基于自对偶量子低密度校验码的量子对话协议
刘芬,贺振兴,徐鹏翱,马鸿洋
基于自对偶量子低密度校验码的量子对话协议
刘芬1,贺振兴2,徐鹏翱1,马鸿洋2
(1. 青岛理工大学信息与控制工程学院,山东 青岛 266033;2. 青岛理工大学理学院,山东 青岛 266033)
在量子信道中,粒子在传输过程中通常会受到噪声的影响,提出基于自对偶量子低密度校验码的量子对话协议来抵抗噪声攻击,使用B构造法和U构造法相结合的方法来构造自对偶量子低密度奇偶校验矩阵。所提量子对话协议能够抵抗常见的外部攻击,且不存在信息泄露,提高了编码和译码的效率。从纠错的角度研究所提量子对话协议的安全性,安全分析表明,该协议具有足够的安全性,能够有效抵御常见的恶意攻击。
量子低密度码;量子对话;自对偶
1 引言
量子密钥分发(QKD,quantum key distribution)利用量子物理定律保证了信息传输的安全性,在理论上已被证明是无条件安全的。QKD允许两个远程用户通过量子信道和公共经典信道生成共享密钥。第一种无条件安全QKD协议由Bennett和Brassard[1]于1984年提出(简称BB84协议)。随后,两种量子直接通信协议被提出,即确定性安全量子通信(DSQC,deterministic secure quantum communication)协议[2-4]和量子安全直接通信(QSDC,quantum secure direct communication)协议[5-10]。这两种量子通信协议可以在不创建共享密钥的情况下实现信息的直接传输,提高了系统的实时性。对于DSQC协议,信息可以直接从发送方传输到接收方,而不需要预先生成共享密钥,接收方只能在传输额外的经典信息后提取信息。然而,QSDC协议可以实现信息的直接传输,而不需要交换经典信息。近年来,QSDC在理论研究和实验实施方面取得了巨大进展。然而,DSQC和QSDC协议只是单向通信协议,两个用户无法实现信息的相互传输。换句话说,在这两种协议中,信息只朝一个方向流动。在实际的传输环境中,两个用户常常需要同时向对方传输信息,如电话通信。因此,有必要研究同时进行的双向量子通信。
量子对话(QD)是一种双向量子通信。QD协议允许两个用户同时向对方传输信息。2004年,Nguyen[11]首先提出了量子对话协议,这是量子通信领域发展的一个里程碑。随后,Gao等[12]指出Nguyen的对话协议存在信息泄露的问题。针对信息泄露问题,许多QD协议[13-17]被提出。
大多数QD协议是在理想的环境下提出的,即假设量子信道中没有噪声。在传输过程中,光子的偏振受到通道噪声的影响。由于量子信道中的噪声是不可避免的,因此如何使量子密码协议在噪声信道下正常工作显得尤为重要。近年来,针对所有问题,许多量子对话协议[18-23]陆续被提出。本文采用量子纠错码提出了基于自对偶量子低密度奇偶校验纠错的量子对话协议。本协议可以提供更高的通信保真度,在一定程度上提高了信息传输的安全性。安全分析表明,所提方法是可行的,并且可以抵抗常见的外部攻击而不存在信息泄露。
2 本文协议
