多重PCR技术在食品检测中的应用与展望
董蕾 黄晓波 刘静璇


摘要 多重PCR技术建立在常规PCR基础上,作为一种高效、快速、高灵敏性及特异性的方法,其被应用在食品检测的各个领域。从食品安全检测角度,简要论述多重PCR技术在金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌和弓形菌等食源性致病菌检测中的应用,并根据长期工作总结多重PCR技术操作的重难点和前景展望,以期为多重PCR技术在食品检测中的工作提供帮助。
关键词 多重PCR;食品致病菌;检测
中图分类号 TS207.4文献标识码 A文章编号 0517-6611(2020)11-0015-04
AbstractMultiplex PCR which is based on conventional PCR is an efficient, fast, sensitive and specific method for food detection. In this paper, the application of multiplex PCR in detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Staphlococcus aureus and Arcobacter, etc. was discussed to provide support for the work of multiplex PCR technology in food detection.
Key words Multiplex PCR;Food pathogenic bateria;Detection
自1988年Chamberlain等[1]首次提出多重PCR技术(multiplex polymerase chain reaction,MPCR),并利用该技术进行杜氏营养不良症(Duchenne musculardystrophy)基因外显子缺失的检测以来,多重PCR技术在医学(包括遗传病诊断、病原体检测等)、食品科学(食品原料溯源、食品病原微生物检测等)等科学领域均有极大贡献,成为检测的一项重要技术工具。笔者从食品安全检测角度,简要论述多重PCR技术在金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌和弓形菌等食源性致病菌检测中的应用,并根据长期工作总结多重PCR技术操作的重难点和前景展望,以期为多重PCR技术在食品检测中的工作提供帮助。
1 多重PCR技术简介
多重PCR技术又称多重引物PCR或复合PCR技术,是一种建立在常规PCR技术基础上,并进行改进的新型PCR技术。不同于常规PCR的单一引物扩增,在多重PCR体系中同时加入多对引物进行多目标DNA片段扩增[2],由于目标片段大小不同,经由多重PCR扩增后,凝胶成像即可直接进行分析[3]。该方法相比常规PCR方法,因其在同一体系中同时进行多目标DNA片段的扩增,从而达到节约模板DNA、节省时间和成本的优势。
