East to west:research progress in traditional Chinese medicine for antiaging strategies
Jing-Ning Yan,Cong Hu,Xiang-Long Meng
1Clinical College of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine,Jinzhong 030619,China; 2School of Pharmacy,Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University,Nanchang 330013,China;3College of Chinese Materia Medica,Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine,Jinzhong 030619,China; 4College of Korean Medicine,Dongguk University,Gyeongju 38066,Rep.of Korea.
Abstract
Delaying the onset of aging is considered an important tool for dealing with the global crisis of the aging population.Accordingly,several antiaging studies have been conducted using strategies of modern medicine and traditional Chinese medicine(TCM).In this review,we summarize the current state of antiaging research related to both modern medicine and TCM and provide suggestions for further research.Various theories related to the aging process have been proposed,including the free radical theory,mitochondrial DNA damage theory,telomere theory,cross-linking theory,and intestinal flora theory,and a number of antiaging chemical treatments have been developed using modern medicine.These theories and achievements have resulted in major advancements in antiaging research.TCM is based on practical experience and has a long history with unique advantages in antiaging research.Some antiaging practices such as moderate diet consumption,acupuncture,Tai Chi (a traditional Chinese martial art that can relax the nerves to slow down the aging process),and Wuqin Xi (a traditional Chinese exercise to strengthen the body) have been adopted to maintain health.Several TCMs and prescriptions,particularly those related to medicine food homology,have been used in antiaging treatment,and their antiaging properties have been demonstrated to be effective based on pharmacological experiments and clinical applications.
Key words: Antiaging,Modern medicine,Traditional Chinese medicine,Medicine food homology,Pharmacological experiments,Clinical applications
Background
Currently,population aging is a serious global concern.According to World Health Organization,617 million people worldwide were aged ≥65 years in 2015.A press conference held by the China Aging Office highlighted that 241 million elderly people in China were aged ≥60 years,accounting for 17.3%of the total population by the end of 2017 [1].Population aging is more prevalent in developed countries,and the proportion of adults aged ≥60 years in Japan,Italy,and Germany was 32.79%,28.59%,and 27.35%,respectively,in 2015 according to population data from the United Nations [2].Moreover,there is an increasing trend of population aging worldwide.Therefore,the number of studies focused on antiaging has drastically increased in recent years,with results indicating that people should pay more attention to their health and longevity.
Although modern medicine has made important achievements in antiaging research and a number of aging theories have been proposed with the development of several promising antiaging drugs,to the best of our knowledge,there is no primary effective strategy for antiaging [3].However,traditional Chinese medicine (TCM),which is based on practical experience,has a history of more than 2,000 years in antiaging research; it is considered to have a substantial advantage in antiaging treatments.The earliest Chinese medicine book,Huangdi Neijing(Yellow Emperor's Canon of Internal Classic;221 B.C.E.-220 C.E.),recorded the process of human aging approximately 2,000 years ago [4].More than 1,700 years ago,medica of the oldest traditional Chinese material,Shennong Bencaojing(Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica; 25-220 C.E.),clarified the use of TCMs in improving health and prolonging lifespan using treatments such as Renshen (Ginseng radix et rhizoma) and Huangqi(Astragali radix).Moreover,certain activities and physical therapies based on the theory of TCMs have been developed to maintain health,and most of these interventions have been shown to be effective through thousands of years of clinical practice and are being used to date.This review summarizes and analyzes the research findings and measures of antiaging related to both modern medicine and TCMs,with the goal of providing guidance for future antiaging research.
Modern aging theories
The aging mechanism,an essential subject in modern geriatric medicine,is a complex,extensive,and challenging concept.With rapid development in modern cell biology,molecular biology,and other disciplines,significant advances have been made in determining the mechanisms of aging,and several theories of aging with scientific value have been proposed[5].
Free radical theory
The free radical theory was proposed by Harman D in 1956 [6].This theory states that free radicals are produced in the body at all times and that the number of free radicals is regulated by free radical scavengers such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) to maintain a balance [5].However,this balance is gradually disrupted with aging owing to reduction in free radical scavenger activity.Consequently,excess free radicals adversely affect cellular function,leading to aging and death[7].
Mitochondrial DNA damage theory
The second theory of aging states that mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is closely related to aging; this theory was proposed by Linnane AW in 1989 [8].Since then,several experiments have been conducted by scholars,with results indicating that the hypothesis is convincing.The main argument of this theory is that mtDNA damage is the molecular basis of cell senescence and death,with mitochondrial degeneration,leakage,and rupture being essential causes of cell senescence.Therefore,lifespan can be prolonged by inhibiting mtDNA degradation[9].
Telomere theory
Harley,an American antiaging expert,proposed the telomere theory of cell senescence in 1990[10].This theory suggests that the chromatid located at the tip of the chromosome,which is also called the telomere,is closely associated with aging and longevity and that telomeres gradually shorten with cell division,which leads to cell aging [11].Modern medical studies have demonstrated that telomeres can preserve the integrity and stability of chromosomes and protect chromosomes from enzymatic digestion,fusion,loss,or rearrangement[12].
Cross-linking theory
The cross-linking theory was proposed by Bjorksten J in 1963 [13].This theory states that macromolecules (e.g.,proteins and nucleic acids)present in organisms can be combined to create giant molecules via a process called cross-linking [14].However,this cross-linking can affect the normal functions of cells and disturb organ homeostasis,which becomes more serious with aging[15].
Intestinal flora theory
The relationship between gut microbiota and aging was proposed by Carmen Garcia-Peña in 2017 [16].This theory argues that the balance of the intestinal microecological system is gradually disrupted with aging,with the resulting imbalance allowing bacteria,viruses,and/or other pathogens to invade the body,further endangering human health [17].Therefore,maintaining the equilibrium of the intestinal microbial system has been hypothesized to prolong cell life and extend the organism’s lifespan[18].
Antiaging chemical medicines
In recent years,antiaging research has garnered increased attention,resulting in the development of several antiaging chemical medicines.According to their formulations,these medicines can be divided into three categories,namely,tablets,capsules,and liquids.These formulations have been designed to delay aging by improving immunity and protecting organs and cells from oxidative damage(Table1).
