The correlation between different ABO blood group gene loci and the pathogenesis and prognosis of acute myocardial infarction
Xiao-Ying Song, Jin-Fang Cai, Hua-Fang Yan , Xiu-Ying Huang, Shu-Yun Wang
Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI)is characterized by sudden onset and rapid progression, so its morbidity and mortality are at a high level. Although there are various treatments methods applied in clinical practice, the prognosis of patients with AMI is still not optimistic [1-4]. In order to understand the progress of AMI and improve the prognosis, clinical scholars are also actively exploring the indicators related to AMI[5]. Birgit et al. [6]showed that ABO blood group genes may increase the risk of myocardial infarction in patients with family history of myocardial infarction. Kong xiangyun, et al. [7] also showed that patients with different ABO blood group gene polymorphisms have different degrees of coronary artery disease, which may be related to the risk of myocardial infarction. Some scholars proposed that ABO blood group gene may be related to the occurrence and prognosis of AMI [8]. However, few studies have conducted in-depth studies on the correlation between ABO blood group gene loci and AMI. Based on this, we investigated the effects of different ABO gene loci on the pathogenesis and prognosis of patients with AMI.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 General Information
100 patients diagnosed with AMI in our hospital from June 2018 to June 2019 were selected as the study subjects and defined as the myocardial infarction group. During the same period, clinical data were selected and matched with 100 samples with healthy physical examination results in our hospital and defined as the control group. The diagnosis of myocardial infarction group was based on China's 2015 guidelines for AMI[9]. Inclusion criteria: ① Diagnosis of AMI; ②first diagnosed patients; ③ received coronary angiography and coronary artery access surgery; ④ control group, no acute physical health as the disease, no coronary heart disease, stroke and other chronic diseases, X-ray examination and ECG results no obvious abnormalities. Exclusion criteria: ① Adverse events occurred in patients caused by surgery; ② primary or secondary thrombocytopenia; ③with severe liver and kidney diseases; ④disagree to join the researcher; ⑤ falling to obtain complete clinical data. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects. All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital and carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines.
2.2 Detection method of single nucleotide polymorphism of ABO blood group gene
Single nucleotide polymorphisms of peripheral blood ABO gene loci rs505922, rs579459, rs643434, rs651007, and rs8176743 were detected.5ml of peripheral venous blood was collected from aseptic anticoagulant vacuum blood collection vessel. DNA extraction kit (purchased from Amy Jet Scientific co., LTD.) was used to detect the blood samples. All operating steps are performed strictly in accordance with the product instruction manual. The DNA was stored in a refrigerator at -80 ° C. Assay Designer 3.1 software was selected to design relevant primers for different ABO blood group gene loci, as shown in Table 1. The typing and detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms of ABO blood group genes were completed by Beijing CapitalBio Co.,LTD.
