Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative brain protection in patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery under inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane:a randomized controlled study
Yong-Pan Liu,Xiao-Fang Gong
Department of Anesthesiology,Taihe Hospital,Shiyan,Hubei Province,China
Abstract
Key words:α2-adrenoceptor agonist;blood glucose;cerebral oxygen metabolism;cortisol;craniocerebral surgery;dexmedetomidine;inhalation anesthesia;randomized controlled trial;sevoflurane
INTRODUCTION
Background
Craniocerebral surgery should be performed under a sufficient degree of anesthesia while maintaining a stable hemo-dynamic level;moreover,it is required that anesthetics are harmless to brain tissue or can even protect brain tissue (McClain and Soriano,2014;Wang and Abramowicz,2017).At present,sevoflurane is often used in craniocerebral surgery (Wang et al.,2014;Gokcek et al.,2016;Kondo et al.,2016;Wu et al.,2017).Anesthesia induction with sevoflurane has the advantages of quick onset,stable circulation,high safety,and fewer adverse reactions (Kondo et al.,2016).Compared with conventional intravenous induction,inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane has a low risk for respiratory inhibition and strong controllability of anesthesia (Wu et al.,2017).However,in craniocerebral surgery,autonomic regulatory function of cerebral blood flow around the injured brain tissue or brain tumor is often weakened.Sudden increases in the patient’s blood pressure may lead to brain swelling or hemorrhage;whereas,a sudden drop of blood pressure may lead to cerebral ischemia,which will seriously affect the prognosis of patients (Dietrich and Erbguth,2013).As the analgesic and muscle-relaxing effects of sevoflurane are limited,muscle relaxants and analgesic drugs are often used as adjuvants (Zhao et al.,2013).In addition,because anesthesia induction with sevoflurane can induce adverse reactions such as increased blood pressure and heart rate,restlessness,and pain (Zhang et al.,2016),an auxiliary anesthetic is needed to reduce these adverse reactions.
Dexmedetomidine is a potent and highly selective α2 adrenergic receptor agonist that has anti-anxiety,hypnotic,an-algesic,sedative,and sympatholytic properties.It can effectively suppress increases of catecholamine concentrations,increase the stability of anesthesia induction,reduce restlessness,and minimize perioperative hemodynamic fluctuation (Lei et al.,2014).Use of dexmedetomidine as an auxiliary anesthetic has been widely reported.Previous related reports mainly focused on subjects undergoing tumor resection,heart surgery,or laparoscopic surgery (Wang et al.,2014;Song,2015;Zhan and Huang,2015;Zhang et al.,2015;Table1).However,there are few reports on craniocerebral surgery.
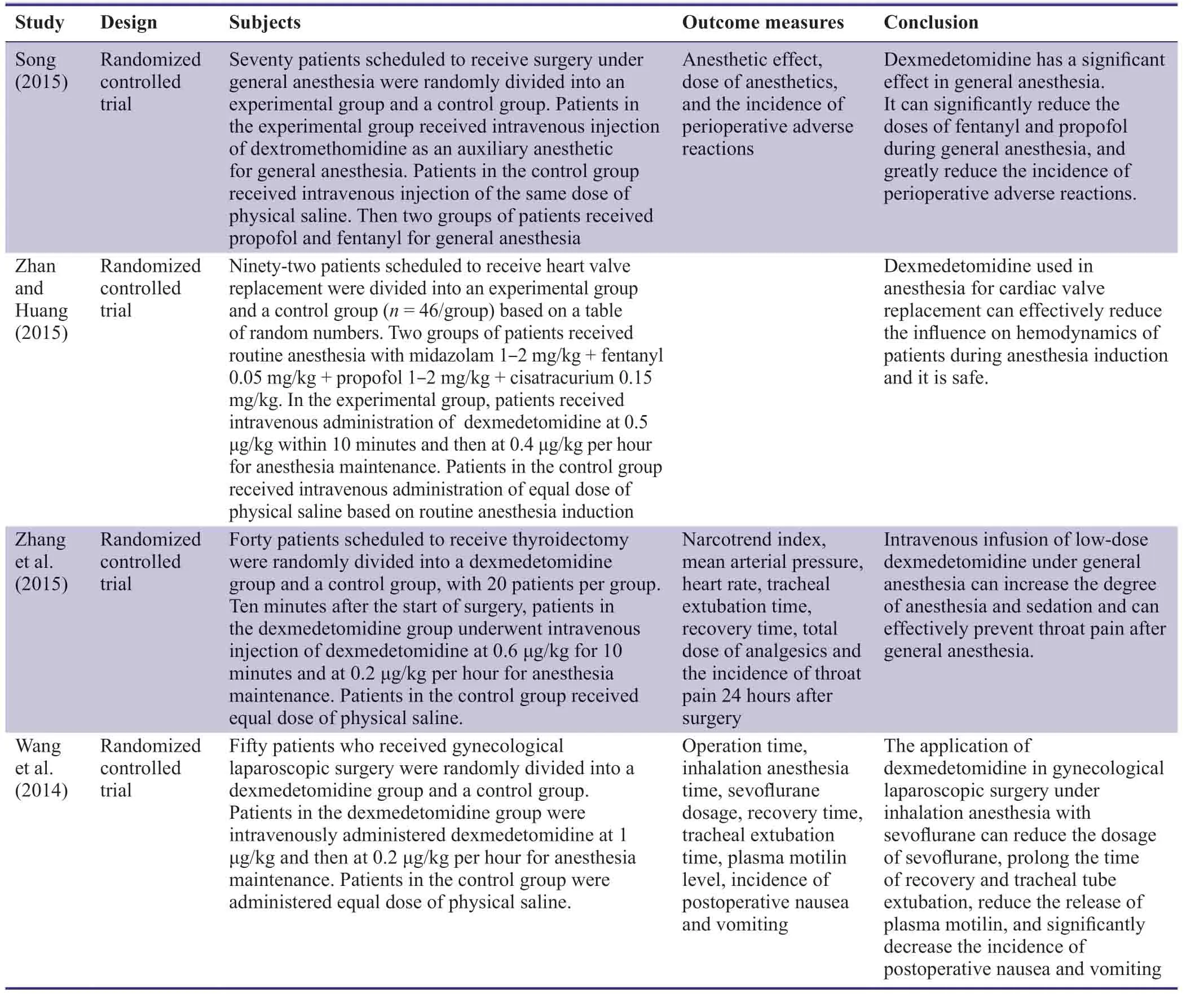
Table1:Previous studies on the efficacy of dexmedetomidine as an auxiliary anesthetic
Study objective
This randomized controlled trial will investigate the effects of dexmedetomidine on patients who receive craniocerebral surgery under inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Study design
A prospective,single-center,randomized controlled trial.