Development stage of TCM in antiaging research
TCM-related antiaging research initiated with the introduction of the Jin Dan theory,which is based on the fact that ancient Chinese people believed that they could live forever if they consumed Jin Dan,a mineral product made by ancient Chinese alchemists.Subsequently,some researchers supplemented and modified various antiaging methods by performing clinical trials at different time periods,thus forming an antiaging system with Chinese characteristics.In Chinese history,TCM-related antiaging research has primarily been described in four stages,namely,infancy,formation,wander,and development[19].
Infancy stage:before the Eastern Han Dynasty(before 25 C.E.)
Before the Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220 C.E.),scientific knowledge was very poor.However,a campaign searching for measures that would confer immortality had spread throughout the country during this period because the emperors of the Qin Dynasty (221-207 B.C.E.) and the Western Han Dynasty (202 B.C.E.-8 C.E.)desired to be immortal.Under these conditions,Huangdi Neijing(Yellow Emperor's Canon of Internal Classic; 221 B.C.E.-220 C.E.) andWuShiEr BingFang(Prescription for Fifty-Two Diseases; 475 B.C.E.-221 B.C.E.) were issued,which provided not only information on antiaging but also a foundation of evidence for modern antiaging research.
Formation stage:from the Eastern Han Dynasty to the Southern and Northern Dynasties of China(25-589 C.E.)
In Chinese history,certain famous experts of TCM,including Zhang Zhongjing,Hua Tuo,and Tao Hongjing,belonged to the period involving the Eastern Han (25-220 C.E.),Three Kingdoms(220-280 C.E.),Jin (280-420 C.E.),and Southern and Northern Dynasties (420-589 C.E.).Some classic works of TCM,such asShennong Bencaojing(Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica; 25-220 C.E.),Mingyi BieLu(Miscellaneous Records of Famous Physicians; 184-220 C.E.),andBencaojing Jizhu(Variorum the Classic of Materia Medica;480-498 C.E.),were produced during this period.
Wander stage:the Sui Dynasty to the Ming Dynasty(581-1644 C.E.)
The Sui Dynasty (581-619 C.E.),Tang Dynasty(618-907 C.E.),Song Dynasty (960-1279 C.E.),and Yuan Dynasty(1271-1368 C.E.)marked the heydays of the Chinese feudal society.Some classic works,including Sun Jing'sXinxiu Bencao(New Revision of Herbs; 659 C.E.),Sun Simiao’sBeiji Qianjin Yao Fang(Essential Recipes for Emergent Use Worth A Thousand Gold; 652 C.E.),and Li Shizhen'sBencao Gangmu(Compendium of Materia Medica; 1518 C.E.-1593 C.E.),were produced during this period.However,because of the ruling class's superstition regarding Taoism (one of the China's native religion)and the Jin Dan theory advocated by alchemists and literary officials during this period,further development of antiaging studies was hindered.
Development stage:from the Qing Dynasty to Date(1636 C.E.-To Date)
From the last years of Qing dynasty until the founding of Republic of China,the feudal autocratic system declined and capitalism gradually grew(1840-1911 C.E.).In this period,the development of natural science,the introduction of Western medicine,and the old government's policy of abandoning TCM therapies had a positive or negative impact on antiaging research.However,some works,including Wang Ang'sYifang Jijie(Collected Exegesis of Recipes;1682 C.E.)and Qing Pu'sShoushi Bian(The Organized of Prolonging Life; 1667 C.E.),were produced.With economic development and social stability,antiaging TCMs and prescriptions have been strongly supported by the government after the founding of the People’s Republic of China (1949 C.E.-To Date).Meanwhile,the China Scientific Research Center on Aging was established,andChinese Pharmacopoeiawas published.Both these works had positive impacts on TCM-related antiaging research.
Antiaging methods in TCM
The law and practices for preventing aging were established as early as the production ofShanggu Tianzhen Lun,article 1 ofSuwen(Plain Questions;770 B.C.E.-221 B.C.E.),which stated that all things are divided into Yin and Yang.Indeed,Yin and Yang are two opposing principles in nature,with the former being feminine and negative and the latter being masculine and positive.Accordingly,correct health care methods based on these principles involve appropriate diet and exercise and avoiding being overworked,which can help people to live in harmony and die at the age of ≥100 years.In this case,TCM not only gives importance to TCM therapies but also emphasizes the critical roles of dietary habits,emotional factors,health campaigns,and alchemy for antiaging purposes[20].
Moderate diet consumption
A moderate diet is the cornerstone of health; it can not only improve the immunity of the body but also treat some diseases.First,meals need to be regular.In China,the traditional schedule for eating includes three meals a day,the benefit of which has been demonstrated both scientifically and in practice.This ensures that digestive organs regularly digest food and absorb nutrition and provides digestive organs with proper balance between work and rest.Second,the dietary intake should be balanced.Accordingly,a variety of foods can meet energy and nutritional needs only when they are properly matched.In addition,dietary intake should not be too little or too much,and the food should not be too cold or too hot.These requirements can protect body organs and make the body strong and healthy [21].Hence,the theory of medicine and food homology was gradually discovered and developed into a unique Chinese medical practice[22,23].
Emotional reconciliation and peace
Yinyang Yingxiang Dalun,article 5 ofSuwen(Plain Questions; 770 B.C.E.-221 B.C.E.),states that emotions such as joy,anger,sorrow,fear,love,hate,desire,and external emotional stimulation exceeding the normal tolerance limits of the human body can generate certain factors that disrupt the functions of organs and reduce Qi (Qi is considered the most basic material basis of the human body according to the TCM theory),and reductions in Qi lead to accelerated body aging[24].
