PMC模型下的h-边容错诊断数
张念蓬 朱强


摘要:系统级诊断是多处理器系统设计和维护中的重要方面,通过诊断参数来衡量系统的容错性能。传统的诊断参数都是在假设系统中仅有处理器发生故障的情形下得到的,但是在实际情形中,系统中的处理器和链接都可能发生故障。该文研究了新的系统级诊断参数—h-边容错诊断数。当系统G中的故障边数不超过h时,G中包含的可以被全部识别的最大故障点数称为系统G的h-边容错诊断数。通过对一般图中公共邻点数的限制,证明了PMC模型下一般图的h边容错诊断数。文中确定了k-元n-方体、平衡立方体、交换立方体和交换折叠立方体4类网络在PMC模型下的h-边容错诊断数,为衡量系统在点边混合故障情形下的容错性能提供了有效参数。
关键词:多处理器系统;PMC模型;混合故障诊断;h-边容错诊断数
中图分类号:O614
DOI:10.16152/j.cnki.xdxbzr.2020-05-012
h-edge tolerant diagnosabilities under the PMC model
ZHANG Nianpeng, ZHU Qiang
(School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xidian University, Xi′an 710071, China)
Abstract: System-level diagnosis is an important aspect in the design and maintenance of multiprocessor systems, the fault tolerance performance of multiprocessor system is measured by diagnostic parameters. Traditional diagnostic parameters are obtained under the assumption that only the processor in the system has failed. However, in the actual situation, both processors and links in the system may fail. In this paper, a new system-level diagnosis parameter, h-edge tolerant diagnosabilities is studied. When the number of fault edges in the system G does not exceed h, the maximum number of fault points included in the system G that can be guaranteed to be identified is called the system′s h-edge tolerant diagnosabilities. By limiting the common adjacent points in general graphs, the number of h-edge tolerant diagnosabilities in PMC models