Characteristic changes of intestinal flora and its correlation with clinical indexes in patients with Behcet's disease based on TCM syndromes
Yong-Zhu Piao, Dan-Nan Sun, Yin Shao, Yan Zhang, Xing-Xing Yuan
1. The First Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of traditional Chinese medicine, Heilongjiang, Harbin, 150040
2. The Second Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of traditional Chinese medicine, Harbin, Heilongjiang, 150001
3. Heilongjiang University of traditional Chinese medicine, Heilongjiang, Harbin, 150040
4. Nangang Branch of Heilongjiang Academy of traditional Chinese medicine, Harbin, Heilongjiang, 1500006
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
Behcet's disease (BD) is a chronic systemic vasculitis disease with unknown causes. Its clinical manifestations are mainly recurrent oral ulcer, vulvar ulcer, uveitis and skin damage. Meanwhile, it can also be accompanied by multiple organ damage such as nerves, blood vessels, joints and gastrointestinal tract [1]. As an immune system disease, the pathological mechanism of BD has not been clear in the medical field at present. Most studies believe that the pathogenesis of BD is closely related to genetic, immune and environmental factors [2]. Under the influence of many factors, it will lead to the change of immune state, and eventually lead to neutrophil infiltration and intravascular thrombosis [3].
BD belongs to the category of "Fox confusion disease" in traditional Chinese medicine, which has been recorded as early as "synopsis of the Golden Chamber · Baihe disease, fox confusion, yin and Yang toxin, pulse syndrome and treatment of the third". The pathogenesis of this disease is mainly damp heat and heat toxin. The damp heat internal disturbance and heat toxin fumigation lead to external carbuncle and sores, so the throat and the two Yin ulcers before and after are common in clinic [4]. In the early stage of BD, the syndrome of Qi, blood, Yin, Yang deficiency and blood stasis can also be seen in the middle and late stage [5]. In recent years, studies have found that there is a close relationship between intestinal flora and immune system diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease [6-8]. Therefore, the research group intends to analyze the characteristic changes of BD intestinal flora by 16S rRNA technology in order to further clarify the pathological mechanism of BD, and provide theoretical basis for TCM syndrome classification of BD.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Clinical data
From March 2019 to October 2019, 49 BD patients were collected from the outpatient department of Rheumatology and immunology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Heilongjiang University of traditional Chinese medicine. At the same time, 43 healthy subjects were selected as the blank control. 49 patients were divided into shire group (n = 19) and non-shire group (n = 30). See Table 1 for basic information of BD patients in two groups
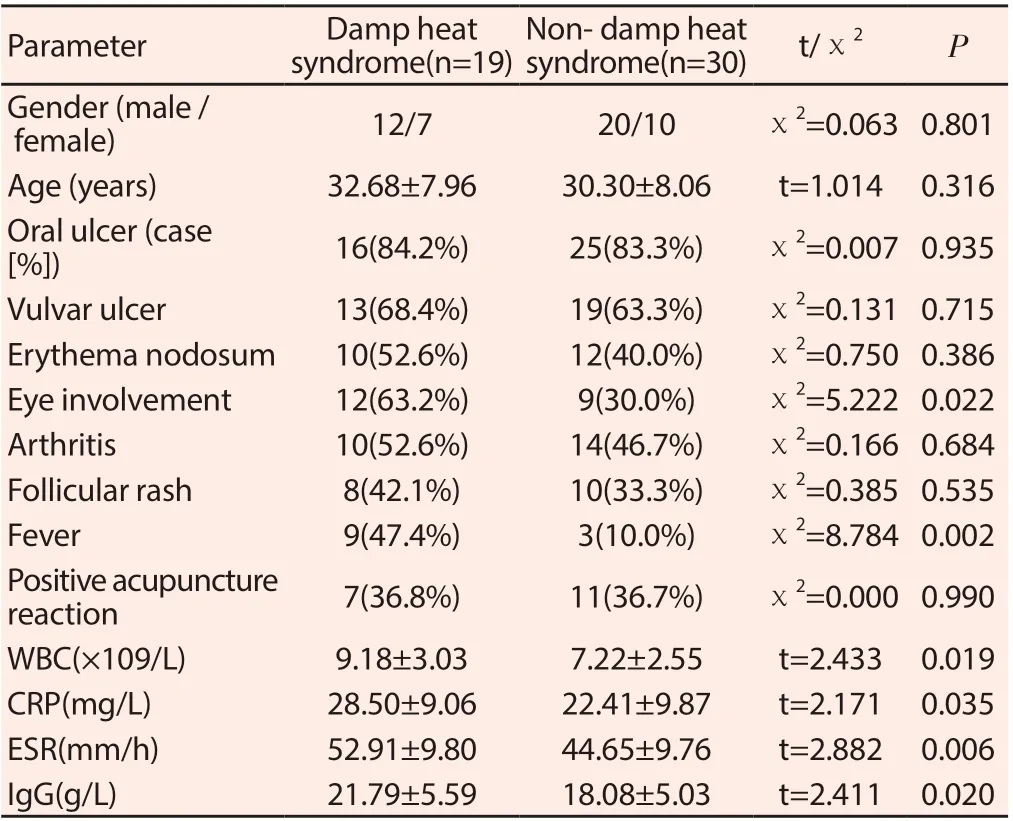
Table 1. Basic clinical information of BD patients in two groups
2.2 BD diagnostic criteria
2.2.1 Diagnosis of Western Medicine
