40个循环。记录每个孔的CT值,并取3个孔的平均值作为结果,以U6为内参基因,并采用2-△△Ct法计算miRNA-29c的相对表达量,每个样本独立重复实验3次。
1.3.4 Q-RT-PCR检测3组细胞中mRNA-29c的表达量 将每组Hep-2细胞转染48 h,按照Trizol说明书方法提取细胞总RNA,具体实验步骤同1.3.3。miRNA-29c和U6引物序列见表1。
1.3.5 CCK-8检测Hep-2细胞增殖能力的变化 在不同的96孔上接种细胞悬液,均设5个重复孔,再进行细胞转染。培养48 h后于每孔中加入10 μL 的CCK-8溶液,培养箱中孵育2 h,用酶标仪测定每孔的吸光值(A值),检测波长为450 nm,A值越高,表明活细胞数越多,细胞增殖活性也就越高。
1.3.6 Transwell法检测Hep-2细胞侵袭能力的变化 Matrigel基质胶利用无血清1640培养基稀释,浓度为50 mg/L,以 50 μL的体积加入Transwell小室的上室。37℃放置30 min。分别将3组细胞(2.0×105个/L)的悬液200 μL加入Transwell细胞培养小室的上室,置于37℃、5% CO2 孵箱培养24 h。0.1%结晶紫染色30 min,自来水洗净后,用湿棉试子除去聚碳酸酯膜上表面的细胞,在倒置显微镜下直接观察穿过膜的细胞。最后,在33%醋酸中洗涤细胞小室,利用紫外分光光度测量570 nm处的A值,独立重复实验3次,取平均值。
1.4 统计学处理
统计分析利用SPSS19.0软件,GraphPad Prims 8.0软件绘制统计图。计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间两两比较采用LSD-t检验,以P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 miRNA-29c在喉癌组织及癌旁组织中的表达情况
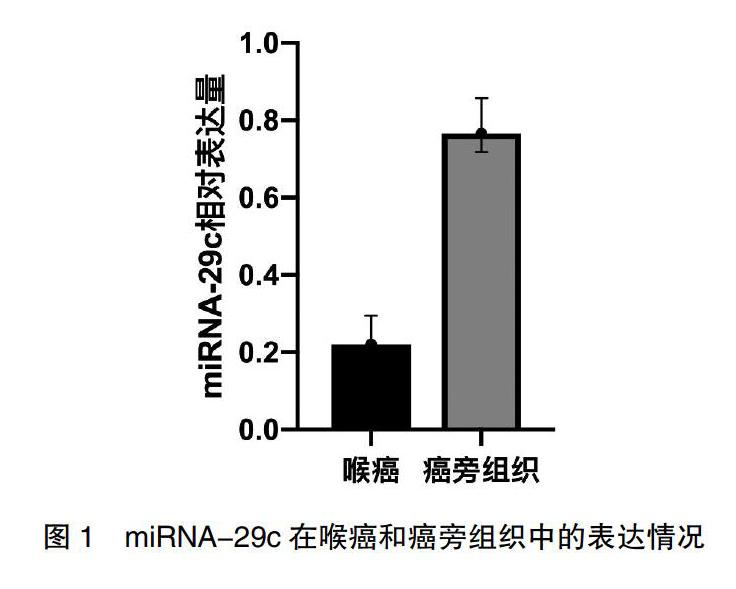
Q-RT-PCR结果显示,miRNA-29c在喉癌组织及癌旁正常喉黏膜上皮组织中的表达水平分别为(0.23±0.09)、(0.78±0.15),miRNA-29c在喉癌组织中的表达明显低于癌旁组织,差异有统计学意义(t=13.96,P<0.01)。见图1。
圖1 miRNA-29c在喉癌和癌旁组织中的表达情况
2.2 miRNA-29c表达与喉癌临床病理的关系
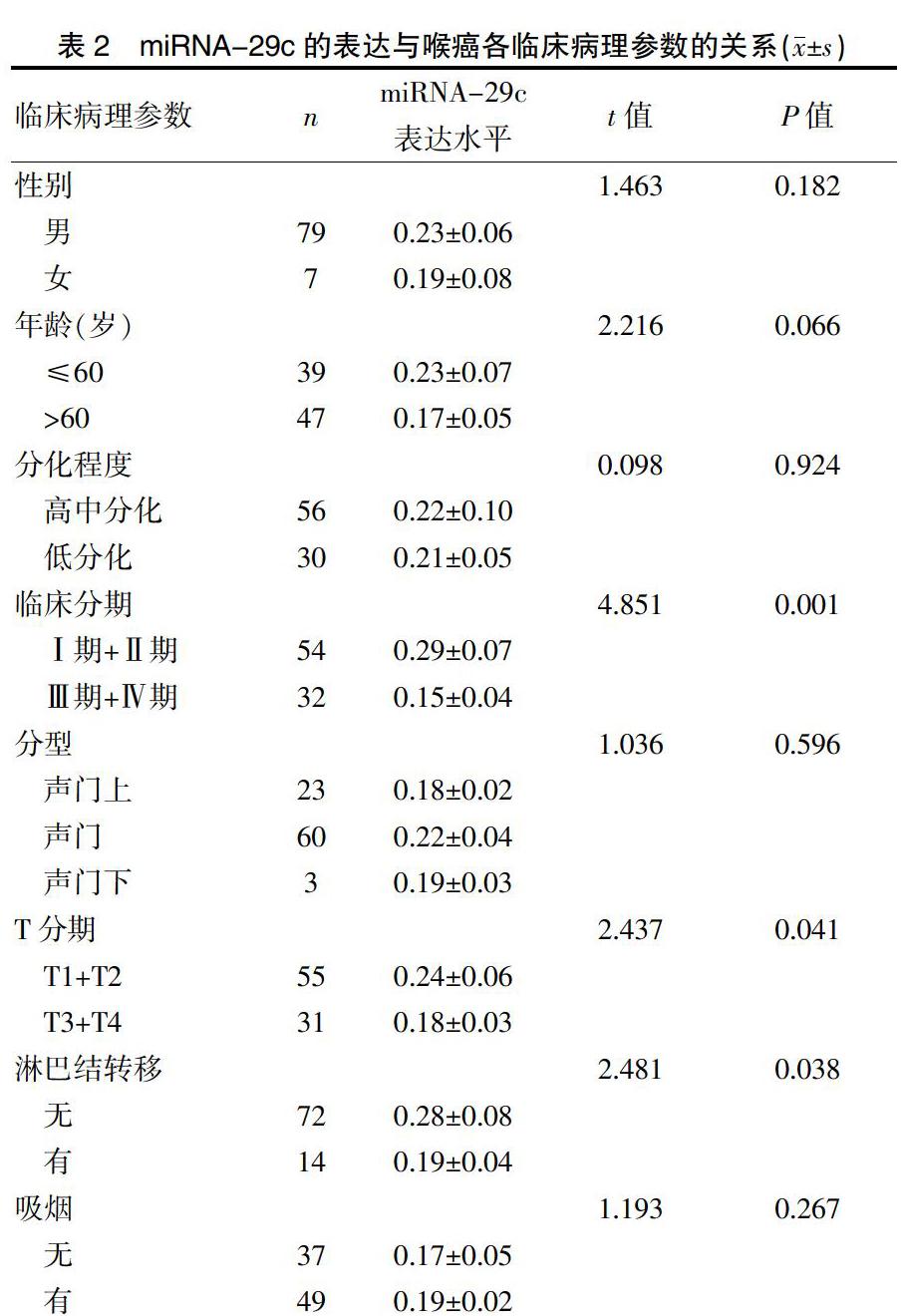
miRNA-29c的表达水平与患者临床分期、T分期及淋巴转移密切相关(P<0.05),而与患者的性别、年龄、吸烟、分型及分化程度无关(P>0.05)。见表2。
表2 miRNA-29c的表达与喉癌各临床病理参数的关系(x±s)
2.3 检测细胞转染效率
Hep-2细胞经带有Cy3荧光蛋白的无关序列(Cy3-NC)转染24 h,在荧光显微镜下观察转染率,转染效率约90%(封三图1)。
