Effects of aerobic exercise on cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder:a parallel randomized controlled clinical trial
Kangguang Lin
The Affiliated Brain Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University (Guangzhou Huiai Hospital),Guangzhou,Guangdong Province,China
Abstract
Key words:aerobic exercise;bicycling;bipolar disorder;clinical trial;cognitive function;depressive symptoms;manic symptoms;mental illness
INTRODUCTION
Bipolar disorder is a common mental illness with symptoms of mania and depression.Mood fluctuations experienced by bipolar disorder patients can affect sleep,judgment,behavior,and thinking.Factors associated with heredity,neurobiochemistry,neuroendocrine status,nerve regeneration,psychological state,and social environment may be implicated in the occurrence of bipolar disorder (Anderson et al.,2012;Grande et al.,2016).An epidemiological study reported that 2.1% of Americans had bipolar disorder in the past 12 months (Harvard Medical School,2019).Further,82.9% of patients with bipolar disorder have been found to experience severe cognitive impairment (Kessler et al.,2005).At present,bipolar disorder is mainly treated by drug therapy combined with psychological intervention.
Aerobic exercise is a type of physical exercise designed to improve human endurance and enhance cardiopulmonary function.Aerobic exercise has been shown to improve cardiovascular status,reduce the risk of heart disease,reduce blood pressure,increase the level of high-density lipoprotein,regulate blood sugar and weight,improve lung function,reduce resting heart rate,regulate the psychological state of healthy volunteers,and effectively prevent and treat emotional disorders such as depression and anxiety (Smith et al.,2010;Hashida et al.,2017;Romero et al.,2017;Wang and Xu,2017).Aerobic exercise has been found to induce beneficial changes in the prefrontal cortex,anterior cingulate cortex,hippocampus,and corpus callosum of depressed patients (Li et al.,2017;Firth et al.,2018).Some researchers have proposed that exercise can be used as a first-line treatment for mild to moderate depression,with an effect that is superior to that of antidepressants (Carek et al.,2011;Stanton and Reaburn,2014).Aerobic exercise can also affect brain structure and cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder (Schuch et al.,2015;Metcalfe et al.,2016;MacIntosh et al.,2017;MacQueen and Memedovich,2017;Phillips,2017a;Verkooijen et al.,2017;Table1).However,no large-sample randomized controlled trials have compared the effects of aerobic exercise and normal activity on cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder.To address this issue,we designed the present parallel randomized controlled trial to analyze the effects of aerobic exercise on cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder.
PARTICIPANTS AND METHODS
Study design
This is a parallel randomized controlled clinical trial.
Study setting
This trial will be conducted at the Affiliated Brain Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University (Guangzhou Huiai Hospital),China.
Participants
Recruitment
Recruitment information will be posted on the bulletin boards of outpatient and inpatient departments,and released through the hospital’s official website and WeChat official account.Interested patients will contact the principal investigator via telephone,email,or WeChat.
Participant selection
Patients with bipolar disorder,who are treated in the Guangzhou Huiai Hospital,China,will be recruited.
Inclusion criteria (determined by members of the research team)
· Accordance with the characteristics of bipolar disorder as defined in The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,4th(American Psychiatric Association,1994)
· Physical agility
· Age 18 to 60 years,either sex
· Provision of written informed consent
Exclusion criteria (determined by members of the research team)
· Previous history of aerobic exercise therapy or other forms of exercise therapy
· Nervous system disease or musculoskeletal disease/injury
· Cardiovascular or metabolic diseases that preclude exercise
· Hypertension
· Suicidal tendencies
· Low intelligence
· Other situations that might limit the degree to which the participant is able to undergo aerobic exercise
· Participation in other clinical trials
Withdrawal criteria
Patients who meet one or more of the following criteria during the trial will be withdrawn from this study:
· Aggravation,serious adverse events,or poor compliance
· Cannot complete the follow-up assessments
During the trial,the research team will provide a set transportation subsidy for all patients.
