Myalgia may not be associated with severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Giuseppe Lippi, Johnny Wong, Brandon Michael Henry3 Section of Clinical Biochemistry, Department of Neuroscience, Biomedicine and Movement, University of Verona, Verona, Italy
2 College of Medicine, SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University, New York, USA
3 Cardiac Intensive Care Unit, The Heart Institute, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Ohio, USA
Dear editor,
A recent study based on the use of experimental artificial intelligence (AI) tool showed 70%–80% accuracy in predicting development of severe disease in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) based on predictive parameters alanine aminotransferase (ALT), myalgia and hemoglobin, whilst only 5 of 53 patients developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), 2 of whom reporting myalgia.[1]It is commonly advocated that myalgia may reflect generalized inflammation and cytokine response.[1]Multiple studies showed that myalgia is a common symptom at onset of COVID-19, seen in up to 36% of such patients.[2]Therefore, in this short article we aim to further assess whether myalgia may be a reliable predictor of severe COVID-19 disease.
A search in Medline (PubMed interface), Scopus, and Web of Science, utilizing the keywords “myalgia” AND “COVID-19” OR “Coronavirus 2019” OR “SARS-CoV-2” in all fields with no date or language restrictions was conducted. Search results were screened by title, abstract, and full text for those reporting data on prevalence of myalgia in patients developing severe or non-severe COVID-19 disease. Articles fitting the criteria with validated definition of “severe disease” (i.e., patient development of severe respiratory distress, requiring ICU admission, ventilatory support, or death) were incorporated into a pooled analysis. Computation of odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of myalgia in severe and non-severe COVID-19 disease was performed with MetaXL, software version 5.3 (EpiGear International Pty Ltd,. Sunrise Beach, Australia). Due to the limited number of studies, no risk of bias or publication bias assessment performed.
This digital search enabled the identification of 16 articles after removing duplicates, 13 of which were excluded after review of title, abstract, and full text due to being review articles (n=3), did not pertain to COVID-19 disease (n=1), did not report prevalence of myalgia (n=8), or did not specify difference in myalgia from fatigue (n=1). Six additional studies were selected using reference search. Final pooled analysis included 9 studies[3–11]with a total sample of 2,445 COVID-19 patients, 786 (32.1%) with severe disease. A total of 448 (18.3%) patients in the pooled sample presented with myalgias, 125 (19.3%) with severe COVID-19 disease and 296 (17.8%) without. Accordingly, myalgia was not found to be statistically associated with severe COVID-19 disease in any the nine individual studies, nor in our pooled analysis (OR 1.02; 95% CI 0.80–1.30; I2=12%, Cochran’s Q, P=0.33) (Figure 1).
The results of this pooled analysis of the current scientific literature suggest that the presence of myalgias shall not be considered a prognostic factor for severe COVID-19 disease. It is hence unlikely that adding the efficiency of stratification models for COVID-19 may be substantially improved by adding the presence of myalgia.
Funding:None.
Ethical approval:Not needed.
Conflicts of interest:Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Contributors:All authors have seen the manuscript and agreed to the content and data. All the authors played a signifi cant role in the paper.
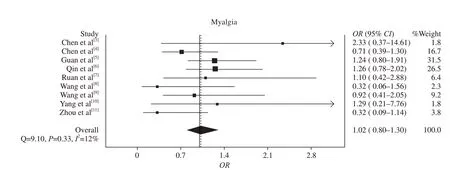
Figure 1. Association of myalgia with COVID-19 disease severity and mortality, odds ratio (OR) and 95% confi dence interval (95% CI).
 World journal of emergency medicine2020年3期
World journal of emergency medicine2020年3期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- Availability of basic life support courses for the general populations in India, Nigeria and the United Kingdom: An internet-based analysis
- The importance of visualization of appendix on abdominal ultrasound for the diagnosis of appendicitis in children: A quality assessment review
- Clinical characteristics and prognosis of communityacquired pneumonia in autoimmune diseaseinduced immunocompromised host: A retrospective observational study
- The life-saving emergency thoracic endovascular aorta repair management on suspected aortoesophageal foreign body injury
- Effects of intracoronary injection of nicorandil and tirof ban on myocardial perfusion and short-term prognosis in elderly patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction after emergency PCI
- Morbidity and mortality risk factors in emergency department patients with Acinetobacter baumannii bacteremia