The diagnosis standard of Western medicine refers to the relevant standards in the guide to diagnosis and treatment of Behcet's disease [9]: main symptoms: ① recurrent aphthous ulcer in the mouth; ② recurrent vulvar ulcer; ③ eye involvement, including retinal uveitis or iridocyclitis; ④ skin damage, including subcutaneous thrombophlebitis, follicular rash, nodular erythema or positive acupuncture reaction. Secondary symptoms: ① vascular disease; ② no ankylosing or deformable arthritis; ③ central nervous system disease; ④ digestive tract symptoms characterized by ileocecal ulcer. BD can be diagnosed by the clinical appearance of typical oral ulcer and any one of ② ~ ④. In addition, if there are four main symptoms in the course of the disease, it is diagnosed as complete type.
2.2.2 Diagnostic criteria of traditional Chinese Medicine
According to the relevant standards [10] in the standard for the diagnosis and curative effect of diseases and syndromes of traditional Chinese medicine, BD patients are divided into five syndrome types: "accumulation of heat and toxin", "excess of dampness and heat", "deficiency of Qi and dampness", "deficiency of yin and stagnation of heat" and "deficiency of spleen and kidney yang".
2.3 Inclusion criteria
① Combined with western medicine diagnosis standard of BD; combined with traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis standard of BD, the syndrome of "accumulation of heat and toxin" and "dampness and heat dampness" are classified as damp heat syndrome, and the syndrome of "deficiency of Qi and dampness", "deficiency of yin and heat" and "deficiency of spleen and kidney yang" are classified as non damp heat syndrome; ③ healthy subjects aged 20-50 years old, smokeless, alcohol addicted, red tongue, white fur and normal pulse.
2.4 Exclusion criteria
① The patients had heart, brain, nervous system and immune system diseases; ② mental system diseases; ③ pregnant women and lactating women; ④ had a recent history of taking antibiotics or microbial regulators.
2.5 Sample collection
The fecal samples of 92 patients and healthy subjects were collected by one-off fecal collection device and stored in - 80 ℃ refrigerator. After sample treatment, DNA was extracted with Qiagen fecal DNA extraction kit. The 16S rRNA amplicon was sequenced by using Illumina hiseq PE250 platform after DNA quality inspection, V4 PCR amplification and product purification. According to the obtained sequence, we classified out, and analyzed the relationship and difference between bacterial species.
2.6 Statistical analysis
SPSS 22.0 software was used for statistical analysis. The count data was represented by [n%], the comparison between groups was performed by χ2test, the measurement data was described by (±s), the comparison between groups was performed by one-way ANOVA, and the comparison between two groups was performed by LSD test. P < 0.05 showed that the difference was statistically signifciant.
3. Result
3.1 Comparison of basic clinical information between two groups of BD patients
It can be seen from table 1 that the incidence of eye involvement in damp heat syndrome BD is higher than that in non-damp heat syndrome, and the difference between the two groups is statistically significant (P < 0.05). At the same time, WBC, CRP, ESR and IgG in patients with damp heat syndrome BD were significantly higher than those in patients with non-damp heat syndrome (P < 0.05). It is suggested that BD in excess heat syndrome is more acute and more severe than that in non-damp heat group.