多重PCR技术建立在常规PCR技术之上,利用模板DNA、多对引物、4种脱氧核糖核苷酸,依赖于DNA聚合酶完成酶促合成反应。多重PCR技术具有高效性:在同一反应体系、反应时间内可以同时检测多种病原菌或目标基因;系統性:对于同一食品或症状相同的病原菌可以进行同时检测;经济简便性:由于在同一体系内同时反应,可大大节约检测时间及检测试剂[4]。
2 多重PCR技术在食品致病菌检测中的应用
多重PCR技术在同一体系中加入不同目标片段的引物,即可完成在一次反应中多个目标片段的同时扩增,多重PCR技术大大提升了检验过程的时长、降低了试剂耗材的损耗,使检验过程快速简便,被广泛应用于食品检验的各个领域。
2.1 金黄色葡萄球菌的检测
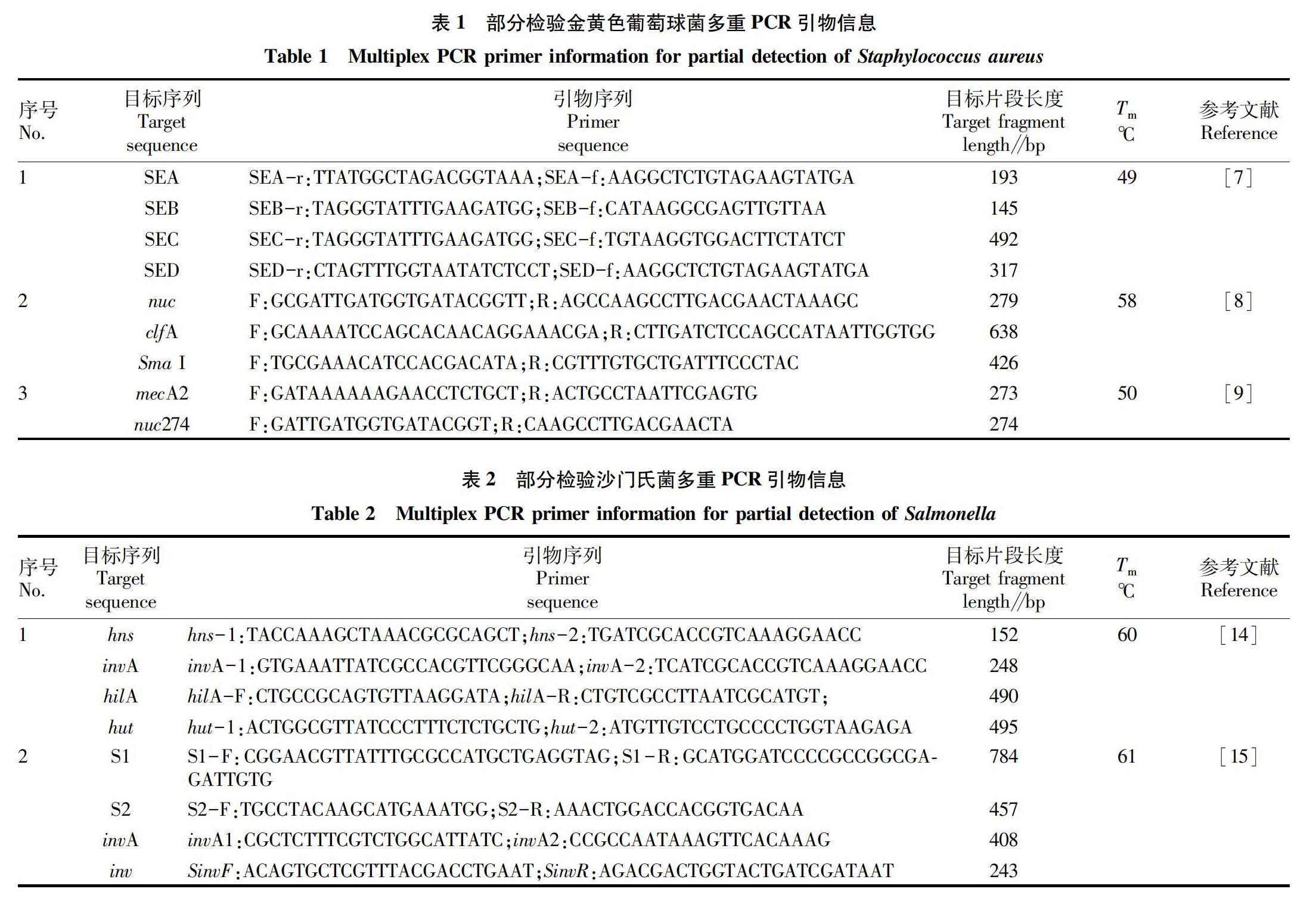
金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphyloccocus aureus,SA)在自然界分布广泛,是革兰氏阳性菌的代表,能够引起人和动物的严重感染发病,是一种重要的人类病原菌[5-6]。该菌所产生的肠毒素(SE)引起的食物中毒是世界性的卫生难题,在美国、加拿大等国家,由于金黄色葡萄球菌引起的食物中毒现象超过30%,中国也时有发生。近年来利用PCR技术诊断检测金黄色葡萄球菌肠毒素,使检测快速准确。
杨玉军等[7]针对金黄色葡萄球菌最常引起食物中毒的4种类别(A、B、C、D型)SE基因保守序列设计4对引物(表1),对SE片段进行扩增,获得最优反应体系,总体积为25 μL体系中,各引物浓度为0.2 μmol/L;徐晓可等[8]以耐热核酸酶基因nuc、纤维蛋白原结合蛋白基因clfA和SmaI限制性酶切片段特异序列为目标片段,设计引物3对(表1),验证灵敏度在模板水平上可达1.197 3 ng;Costa等[9]针对mecA和nuc目标片段,设计荧光定量PCR引物进行检测验证,效果优异(表1)。
2.2 沙门氏菌的检测
沙门氏菌(Salmonella)是一类革兰氏阴性菌,属肠杆菌科,除感染人以外,也会感染哺乳类、鸟类、鱼类等,当人接触含这类菌的食物时均会引起食物中毒,出现伤寒、肠胃炎、肠毒症、败血症等肠道疾病。每年全球由于沙门氏菌引发的食源性疾病均居于食源性疾病病因的前列[10-13]。
邵碧英等[14]根据沙门氏属特异基因hut基因、hilA基因、invA基因和hns基因设计特异性引物,实现沙门氏菌的三重PCR;唐雨德等[15]针对S1、S2、invA基因设计4对特异性引物,对16株沙门氏菌进行PCR检测,灵敏度平均为100 CFU,人工污染样品最低检出限为10 CFU,大大缩短检验时间(表2)。
[2] KIM J,DEMEKE T,CLEAR R M,et al.Simultaneous detection by PCR of Escherichia coli,Listeria monocytogenes and Salmomella typhimurium in artificially inoculated wheat grain[J].Int J Food Microbiol,2006,111:21-25.