is proved. In this paper, the h-edge fault tolerant diagnosabilities for the following four types of networks is determined: k-ary n-cubes, balanced hypercubes, exchange hypercubes and exchange folded hypercubes under the PMC model, which provides an effective parameter for measuring the fault-tolerant performance of multiprocessor systems in the case of mixed faults.
Key words: multiprocessor system; PMC model; hybrid faulty diagnosis; h-edge tolerant diagnosabilities
随着大规模多处理器系统中包含的处理器数目不断增多,系统中的处理器及其之间的链接就不可避免地出现故障。因此,处理器的故障诊断已经成为了系统容错性能研究中的一个重要问题。多处理器系统往往以互连网络作为拓扑结构,用点表示处理器、边表示处理器之间的链接来建立图论模型。通过研究互连网络的可靠性可以反映出相应的多处理器系统的容错性能。
系统级诊断是识别系统中故障节点和非故障节点的过程,也是多处理器系统的故障诊断中最重要的方式之一。系统中处理器之间的测试结果称为该处理器的症状,所有测试结果组成的集合称为系统的一个综合病症。系统级故障诊断充分利用了多处理器系统中每一个处理器的测试能力,让处理器之间进行相互测试,通过诊断算法对系统的综合病症进行分析来识别出故障节点的所在。根据测试的定义和结果假设的不同可以建立不同的诊断模型,如PMC模型、MM模型和BGM模型等[1-5]。PMC模型作为最著名的系统级诊断模型之一,由Prearata,Metze和Chien[6]在1976年提出。在PMC模型中,两个节点可以互相测试,当且仅当节点之间存在一条链接。假设测试节点是无故障的,则被测节点的测试结果是可靠的;否则,测试结果是不可靠的。一个系统的可诊断数是使得系统中包含的故障节点可以被全部识别的最大故障点数,通常是假设系统中某一节点的所有邻点同时发生故障而得到的。但是在大规模多处理器系统的实际运行中,这种情形出现的概率是极小的。为了更好地衡量系统的故障诊断能力,Lai提出了条件诊断数[7],从理论上提高了多处理器系统的容错性能。随后,t/k条件诊断数、g-好邻条件诊断数和h-额外条件诊断数等故障诊断参数被相继提出,目前,这些参数在PMC模型下的許多网络中得到研究[8-12]。
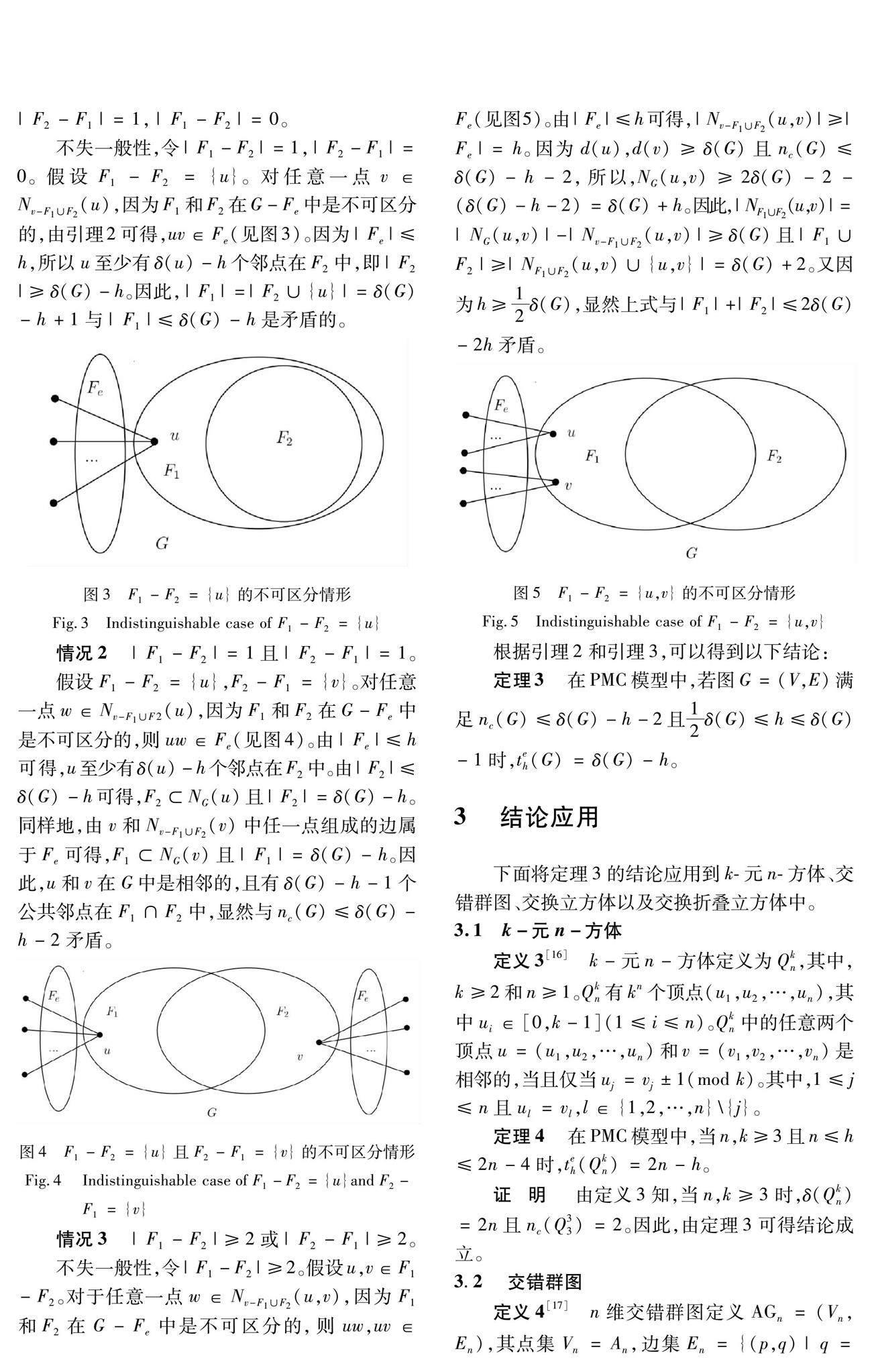
上述的各類诊断参数都是在假设系统中只有节点发生故障的情形下提出的。然而在实际情形中,系统中的节点和边都可能发生故障。为了更好地衡量系统在点边混合故障情形下的可靠性,Zhu[13]提出了h-边容错诊断数。作为传统诊断数的一种推广,h-边容错诊断数是假设系统中故障链接不超多h时,使系统是t-可诊断的最大故障点数。因此,h-边容错诊断数可以在实际情形中更好地衡量多处理器系统的容错性能。随后,Wei和Xu[14]证明了在PMC模型中k-正则图的h-边容错诊断数如下:
定理1[9] 在PMC模型中,令k-正则图G=(V,E)满足g(G)≥4且nc(G)≤k-1。当0≤h≤k时,则teh (G)=k-h。
然而许多著名的互连网络中的h-边容错诊断数不能通过定理1得到,如当k,n≥3时,k-元n-方体Qkn和交错群图AGn的围长等于3;当s≠t时,交换立方体EH(s,t)和交换折叠立方体EFH(s,t)不是正则的。本文将h-边容错诊断数的结果推广到一般图中,证明了在PMC模型中,对于满足nc(G)≤δ(G)-h-2的图G,当12δ(G)≤h≤δ(G)-1时,G的h-边容错诊断数为δ(G)-h。通过该结论,k-元n-方体、交错群图、交换立方体以及交换折叠立方体在PMC模型下的h-边容错诊断数可以被确定。
1 准备知识
给定一个简单无向图G=(V,E),V(G)和E(G)分别表示G的顶点集和边集。e=uv表示G中以u和v为端点的边e,同时称u和v是相邻的,e与u,v是连接的。对于图G中任意一点u,NG(u)定义为u在G中的所有相所有相邻顶点组成的集合。d(u)=|NG(u)|称为u的度,G中最小的度数记为δ(G),即δ(G)=min{d(u)|u∈V}。对于G中的任意两点u和v,nc(u,v)记为u和v的公共邻点数,nc(G)=max{nc(u,v)|u,v∈V}。令F1,F2V,F1ΔF2=(F1∪F2)-(F1∩F2)。令F是图G的任一边集,则G-F是在G中去掉F包含的所有边而导出的子图。
在PMC模型中,给定图G及其一个综合病症δ。G的点集F一致于δ当且仅当F中包含的所有节点都是故障的,并且所有不在F中的节点都是无故障的。因为故障节点的测试结果是不可靠的,所以一个故障点集F可能会一致于多个综合病症。我们把所有一致于故障集F的综合病症组成的集合记为δ(F)。两个故障集F1和F2是可区分的,当且仅当δ(F1)∩δ(F2)=;否则,F1和F2是不可区分的。
定义1[15] 一个系统称为t-可诊断的,如果当系统中发生故障的节点数目不超过t时,所有的节点都能被准确地识别是否故障。系统的可诊断数定义为使得G是t-可诊断的最大值,记为t(G)。
4 结 语
多处理器系统容错性能一直是人们关心的重要问题之一。PMC模型下的h-边容错诊断数相比以往诊断参数可以更好地衡量系统在点边混合故障情形下的容错性能,因而提高了系统在实际情形中的故障诊断性能。本文首先给出了在PMC模型下一般图G的h-边容错诊断数的单调性质。然后证明了当一般图G满足nc(G)=δ(G)-h-2时,G的h-边容错诊断数为teh (G)=δ(G)-h,其中,12δ(G)≤h≤δ(G)-1。相比目前的研究成果,该结论不再局限于正则图,同时也不对网络的围长作出要求,可以更广泛地应用到多处理器系统在PMC模型下的点边混合故障诊断。最后,将结论应用到k-元n-方体、交错群图、交换立方体和交换折叠立方体4类网络中,得到表2中的结果。
参考文献:
[1] DAHBURA A T,SABNANI K K, KING L.The comparison approach to multiprocessor fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers,1987,36(3):373-378.