2.4 Q-RT-PCR检测miRNA-29c在Hep-2细胞中的表达情况
Q-RP-PCR结果显示,miRNA-29c mimics组、NC组和空白对照组中miRNA-29c的表达水平分别为(17.25±1.51)、(1.63±0.52)、(1.71±0.69)。结果表明,转染miRNA-29c mimics的Hep-2细胞与NC组及空白对照组相比,miRNA-29c的表达水平显著升高(P<0.01)。转染miRNA-29c mimics可以明显上调Hep-2细胞的miRNA-29c表达水平。
2.5 转染miRNA-29c对Hep-2细胞增殖的影响
CCK-8测定的结果显示(封三图2),miRNA-29c mimics组、NC组和空白对照组的A值分别为(0.61±0.20)、(0.87±0.21)、(0.86±0.24)。结果表明,NC组和空白对照组细胞增殖能力明显高于转染miRNA-29c mimics后的Hep-2细胞,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),NC组和空白对照组相比细胞增殖无明显差异(P>0.05)。转染miRNA-29c mimics能抑制Hep-2细胞的增殖活性(封三图3)。
2.6 miRNA-29c mimics转染对Hep-2细胞侵袭力的影响
Transwell体外侵袭实验结果显示,miRNA-29c mimics组、NC组和空白对照组的穿膜细胞数分别为(0.21±0.09)、(0.77±0.11)、(0.78±0.13)。结果表明,转染miRNA-29c mimics后,Hep-2细胞侵袭能力显著低于NC组及空白对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),NC组和空白对照组间侵袭能力差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见封三图4。
3 讨论
近年来研究发现,恶性肿瘤发生发展与细胞内各种基因突变相关,并且与表观遗传调控网络的紊乱密切相关。miRNA作为表观遗传调控网络的重要组成部分,它的发现为肿瘤的诊断治疗研究提供了新的方向, miRNA的表达具有明显的组织特异性,其表达紊乱可能和许多肿瘤的发生发展相关。近年来,许多研究表明,miRNA的异常表达与喉癌的增殖、分化、浸润和转移等生物学行为密切相关[9-12]。
深入研究miRNA与喉癌发生发展的关系,将为生物学治疗喉癌提供有力的理论指导。既往研究表明,miRNA-23a[13]、miRNA-16[14]在喉癌组织中表达异常,这说明miRNA与喉癌的发生发展密切相关。因此,深入研究miRNA在喉癌中的表达对其临床诊疗具有重要意义。miRNA-29c是Yu等[15]最早在血液系统疾病中发现其与疾病相关,之后诸多文献报道miRNA-29c参与如膀胱癌[16]、子宫内膜癌[17]、黑色素瘤[18]等疾病的发生发展过程。