Methanolic extract of Clausena excavata promotes wound healing via antiinflammatory and anti-apoptotic activities
Shaymaa Fadhel Abbas Albaayit, Abdullah Rasedee, Noorlidah Abdullah, Yusuf Abba
1Department of Biology, College of Science, University of Baghdad, Baghdad-Iraq
2Department of Veterinary Laboratory Diagnosis, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
3Institute of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
4Department of Veterinary Pathology and Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the anti-inflammatory properties of methanolic extract of Clausena excavata in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated macrophages (J774A.1) and the effect on skin wound in a rat model through determining cytokine levels and gene expressions. Methods: The effects of methanolic extract of Clausena excavata on in vitro viability and TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and nitric oxide release by LPS-activated J774A.1 cells were determined. In addition, relative expressions of BAX, BCL-2 and COX-2 genes were examined in healed wounds of rats. Results: The methanolic extract of Clausena excavata was not toxic to J774A.1 cells at the highest dose of 400 µg/mL. It decreased levels of TNF-α and IL-6, while increasing IL-10 level in LPSactivated J774A.1 cells and in the healed wounds of rats. The methanolic extract of Clausena excavata also inhibited nitric oxide production in LPS-activated J774A.1 cells. The BAX and COX-2 genes were downregulated while the BCL-2 gene was upregulated in the healed wound of rats. Conclusions: The methanolic extract of Clausena excavata promotes wound healing via its anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activities.
KEYWORDS: Clausena excavata leaves; Anti-inflammatory cytokines; Cytotoxicity; Apoptotic genes
1. Introduction
Inflammatory response plays a key role in the development of diseases such as cancers, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and arthritis[1,2]. In inflammation, macrophages perform three main functions: antigen-presentation, phagocytosis, and immunomodulation through the production of cytokines. In fact, macrophages play critical roles in the initiation, maintenance, and resolution of inflammation[3]. Macrophages can be stimulated and activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a major component of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Activated macrophages produce various pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Pro-inflammatory cytokines in acute inflammation include tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), while anti-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-10 (IL-10) are responsible for the inhibition of inflammation and regulation and maintenance of homeostasis[4,5]. IL-10 acts as a potent inhibitor of macrophage function by blocking the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12, reducing the harmful effects of excessive inflammatory responses[6].
Clausena excavata (C. excavata) Burm. f. (Rutaceae family) is a small shrub that grows widely in Southeast Asia. All parts of this plant have been reported to exhibit various pharmacological properties including anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, immunomodulatory, antioxidative, anti-microbial, and anti-fungal effects. The leaves of this plant are used in folklore medicine in the treatment of diseases and conditions such as wounds, malaria, headache, fever, abdominal pain, dysentery, pulmonary tuberculosis, diarrhea, cold, snake-bites, and poisoning[7].
Our previous studies showed that the methanol extract of C. excavata leaves exhibited high antioxidant, wound and gastric ulcer healing activities[8,9]. However, the effects of the methanol extract of C. excavata on the release of inflammatory cytokines by macrophages and on wound healing are not clear. Similarly, its effect on the expression of the apoptosis-related genes in healed skin wound tissues has not been reported. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory properties of the methanolic extract of C. excavata in LPS-activated macrophage cells (J774A.1) and the effect on skin wound in a rat model.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Plant material and extraction
C. excavata plant was authenticated by Dr. Shamsul Khamis (Resident Botanist) of the Biodiversity Unit, Institute of Bioscience, Universiti Putra Malaysia (Specimen voucher: TI-013201- CE). Fresh leaves were dried at room temperature, powdered and extracted according to the procedure described previously[7,9]. Briefly, the extraction was done using a 1:5 dried plant: petroleum ether (weight to volume) suspension for 3 d. The filtrate was collected and subjected to further extraction with methanol. All filtrates from methanol extraction were evaporated to dryness using a rotary evaporator under reduced pressure at 45 to 50 ℃ to obtain the crude extract. The yield of the methanolic extract of C. excavata (wt. of crude extract /wt. of fresh plant) was 0.94%.
2.2. Cell maintenance
The J774A.1 macrophage cell line (American Type Culture Collection, USA) was cultured in Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium, fortified with 10% fetal bovine serum and incubated under 5% CO2humidified incubator at 37 ℃. Upon reaching 80% confluency, the cells were detached using a cell scraper, followed by centrifugation at 2 000 ×g for 10 min. The cells were stained with trypan blue stain and counted in a Neubauer chamber. One µL of 1 mg/mL LPS was added to each treatment well of the 96-well plate according to methods described previously[10].