Acupuncture
Acupuncture has long been used as an antiaging strategy.As early as theHuangdi Neijing(Yellow Emperor's Canon of Internal Classic; 221 B.C.E.-220 C.E.),more than 30 types of acupuncture measures have been recorded in detail for disease syndromes.These included several acupuncture prescriptions and tests for aging-related diseases,which served to establish the foundation for use of clinical acupuncture as part of an antiaging strategy[25].In recent years,World Health Organization has paid increasing attention to acupuncture and its benefits.In addition,a number of experts worldwide have studied acupuncture and found that it can activate brain cells,improve brain blood circulation and brain cell nutrition,and delay brain cell aging.Moreover,it has been found that acupuncture slows down the aging process through various mechanisms,such as eliminating free radical damage,regulating immunity and neuroendocrine function,adjusting lipid metabolism,improving blood rheology,and regulating the levels of trace elements.Some studies have also demonstrated that acupuncture has far-reaching antiaging effects,with Zusanli (ST 36),Quchi (LI 11),and Sanyinjiao (SP 6) (3 acupoints)being most closely associated with antiaging[26].
Traditional health care movement
Tai Chi.Elimination of diseases and prolongation of lifespan are essential factors for Tai Chi(a traditional Chinese martial art that can relax the nerves to slow down the aging process),which has won the favor of people worldwide.The ultimate goal of practicing Tai Chi is to provide health and a long lifespan to its practitioners.In addition,Tai Chi has been stated to provide a life as vigorous and beautiful as spring,which was recorded in the ancient Tai Chi classic—Taiji Shisanshi Xinggong Gejue(Tai Chi 13 Essential Technique Drills; 1525-1606 C.E.).This recording demonstrates that one of the ultimate aims of the ancient Chinese practice of Tai Chi is to prolong lifespan [27].The fundamental reason why practicing Tai Chi has been reported to expel diseases and prolong lifespan is that practicing Tai Chi can balance the Yin and Yang and the smooth Qi and the blood as well as increase overall vitality.Thus,sick and subhealthy individuals can recover,and the elderly can be rejuvenated by practicing Tai Chi[28].
Wuqin Xi.Hua Tuo,a famous doctor of the Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220 C.E.),studied activities of the tiger,crane,leopard,snake,and dragon and combined the functions of human viscera,the meridians,and Qi and blood to create“Wuqin Xi” (a traditional Chinese exercise to strengthen the body)[29].In Wuqin Xi,all the major muscles and joints of the body participate in various activities,thus improving blood circulation and promoting viscera metabolism.Taken together,this can directly and indirectly prevent lipid peroxidation in the body [30,31].Indeed,some studies have demonstrated that long-term exercise (e.g.,Wuqin Xi) can increase SOD activity in the peripheral blood of the elderly and delay free radical damage to delay aging [32,33].
Baduanjin.Baduanjin (a traditional Chinese exercise to strengthen the body) can improve the balancing ability of the elderly [34,35].Achieving good balance is of great significance to the elderly because it provides a fundamental guarantee for maintenance of an independent life.Many movements in Baduanjin require the fingers to grasphard and involve full exercise of the forearm and hand muscles [54].Some studies have demonstrated that long-term practice of Baduanjin can enhance blood supply and improve blood circulation speed[55].It can also promote functions of the human respiratory system and increase vital capacity [56,57].
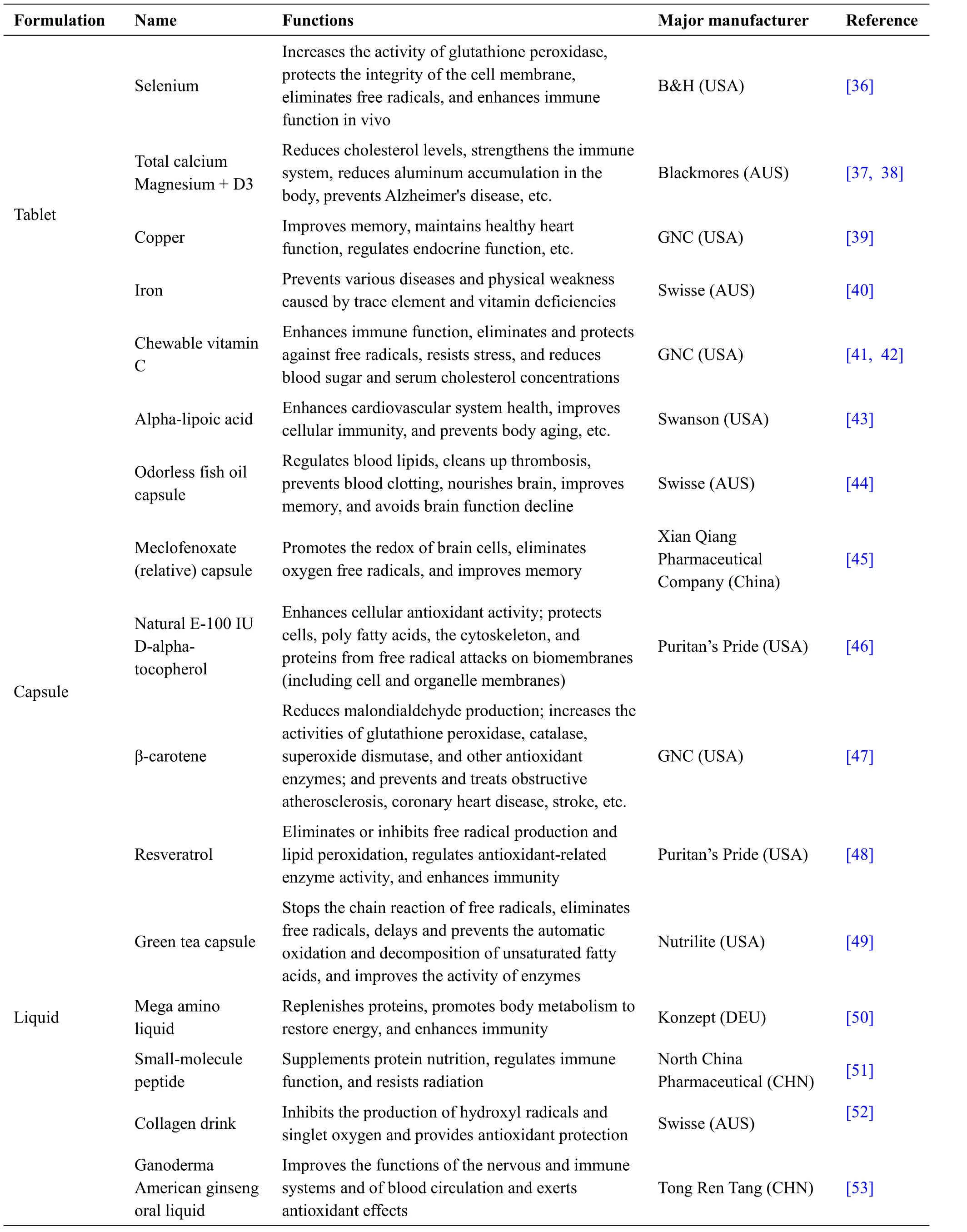
Table1 Antiaging chemical medicines
Antiaging TCMs
There is a long history of using drugs to delay aging in China,which has been recorded in many ancient books.Shennong Bencaojing(Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica;25-220 C.E.)comprises 365 TCMs,of which 133 are associated with prolonging life,immortality,aging tolerance,longevity,etc.[58].