本文所提协议依赖于自对偶量子低密度校验码,量子信息的传输过程依赖于量子信道,而误码率的计算依赖于经典信道。
2.1 构建自对偶量子低密度奇偶校验码
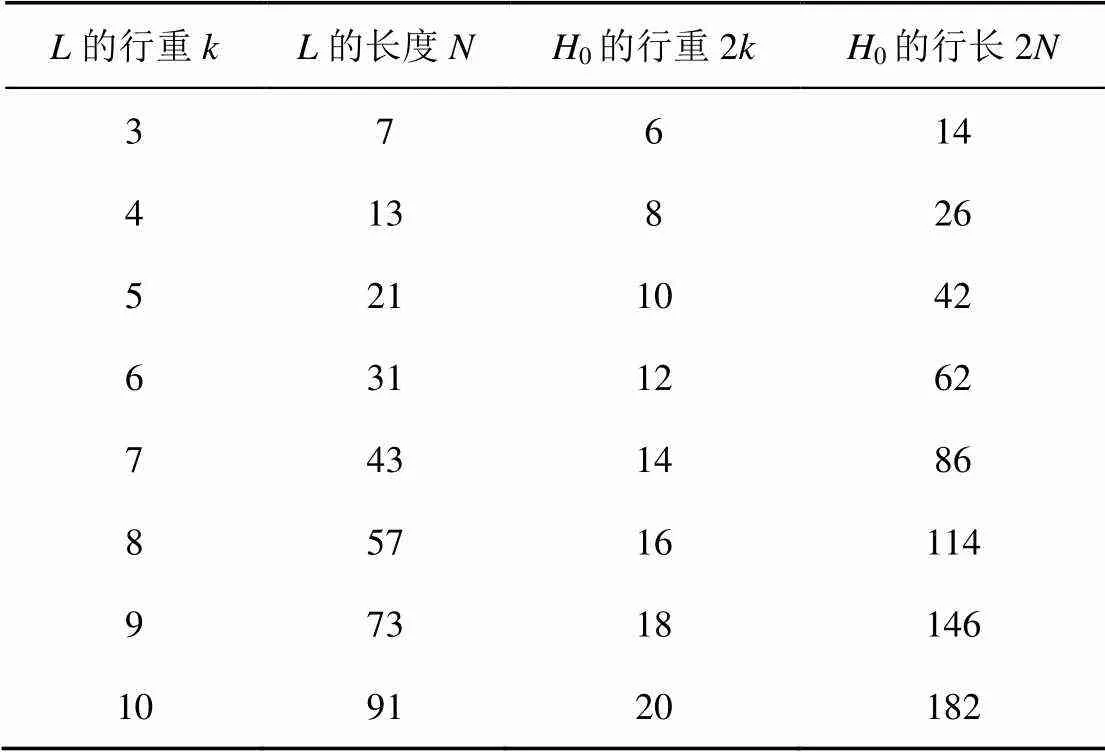
表1 循环稀疏序列L的不同行重下对应H0的2N、2k取值
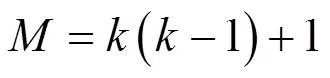
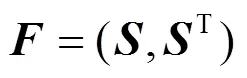
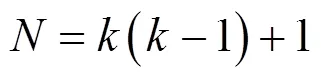
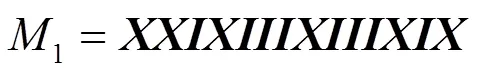
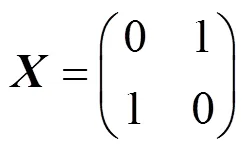
2.2 数据传输阶段
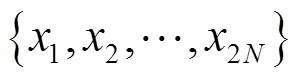
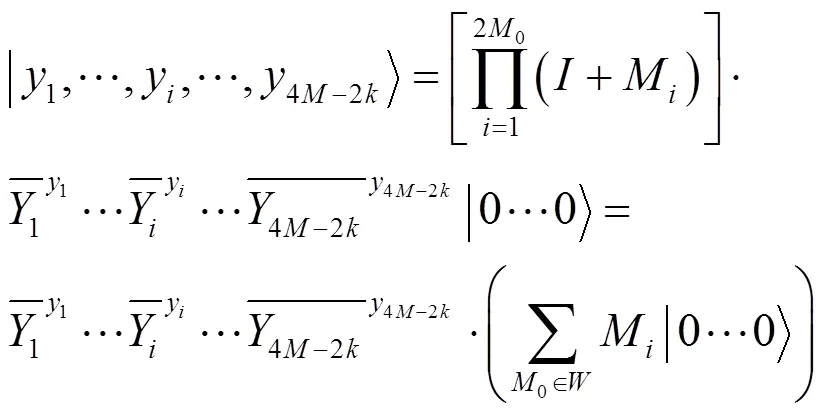
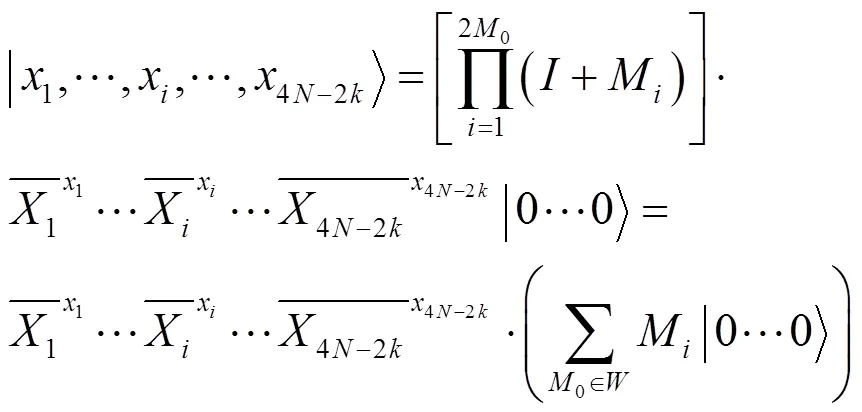
8) 量子对话完成。
3 安全性分析
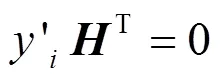
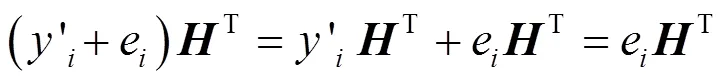
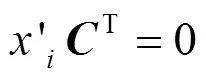
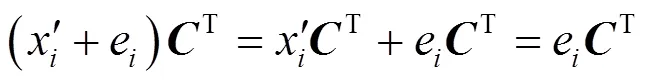
4 结束语
本文提出基于自对偶量子低密度校验码的量子对话协议,用自对偶量子低密度校验码对通信双方的信息进行编码,并相互传输,以便实现量子比特的正确传输。安全分析表明,该协议具有足够的安全性,能够有效抵御常见的恶意攻击。本文从纠错的角度研究所提量子对话协议的安全性。
[1] BENNETT C H. Quantum cryptography : public key distribution and coin tossing[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing. 1984: 175-179.
[2] CAI Q Y , LI B W. Deterministic secure communication without using entanglement[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2004, 21(4): 601-603.
[3] LI X H, DENG F G, LI C Y, et al. Quantum secure direct communication without maximally entangled states[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2006, (49): 1354-1359.