Study setting
Taihe Hospital,Shiyan,Hubei Province,China.
Investigator qualification
Taihe Hospital is a medical,teaching,and scientific research center for major neurological and psychiatric diseases.The investigators who participate in this trial will provide professional licenses,hold a professional title of deputy senior or above,and have many years of clinical experience.
Recruitment
Recruitment will be performed using advertising posters to recruit patients scheduled to undergo craniocerebral surgery in the clinics and wards of the Department of Neurosurgery at Taihe Hospital,China.Interested patients can contact the attending physician or project manager via telephone,email,or Wechat.
Study population
Patients scheduled to undergo craniocerebral surgery in the Department of Neurosurgery,Taihe Hospital,China will be considered for inclusion.
Inclusion criteria
- Patients scheduled to undergo craniotomy under general anesthesia
- American Society of Anesthesiologists class II or III (Fitz-Henry,2011)
- Aged 20-80 years,of either sex
- Provision of written informed consentExclusion criteria
- Patients with abnormal liver or kidney function
- Patients with cardiovascular,respiratory,or endocrine diseases or a history of cardiovascular,respiratory,or endocrine diseases
- Patients with a history of taking vasoactive drugs
- Patients with water-electrolyte imbalance
- Patients who take α2-adrenergic receptor agonists within 4 weeks before surgery
- Patients with pathological obesity
- Patients with consciousness disorder,drowsiness,or coma before surgery
- Patients with second-degree or third-degree atrioventricular block
- Patients with severe mental illness
- Patients with allergic constitution
- Lactating or pregnant women
- Patients who are participating in clinical trials of other drugs
Withdrawal criteria
- Poor compliance
- Serious adverse reactions
- Serious diseases of the heart,liver,kidney,hematopoietic system or endocrine system
- Lost to follow-up
Procedures
The vein channel will be opened and a cannula will be put in the opposite elbow vein.The end tidal concentration of sevoflurane (CETSev) will be monitored using a Vamos anesthetic gas monitor (Drägerwerk,Lübeck,Germany).
In the trial group,1 μg/kg dexmedetomidine (Jiangsu Nhwa Pharmaceutical,Jiangsu,China;National Drug Approval Number H20110085) will be injected intravenously for 10 minutes commencing 15 minutes before anesthesia induction,and then continuously pumped at 0.3 μg/kg per hour until 30 minutes before surgery.In the control group,0.9% sodium chloride injection will be administered in the same way and at the same injection rate.
After oxygen inhalation for 3 minutes through a facemask,a sevoflurane-containing volatilization tank (Shanghai Hengrui Pharmaceutical,Shanghai,China;National Drug Approval No.H20070172) will be opened.The scale of the volatilization tank will be adjusted to 8%,and oxygen flow rate will be fixed at 6 L/min to pre-charge the loop.When CETSev is > 75%,the facemask will be tightly closed.For anesthesia induction,the patient will be guided to inhale sevoflurane and breathe deeply.When the patient loses consciousness,auxiliary ventilation will be used and CETSev will be adjusted to be 2MAC.One minute later,succinylcholine chloride injection (Beijing CR Double Crane Pharmaceutical,Beijing,China;National Drug Approval No.H11021581) will be intravenously injected at 1 mg/kg.Sixty seconds later,a laryngeal mask will be used for mechanical ventilation with a tidal volume of 8-10 mL/kg and respiratory rate of 12 breaths/minute.During the anesthesia period,CETSev will be maintained at 1-2%,and anesthetics vecuronium (Xianju Pharm,Xianju,China;National Drug Approval No.H19991172) and fentanyl (Yichang Humanwell Pharmaceutical,Yichang,China;National Drug Approval No.H42022076) will be used intermittently.If the following conditions occur during surgery and last for more than 5 minutes,corresponding treatments will be given.If mean arterial pressure is lower than 50% of the basic value,the infusion rate will be accelerated and 0.5 mg ephedrine (Shenyang No.1 Pharmaceutical,Shenyang,China;National Drug Approval No.H21022412) will be intravenously injected.If mean arterial pressure is higher than 10% of the basic value,0.25 mg nicardipine (Astellas Tokai,Yaizu,Japan;Approval No.J20100074) will be intravenously administered.If the heart rate is lower than 50 beats/minute,0.5 mg atropine (Wuhu Kangqi Pharmaceutical,Wuhu,China;National Drug Approval No.H34021906) will be intravenously injected.If the heart rate is > 100 beats/minute,20 mg esmolol (Qilu Pharmaceutical,Jinan,China;National Drug Approval No.H19991058) will be intravenously administered.