Bencao Gangmu(Compendium of Materia Medica;1518 C.E.-1593 C.E.) includes 1,539 TCMs,of which 197 are associated with prolonging lifespan and replenishing the body [59].Other books,such as
Yaoxing Bencao(Materia Medica of Medicinal Properties; 1520 C.E.),Shiliao Bencao(Materia Medica for Dietary Therapy; 713-741 C.E.),andShiwu Bencao(Food as Materia Medica;1506-1521 C.E.),have recorded additional antiaging TCMs.With the development of TCMs,some researchers have combined traditional antiaging TCMs with modern science to perform a series of experimental studies for delaying aging.
Antiaging TCMs represented by “medicine food homology”
In recent years,people have become more interested in food therapy based on the theory of “medicinal and food homology.” Modern medical studies have demonstrated that antiaging TCMs can reverse aging and prolong longevity because they activate the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase pathway [60],scavenge free radicals [61],and improve body immunity [62].In 2002,the Ministry of Health issued the “List of Traditional Goods that Are Both Food and Medicine”.This list comprised 87 TCMs.In recent years,the National Health and Family Planning Commission has updated this list to include 110 TCMs.In addition,Sun QS [63]researched ancient books and TCM documents and summarized that 226 TCMs have antiaging properties.On the basis of this study,59 antiaging medicine food homologous drugs were identified by further analysis (Table2,Chinese Pinyin (Chinese phonetic alphabets) names in an alphabetical order).The main components of their antiaging properties and the antiaging mechanisms are shown in Figure1.
Pharmacological studies of TCMs
Some TCMs are considered to have excellent effects on antiaging,and many effects have been confirmed by experimental studies.Below,we summarize the main experimental studies related to antiaging TCMs.
Renshen (Ginseng radix et rhizoma).Renshen(Ginseng radix et rhizoma),a traditional antiaging medicine,is the dry root ofPanax ginsengC.A.Mey.With rapid development in modern science and technology,increasing research has focused on mechanisms underlying the antiaging properties of Renshen (Ginseng radix et rhizoma).A study used D-galactose-induced aging male Sprague-Dawley rats to investigate the antiaging properties of ginsenoside Rg1,and after 42 days of comparative testing,this study concluded that ginsenosides Rg1 had potent antioxidant activity and that it regulated the senescence of hematopoietic stem cells,promoted the activity of SOD,and decreased levels of reactive oxygen species and content of malondialdehyde(MDA) in aging rats [64].In addition,the administration of ginsenoside Rg1 was shown to increase telomerase activity,inhibit telomere shortening,and delay aging in D-galactose-induced aging rats [65].In addition,the aqueous extract of Renshen (Ginseng radix et rhizoma) has shown to increase SOD and catalase (CAT) activities and decrease MDA content in drosophila melanogaster.Simultaneously,quantitative real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction results demonstrated that the aqueous extract of Renshen (Ginseng radix et rhizoma) could significantly upregulate the expressions of SOD and CAT in drosophila melanogasters.Thus,it is concluded that the antiaging properties of Renshen(Ginseng radix et rhizoma) are primarily associated with increased activities of relevant antioxidant enzymes and enhanced free radical scavenging ability in vivo[66].
Huangqi(Astragali radix).Huangqi(Astragali radix)is the dried root ofAstragalus membranaceus(Fisch.)Bge.and has shown to have unique curative effects in terms of antiaging and antioxidation.A previous study investigated the antiaging properties of the aqueous extract of Huangqi(Astragali radix)in mice with cardiac dysfunction and found that Huangqi(Astragali radix) was able to prolong the lifespan of the mice through varied mechanisms,including maintaining SOD activity in mice with cerebral ischemia,reducing MDA content and free radical levels,decreasing apoptosis,and exerting antioxidant effects [67].In addition,relevant physiological changes due to aging were simulated in naturally aging rats,and the antiaging mechanisms of Huangqi(Astragali radix) were discussed in Van’s research.The study showed that the aqueous extract of Huangqi (Astragali radix) could reduce mtDNA damage caused by free radicals,thus preventing the loss of mtDNA fragments and exhibiting good antiaging properties.The effects of Huangqi(Astragali radix) are reportedly similar to those ofvitamin E[68].Moreover,the regulation of intestinal flora by Huangqi (Astragali radix) was studied in aging mice,and the results indicated that the amount of bifidobacteria,which is closely associated with health,returned to normal levels after administration of the aqueous extract of Huangqi (Astragali radix)[69].