一项针对110例患者长达平均72 个月的随访发现miRNA-29c可作为慢性淋巴细胞白血病的预后指标,但尚未进行功能研究[19]。Pass 等[20]也证明miRNA-29c可评估恶性胸膜间皮瘤独立的预后情况,并通过细胞实验证实随着miRNA-29c的表达增加、肿瘤细胞的增殖、侵袭、迁移和克隆生长降低。国内代大伟等[21]通过转染miRNA-29c 提高胶质瘤U251细胞内miRNA-29c表达量,并通过MTT实验证实,过表达miRNA-29c可抑制细胞增殖能力。实验组细胞的凋亡比例明显升高,同时侵袭能力明显下降,提示miRNA-29c可能具有抑制脑胶质瘤细胞侵袭和促进肿瘤细胞凋亡的作用。miRNA-29c在肿瘤中发挥如此重要的作用,但是在喉癌中的功能却未见报道。
本研究通过Q-RT-PCR检测miRNA-29c在86例喉癌组织和42例癌旁组织中的表达情况。结果发现喉癌中miRNA-29c的表达水平明显低于正常组织,研究还发现临床分期越晚,分化程度越低或伴有淋巴结转移患者喉癌组织中miRNA-29c的表达水平也相对较低,miRNA-29c的低表达对肿瘤预后有不利影响,它是喉癌患者预后不良的重要危险因素。为了进一步探讨将miRNA-29c用于喉癌生物靶向治疗的可能性,以喉癌Hep-2为研究对象,通过转染miRNA-29c mimics来进行一系列的研究。通过荧光显微镜观察发现Lipo2000瞬时转染法的转染效率约为90%;Q-RT-PCR实验结果显示,转染模拟物后miRNA-29c的表达上调了10倍以上,表明转染的效果显著;CCK-8及Transwell体外侵袭实验结果表明,转染miRNA-29c后Hep-2细胞的增殖、侵袭能力受到明显抑制,较NC组及空白对照组有显著差异(P<0.01);这表明miRNA-29c可在体外显著抑制Hep-2细胞的增殖生长及侵袭能力。
综上所述,在喉癌中miRNA-29c是一个抑制性miRNA,过表达miRNA-29c可以显著抑制喉癌Hep-2细胞的恶性生物学行为,如喉癌Hep-2细胞的增殖及侵袭能力。miRNA-29c可能参与喉癌的发生、发展、侵袭和转移。其作用机制探讨将成为本课题组下一步研究的方向,阐明这些机制也将更有助于miRNA-29c介导的生物靶向治疗作为一种新型的诊疗技术应用于喉癌的临床治疗及预后判断。
[参考文献]
[1] Gorphe P,Tao Y,Blanchard P,et al. Relationship between the time to locoregional recurrence and survival in laryngeal squamous-cell carcinoma[J]. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology,2017,274(5):2267-2271.