Outcome measures
Primary outcome measure
- Recovery time
Secondary outcome measure
- Anesthesia and recovery conditions:Anesthesia time,intraoperative blood loss,amount of intraoperative fluid infusion,extubation time,and the dosage of vasoactive drugs ephedrine and nimodipine will be recorded.
- Vital signs:Vital signs will be recorded before (T0) and after administration of the loading dose of dexmedetomidine (T1),during anesthesia induction (T2),at the beginning of craniocerebral surgery (T3),during craniocerebral surgery (T4),at the end of craniocerebral surgery (T5),and at the time of recovery (T6).Vital signs include heart rate,mean arterial pressure,and bispectral index [detected by AEP Monitor 2 (Danmeter A/S,Odense,Denmark)].
- Stress index:2.5 mL of intravenous blood will be collected at T1-T6 for detection of stress index.Blood glucose levels will be measured using a blood glucose meter [Accu-Chek®Performa,Roche Diagnostics,Basel,Switzerland;SFDA Certified No.(2014):2404375] and blood glucose test paper [Johnson &Johnson,New Brunswick,NJ,USA;SFDA Certified No.(2010):2401197].The concentration of cortisol will be measured by radioimmunoassay (LDN,Nordhorn,Germany;Kit Batch No.R/E-6600).
- Cerebral oxygen metabolism index:5 mL of blood will be collected from the radial artery and the bulb of the internal jugular vein at T1-T6 for blood gas analysis [Cobas B 123 Automatic Blood Gas Analyzer,Roche;SFDA Certified No.(2013):2404148].Changes in blood oxygen saturation will be recorded as jugular venous oxygen saturation (SjvO2),arteriovenous oxygen difference (Da-jvO2),and cerebral oxygen extraction ratio (CERO2).
- Adverse events:Any unexpected symptoms,signs,or health conditions at T1-T6 will be recorded.Drug-related adverse reactions include hypotension,nausea,bradycardia,hypoxia,and atrial fibrillation.If hypotension or brady-cardia occurs,the dose of dexmedetomidine will be reduced or dexmedetomidine administration will be terminated and corresponding treatments will be administered.Transient hypertension and bradycardia will be relieved as long as the administration speed is slowed down,generally without special treatment.Outcome evaluation is shown in Table2.
Sample size
Recovery time will be taken as the primary outcome measure to calculate sample size.Results of a pilot study showed that the recovery time of simple sevoflurane anesthesia was 25.11 minutes,while the recovery time of dexmedetomidine and sevoflurane anesthesia was 27.15 minutes,with a standard error of 12.6.Takingα= 0.05 and 1 - β = 0.8,a sample size ofn= 654 per group was calculated using PASS 11.0 software (PASS,Kaysville,UT,USA).No loss was designed because the study will be performed only during the perioperative period.
Randomization
A random number will be selected starting from any number in the random number table for each research center in the same direction.The random number will be divided by two to get the remainder.Research centers assigned a zero-value remainder will be designated as the trial group,while those assigned a value of one will be designated as the control group.The data distribution table will be sealed and signed,and kept strictly confidential.
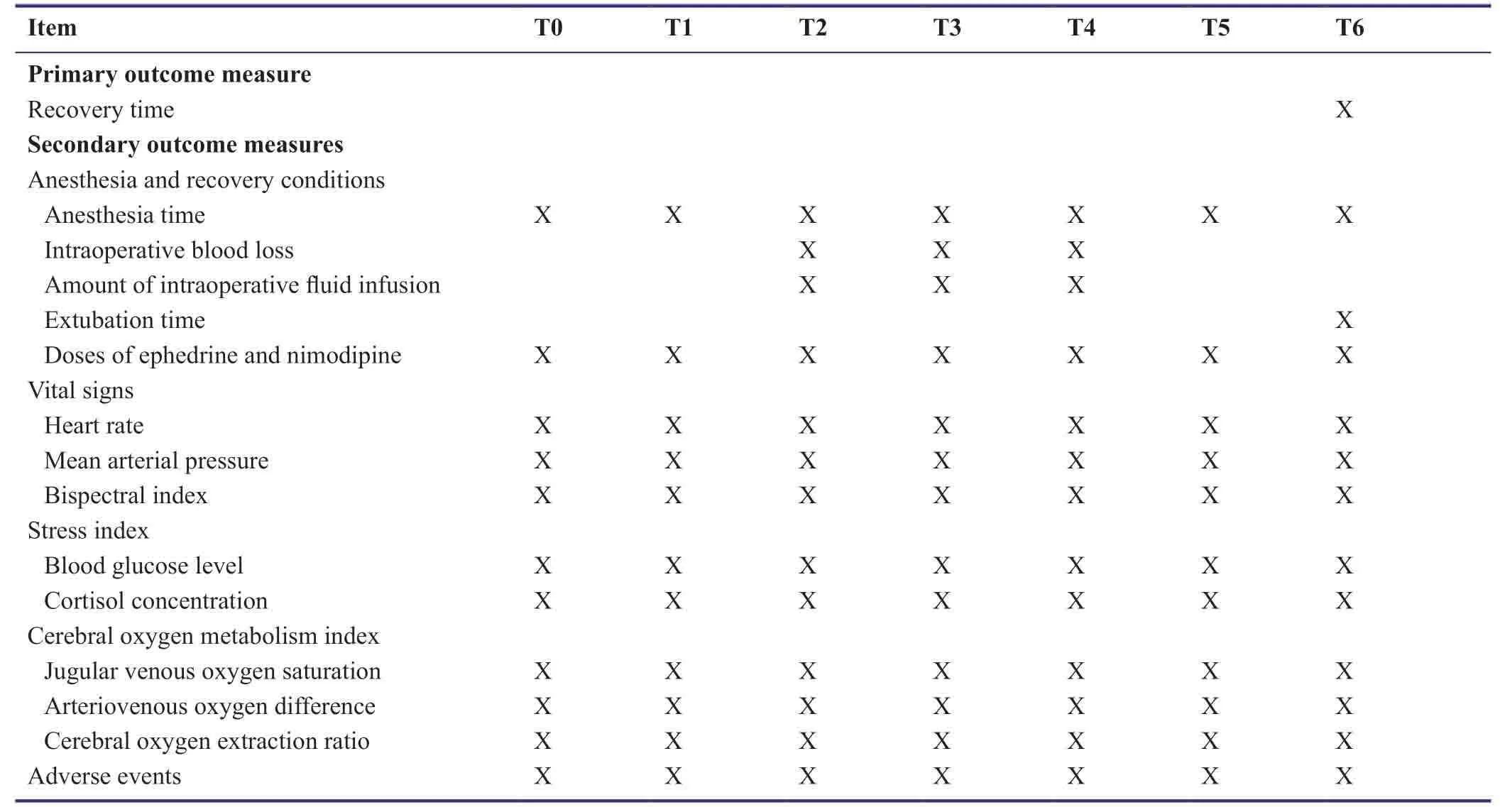
Table2:Schedule of outcome measures
Blinding
As surgery is the intervention method,it is impossible to blind surgeons.Thus,only patients and outcome evaluators in the trial will be blind to grouping.