[3] 李业鹏,钟凯,杨宝兰,等.食品中沙门菌PCR检测方法的建立[J].中国食品卫生杂志,2006,18(1):17-22.
[4] 谭贵良,赖心田.现代分子生物学及组学技术在食品安全检测中的应用[M].广州:中山大学出版社,2014.
[5] 胡晓宁,苏诚玉,权玉玲,等.甘肃省生鲜乳中金黄色葡萄球菌及肠毒素污染状况调查[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2013,23(4):984-985,989.
[6] 白晓娟.多重PCR检测原料乳品中微生物研究[J].食品工业,2018,39(4):313-315.
[7] 杨玉军,黄韦唯,王志云,等.多重PCR快速检测金黄色葡萄球菌四型肠毒素基因的研究[J].现代预防医学,2009,36(9):1713-1715.
[8] 徐晓可,吴清平,张菊梅,等.食品中金黄色葡萄球菌多重PCR检测方法的研究[J].食品与生物技术学报,2011,30(1):84-89.
[9] COSTA A M,KAY I,PALLADINO S.Rapid detection of mecA and nuc genes in staphylococci by realtime multiplex polymerase chain reaction[J].Diagnostic microbiology and infectious disease,2005,51(1):13-17.
[10] European Food Safety Authority(EFSA).The European union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses,zoonotic agents and foodborne outbreaks in 2011[R].EFSA,2013.
[11] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.Salmonella[R].CDC,2011.
[12] ALMEIDA C,CERQUEIRA L,AZEVEDO N F,et al.Detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis using real time PCR,immunocapture assay,PNA FISH and standard culture methods in different types of food samples[J].Int J Food Microbiol,2013,161(1):16-22.
[13] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.Investigation update:Multistate outbreak of human Salmonella Enteritidis infections associated with shell eggs[R].CDC,2010.
[14] 邵碧英,陳彬,汤敏英,等.沙门氏菌多重PCR检测方法的建立[J].食品科学,2007,28(10):489-492.
[15] 唐雨德,梁洪军,周东明,等.应用多重PCR检测食品中的沙门菌[J].实用预防医学,2009,16(5):1366-1369.
[16] HO H T K,LIPMAN L J A,GAASTRA W.Arcobacter,what is known and unknown about a potential foodborne zoonotic agent![J].Vet Microbiol,2006,115(1/2/3):1-13.
[17] VANDAMME P,DE LEY J.Proposal for a new family,Campylobacteraceae[J].Int J Syst Bacteriol,1991,41(3):451-455.
[18] VANDAMME P,FALSEN E,ROSSAU R,et al.Revision of Campylobacter,Helicobacter and Wolinella taxonomy:Emendation of generic descriptions and proposal of Arcobacter gen.nov.[J].Int J Syst Bacteriol,1991,41(1):88-103.
[19] CHINIVASAGAM H N,CORNEY B G,WRIGHT L L,et al.Detection of Arcobacter spp.in piggery effluent and effluentirrigated soils in southeast Queensland[J].Appl Environ Microb,2007,103(2):418-426.
[20] RIVAS L,FEGAN N,VANDERLINDE P.Isolation and characterisation of Arcobacter butzleri from meat[J].Int J Food Microbiol,2004,91(1):31-41.