2.3. 3-(4, 5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2.5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) colorimetric assay
The vehicle for the initial stock of drug was 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide. The J774A.1 cells were seeded at a density of 5.0 × 103cells/mL in 100 µL suspensions and then 100 µL methanolic extract of C. excavata at concentrations of 25, 50, 100, 200 and 400 µg/mL were added to the respective well of a 96-well plate and incubated for 24 h under 5% CO2at 37 ℃. Cell viability was determined by adding 20 µL of MTT reagent to each well and the plate incubated for another 3 h under 5% CO2at 37 ℃. The purple formazan crystals formed were solubilized with 100 µL dimethyl sulfoxide and the plate was kept in the dark at room temperature for approximately 30 min. The absorbance was determined using a microplate reader (Tecan, Austria) at 570 nm with reference at 630 nm. Each experiment was repeated thrice in triplicate wells for each concentration[8].
2.4. Determination of nitrite concentration
Nitric oxide (NO) released by J774A.1 cells in the culture medium was determined by a quantitative colorimetric assay based on the Griess reaction[11]. Aliquots of 50 µL of cell culture supernatants were incubated with 50 µL of Griess reagent (Sigma, USA). After 10 min at room temperature, the optical density was measured using a microplate reader (Tecan, Salzburg, Austria) at 570 nm. Nitrite concentration was determined from the calibration curve of 0 to 30 µM sodium nitrite standard solutions.
2.5. Cytokine determination
A total of 500 µL J774A.1 cell suspension with concentrations adjusted to 3 × 105cells/mL were seeded into 24-well plates, cultured for 24 h and treated with 200, 100, and 50 µg/mL methanolic extract of C. excavata. The control cell was treated with 0.5 µg/mL dexamethasone. The plates were incubated for 1 h under the same culture conditions. One µL of 1 mg/mL LPS was then added to the wells with methanolic extract and dexamethasone treatment to activate the macrophages. The supernatants were subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Cusabio Biotech Co. Ltd, USA) to determine IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 cytokine concentrations according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The cytokine concentrations were calculated from the standard curve. All experiments were run in triplicates.
2.6. Wound infliction in rats
Wound infliction was done as previously described[9]. Briefly, 30 rats were divided into five groups of six animals each. A 2 cm wound was inflicted on the skin at the dorsal neck of the rat, disinfected, and locally anesthetized with 0.1 mL lignocaine hydrochloride. Group 1 (negative control) was treated with 20 mg/mL gum acacia in normal saline (vehicle) and served as a negative control; Group 2 received 0.2 mL intrasite gel (Smith and Nephew, UK) and served as a positive control; Groups 3, 4, and 5 were treated with 0.2 mL methanolic extract of C. excavata at concentrations of 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg body weight. All treatments were topically applied twice daily for 14 d, beginning on the first day of wound infliction.
2.7. Cytokine activity in healed wound
After the experimental period, the animals were euthanized and healed wound tissue homogenates were obtained for TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 determinations. Briefly, 0.2 g of wound tissues were collected from each rat at 14 days post-wound infliction and homogenized on ice with 2 mL of cold PBS using a tissue Ruptor (Qiagen, Germany). The homogenate was centrifuged at 10 000 ×g for 10 min and the supernatant collected in microcentrifuge tubes and stored at -80 ℃ until analysis. Estimation of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 concentrations in the supernatant was done with ELISA kits (Cusabio Biotech Co. Ltd, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All experiments were performed in triplicates.
2.8. Gene expression profile
Total RNA was isolated from healed wound tissue collected on day 14 post-wound infliction using the RNeasy Tissue Mini kit (Qiagen, USA). One µg of total RNA was used for the PCR reaction. Reverse transcription was carried out using the Tetro cDNA synthesis kit (Bioline, USA). Subsequently, 1 µL of cDNA was amplified by realtime PCR using appropriate primers (Supplementary Table). The amplification for all gene expression assays was performed using the Universal SYBR Green PCR Kit (BIO-RAD, Malaysia) and results were generated by the CFX Manager System Software (Ver. 1.6, BIO-RAD Laboratories). To ensure the specificity of target genes, all the primer pairs were analyzed by Primer-BLAST (NCBI). The expression of the genes was normalized with the housekeeping genes, β-actin and GAPDH. The comparative Cq method was used to calculate the relative amount of transcripts in all groups in comparison with normal control using CFX Manager System Software (BIO-RAD, Malaysia).