Ethics
This trial will be performed in accordance with theDeclaration of Helsinkiand ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations in China.This study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of Taihe Hospital on December 8,2015 (approval No.2015GJJ-087) (Additional file 1).This study was registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (registration number:ChiCTR2000030459).
Informed consent
Prior to recruitment,investigators will explain the study process to patients and their legal guardians,and the patients and their guardians will sign the informed consent (Additional file 2).The manuscript was written and revised in accordance with CONsolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) (Additional file 3).
Statistical analysis
All data will be statistically processed using SPSS 19.0 software (IBM,Armonk,NY,USA) and expressed as mean ± standard deviation.Repeated measures analysis of variance will be used to compare measurement data among groups.The least significant difference test will be used to compare measurement data between groups.The chi-square test will be used to compare count data between groups.A level ofP< 0.05 will be considered statistically significant.Data analysis will follow the intention-to-treat principle.Multiple imputation will be used for handling missing data.
RESULTS
Study flowchart
A randomized controlled trial involving a large-sized sample is shown in Figure1.A total of 1308 eligible patients will be included for analysis.
Subject recruitment
The Department of Neurosurgery of Taihe Hospital in Shiyan (China) carries out more than 1000 cerebrovascular disease operations every year.It is estimated that the recruitment of patients will be completed on December 31,2025 based on annual recruitment of 300 patients.
Basic recruitment requirements
Prior to recruitment,the patient’s gender,age,past medical history,and medication history will be recorded in detail.
Anticipated outcome measures
Recovery time,anesthesia time,intraoperative blood loss,amount of intraoperative fluid infusion,extubation time,doses of ephedrine and nimodipine,heart rate,mean arterial pressure,bispectral index,blood glucose level,cortisol concentration,jugular venous oxygen saturation,arteriovenous oxygen difference,cerebral oxygen extraction ratio,and adverse events.
Anticipated adverse events
The main adverse events anticipated for this trial are abnormal blood pressure and heart rate,restlessness,pain,cough,and shiver.All adverse reactions will be recorded in case report form and reported to the research team and Ethics Review Committee within 24 hours.
Results of a pilot study
Grouping of 190 patients
We performed a pilot study involving 190 patients scheduled to undergo craniocerebral surgery between March 2016 and February 2017.These patients were randomly assigned to receive anesthesia with sevoflurane (control group) or dexmedetomidine and sevoflurane (trial group).
General information of 190 patients
There was no significant difference in patients’ general information between trial and control groups (P> 0.05;Table3).
Anesthesia and recovery of 190 patients
There were no significant differences in anesthesia time,intraoperative blood loss,amount of intraoperative fluid infusion,recovery time,or extubation time between control and trial groups (P> 0.05).However,the doses of ephedrine and esmolol in the trial group were significantly lower compared with the control group (P< 0.05;Table4).
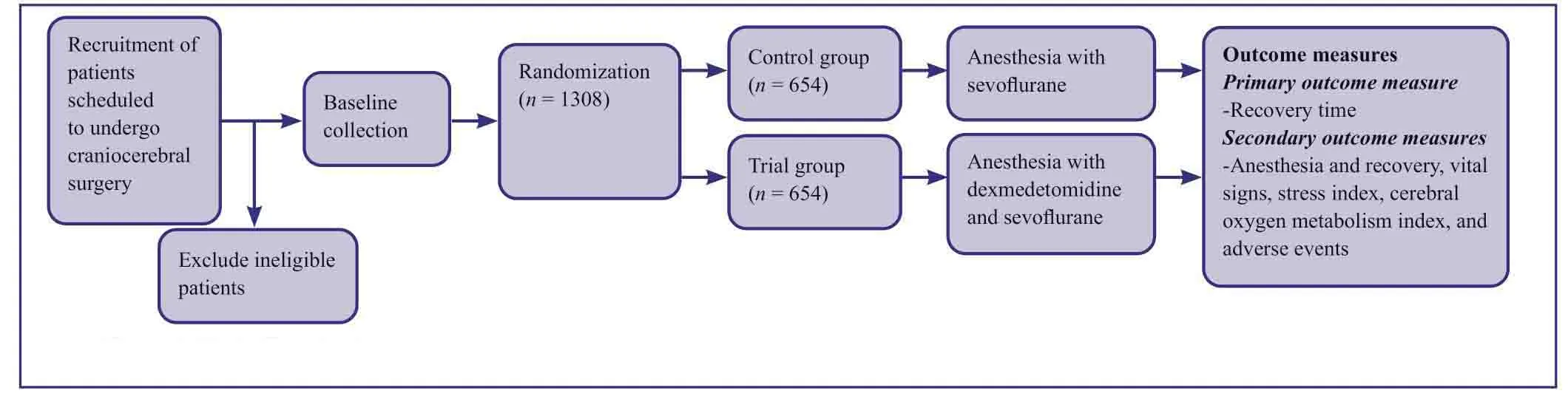
Figure1:Study flow chart.