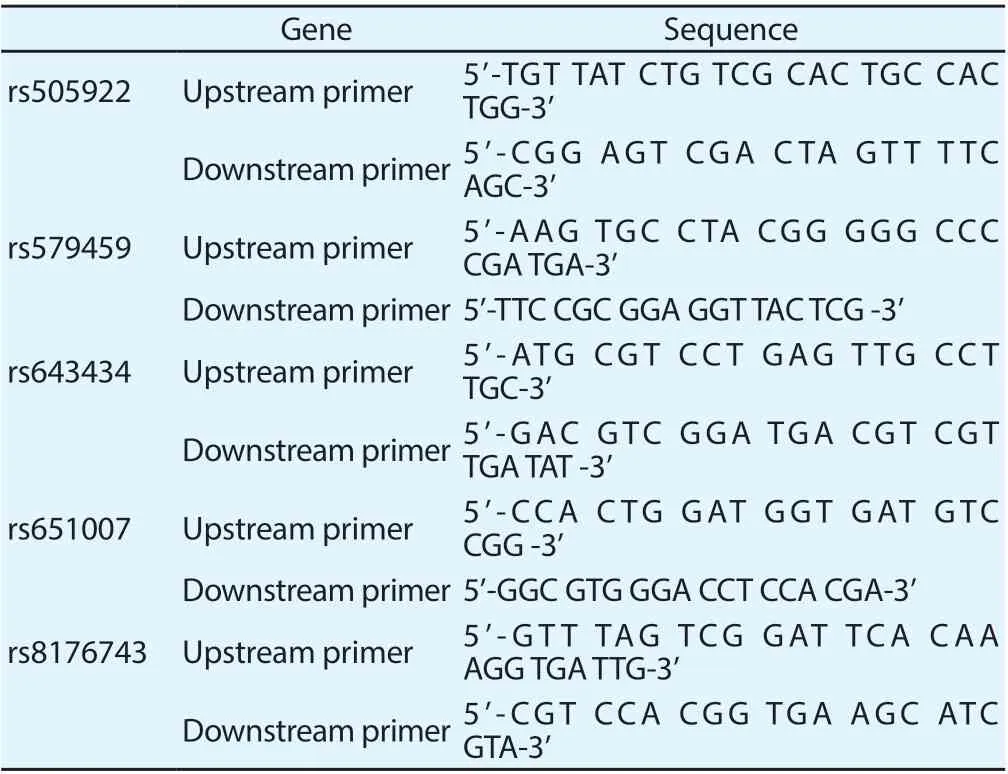
Table 1 Primer sequences of single nucleotide polymorphisms of ABO blood group genesww
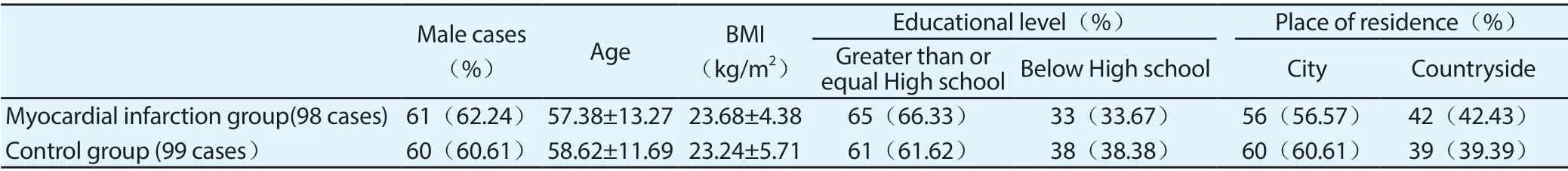
Table 2 Comparison of clinical data between two groups of patients
2.3 Observation indicators
General indicators include gender, age, Body Mass Index (BMI), blood pressure, heart rate, previous medical history and other personal clinical data. Outcome measures include the ABO blood group gene locus genotype frequency and the disease status of patients with AMI (Gensini score,TIMI grade, left ventricular ejection fraction, troponin) and major adverse cardiac events (MACE) were recorded after 6 months of follow-up, including acute heart failure, recurrent myocardial infarction, cardiogenic shock, malignant arrhythmia, and cardiogenic death.
2. 4 Statistical treatment
Statistical analysis was completed by SPSS 21.0 software. The SW method was used to check whether the measurement data obeyed the normal distribution. The measurement data obeyed the normal distribution were expressed as(±s ). The non-submission normal distribution was expressed by the median. The correlation between different ABO blood group locus and AMI was tested by t test. The χ2test was used to compare the correlation between different ABO blood group gene locus and MACE. The results were expressed as relative risk (OR value) and 95% confidence interval. A difference was considered signifciant when P<0.05.
3. Results
3.1 Baseline data of two groups
Because the family members of two patients in the myocardial infarction group refused to continue to join, so 98 cases were finally included in the study. In the control group, one case had AMI within 1 week of physical examination, therefore 99 cases were finally included in the study. There was no statistically significant difference in gender, age and BMI between the two groups (P > 0.05), as shown in Table 2 .