2.9. Statistical analysis
All data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and statistical significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Turkey post hoc test using Graph Pad Prism 6.0 statistical software with significant differences set at P<0.05.
2.10. Ethical statement
This study was carried out in compliance with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, University of Malaya (ISN/22/007/2013/1111/SFA). All experimental animals were humanely handled and procedures performed under sterile conditions at the Experimental Unit, University of Malaya, Malaysia.
3. Results
3.1. Cytotoxicity assay
The MTT cytotoxicity assay showed that the viability of the LPSactivated J774A.1 cells after treatment with 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/mL methanolic extract of C. excavata for 24 h was (133.0 ± 17.1)%, (131.3 ± 16.3)%, (139.0 ± 6.3)%, (121.7 ± 3.3)% and (91.0 ± 7.0)%, respectively. The result showed that the methanolic extract of C. excavata was not toxic to J774A.1 cells even at the highest concentration of 400 µg/mL. The viability of J774A.1 cells peaked at 100 µg/mL methanolic extract of C. excavata (Figure 1).
3.2. Effects of the methanolic extract of C. excavata on NO production, as well as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 levels in LPS-stimulated J774A.1 macrophage
LPS significantly increased the NO production while the methanolic extract of C. excavata at all concentrations and dexamethasone decreased NO production in the LPS-activated J774A.1 cells (P<0.05) (Figure 2). In addition, the methanolic extract of C. excavata significantly decreased TNF-α and IL-6 levels in LPS-activated J774A.1 cells (P<0.05), while increasing IL-10 level (Figure 3), suggesting that the extract had anti-inflammatory effects.
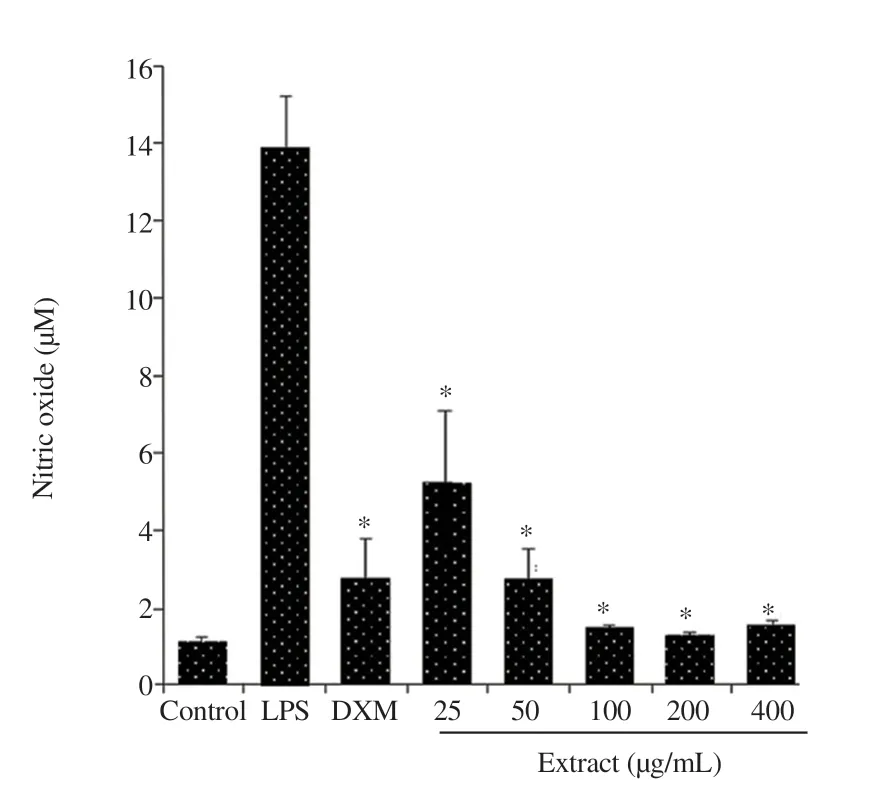
Figure 2. Effect of the methanolic extract of Clausena excavata leaf and dexamethasone (DXM) on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated J774A.1 cells. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). *Means significantly different from those of the LPS control at P < 0.05.
3.3. Cytokines production in wound tissue
LPS showed significant increases in IL-6 and TNF-α and a decrease in IL-10 production while treatment with the methanolic extract of C. excavata reversed the changes induced by LPS (P<0.05), especially at the high dose. Similarly, intrasite gel reduced IL-6 and TNF-α while increased IL-10 production (Figure 4).