Hemodynamic indexes of 190 patients
At T0,there were no significant differences in heart rate,mean arterial pressure,or bispectral index between trial and control groups (P> 0.05).Mean arterial pressure and bispectral index at T2-T5 were significantly lower than at T0 (P< 0.05).In the trial group,heart rates at T3-T5 were significantly lower than at T0,T1,and T6 (P< 0.05).In the control group,heart rates at T1-T5 were significantly lower than at T0 and T6 (P< 0.05).In the control group,heart rate and mean arterial pressure at T6 were significantly lower than those at T0-T5 (P< 0.05).At T1-T6,heart rates and bispectral index were significantly higher in the trial group compared with the control group (P< 0.05).At T3-T6,mean arterial pressure in the trial group was significantly higher compared with the control group (P< 0.05;Table5).
Stress index of 190 patients
At T0,blood glucose level and cortisol concentration were similar between trial and control groups (P> 0.05).In the trial group,blood glucose levels at T1-T6 were significantly higher than at T0 (P< 0.05),and cortisol concentrations at T1-T6 were significantly lower than at T0 (P< 0.05).In the control group,blood glucose levels at T2-T5 were significantly lower than at T0,T1,and T6 (P< 0.05),and cortisol concentrations at T3-T5 were significantly lower than at T0-T2 and T6 (P< 0.05).At T1-T6,blood glucose levels in the trial group were significantly higher compared with the control group (P< 0.05).At T1-T3,cortisol concentrations in the trial group were significantly lower compared with the control group (P< 0.05;Table6).
Cerebral oxygen metabolism index of 190 patients
At T0,jugular venous oxygen saturation,arteriovenous oxygen difference,and cerebral oxygen extraction ratio were similar between trial and control groups (P> 0.05).In the control group,jugular venous oxygen saturation at T2-T6 was significantly lower than at T0 (P< 0.05),arteriovenous oxygen difference at T3-T6 was significantly lower than at T0-T2 (P< 0.05),and cerebral oxygen extraction ratios at T2 and T4-T6 were significantly lower than at T0,T1,and T3 (P< 0.05).In the trial group,arteriovenous oxygen differences and cerebral oxygen extraction ratios at T4 and T5 were significantly lower than those observed at other time points studied (P< 0.05).At T4-T6,jugular venous oxygen saturation,arteriovenous oxygen difference,and cerebral oxygen extraction ratio in the trial group were significantly higher compared with the control group (P< 0.05;Table7).
DISCUSSION
Study limitations
This study only analyzed the data collected during surgery and within a short time period after surgery,and did not perform long-term follow-up;moreover,the monitoring equipment was limited.In addition,there were significant differences in the type of craniocerebral operations and surgical difficulties between patients.All of these may influence the trial outcomes.Note:Data were expressed as the mean ± SD.Repeated measures analysis of variance and the Least Significant Difference-ttest were used to compare data between groups.*P< 0.05,vs.T0;#P< 0.05,vs.control group.T0:Before administration of loading dose of dex-medetomidine;T1:after administration of loading dose of dexmedetomidine;T2:during anesthesia induction;T3:at the beginning of craniocerebral surgery;T4:during craniocerebral surgery;T5:at the end of craniocerebral surgery;T6:at the time of recovery.