3.2 Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium test results of ABO blood group gene locus
In the rs505922 hardy-weinberg results of the control group, P < 0.05, was not representative of the population. In the results of rs579459, rs643434, rs651007 and rs8176743 hardy-weinberg, P > 0.05, and the gene distribution was representative of the population, as shown in table 3.
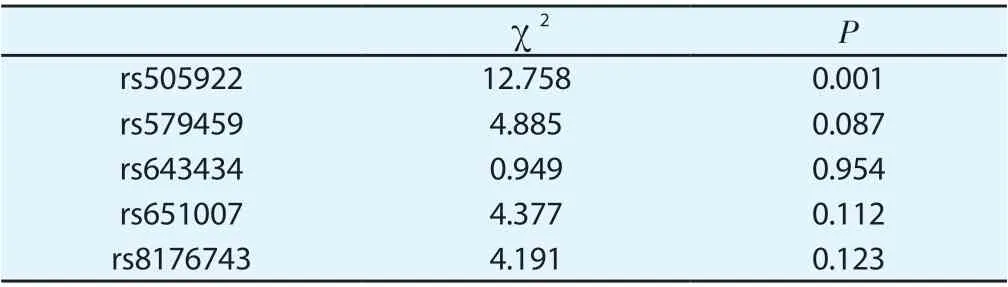
Table 3 Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium test results of ABO blood group gene locus in the control group
3.3 Comparison of genotype frequencies of ABO blood group loci in two groups
Compared with the control group, the genotypes of the rs643434 and rs651007 gene locus in the myocardial infarction group were statistically significant ( P < 0.05 ). There was no significant difference in genotypes between the myocardial infarction group and the control group at the rs579459 and rs8176743 gene loci ( P > 0.05 ) ,as shown in Table 4 .
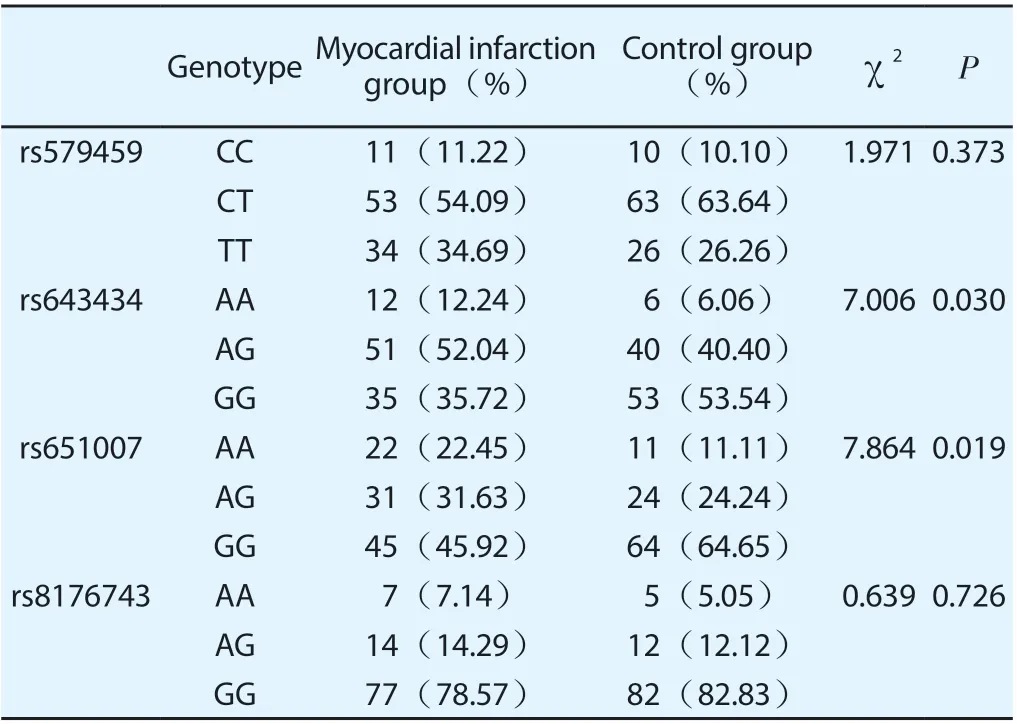
Table4 Comparison of genotype frequencies of ABO blood group loci in two groups
3.4 Comparison of ABO blood group genotypes in two groups under different genetic models
Analysis under different genetic modes showed that, compared with the control group, the myocardial infarction group had statistically significant differences in the dominant mode of rs643434 gene, the dominant mode and the recessive mode of rs651007 gene.(P < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference between the two groups under other gene models (P > 0.05), as shown in table 5.