[2] LOMBARDI F.Comparison-based diagnosis with faulty comparators[J]. Electronics Letters,1986,22(22):1158.
[3] RANGARAJAN S, FUSSELL D. Probabilistic diagnosis algorithms tailored to system topology[J].Fault-Tolerant Computing: The Twenty-First International Symposium, 1991:230-237.
[4]PELC A.Undirected graph models for system-level fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers,1991,40(11):1271-1276.
[5]RANGARAJAN S, FUSSELL D.Diagnosing arbitrarily connected parallel computers with high probability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers,1992,41(5):606-615.
[6]PREPARATA F P, METZE G, CHIEN R T.On the connection assignment problem of diagnosable systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Electronic Computers, 1967,12(6):848-854.
[7] LAI P L, TAN J J M, CHANG C P, et al.Conditional diagnosability measures for large multiprocessor systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers,2005,54(2):165-175.
[8] CHANG N W, HSIEH S Y.Conditional diagnosability of (n, k)-star graphs under the PMC model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2018, 15(2):207-216.
[9] WEI Y L, XU M.The g-good-neighbor conditional diagnosability of locally twisted cubes[J]. Journal of the Operations Research Society of China, 2018, 6(2):333-347.
[10]WANG S Y,WANG Z H, WANG M J S, et al.g-good-neighbor conditional diagnosability of star graph networks under PMC model and MM* model[J]. Frontiers of Mathematics in China, 2017,12(5):1221-1234.
[11]JIRIMUTU J, WANG S Y.The 1-good-neighbor diagno-sability of alternating group graph networks under the PMC model and MM* model[J].Recent Patents on Computer Science, 2017,10(2):108-115.
[12]張兴, 李莉莉, 陈敬,等. 平衡立方体的h-额外连通度及h-额外条件诊断数[J].高校应用数学学报A辑, 2019, 34(1):72-82.
ZHANG X, LI L L, CHEN J,et al. The h-extra connectivity and h-extra conditional diagnosability of balanced hypercubes[J].Applied Mathematics A Journal of Chinese University, 2019, 34(1):72-82.
[13]ZHU Q, LI L L, LIU S Y,et al.Hybrid fault diagnosis capability analysis of hypercubes under the PMC model and MM model[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2019,758:1-8.
[14]WEI Y L, XU M.Hybrid fault diagnosis capability analysis of regular graphs[J]. Theoretical Computer Science,2019,760(14):1-14.
[15]DAHBURA A T,MASSON G M.An 0(n2.5) faulty identification algorithm for diagnosable systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Computers,1984,33(6):486-492.
[16]翟登鑫.k元n立方体的条件容错强Menger边连通性[J].沈阳大学学报(自然科学版),2019,31(2):168-172.
ZHAI D X.Strong Menger edge-connectivity with conditional fault tolerance of k-ary n-cubes[J].Journal of Shenyang University(Natural Science), 2019, 31(2):168-172.
[17]谭秋月.交错群图AGn的5类子图可靠性研究[J].西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,42(11):21-24.
TAN Q Y. On Reliability of five kinds of subgraphs of alternating group graph AGn[J].Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science), 2017, 42(11):21-24.
[18]LOH P K K, HSU W J, PAN Y.The exchanged hypercube[J].IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems,2005,16(9):866-874.
[19]蔡学鹏, 杨伟, 任佰通,等. 交换折叠超立方体的连通度[J].井冈山大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(4):8-11.
CAI X P, YANG W, REN B T, et al.The connectivity of exchangedfolded hypercube[J].Journal of Jinggangshan University(Natural Science), 2019,40(4):8-11.
(编 辑 李 静)