[4] BOSTRÖM K, FELBINGER T. Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 89(18): 187902.
[5] LONG G L, LIU X S. Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme[J]. Physical Review A, 2002, 65(3): 032302.
[6] DENG F G, LONG G L. Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad[J]. Physical Review A, 2004, 69(5): 052319.
[7] GUERRA A G D A H, RIOS F F S, RAMOS R V. Quantum secure direct communication of digital and analog signals using continuum coherent states[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2016, 15(11): 4747-4758.
[8] WANG C, DENG F G , LI Y S , et al. Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding[J]. Physical Review A, 2005, 71(4): 044305.
[9] ZHU F, ZHANG W, SHENG Y B, et al. Experimental long-distance quantum secure direct communication[J]. Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(22): 1519-1524.
[10] WU F Z, YANG G J, WANG H B, et al. High-capacity quantum secure direct communication with two-photon six-qubit hyperentangled states[J]. Science China(Physics,Mechanics & Astronomy), 2017, 60(12): 24-30.
[11] NGUYEN B A. Quantum dialogue[J]. Physics Letters A, 2004, 328(1): 6-10.
[12] GAO F, GUO F Z, WEN Q Y, et al. Revisiting the security of quantum dialogue and bidirectional quantum secure direct communication[J]. Science in China, 2008(5): 111-118.