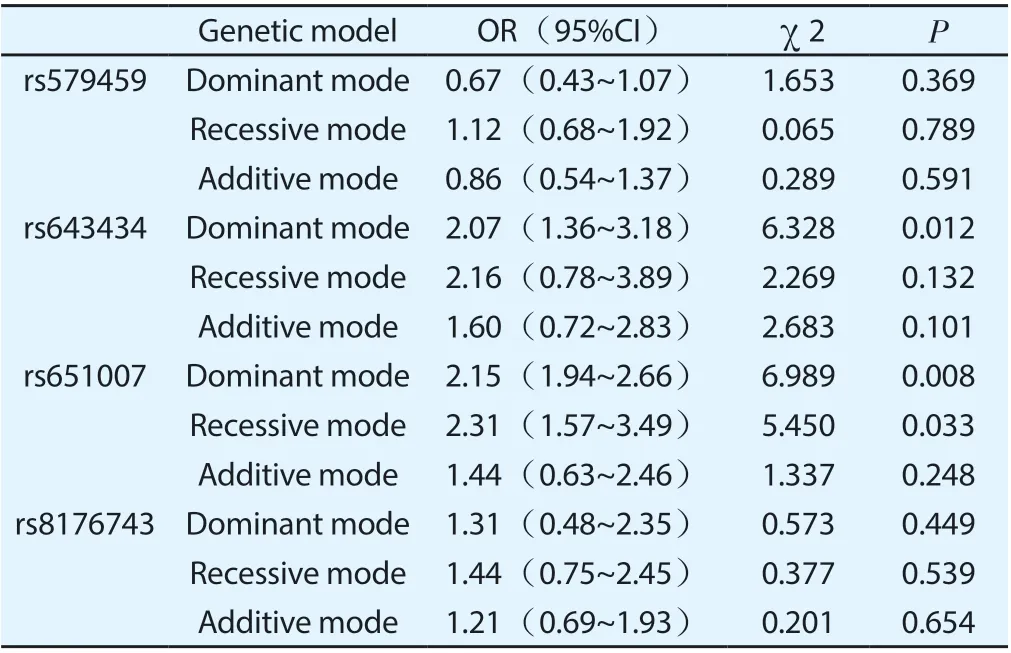
Table 5 Comparison of ABO blood group genotypes in two groups under different genetic models
3.5 Correlation between different ABO blood group gene locus and condition of AMI
Based on the correlation between the genotypes of different ABO blood group locus and the disease status in patients with myocardial infarction, the results showed that rs643434 in the dominant mode was correlated with Gensini score and TIMI grade. rs651007 in the dominant mode was correlated with Gensini score、 TIMI grade and troponin. And rs651007 in the recessive mode was correlated with Gensini score, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Rs643434 and rs651007 were not correlated with the disease index in other modes, and the differences were not statistically significant (P > 0.05),as shown in Table 6.
3.6 Correlation between ABO blood group gene locus and MACE
The relationship between ABO blood group gene locus and MACE in the myocardial infarction group was studied, the results indicatedthat the dominant mode of rs643434 was related to the occurrence of MACE, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference between other genetic models of rs643434 and rs651007 (P > 0.05), as shown in table 7.