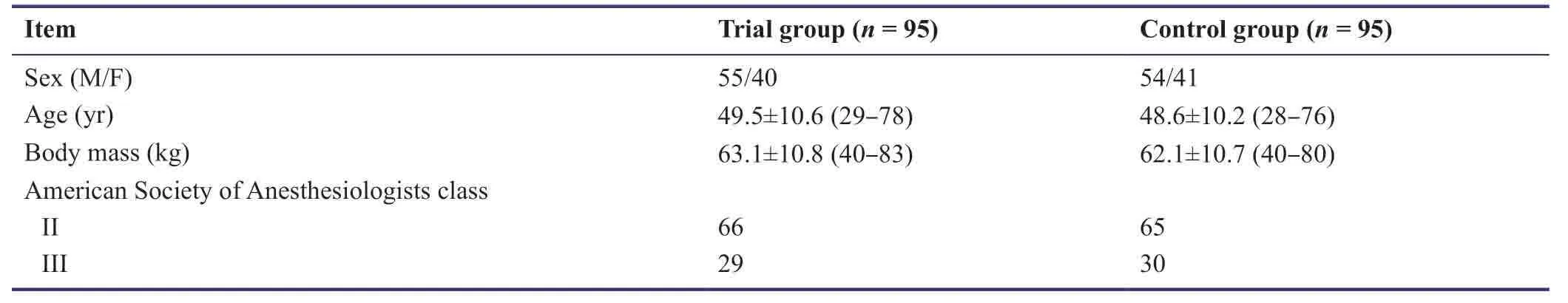
Table3:General information of 190 patients scheduled to receive craniocerebral surgery in the pilot study
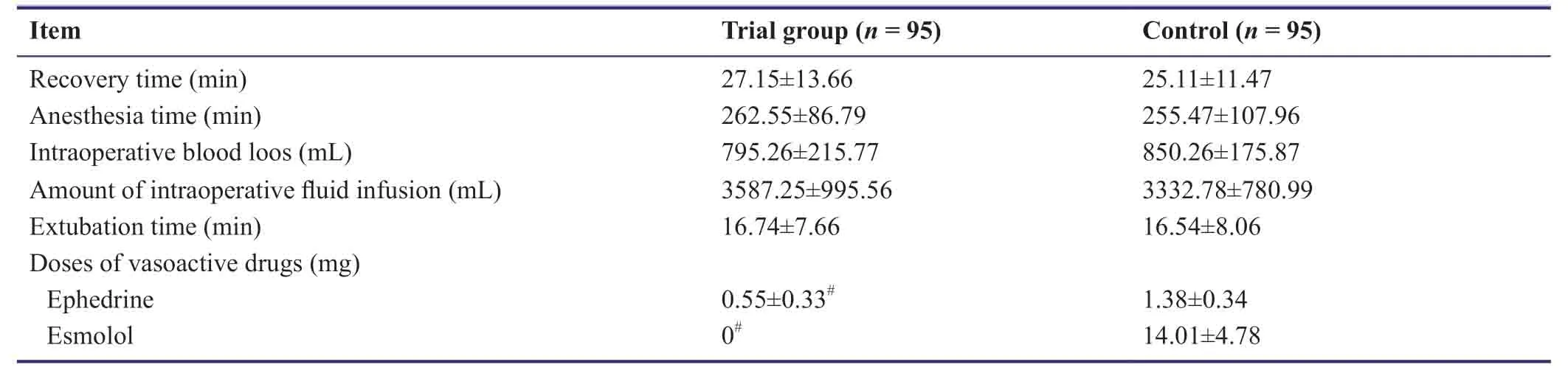
Table4:Effects of dexmedetomidine on anesthesia and recovery of patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery under inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane
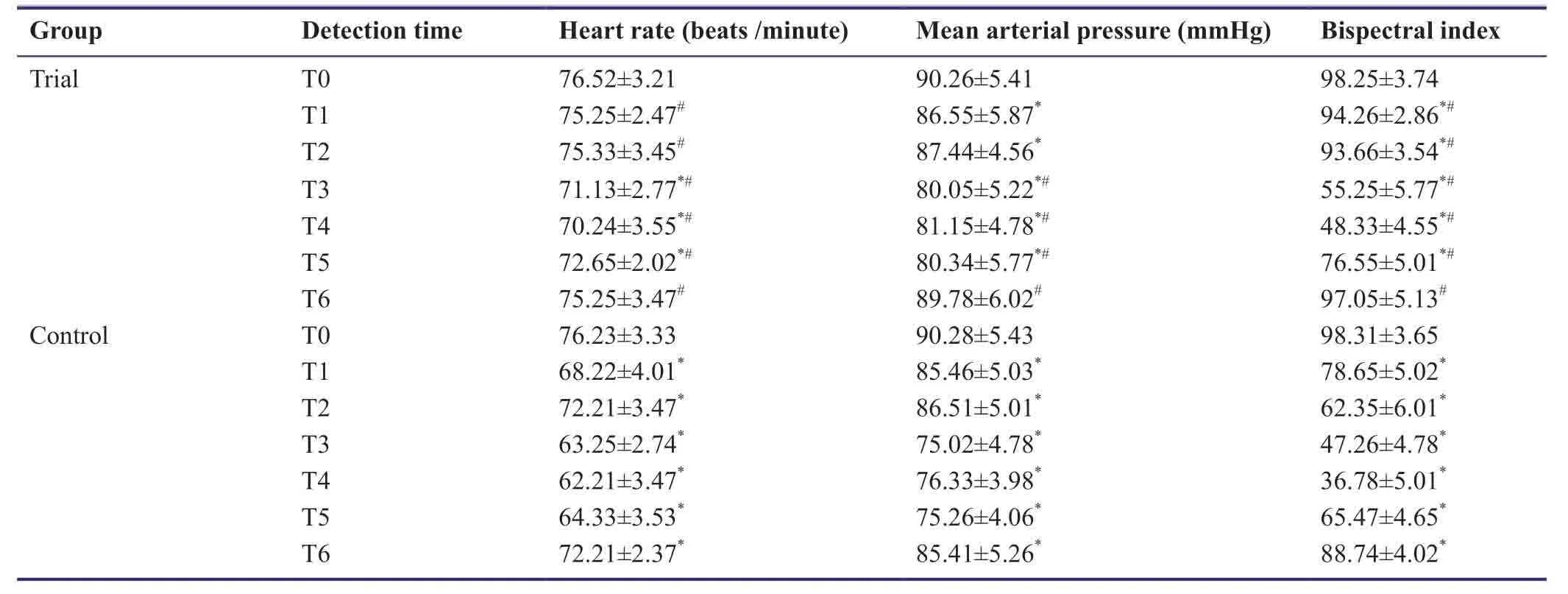
Table5:Effects of dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic indexes of patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery under anesthesia with sevoflurane
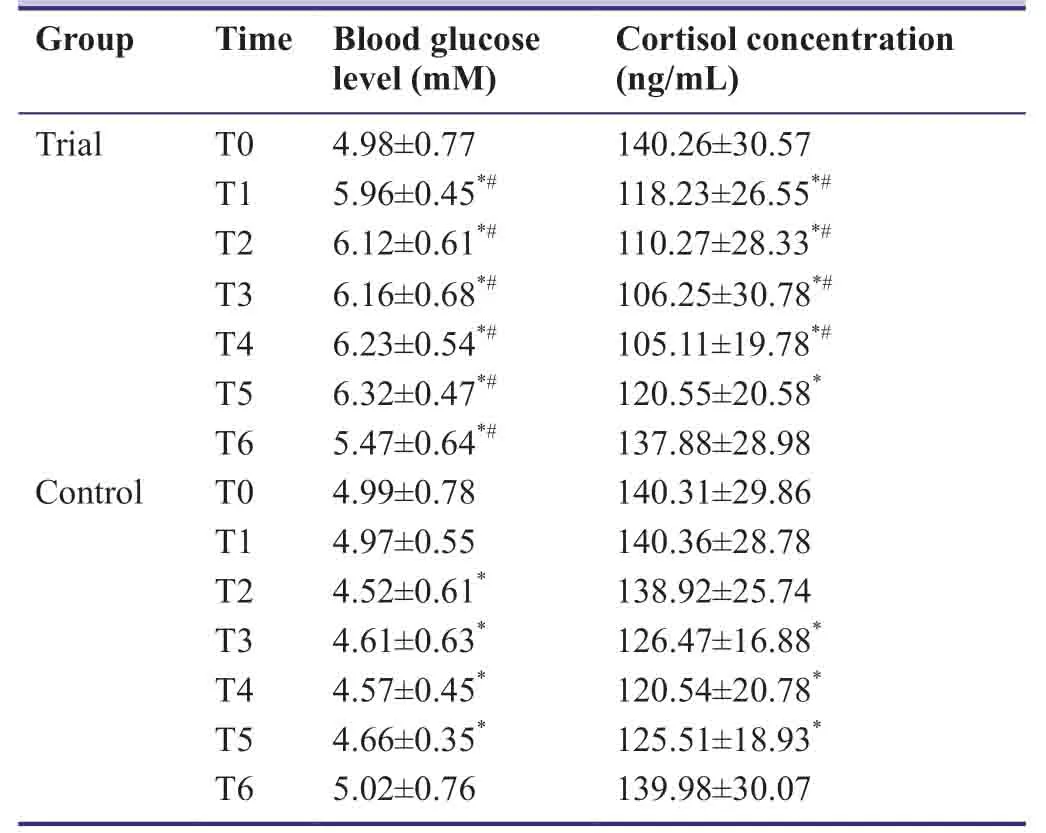
Table6:Effect of dexmedetomidine on stress index of patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery under inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane
Treatment applicability
Anesthesia and recovery-related conditions,vital signs,stress index,cerebral oxygen metabolism,and adverse events were recorded to investigate the efficacy of dexmedetomidine in craniocerebral surgery under anesthesia with sevoflurane.The results provide evidence for a preferred anesthesia method for craniocerebral surgery.
Interpretation
Dexmedetomidine,a highly selective α2-adrenergic receptor agonist,has a much higher potency ratio than clonidine (Yang and Liu,2017),elicits sedative and analgesic effects while reducing sympathetic tone,and does not produce respiratory depression.Therefore,dexme-detomidine is a good anesthetic acid.However,as craniocerebral surgery generally takes a long time,conventional intravenous general anesthesia may