[2] Schwarzenbach H,Nishida N,Calin GA,et al. Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in cancer[J].Nat Rev Clin Oncol,2014,11(3):145-156.
[3] Melo SA,Kalluri R. Molecular pathways:microRNAs as cancer therapeutics[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2012,18(16):4234-4239.
[4] Hong L,Qing O,Ji Z,et al. Downregulation of miR-16 via URGCP pathway contributes to glioma growth[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):13470.
[5] Cutrona G,Matis S,Colombo M,et al. Effects of miRNA- 15 and miRNA-16 expression replacement in chronic lym-phocytic leukemia:Implication for therapy[J]. Leukemia,2017,31(9):1894-1904.
[6] Kriegel AJ,Liu Y,Fang Y,et al. The miR-29 family: Genomics,cell biology,and relevance to renal and cardiovascular injury[J]. Physiol Genomics,2012,44(4):237-244.
[7] Wang H,Zhu Y,Zhao M,et al. miRNA-29c suppresses lung cancer cell adhesion to extracellular matrix and metastasis by targeting integrin β1 and matrix metalloproteinase2(MMP2)[J]. Plos One,2013,8(8):e70192.
[8] Bhardwaj A,Singh H,Rajapakshe K,et al. Regulation of miRNA-29c and its downstream pathways in preneoplastic progression of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(12):19645-19660.
[9] Song Y,Tian Y,Bai WL,et al. Expression and clinical significance of microRNA-152 in supragalottic laryngeal carcinoma[J]. Tumor Biology,2014,35(11):11075-11079.
[10] Yu CH,Xing FY,Zhang JY,et al. A combination of mRNA expression profile and miRNA expression profile identifies detection biomarkers in different tumor stages of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018,22(21):7296-7304.
[11] Zhang F,Cao H. MicroRNA 143 3p suppresses cell growth and invasion in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomavia targeting the k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway[J]. Int J Oncol,2019,54(2):689-701.
[12] 馬志超,江波,蔡志毅,等.MiR-155对喉鳞癌细胞株Hep-2细胞增殖与侵袭能力的影响[J].中国现代医生,2019,57(11):48-51.
[13] Zhang XW,Liu N,Chen S,et al. Upregulation of microRNA-23a regulates proliferation and apoptosis by targeting APAF-1 in laryngeal carcinoma[J]. Oncology Letters,2015,10(1):410-416.
[14] Wu H. MicroRNA-16 targets zyxin and promotes cell motility in human laryngeal carcinoma cell line HEp-2[J].Iubmb Life,2015,63(2):101-108.
[15] Yu J,Wang F,Yang GH,et al. Human microRNA clusters:genomic organization and expression profile in leuke-mia cell lines[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2006, 349(1): 59-68.
[16] Wang G,Zhang H,He H,et al. Up-regulation of microRNA in bladder tumor tissue is not common[J]. Int Urol Nephrol,2010,42(1): 95-102.
[17] Castilla MA,Moreno-Bueno G,Romero-Pérez L,et al. Micro-RNA signature of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometrial carcinosarcoma[J]. J Pathol,2011, 223(1):72-90.
[18] Nguyen T,Kuo C,Nicholl MB,et al. Downregulation of microRNA-29c is associated with hypermethylation of tumor-related genes and diseaseoutcome in cutaneous melanoina[J]. Epigenetics,2011,6(3):388-394.
[19] Stamatopoulos B,Meuleman N,Haibe-Kains B,et al. microRNA-29c and microRNA-223 down-regulation has in vivo significance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and improves disease risk stratification[J]. Blood,2009,113(21):5237 -5245.
[20] Pass HI,Goparaju C,Ivanov S,et al. has-miR-29c is linked to the prognosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Cancer Res,2010,70(5):1916-1924.
[21] 代大偉,田恒力,陈鑫. miR-29c对脑胶质瘤U251细胞生物学活性的影响[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2012, 17(6):277-279.
(收稿日期:2020-06-19)