Interventions
In the aerobic exercise group,the patients will individually perform 30 minutes of bicycling indoors,4 days per week,for 30 consecutive days.The exercise intensity will be 50-70% of the maximum heart rate (220-age).
In the control group,the patients will perform recreational activities with a normal intensity,such as making handicrafts,reading,singing,and walking,for 30 minutes,4 days per week,for 30 consecutive days.
The original drug treatment regimen will be unchanged in both groups.
Outcome measures
Primary outcome measure
· The difference in the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Bat-tery (MCCB) score between baseline and at 12 months
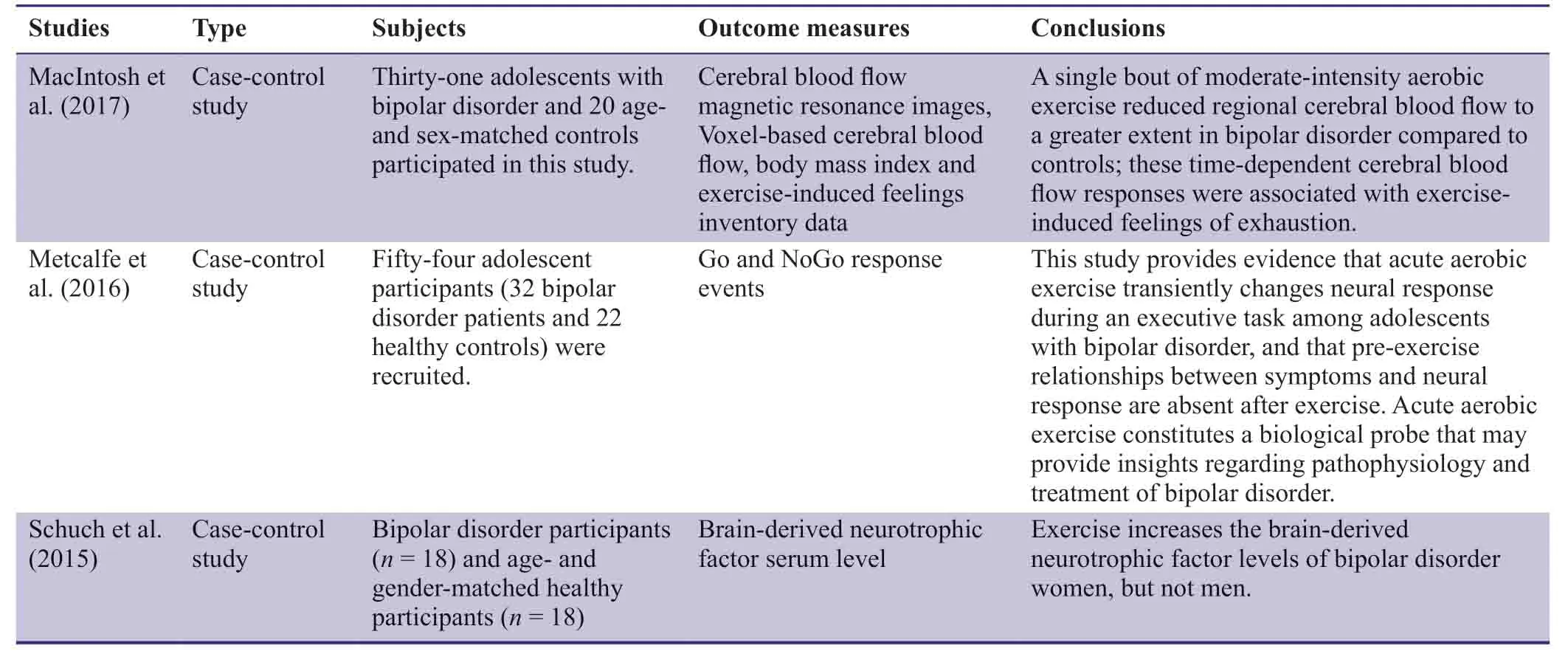
Table1:Previous clinical study regarding aerobic exercise for bipolar disorder
Neurocognitive function was evaluated using the MCCB.The MCCB includes the following tests:Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia:Symbol Coding;Category Fluency:Animal Naming;Trial Making Test:Part A;Continuous Performance Test-Identical Pairs;Wechsler Memory Scale-3rdEd;Letter-Number Span;Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised;Brief Visuospatial Memory Test-Revised;Neuropsychological Assessment Battery:Mazes;Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test:Managing Emotions.Scores range from 0-80,with the highest score representing good cognitive function (Shi et al.,2015).