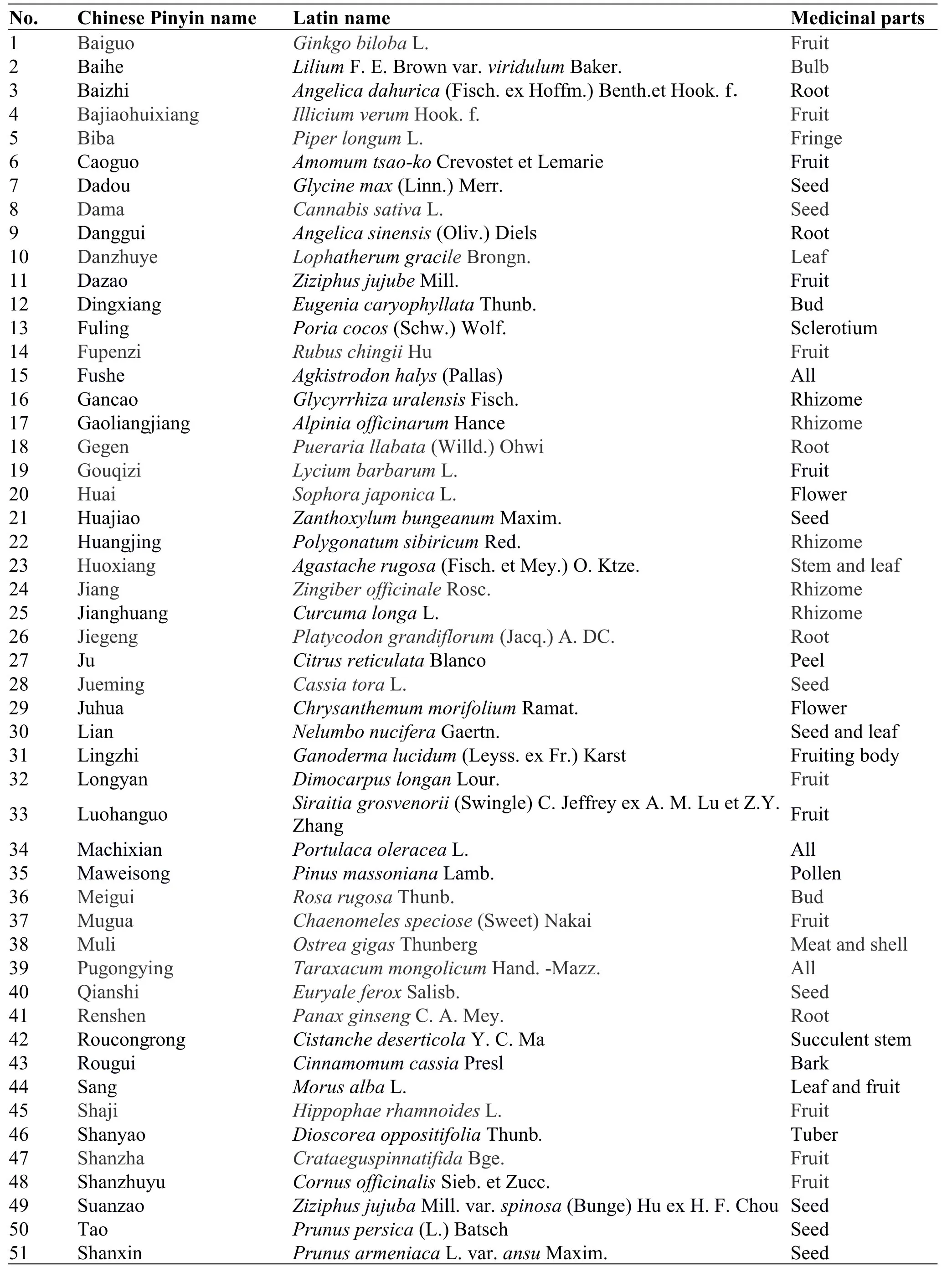
Table2 Traditional Chinese medicines with food homology

Table2 Traditional Chinese medicines with food homology(continued)
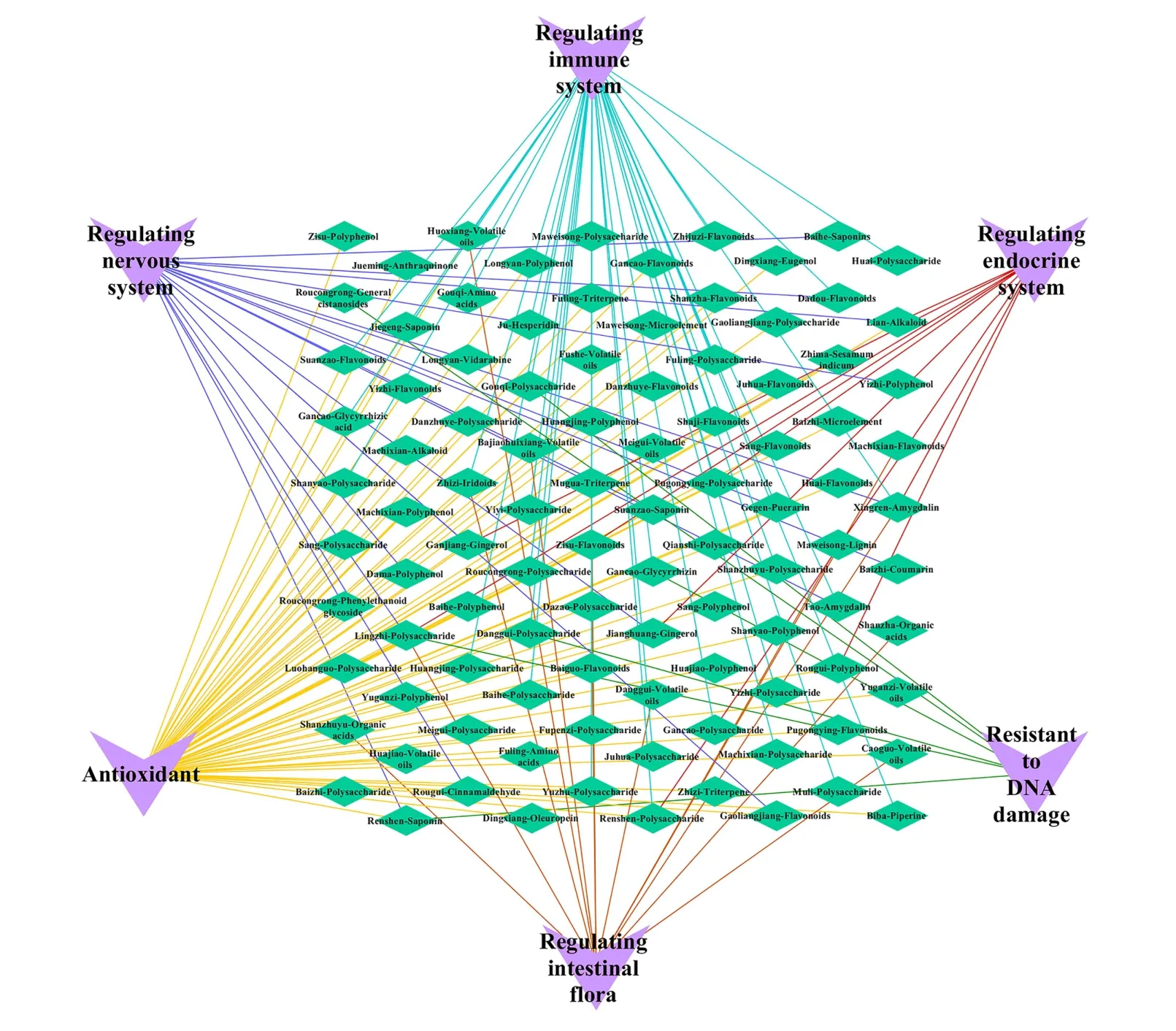
Figure1 The antiaging mechanisms of 59 TCMs
Heshouwu (Polygoni multiflori radix) (Polygoni multiflori radix).Heshouwu (Polygoni multiflori radix)is the dry root tuber ofPolygonum multiflorumThunb.,and its primary functions involve reducing blood lipid levels and exerting antiaging properties such as improved immunity and increased intelligence.The emodin derivative,emodin-8-o-(6'-o-malonyl)-glucoside,was isolated from Heshouwu (Polygoni multiflori radix) by Lo et al..This derivative was shown to stimulate growth hormone release in rat anterior pituitary cells by activating the auxin receptor,which serves to induce auxin release and has antiaging properties [70].In addition,Chen et al.[71] found that the aqueous extract of Heshouwu (Polygoni multiflori radix)obviously inhibited the activity of monoamine oxidase in the brain and liver tissues of aged mice,suggesting that Heshouwu(Polygoni multiflori radix)prevents and treats senile diseases such as depression and Parkinson's disease related to disorder of monoamines in the brain.Tang et al.studied the effects of ethyl acetate extract of Heshouwu(Polygoni multiflori radix) on the lifespan ofCaenorhabditis elegansand demonstrated that the average lifespan of the nematodes was significantly longer in the low,medium,and high concentration groups (25,37.5,and 50 mg/L ethyl acetate,respectively,calculated based on the crude drug)than in the blank group,particularly of those in the medium concentration group.A further discussion regarding the ability of 37.5 mg/L ethyl acetate to delay senescence in the nematodes without damaging its reproductive ability was presented[72].
Danggui (Angelicae sinensis radix) (Angelicae sinensis radix).Danggui (Angelicae sinensis radix)is the dry root ofAngelica sinensis(Oliv.) Diels.Modern pharmacological experiments have demonstrated that Danggui(Angelicae sinensis radix)has various antiaging roles via several mechanisms[73].Qi et al.[74] used D-galactose-induced aging mice as research models to study the antiaging properties of Danggui (Angelicae sinensis radix).The water decoction of Danggui (Angelicae sinensis radix) demonstrated good antiaging properties that were dose dependent.In addition,the antiaging mechanisms of Danggui (Angelicae sinensis radix)include increasing the activity of Ca2+-ATP enzyme and stabilizing the concentrations of nitric oxide synthase and Ca2+,thus balancing the content of NO.Furthermore,An et al.