result in anesthetic drug accumulation and delay the patient’s recovery time (Jiang et al.,2016).In contrast,anesthesia with sevoflurane takes effect quickly,has little effect on the human circulatory system,produces little respiratory depression,has a low risk of airway complications,exhibits muscle-relaxing and analgesic effects,and therefore has higher clinical safety (Wang et al.,2017).However,general anesthesia with sevoflurane alone cannot completely eliminate the adverse stress of craniocerebral surgery;thus,it is a more rea-sonable choice to combine sevoflurane with other drugs to improve anesthesia induction (Takahashi et al.,2016).A previous study used anesthesia with a combination of opioids and sevoflurane,but this method may lead to respiratory depression and a high incidence of cough (Li et al.,2013).Recent studies have confirmed that dexmedetomidine can reduce hemodynamic fluctuations and the incidence of restlessness during the recovery period (Hwang et al.,2013;Jin et al.,2017).Moreover,Jin et al.(2017) reported that dexmedetomidine can inhibit stress responses and decrease cortisol concentration.There is also evidence that dexmedetomidine can inhibit increases of blood glucose levels (Lehto et al.,2016;Yuan et al.,2016).Therefore,the results of this study will further confirm whether dexmedetomidine can reduce hemodynamic fluctuation and stress index levels,and validate its protective effects on the brain.Our findings will provide important information about the application of dexmedetomidine in combination with sevoflurane for craniocerebral surgery.