[13] SUN Y, WEN Q Y, GAO F, et al. Improving the security of secure quantum telephone against an attack with fake particles and local operations[J]. Optics Communications, 2009, 282(11): 2278-2280.
[14] WANG H, ZHANG Y Q, LIU X F, et al. Efficient quantum dialogue using entangled states and entanglement swapping without information leakage[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2016, 15(6): 2593-2603.
[15] GAO G. Two quantum dialogue protocols without information leakage[J]. Optics Communications, 2010, 283(10): 2288-2293.
[16] YE T Y. Quantum dialogue without information leakage using a single quantum entangled state[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2014, 53(11): 3719-3727.
[17] ZHENG C, LONG G F. Quantum secure direct dialogue using Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pairs[J]. Science China Physics Mechanics & Astronomy, 2014, 57(7): 1238-1243.
[18] QI J M, XU G, CHEN X B, et al. Two authenticated quantum dialogue protocols based on three-particle entangled states[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2018, 17(9): 247.
[19] ZHANG L, DONG S, ZHANG K J, et al. A controller-independent quantum dialogue protocol with four-particle states[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2019, 58(6): 1927-1936.
[20] LIU Z H, CHEN H W. Security loopholes in the controlled quantum dialogue robust against conspiring users protocol[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2019, 18(7): 228
[21] ZHANG M H, CAO Z W, PENG J Y, et al. Fault tolerant quantum dialogue protocol over a collective noise channel[J]. The European Physical Journal D, 2019, 73(3): 57.
[22] YANG Y, GAO S, ZHOU Y, et al. New secure quantum dialogue protocols over collective noisy channels[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2019, 58(9): 2810-2822.
[23] 齐佳敏. 基于纠缠态和身份认证的量子对话协议的设计与研究[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2019.
QI J M. Design and research of quantum dialogue protocol based on entangled state and identity authentication[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019.
Quantum dialogue protocol based on self-dual quantum low density parity check codes
LIU Fen1, HE Zhenxing2, XU Pengao1, MA Hongyang2
1. School of Information and Control Engineering, Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao 266033, China 2. School of Sciences, Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao 266033, China
In quantum channels, particles are usually affected by noise during transmission. A quantum dialogue protocol based on self-dual quantum low density parity check codes was proposed to resist noise attacks. A combination of B construction method and U construction method was used to construct a self-dual quantum low density parity check matrix. The proposed quantum dialogue protocol can resist common external attacks, and there was no information leakage, which improved the efficiency of encoding and decoding. The security of quantum dialogue protocol was studied from the perspective of error correction. Security analysis shows that the protocol has sufficient security and can effectively resist common malicious attacks.
quantum low-density parity code, quantum dialogue, self-dual
s: TheNational Natural Science Foundation of China(61772295, 11975132), The University Scientific Research Project of Shandong Province, China (J18KZ012), The Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province , China (ZR2019YQ01)
TN918
A
10.11959/j.issn.2096−109x.2020051

刘芬(1996-),女,山东潍坊人,青岛理工大学硕士生,主要研究方向为量子通信。
贺振兴(1995-),男,山东淄博人,青岛理工大学硕士生,主要研究方向为应用数学。

徐鹏翱(1995-),男,山东菏泽人,青岛理工学硕士生,主要研究方向为量子通信。
马鸿洋(1976-),男,山东即墨人,博士,青岛理工大学教授,主要研究方向为网络空间安全、量子信息、量子保密通信。
论文引用格式:刘芬, 贺振兴, 徐鹏翱, 等. 基于自对偶量子低密度校验码的量子对话协议[J]. 网络与信息安全学报, 2020, 6(4): 148-152.
LIU F, HE Z X, XU P A, et al. Quantum dialogue protocol based on self-dual quantum low density parity check codes[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2020, 6(4): 148-152.
2019-09-18;
2019-10-15
马鸿洋,hongyang_ma@aliyun.com
国家自然科学基金(61772295,11975132);山东省高等学校科技计划项目(J18KZ012);山东省自然科学基金(ZR2019YQ01)