3.2 Analysis of species accumulation curve
It can be seen from Figure 1 that as the number of samples increases, so does the number of species obtain. When the sample quantity reaches 80, the curve tends to be stable, which indicates that the sample quantity in this study is sufficient for data analysis.
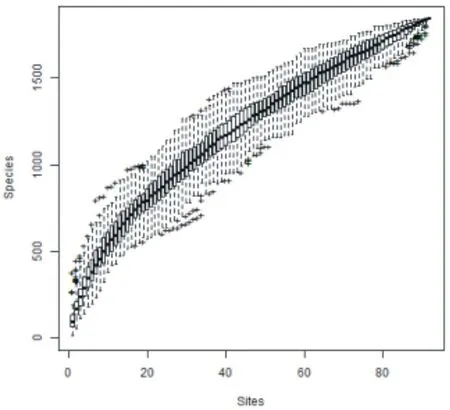
Figure 1. Species accumulation curve
3.3 Alpha diversity analysis
Alpha diversity analysis is to analyze species diversity in a single sample, including ACE, Chao1, Shannon and Simpson indexes. The larger ace, Chao1 and Shannon indexes are, the smaller Simpson index is, indicating the higher species richness in the sample. As can be seen from Figure 2, compared with the healthy group and the non humid heat group, the ace, Chao1 and Shannon indexes of the humid heat group were significantly lower, while the Simpson index was significantly higher, and the difference between the groups was statistically significant (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in ace, Chao 1, Shannon and Simpson indexes between the two groups (P > 0.05).
3.4 Beta diversity analysis
The closer the intestinal flora is, the closer it is in PCA. It can be seen from Figure 3 that, compared with the healthy group, the bacteria groups of BD damp heat syndrome and non damp heat syndrome are significantly different. Compared with the non damp heat syndrome, some of the bacteria groups of BD damp heat syndrome overlapped, but there were still some differences.
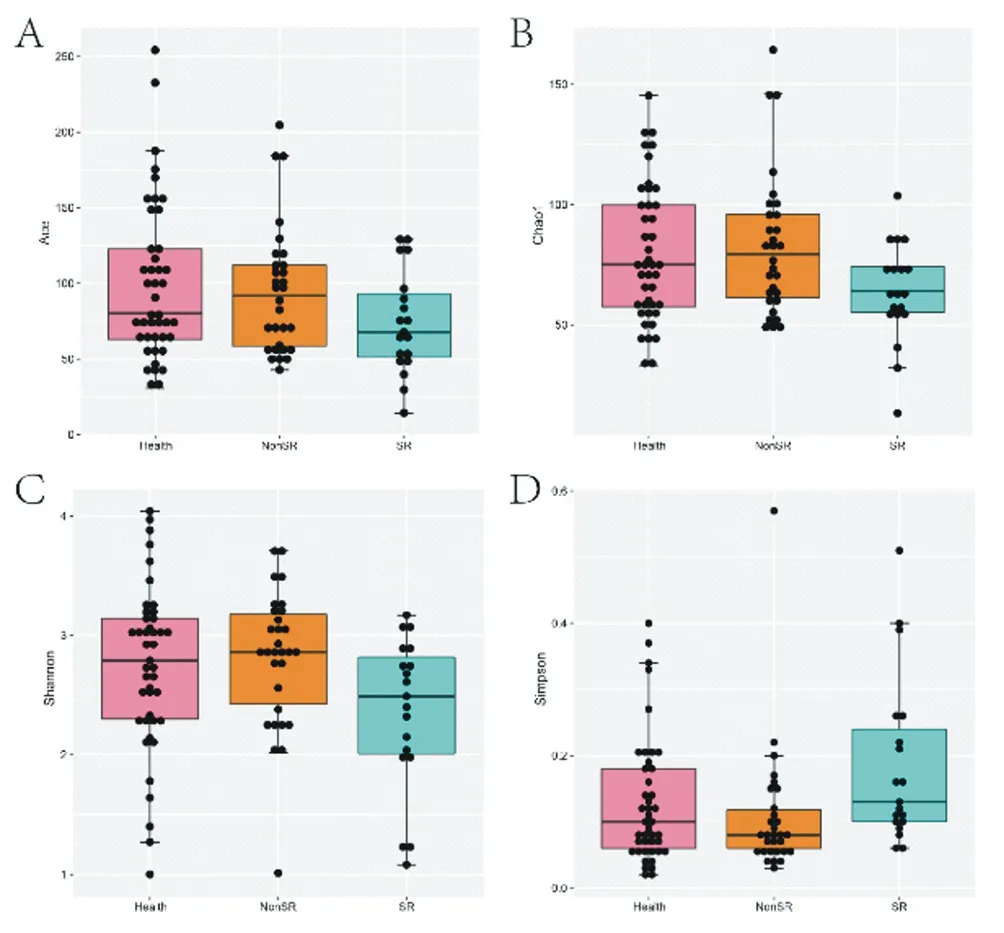
Figure 2. Comparison of alpha diversity among groups

Figure 3. Principal component analysis (PCA) of three groups of samples
3.5 Species distribution at the gate level of three groups of samples
The distribution of species at the sample gate level of each group is shown in the heat map, as shown in Fig.4. The 15 phylum detected by the behavior of the heat map are listed as various product names, and the low, medium and high levels of relative species abundance are respectively shown in blue, yellow and red colors. At the same time, t-test was used to test the differences of species distribution at the