[75] found that Danggui(Angelicae sinensis radix) could reduce the protein expression of p16 in brain tissues and decrease the activity of monoamine oxidase in brain and kidney tissues,while enhance the activity of CAT in liver and kidney tissues.Thus,the antiaging mechanism of Danggui (Angelicae sinensis radix) may be associated with enhancement of antioxidant capacity,downregulation of p16 expression,and inhibition of aging cell proliferation.In addition,Danggui(Angelicae sinensis radix) can also increase SOD activity in blood and tissue and enhance free radical scavenging ability,which results in reduced MDA production,protein dissolution,and protein denaturation,thus ensuring the integrity of the cell membrane structure and function and subsequently delaying the occurrence of apoptosis[76].
Gouqizi (Lycii fructus) (Lycii fructus).Gouqizi(Lycii fructus),a common medicine food homologous drug,is the dry ripe fruit ofLycium barbarumL.A previous study used human fetal lung diploid fibroblasts (2BS cells) as aging models to study the antiaging properties of Gouqizi (Lycii fructus)and demonstrated that the aqueous extract of Gouqizi (Lycii fructus) could accelerate the rate of DNA synthesis in the fusion cells of 2BS and thus prolong their lifespan [77].Medlar polysaccharide(MP) is a type of water-soluble polysaccharide comprising six monosaccharide components;it is the main active component of Gouqizi (Lycii fructus)and is believed to be the primary ingredient responsible for the antiaging properties of Gouqizi(Lycii fructus),indicating its important role in the pharmacological significance of Gouqizi (Lycii fructus).In addition,it has been found that MP can increase SOD activity and decrease MDA content in aging mice [78].MP can also significantly increase glutathione peroxidase and SOD activities and reduce MDA content in the plasma of MP-treated aging rats with cavernous nerve injury [79].Furthermore,it has been demonstrated that MP plays an antiaging role by increasing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes to slow down the processes associated with oxidative damage,and this mechanism may be associated with the activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway by MP[80].
Study on the prescription of antiaging TCM
The unique understanding of cell senescence and antiaging as related to TCM prescriptions has great advantages,gaining considerable attention from Chinese scholars in particular.
Pharmacological studies of prescription of antiaging TCMs
More than 100 prescriptions of antiaging TCMs are available.Some of the main prescriptions are summarized below.