Secondary outcome measures
· MCCB score at baseline and at a 3-month follow-up assessment
· Recurrence rate:Rates of recurrent depression and/or mania at 12 months after the exercise intervention
· Depressive symptoms:Depressive symptoms will be assessed using the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale at baseline,4-week,4-month,and 12-month follow-up assessments.The Hamilton Depression Rating Scale contains 17 items,including depressed mood,guilt,suicide,initial insomnia,middle insomnia,delayed insomnia,changes in work and interests,psychomotor retardation,agitation,anxiety,somatic anxiety,gastrointestinal somatic symptoms,general somatic symptoms,somatic genital symptoms,hypochondriasis,changes in insight,and weight loss.Scores range from 0-54,with the highest score representing severe depression (Hamilton,1960).
· Manic symptoms:Manic symptoms will be evaluated using the Young Mania Rating Scale at baseline,4-week,4-month,and 12-month follow-up assessments.The Young Mania Rating Scale includes 11 items,including mood,motor activity-energy,sexual interest,sleep,irritability,speech (rate and amount),language-thought disorder,thought content,disruptive-aggressive behavior,appearance,and insight.Scores range from 0-30,with the highest score representing severe mania (Young et al.,1978).
· Incidence of adverse events:The incidence of adverse events will be collected within 12 months of follow-up.Adverse events could include the exacerbation of existing depressive or manic symptoms/signs,or laboratory abnormalities,the presentation of new diseases or laboratory abnormalities,and may or may not be related to aerobic exercise.A specified individual will be responsible for collecting data regarding adverse events during the study,and will record the symptoms,degree of severity,occurrence time,duration,treatment measures,and treatment process on the case report form.This individual will also evaluate the relationships between adverse events and aerobic exercise.In the event of an adverse event,the study physician may decide whether to terminate the study based on the patient’s condition.Serious adverse events will be reported to the main researcher and ethics committee immediately.
Trial procedure
Figure1 contains a flow chart of the study protocol.The schedule of outcome assessments is shown in Table2.

Figure1:Trial flow chart.
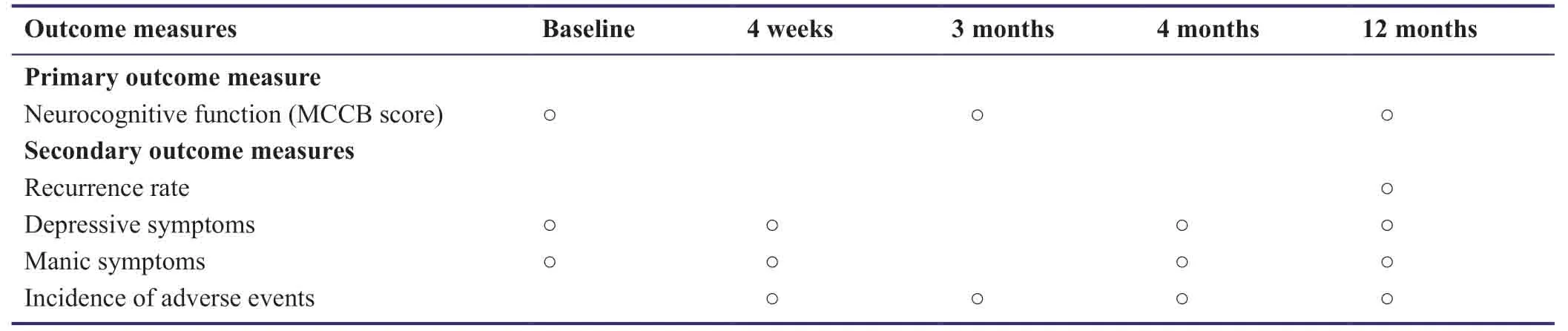

Table2:Schedule of outcome assessments
Sample size
In a preliminary test conducted by the authors,the MCCB score was reduced by about 10.0 in the aerobic exercise group,and by about 8.0 in the control group.The combined standard deviation was 4.45.Taking a power value of 0.9 with a significance level ofα= 0.05,the calculated sample size will ben= 86 according to a ratio of 1:1.Assuming a patient loss rate of 20%,the sample size will be at leastn= 104.Thus,the final sample size will ben= 105 per group,for a total of 210 cases.