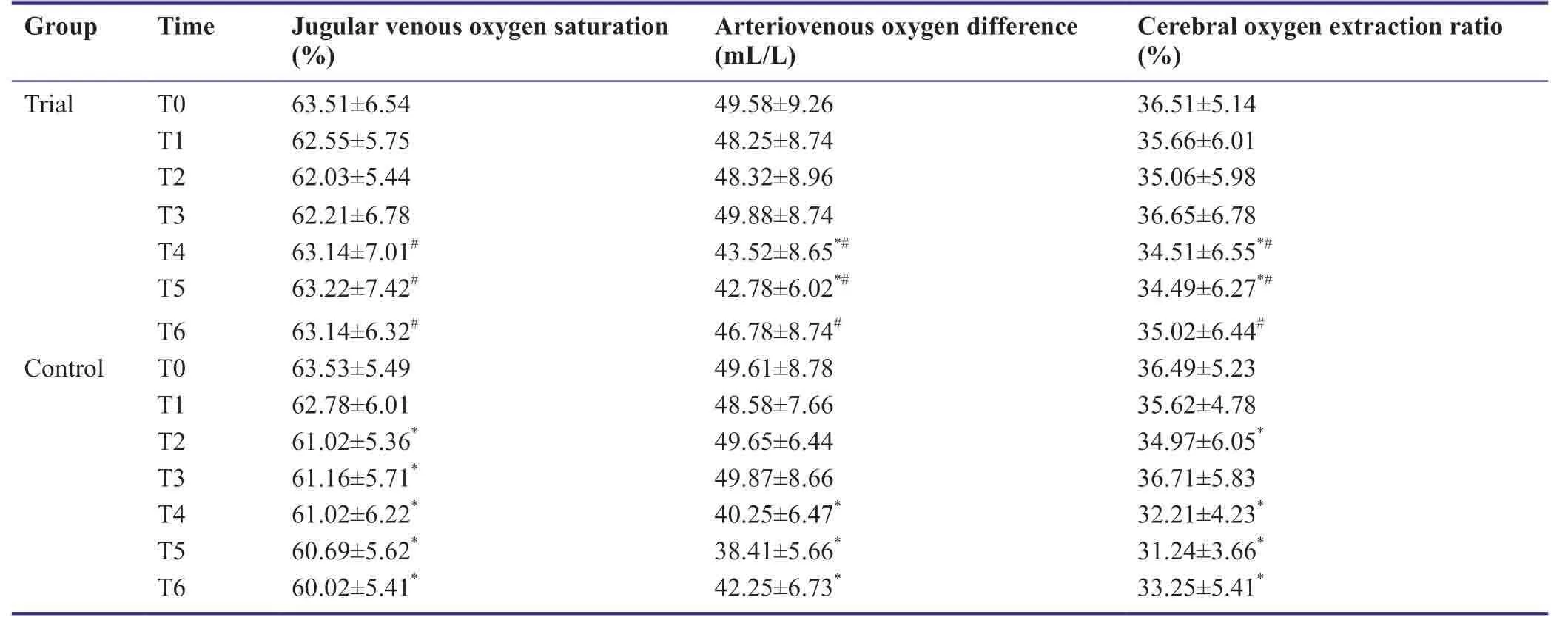
Table7:Effects of dexmedetomidine on cerebral oxygen metabolism index of patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery under anesthesia with sevoflurane
Data authenticity management
Data collection
Baseline data will be collected directly from patients when they will be enrolled.Anesthesia-related information will be collected through the anesthesia clinical information management system V5.0 (Docare,Suzhou MedicalSystem Technology Co.,Ltd.,China) and then recorded in clinical trial data collection and management system (PharmaSun-EDC,MedTop Medical Science and Technology Co.,Ltd.,China) by a trained investigator.
Data management
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data,the project manager will verify and cross check the case report form based on the investigator’s original records and drug logs.Missing information or specific errors in the data will be detected by the program and the results will be sent to the investigator for resolution.After the completion of the study,the original case report form will be kept in the test center for 5 years.
Data quality control
The Medical Ethics Committee of Taihe Hospital will supervise the data collection process to control data quality.In case of any adverse event,it will be reported to the Ethics Review Committee of Taihe Hospital immediately,and the Ethics Review Committee will decide whether to continue the test after evaluation.
Modification of study protocol
The modification of RCT protocol will be approved by all study teams,ethics review committee,and Chinese Clinical Trial Registry before the clinical trial can be carried out according to the modified content.The date of implementation will be recorded in the trial file.
Monitor
The monitors who will not participate in the trial will check the ethical review and contract signing,the record and filing of all the test documents (informed consent,medical record on admission and at discharge,research medical record,case report form,summary report,etc.),blinding document,and randomness.This procedure will be performed once every 3 months.
Anticipated recruitment duration:April 1,2019 to December 31,2025
Anticipated study completion:December 31,2026
Study status:Design of study is ongoing.
Additional files
Additional file 1:Hospital Ethics Documentation.
Additional file 2:Informed consent.
Additional file 3:CONSORT checklist.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Taihe Hospital for providing experimental site and technical support.
Author contributions
Trial design:YPL;trial performance and data collection:XFG;trial authorization and manuscript review:YPL.Both authors approved the final version of this manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Financial support
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province,No.2015CKB713.Both authors declare that trial conception,design,performance and data collection,trial authorization,as well as the preparation of and decision to publish this manuscript were made independent of this funding organization.
Institutional review board statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of Taihe Hospital on December 8,2015 (approval No.2015GJJ-087) and will be performed in strict accordance with theDeclaration of Helsinkiformulated by the World Medical Association.
Declaration of participant consent
The authors certify that they will obtain the appropriate consent forms from all patients or their guardians.In the form,the patients or their guardians will give their consent for patients’ images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal.The patients or their guardians understand that the patients’ names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity,but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Reporting statement
This study followed the CONsolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) statement.
Biostatistics statement
The statistical methods of this study were reviewed by the biostatistician of Taihe Hospital,China
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by both authors before publication.
Data sharing statement
Individual participant data that underlie the results reported in this article,after deidentification (text,tables,figures,and appendices) will be shared.Study protocol and informed consent form will be available immediately following publication,without end date.Other data will be accessible from the corresponding author on reasonable request.Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal.Anonymized trial data will be available indefinitely at www.figshare.com.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal,and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix,tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially,as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
 Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Trials:Nervous System Diseases2020年1期
Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Trials:Nervous System Diseases2020年1期
- Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Trials:Nervous System Diseases的其它文章
- Effects of aerobic exercise on cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder:a parallel randomized controlled clinical trial
- Relationship of body mass index,abdominal obesity,and metabolic parameters with depression among reproductive-age women
- Information for Authors - Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Trials:Nervous System Diseases