Classic ancient prescription of Liuwei Dihuang pill.In a study on Liuwei Dihuang pill (LWDH),naturally aging ICR mice were intragastrically treated with LWDH for 30 days,and the antiaging properties of LWDH were investigated using metabonomics.In this previous study,10 biomarkers related to the antiaging properties of LWDH were obtained and various antiaging mechanisms were identified,including those related to linoleic acid metabolism,pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis,glycerophospholipid metabolism,and amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism [81].In addition,Zhou et al.have reported that LWDH can significantly inhibit the distortion and rate of sister chromatid exchange in mouse bone marrow cells exposed to cyclophosphamide,which has good DNA damaging properties.These results suggest that LWDH plays a role in delaying aging by improving the ability of the body to resist DNA damage [82].In addition,LWDH can increase SOD activity and decrease MDA and lipid peroxide contents in the serum of mice; it also exhibits good scavenging ability against free radicals in the body[83].
Classic ancient prescription of Jingui Shenqi pill.Yan et al.studied the pharmacological effects of Jingui Shenqi pill (JGSQ) on autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse models and demonstrated that JGSQ significantly decreased neurological function scores,shortened the course of the disease,and regulated the ratio of CD4/CD8 cells and the number of NK cells in the autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse models [84].In another study,the effects of JGSQ on telomerase in the liver and brain of aging mouse models were studied using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and qRT-PCR at the protein and transcription levels,respectively.The results showed that the expression of telomerase in the tissues of aging mice was enhanced after JGSQ administration.It is believed that the therapeutic effects of JGSQ on aging mice are related to the upregulation of telomerase expression in some tissues [85].Moreover,JGSQ can restrain apoptosis of renal tissue cells by inhibiting the expression of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6,promoting the expression of Bcl-2,and increasing the levels of testosterone and testicular SOD in the serum of rats,indicating that it has good antioxidant properties[86].
Classic ancient prescription of Erzhi pill.Zhang et al.[87] treated aged rats induced with D-galactose with Erzhi pill (EZ) and demonstrated that the activity of serum peroxides and the content of lipid peroxides were significantly higher in the EZ-treated rats than in the control rats,suggesting that EZ improves the antioxidant capacity and delays the aging processes.Furthermore,Yao et al.[88] found that EZ could significantly increase the proliferation of spleen lymphocytes; the phagocytosis of abdominal macrophages;and the levels of IL-1,IL-2,and IL-12 in the serum after EZ administration,indicating that EZ has immunomodulatory properties related to enhanced mRNA expression of T-lymphocyte factor.Zhao et al.used EZ-containing serum to culture the liver cancer cell line BEL-7402 and the lung cancer cell line A549 and found that the inhibition rates of the two cancer cell lines were significantly higher than that of the serum culture,suggesting that EZ has inhibitory effects on tumor growth [89].In addition,it has also been reported that EZ has many pharmacological properties such as reducing blood lipid levels [90],improving iron deficiency anemia [91],and preventing osteoporosis[92].
Classic ancient prescription of Sijunzi decoction.The antiaging mechanism of SJZ was studied in D-galactose-induced aging rats,and the results showed that Sijunzi decoction (SJZ) could increase glutathione peroxidase levels and MDA content in the tissues (e.g.,the brain and liver tissues) and serum of aging rats,thus enhancing the antioxidative properties of SJZ and delaying the aging process[93].Pang [94] also studied the antiaging mechanisms of SJZ and found that SJZ could improve functioning of the mitochondrial respiratory chain enzyme complex,reduce damage to mtDNA,and increase the synthesis of ATP in brain mitochondria in aged rats.These results suggest that SJZ exhibits antiaging properties by protecting mtDNA.In addition,Yang[95]studied the effects of SJZ on telomerase activity in the heart,brain,and liver of aging mice.The results showed that SJZ could increase the telomerase activity in the thymus of D-galactose-induced aging mice and that this effect was related to the activation of T lymphocytes in the thymus.Moreover,Liu et al.[96]studied the effects of SJZ on intestinal dysbacteriosis in aging mice and found that intestinalEnterobacter,Enterococcus,Bifidobacterium,andLactobacillusreturned to normal levels and the lifespan of the aging mice prolonged after administration of SJZ.In addition,SJZ could inhibit the mammalian target of the rapamycin signaling pathway and decrease the expression of p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase by reducing the activation of phosphoinosmde-3-kinase to reduce the damage caused by oxidative stress,thus delaying aging[97].
Clinical study of antiaging prescriptions LWDH.Qing et al.investigated the effects of LWDH on Alzheimer's disease; 50 patients in the treatment group were administered LWDH and 52 in the control group were administered piracetam tablets (a medicine for Alzheimer's disease),and the experiment lasted for 6 months.The results of this clinical study showed that LWDH had better effects in terms of improving intelligence,living ability,and memory of patients with Alzheimer's disease than the piracetam tablets[98].In another study,Zhong et al.studied the effects of LWDH on Parkinson's disease in 53 patients who were treated with both a conventional Parkinson's disease drug and LWDH(treatment group) and 36 patients who were treated with the conventional Parkinson's disease drug alone(control group).The duration of administration was 6 months,and the results demonstrated that the total clinical efficacy rates of the treatment and control groups were 81% and 61.5%,respectively,suggesting that LWDH had better effects in improving Parkinson's disease than the conventional drug [99].In addition,Zhang et al.studied LWDH for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.In the clinical experiment,150 patients were treated with LWDH(6 pills a day) for 6 months.The results showed that fasting blood glucose,postprandial blood glucose,and glycosylated hemoglobin levels decreased,whereas C-peptide levels increased after LWDH administration.In addition,there were no adverse reactions such as heart,liver,or kidney function damage after taking the medicine[100].
