Targetoid Hemosiderotic Nevus
Kai-Lv Sun and Jian-Min Chang,*
1Department of Dermatology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Beijing 100730, China, 2Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China.

Figure 1.Histopathological findings of the lesion from patient with targetoid hemosiderotic nevus.Nest-forming nevus cells in the dermis.There are numerous dilated irregular vascular spaces below and surrounding the nevus.Red blood cell extravasation and hemosiderin deposits are present in the papillary dermis.A and B: × 40.
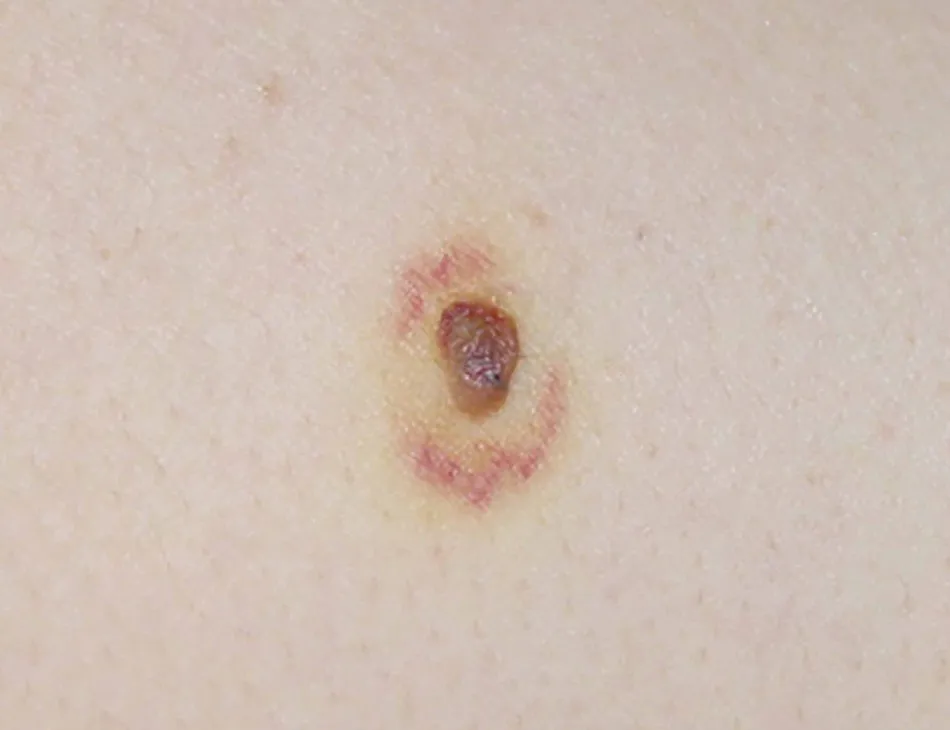
Figure 2.Photograph presentation of the targetoid hemosiderotic nevus lesion.A single, small, well-circumscribed, brownish papule was surrounded by a targetoid violaceous ring.
Histopathology
Targetoid hemosiderotic nevus (THN) comprises two distinctive components: a central, mostly melanocytic component and a peripheral, mostly hemorrhagic component.1The central melanocytic nevus can either be an intradermal nevus or a compound nevus.No junctional nevi have been reported yet.There are numerous dilated irregular vascular spaces present in the region below and surrounding the nevus, accompanied by scattered lymphocytes and histiocytes.The peripheral hemorrhagic halo comprises red blood cell extravasation and hemosiderin deposits in the papillary dermis (Fig.1).
Clinical features
THN, also known as traumatized nevus, was first described in 2005 by Tomasini et al.1Reports of THN are still rare.A literature search revealed only 10 cases of THN reported as case reports or case series reports.The mechanism of THN remains unknown, but might be related to chronic stimulation, such as friction from clothing.THN often occurs in young women.Clinically,THN is characterized by the sudden appearance of a targetoid violaceous ring surrounding a melanocytic nevus(Fig.2).Most patients report no history of trauma.Furthermore,no pruritus,tenderness,or burning sensation is experienced before the appearance of the halo.Due to the hemorrhagic symptoms of THN,dermoscopy is required to rule out malignant melanoma.Dermoscopically, THN shows the typical pattern of a melanocytic nevus,with jetblack areas and comma-shaped capillaries and a reddish halo.2THN must also be distinguished from targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma, cockarde nevus, Meyerson nevus, and other skin diseases with targetoid lesions.3Surgery is a treatment option for THN.However,the lesion usually spontaneously resolves in about 4 weeks.4
- 国际皮肤性病学杂志的其它文章
- Eccrine Spiradenoma of the Forehead: A Case Report
- Lues Maligna in an Immune-Reconstituted Patient with Retroviral Infection: A Case Report
- Seborrheic Keratosis in a Young Woman:A Mimicker of Keratoacanthoma
- A Case of Condyloma Acuminatum on the Nipple Detected via Dermoscopy
- Azathioprine Hypersensitivity Syndrome in an Asian Woman
- Linagliptin-Associated Bullous Pemphigoid: The First Case in China