Randomization
Non-participating statisticians will use randomized block design to divide the 210 patients into an aerobic exercise group and a control group.According to admission time,groups of 6 adjacent patients will be grouped into blocks,for 35 blocks in total.The patients in each block will be numbered from 1-6.Three numbers will be randomly selected from a certain position in the random number table for each participant in each block,and each participant will be numbered according to the value of the random number.Those with a random number assignment of 1-3 in each block will enter the aerobic exercise group,and those with a random number assignment of 4-6 will enter the control group.
Each grouping scheme will be placed into an opaque envelope with a code written on the outside.The corresponding numbered envelope will be opened after each patient enters the study.The patient will be grouped according to the scheme in the envelope.
Blinding method
Because the interventions in the aerobic exercise and control groups will clearly differ,the participants will be informed regarding group allocation.However,the evaluators will be blind to group allocation.
Ethical approval
This trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Affiliated Brain Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University (Guangzhou Huiai Hospital),China on July 24,2017 (approval No.2017026) (Additional file 1).This trial had been registered in the ClinicalTrials.gov (identifier:NCT03353337) on November 27,2017.Protocol version (1.0).Any changes to the study protocol will be approved by the ethics committee and the patient's informed consent will be regained,with changes made at ClinicalTrials.gov.This study will be performed in strict accordance with theDeclaration of Helsinkiformulated by the World Medical Association and relevant national laws and regulations.
A researcher or designated representative will explain the purpose,duration,required procedures,risks,and potential benefits of the study to the participant,and give them information regarding the main contact person of the clinical trial.The patients will sign the written informed consent form (Additional file 2) before entering the trial.If new benefits,risks,or side effects are found during the study,the participants will be informed immediately.
The writing and editing of the study report will be performed in accordance with the Standard Protocol Items:Recommendations for Interventional Trials (SPIRIT) (Additional file 3).Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal.Anonymized trial data will be available indefinitely at www.figshare.com.
Statistical analysis
In accordance with the intention-to-treat principle,data from all participants who will perform one intervention and complete the baseline evaluation will be analyzed.For case data for participants who did not complete the entire course of treatment,data from the last observation period will be analyzed using the last observation carry forward method.All data will be analyzed using SPSS 23.0 software (IBM Corp.,Armonk,NY,USA).Measurement data will be compared between the groups using parametric/nonparametric tests based on data distribution.Count data will be compared between groups using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test.A value ofP< 0.05 will be considered statistically significant.
Data collection and management
The researchers will maintain a case report form for all participants.The principal investigator will be blinded to the data until the trial is complete.All patient names will be replaced by four digits.Data checks and reviews will be performed before data locking.Once the input data are saved,the system will not allow any user to modify the input data.The system will automatically back up the system data in real time.The database will be monitored by a complete audit trail,and will record all added,modified,and deleted user information.The original data will be kept for at least 5 years after the experimental results.
Data quality control and audits
Inspectors from Guangzhou Huiai Hospital will be responsible for supervising the data collection and analysis,researcher training,participant compliance,and research supervision.The inspectors will ensure that the researchers strictly follow the trial scheme,relevant standard operating procedures,guiding principles,and regulatory requirements during the trial.At the end of the trial,the inspectors will check all the documents in the research center and archive them.