JGSQ.The clinical effects of JGSQ were studied in 76 patients with Alzheimer's disease who were randomly divided into a treatment group and a control group,with 38 patients in each group.This study was conducted to evaluate the clinical effects of JGSQ on Alzheimer's disease.To this end,the treatment group was administered JGSQ,and the control group was administered piracetam tablets.Activities of daily living and functionality questionnaire scores were determined 3 months after treatment.The experimental results showed that the total clinical efficacy rate was 82.05% in the treatment group and 39.74% in the control group,indicating that JGSQ exhibits good effects in terms of improving Alzheimer's disease [101].Cao treated 24 elderly patients with secondary fungal infection with JGSQ and fluconazole.The results showed that all the patients were cured except 1 patient with lung cancer who died of multiple organ failure,suggesting that JGSQ not only treats several basic diseases found in elderly patients but also prevents the side effects of fluconazole [102].Zhao studied 30 elderly patients with hypertension who were to be treated with JGSQ.Among them,12 developed hyperlipidemia,6 developed coronary heart disease,and 2 developed diabetes.The treatment results showed that the systolic blood pressure of some patients decreased to normal,and the blood lipid levels also improved significantly after treatment[103].
SJZ.Yang et al.used SJZ to treat 62 elderly patients with functional constipation and studied the clinical effects of SJZ; these patients were randomly divided into a treatment group (31 patients) and a control group (31 patients).The treatment group was administered SJZ,whereas the control group was administered phenolphthalein tablets (a medicine for treating functional constipation).The results of this study showed that the total clinical efficacy rates in the treatment and control groups were 87.09% and 54.83%,respectively.The efficacy of SJZ combined with saxagliptin (a medicine for regulating blood glucose) in treating elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus was also studied,and this combination was found to be effective in reducing blood glucose levels and improving insulin-related indicators.Besides,this treatment also regulated nesfatin-1 and sex hormone-binding globulin levels,thus effectively improving insulin resistance and reducing the risk of diabetic complications[104].
Prospects and summary
Effective methods to delay aging have been extensively studied with promising results.Indeed,with development in modern medicine and molecular biology,great achievements have been made in the study of aging mechanisms.However,a complete understanding of aging mechanisms has not been achieved because aging is a complex biological process caused by multiple factors.Accordingly,because of the complexity and uncertainty surrounding the aging process,aging cannot be explained by a single mechanism but must be explored in many aspects and at deeper levels.Based on the common point of aging,it is considered that there must be some internal connection in the research of aging mechanisms.Further research on this connection should help to expand our understanding of aging mechanisms.In view of the importance of interdisciplinary research,the combination of antiaging research with cell biology,molecular biology,genomics,metabonomics,and other disciplines should broaden the research findings related to the study of aging mechanisms in the future.
Care movements are widely used in antiaging strategies because they are natural,simple,and not limited by any equipment or site.Although care movements have unique advantages in antiaging strategies,they may also have negative impacts if they are not suitable for a particular patient.Therefore,it is considered that the best results related to the antiaging properties of care movements are achieved by choosing the appropriate care movement method for individual patients.This requires individuals to comprehensively improve the efficiency and quality of healthcare and promote the development of their physical and mental health according to their physical conditions and doctors'suggestions.Indeed,this strategy considers different perspectives,including those related to diet,health care,mental health,and sports and exercise.
With the development of modern research technologies associated with TCMs,more and more antiaging TCMs are being discovered.Indeed,the research and development of new antiaging drugs based on TCMs are expected to usher in a new chapter.However,there are some shortcomings in TCM-related antiaging research.First,most of the studies on the antiaging mechanisms of TCMs have focused on antioxidation and immune regulation.Therefore,studies must explore additional antiaging mechanisms in the future.In addition,combining strategies from the perspective of various antiaging mechanisms along with the concept of integrity and systematization should contribute to the research and development of health foods and antiaging drugs.Second,only a small part of the active antiaging ingredients of TCMs have been identified at present,with many active antiaging ingredients still requiring additional pharmacological studies.Third,further studies on the pharmacokinetics of TCMs will help in promoting the internationalization and recognition of TCMs.However,for a large number of TCMs,particularly those related to compound prescriptions,the ingredients are quite complex,thus affecting the feasibility of in-depth analyses and pharmacodynamic evaluations.Therefore,it is necessary to explore additional scientific research methods of pharmacology involving the combination of TCM theory and modern science and technology.
In the body,aging and regeneration occur simultaneously,and the process of aging occurs when the ability of regeneration cannot match that of aging.If the cells are immortalized,the process of tissue aging would be expected to be delayed or even blocked.Autologous stem cells are a class of multipotent cells with self-renewal and self-replication abilities.Under certain conditions,these cells can differentiate into a variety of adult pluripotent stem cells.Pluripotent cells supplement and regulate diseased cells,activate the functions of aging cells,increase the number of normal cells,improve the quality of cells,prevent and delay the lesion of cells,and restore the normal physiological functions of cells.At present,autologous stem cells have provided good results in the treatment of some diseases such as myeloma [105],heart disease [106],and thyroid dysfunction[107].In addition,these cells have advantages of safety and reliability,with minimal immune rejection,thus presenting a promising strategy for future antiaging research.
Conclusion
In this study,the progress in research on antiaging strategies from east to west were reviewed,with particular focus on the antiaging properties of various TCMs.Western medicine has made great achievements in research on aging mechanisms,and TCM has played an important role in the study of antiaging methods.With recent advancements in molecular biology techniques,an increasing number of studies on antiaging TCMs are being conducted using modern technology,which provides an opportunity for the in-depth study of antiaging.However,despite these advances,limitations such as unclear and unidentified active compounds and single mechanism research on antiaging TCMs require investigators across disciplines to work together.In recent years,methods aimed at delaying aging using autologous stem cell transplantation have been reported,which may represent a new direction in antiaging research.
 Traditional Medicine Research2020年5期
Traditional Medicine Research2020年5期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Inner peace makes you live longer
- The effects of nutritional ketosis induced by Bigu-herbs regimen and ketogenic diet on diseases and aging
- From religious manual to herbal pharmacopoeia:a textual study of the formation and transformation of Shennong’s Classic of Materia Medica
- South Asian medicinal plants and chronic kidney disease
- Molecular mechanism prediction analysis of compound Kushen injection in the treatment of COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- Ethnoveterinary medicines used against various livestock disorders in the flora of Shamozai Valley,Swat,KP Pakistan