gate level of three groups of samples. The results showed that, compared with the healthy group, the abundance of Firmicutes gate increased, the abundance of actinobacteria gate and Bacteroides gate decreased (P < 0.05); the abundance of Firmicutes gate increased, the abundance of actinobacteria gate and Bacteroidetes gate decreased (P < 0.05) in the non humid heat group. Compared with the non humid heat group, the abundance of actinobacteria door in the humid heat group increased significantly (P < 0.05). See Figure 5.
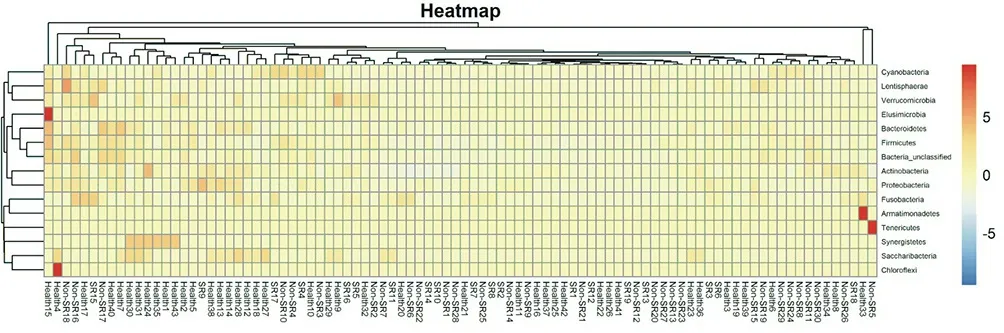
Figure 4. Heatmap of species distribution at three sample gate levels

Figure 5. Analysis of species distribution differences at the gate level of three groups of samples
3.6 Species distribution at genus level in three groups of samples
The species distribution at the genus level of the frist 90 samples in each group is shown by thermogram, as shown in Figure 4 The results of difference analysis showed that, compared with the healthy group, the level abundances of ruminocaccae , ucg014, ruminocacus, 1, ruminocaccae, ucg003, faecalibacterium, intellimonas, family , XIII, uc001, Microbacterium and cetobacterium were increased, and the level abundances of bacteroidea , unclassifeid, closerdiales , unclassifeid, Bacteroides ,unclassified, Bacteroides , unclassified, Bacteroides , unclassified, sac were increased The level abundance of characteria, eucharacterium, nodatum, ruminoccus, gauvreauii and non humid group decreased significantly (P < 0.05); lachnospiraceae, ruminocaccae, ucg014, ruminocaccae, ucg003, ruminocaccae, nk4a214, occillibacter, occillospira, family, family, uc001 The level abundance of collinsella, bacteroides'unclassified, saccharicteria'unclassified, eucharacterium, eucharacterium'nodatum'group, atopium and veillenellaceae'unclassified genera decreased with statistical significance (P < 0.05). Compared with the non humid heat group, the levels of collinsella, integinimonas and Enterobacteriaceae were increased, while the levels of clostridiales, ruminocaccae, ucg009, ruminocaccae, ucg007 and ruminocacus, gauvre auii group were decreased (P < 0.05).