The trial audit committee will be composed of persons who are not directly involved in the trial.This clinical trial will be audited to determine whether the implementation of the trial,data recording,and analysis are consistent with the trial scheme,clinical trial management specifications,and regulatory requirements.The audits will be carried out every six months after the start of the test.
Confidentiality
The privacy of all participants will be protected.The personal information of patients will be accessed only when required by the ethics committee and the medical management department.Any public report addressing the results of this trial will not disclose the personal data of the participants.
DISCUSSION
Limitations
Because the participants will be bipolar disorder patients,the evaluation indexes will often include subjective scales such as the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery,Hamilton Depression Rating Scale,and Young Mania Rating Scale.Although the evaluators will receive unified training and a consistency test before the evaluation,the results will be influenced by subjective factors.Objective evaluation indexes such as imaging may be added in the future.
Generalizability
The aerobic exercise used in the trial is bicycling,which requires simple equipment and is expected to be relatively easy for patients to implement.If bicycling is found to improve cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder,this will represent a new element of clinical treatment.
Explanation
Previous studies have found that aerobic exercise has an impact on cerebral blood flow,serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor,brain structure,and cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder (Schuch et al.,2015;Metcalfe et al.,2016;MacIntosh et al.,2017;MacQueen and Memedovich,2017;Phillips,2017a;Verkooijen et al.,2017).However,no studies have compared the effects of aerobic exercise and normal activity on cognitive function in patients with bipolar disorder.Aerobic exercise may disperse negative mood in bipolar disorder patients and improve their psychological state.Simultaneously,aerobic exercise increases oxygen intake,improves brain and cardiopulmonary functions,and affects the secretion of cytokines (Schuch et al.,2015;MacQueen and Memedovich,2017;Phillips,2017a;Verkooijen et al.,2017),which are associated with mood state.The above changes may regulate depression and anxiety (Metcalfe et al.,2016;Phillips,2017b;Ott et al.,2019).Furthermore,aerobic exercise may increase opportunities for communication between patients with bipolar disorder and others,and this social interaction could improve emotional state.Aerobic exercise is an important treatment consideration because patients may more readily accept it compared with traditional medicine and psychotherapy.
TRIAL STATUS
Registration time:November 27,2017
Recruitment time:December 1,2017
Study completed:December 31,2020
Trial status:Active,recruiting.
Additional files
Additional file 1:Hospital Ethics Approval (Chinese).
Additional file 2:Informed Consent Form (Chinese).
Additional file 3:SPIRIT checklist.
Author contributions
Study design,manuscript writing,and approval of the final version of this manuscript:KL.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that the research is conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that can be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Financial support
None.
Institutional review board statement
This study will be performed in strict accordance with theDeclaration of Helsinkiformulated by the World Medical Association.This trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of Guangzhou Huiai Hospital,China on July 24,2017 (approval No.2017026).
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they will obtain all appropriate consent forms from the participants and their legal guardians.In the forms,the participants and their legal guardians will give their consent for participants’ images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal.The participants or their legal guardians understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity.
Reporting statement
The writing and editing of the study report will be performed in accordance with the Standard Protocol Items:Recommendations for Interventional Trials (SPIRIT).
Biostatistics statement
The statistical methods of this study were reviewed by the biostatistician of Guangzhou Huiai Hospital,China.
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by the author before publication.
Data sharing statement
Individual participant data that underlie the results reported in this article,after deidentification (text,tables,figures,and appendices).Data will be available immediately following publication,with no end date.Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal.Anonymized trial data will be available indefinitely at www.figshare.com.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal,and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix,tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially,as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
 Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Trials:Nervous System Diseases2020年1期
Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Trials:Nervous System Diseases2020年1期
- Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Trials:Nervous System Diseases的其它文章
- Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative brain protection in patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery under inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane:a randomized controlled study
- Relationship of body mass index,abdominal obesity,and metabolic parameters with depression among reproductive-age women
- Information for Authors - Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Trials:Nervous System Diseases