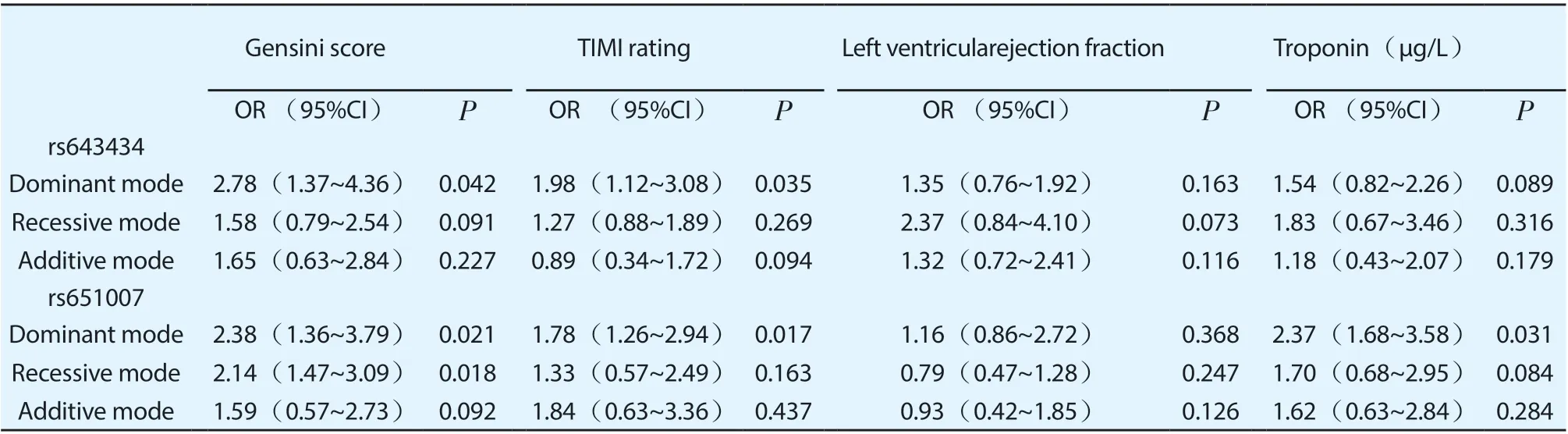
Table 6 Correlation between different ABO blood group gene loci and condition of AMI
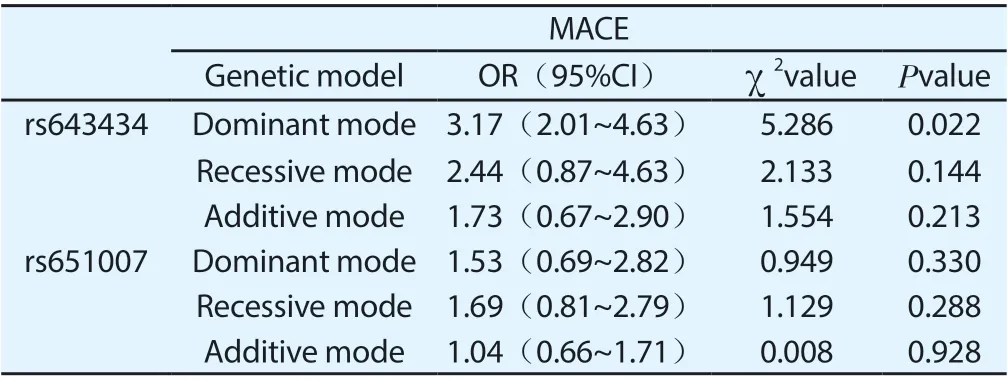
Table 7 Correlation between ABO blood group gene locus and MACE in myocardial infarction group
4. Discussion
AMI is one of the more serious clinical disease. Currently, most scholars believe that early and effective prevention, diagnosis and evaluation can be beneficial to the prognosis of patients [10-11] . ABO blood group gene has the function of regulating the expression of ABO blood group surface antigen. Some studies [12-14] suggest that ABO blood group gene is related to atherosclerosis and the incidence of stroke patients. We speculated that ABO blood group genes are associated with AMI and and further study has been carried out.