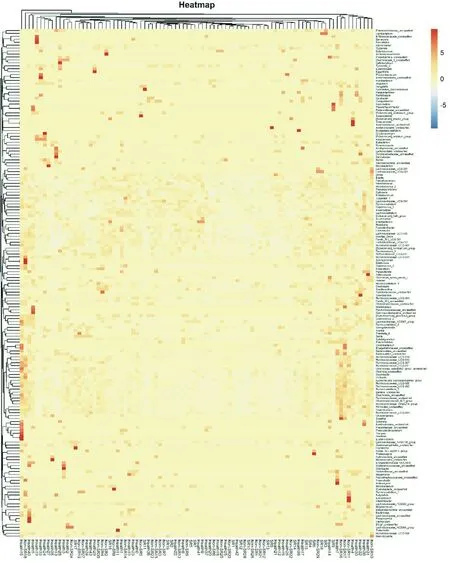
Figure 6. Heat map of species distribution at the level of three sample genera
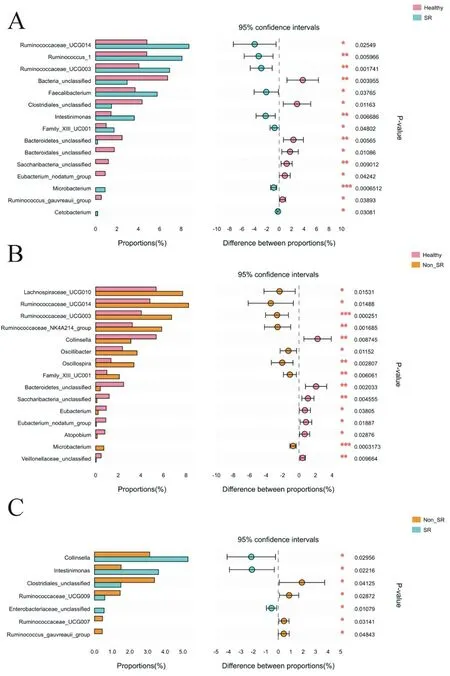
Figure 7. Analysis of species distribution differences at the genus level of three groups of samples
3.7 Correlation analysis
Pearson correlation analysis was carried out on 49 BD patients' laboratory tests and obtained differences. The results are shown in Figure 8. Osillospira abundance was positively correlated with WBC, CRP, ESR and IgG levels, while Eubacterium and cetobacterium abundance was negatively correlated with WBC, CRP, ESR and IgG levels.
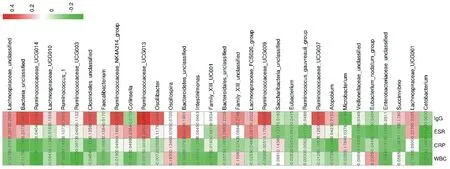
Figure 8. Correlation analysis of differential flora and clinical indicators
4. Discussion
According to the latest classification standard, BD has been classified as systemic vasculitis. The clinical manifestations of BD are highly heterogeneous, which can invade all sizes and types of blood vessels around the body. At present, there is no specific therapeutic drug for the complex pathological mechanism of BD. Considering that BD is characterized by alternation of recurrence and remission, the current treatment is to reduce clinical symptoms, delay progress, prevent complications and reduce recurrence [11]. However, whether alone or in combination, current clinical drugs still can not completely control BD inflammation or delay the progress [12]. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has the characteristics of syndrome differentiation, treatment and overall regulation, and has thousands of years of history in the treatment of BD. As early as in "synopsis of the Golden Chamber" of Zhang Zhongjing in the Han Dynasty, there were records about "liquorice and Xiexin Decoction", "Kushen Decoction" and realgar for internal, external or combined use in the treatment of BD, and it has been continued to this day and achieved good results. In the treatise on the origin of various diseases, Volume 8, under the diseases of typhoid fever, it is recorded that "the two diseases are the throat and the Yin It's all done by wet gas. " With the development of a large number of clinical practice and the continuous inheritance and innovation of BD etiology and pathogenesis, there are more in-depth views on this disease. According to Zhou Zhongying, a master of traditional Chinese medicine, the pathogenesis of BD is mainly due to the accumulation of damp and heat, which are intertwined and indissoluble, while the visible damp and evil are indissoluble, while the invisible heat is indissoluble [13]. Based on the long-term study of the research group and the characteristics of BD damp heat, we have achieved good clinical effect in the early study with Huangqin decoction, the third of heat clearing, dampness drying and blood cooling, which further confirmed the position of damp heat theory in the pathogenesis of BD [14].