[21] HOUF K,TUTENEL A,DE ZUTTER L,et al.Development of a multiplex PCR assay for the simultaneous detection and identification of Arcobacter butzleri,Arcobacter cryaerophilus and Arcobacter skirrowii[J].FEMS Microbiol Lett,2000,193(1):89-94.
[22] 毕水莲,刘一鸣,陈金,等.多重PCR法检测鸡肉中3种食源性弓形菌[J].中国食品学报,2014,14(8):227-232.
[23] 冯可,胡文忠,姜爱丽,等.鲜切果蔬中4种病原微生物多重PCR检测技术[J].食品科学,2018,39(6):276-283.
[24] 姜华,焦阳,李远宏,等.多重PCR检测婴幼儿配方奶粉中3种食源性致病菌[J].食品工业科技,2018,39(14):213-218.
[25] 苗小草,陈万义,施春雷,等.乳品中4种常见致病菌多重PCR检测方法的建立[J].河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(1):63-71.
[26] 李远宏,张逸飞,张庆成,等.谷类食品中克罗诺杆菌的分离与鉴定[J].食品工业科技,2016,37(15):154-158,164.
[27] MALORNY B,HOORFAR J,BUNGE C,et al.Multicenter validation of the analytical accuracy of Salmonella PCR:Towards an international standard[J].Applied and environmental microbiology,2003,69(1):290-296.
[28] CHEN W Y,AI L Z,YANG J L,et al.Development of a PCR assay for rapid detection of Cronobacter spp.from food[J].Canadian journal of microbiology,2013,59(10):656-661.
[29] 杨帆,王红宁,张安云,等.多重PCR检测病死鸡中沙门氏菌方法的研究[J].四川大学学报(自然科学版),2015,52(1):163-169.
[30] KIM C H,KHAN M,MORIN D E,et al.Optimization of the PCR for detection of Staphylococcus aureus nuc gen in bovine milk[J].Journal of dairy science,2001,84(1):74-83.
[31] PARK Y S,LEE S R,KMI Y G.Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7,Salmonella spp.,Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes in kimchi by multiplex polymerase chain reaction(mPCR)[J].The journal of microbiology,2006,44:92-97.
[32] DOOLEY J J,PAINE K E,GARRETT S D,et al.Detection of meat species using TaqMan realtime PCR assays[J].Meat science,2004,68(3):431-438.
[33] GIRISH P S,ANJANEYULU A S R,VISWAS K N,et al.Meat species identification by polymerase chain reactionrestriction fragment length polymorphism(PCRRFLP)of mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene[J].Meat science,2005,70(1):107-112.
[34] GHOVVATI S,NASSIRI M R,MIRHOSEINI S Z,et al.Fraud identification in industrial meat products by multiplex PCR assay[J].Food control,2009,20(8):696-699.
[35] YIN R H,BAI W L,WANG J M,et al.Development of an assay for rapid identification of meat from yak and cattle using polymerase chain reaction technique[J].Meat science,2009,83(1):38-44.
[36] SOARES S,AMARAL J S,MAFRA I,et al.Quantitative detection of poultry meat adulteration with pork by a duplex PCR assay[J].Meat science,2010,85(3):531-536.
[37] 苏葳艺,李欣南,于雷,等.利用多重PCR方法检测牛肉中的掺假肉[J].食品工业,2015,36(2):277-280.
[38] 许晓丹,刘畅,史永翠,等.转基因大豆食品中外源基因種类及食用安全性分析[J].食品与药品,2013,15(6):446-449.
[39] KPPEL R,SENDIC A,WAIBLINGER H U.Two quantitative multiplex realtime PCR systems for the efficient GMO screening of food products[J].European food research and technology,2014,239:653-659.
[40] KPPEL R,BUCHER T,FREI A,et al.Droplet digital PCR versus multiplex realtime PCR method for the detection and quantification of DNA from the four transgenic soy traits MON87769,MON87708,MON87705 and FG72,and lectin[J].European food research and technology,2015,241:521-527.
[41] WANG F J,ZHANG X L,FENG J L,et al.Establishment of a quadruplex realtime PCR for screening of genetically modified tomatoes[J].European food research and technology,2014,238(4):683-690.