In this study, we detected the genotypes of ABO blood group genes at rs505922, rs579459, rs643434, rs651007 and rs8176743. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium test analysis was performed on the gene locus , and the results showed that rs505922 was not representative of the population. Therefore, no follow-up study was performed and the representative of the remaining four genes was analyzed. In AMI patients and healthy people, rs643434 and rs651007 site genotypes point of comparison was statistically significant ( P < 0.05 ), and rs579459 , rs8176743 locus genotypes is meaningless. There may be genetic susceptibility between AMI and rs643434 and rs651007. The possible cause is that rs643434 and rs651007 are involved in mediating the occurrence of AMI. The analysis of each gene locus in different genetic models showed that the patients with myocardial infarction had differences from the healthy people in the dominant mode of rs643434 gene, the dominant mode of rs651007 gene, and the recessive mode of rs651007 gene.The genetic susceptibility of AMI under different genetic models of rs643434 and rs651007 was further explained. Cao ming-hua et al. [15] discussed the susceptibility of cerebrovascular disease and ABO blood group gene polymorphism, and the results showed that ABO blood group genes rs505922 and rs8176743 are susceptible genes of cerebrovascular disease, while rs651007 is not susceptible genes of cerebrovascular disease. Among them, rs643434 was not analyzed because it did not meet the Hardy -Weinberg balance test. There is a difference with the results of this study, and the analysis reasons may be different for the included objects and research purposes, but AMI and cerebrovascular disease are vascular diseases, there is a certain correlation can be used as a reference control.
The correlation between different genetic patterns of rs643434 and rs651007 and the condition of AMI was discussed. The results reflected that rs643434 in the dominant mode was correlated with Gensini score and TIMI grade, rs651007 in the dominant mode was correlated with Gensini score, TIMI grade and troponin, and rs651007 in the recessive mode was correlated with Gensini score. The reason may be that rs643434 and rs651007 are related to the pathogenesis of AMI. And in the genetic model of different gene locus, the expression of gene locus may also participate in the progress of the disease. Alex-Ander et al.[16]analyzed the correlation between the ABO blood group gene rs644234 and E- selectin and blood lipid levels.The results indicated that the rs 644234 gene locus was related to the change of in E- selectin and blood lipid levels. Therefore, we speculated that ABO blood group genes may be involved in the pathogenesis and progression of patients with AMI by regulating blood lipid levels. In the study of major cardiac adverse events, we found that the ABO blood group locus rs643434 was associated with MACE in a dominant mode . The cause is possible that rs643434 affect the occurrence of adverse events in patients with AMI by regulating the expression level of the protein. Mohamed et al. [17-18] supported the results of this study.
In summary, in patients with AMI, the ABO blood group genes rs643434 and rs651007 have abnormal expressions, which may be related to the condition and prognosis of AMI. Due to the small sample size and few detection sites included in this study, it is necessary to improve in future studies to confirm the influence of ABO blood group gene on AMI.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年13期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年13期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Effects of lumbar sagittal balance remodeling on natural absorption after lumbar disc herniation
- Network pharmacology of threatened abortion treated by ShouTaiWan
- Characteristic changes of intestinal flora and its correlation with clinical indexes in patients with Behcet's disease based on TCM syndromes
- The analysis of acupoint selection rules for acupuncture treating functional constipation
- Meta analysis of clinical efficacy of combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of venous ulcer of lower extremities
- Effect of high flux hemodialysis on renal anemia and soluble transferrin receptor in hemodialysis patients