There are a large number of symbiotic microorganisms in the human body, especially a complex microbial community composed of a variety of microorganisms in the human gut, which plays an extremely important role in maintaining the stability of the internal environment [15]. As the largest micro ecosystem and immune organ of human body, intestinal microorganisms include symbiotic bacteria, pathogenic bacteria and conditional pathogens, which encode more genes than human genome, also known as the "second genome" of human body. Some bacteria and their metabolites in the intestine can have a good protective effect on the body's immunity. However, some overgrown bacteria and their metabolites can reach the extraintestinal organs through the systemic circulation, thus affecting the normal immune response and generating the inflammatory response [16]. With the rapid development of 16S and metagenomic technology in recent years, we have a deeper understanding of this complex and huge community. Based on the understanding of intestinal flora, it is the key to understand the pathological mechanism of disease and its relationship with TCM syndrome types[17]. A study from Japan showed that there was a significant difference between the abundance of 11 bacteria in BD intestinal tract and that in healthy group, the abundance of megamonas and Prevotella decreased, and that of eggerthella and Bifidobacterium increased significantly [18]. Another study from the United States found that the diversity of BD oral flora was significantly lower than that of the healthy group, while the abundance of alloprevotella and Haemophilus parainfluenzae increased significantly [19].
In this study, the results of the research group found that the diversity of intestinal flora in the damp heat group was significantly lower than that in the healthy control group, while the diversity of intestinal flora in the non-damp heat group was not significantly different from that in the healthy control group. At the same time, the results of beta diversity showed that there were significant differences between BD intestinal flora and healthy control, while some samples of damp heat syndrome and non damp heat syndrome were overlapped, but there were still some differences. In terms of species distribution, BD patients showed an increase in Firmicutes gate abundance and a decrease in actinobacteria gate abundance, while in the damp heat group, the actinobacteria gate abundance increased compared with the non-damp heat group. At the genus level, the abundance of rubinoccaceae, rubinoccaceae, family, family and microbacteria in BD patients increased, while that of Bacteroidetes, unclassified and eucharacterium, nodatum and group decreased; compared with the non humid heat group, collinsella, integinimonas and The horizontal abundance of Enterobacteriaceae, luminococcaceae, luminococcaceae, luminococcaceae and luminococcus gauvreauii groups increased, but decreased. Considering that the clinical manifestation of BD is the alternation of recurrence and remission, it is considered that CRP and ESR are better serological indexes for the evaluation of BD [20]. Pearson correlation analysis showed that osillospira abundance was positively correlated with WBC, CRP, ESR and IgG levels, while eucharaterium and cetobacterium abundance was negatively correlated with WBC, CRP, ESR and IgG levels.
To sum up, this study shows that the change of intestinal flora is involved in the pathogenesis of BD. at the same time, there are differences in intestinal flora in different syndromes of BD patients, which leads to the pathogenesis change of different syndromes of BD. In addition, the specific bacteria in the intestine are closely related to the serum inflammation and immune indexes of BD.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年13期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年13期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Effects of lumbar sagittal balance remodeling on natural absorption after lumbar disc herniation
- Network pharmacology of threatened abortion treated by ShouTaiWan
- The analysis of acupoint selection rules for acupuncture treating functional constipation
- Meta analysis of clinical efficacy of combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of venous ulcer of lower extremities
- Effect of high flux hemodialysis on renal anemia and soluble transferrin receptor in hemodialysis patients
- The correlation between different ABO blood group gene loci and the pathogenesis and prognosis of acute myocardial infarction