3.4. Gene expression of wound tissue
The expression of BAX gene was down-regulated and BCL-2 gene up-regulated in the healed wound tissues of rats treated with the methanolic extract of C. excavata. However, the expression of BAX gene in the treatment with the methanolic extract of C. excavata did not differ (P>0.05) significantly from that of the control. The relative expression of COX-2 in healed wounds, although down-regulated in the methanolic extract of C. excavata-treated group, was not significantly (P>0.05) different from the control or the intrasite geltreated group (Figure 5).

Figure 3. Effects of the methanolic extract of Clausena excavata extract on TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated J774A.1 cells at 24 hours post-treatment. Dexamethasone (DXM, 0.5 µg/mL) served as a positive control. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). *Means significantly different from those of the LPS control at P < 0.05.

Figure 4. Effects of the methanolic extract of Clausena excavata leaf on the production of (A) TNF-α, (B) IL-6, and (C) IL-10 in healed wounds of rats. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). MECE-LD, MECE-MD, MECE-HD: methanolic extract of Clausena excavata leaf at 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg. *Means significantly different from those of the control at P < 0.05.

Figure 5. Real-time PCR mRNA expression of BAX, BCL-2 and COX-2 genes in skin wound tissue of rats. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6).
4. Discussion
Numerous chemical compounds have been isolated from plants that showed excellent medicinal properties against various ailments[12]. C. excavata is widely used in traditional medicine for treating different diseases in various cultures worldwide. However, the mechanism of action, efficacy, and side-effects of the chemical components of this plant are largely unknown[13,14]. Our previous study showed that the methanolic extract of C. excavata demonstrates promising wound healing and anti-ulcer properties via their antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities[8,9].
Inflammation involves the release of several cytokines by macrophages, such as TNF-α and IL-6[15]. In wound healing, the balance between the production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines ultimately determines the rate of healing. The modulation of cytokine production in tissue injury and damage with treatment would be an appropriate approach to facilitate healing and recovery[16]. In tissue injury and inflammation, the macrophages, through the production of inflammatory cytokines[17], play a predominant role, especially during the chronic phase. The cell is also the primary inflammatory modulator in the formation of granulation tissue. Thus, one of the most commonly used cell line as an in vitro model to determine inflammatory responses is the macrophage, J774A.1 cell line[18-20].
The methanolic extract of C. excavata was not toxic to J774A.1 cells since treatment with the high concentration of the extract at 400 µg/mL did not appreciably decrease cell viability. In fact, the quercetin and myricetin contents of this extract have been shown to enhance the growth of normal human skin fibroblast and keratinocyte cells[8].
Among the inflammatory mediators released by macrophages is NO, a signaling protein that regulates function, growth, and death of immune and inflammatory cells. NO is partly responsible for the induction of necrosis and apoptosis. In infections, LPS released by bacteria activates macrophages to produce large amounts of NO that enhances vasodilation and leukocyte activities during the subsequent inflammatory response[6,21]. In our study, the methanolic extract of C. excavata dose-dependently inhibited NO production in the LPS-activated J774A.1 cells. Not only the extract but also its active components scavenge NO radical (·NO) through antioxidant activities, facilitating tissue recovery and healing by reducing damage caused by the inflammatory responses. The antioxidant activities of the methanolic extract of C. excavata can be attributed to its rich phenolic content[7,22].
TNF-α stimulates the expression of other inflammatory cytokines, mediators, and collagenase, causing apoptosis and cytostatic/cytocidal effects on endothelial cells. The result of these effects is the suppression of angiogenesis and retardation of woundhealing[5,23]. IL-6 is a mediator of acute-phase response that induces matrix metalloproteinase synthesis by fibroblasts and inflammatory cells, which in turn facilitates angiogenesis. IL-10 is a late cytokine produced by several cell types and acts as a potent inhibitor of macrophage function by blocking the synthesis of IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and COX-2. IL-10 also protects cells and tissues from the deleterious effects of free radicals[5,6,24]. In the present study, the methanolic extract of C. excavata decreased production of TNF-α and IL-6 and promoted the production of IL-10 in the macrophage, J774A.1 cell line, suggesting anti-inflammatory effects.
The methanolic extract of C. excavata is rich in polyphenols such as furocoumarins and flavonoids that regulate inflammation via inhibition of the MAPK/NF-κB pathways[9]. Furocoumarins and flavonoids were also reported to possess antioxidant and immune-modulating properties[7,9,25-30]. One of the oxidant molecules produced by phagocytic cells is the reactive oxygen species (ROS)[31,32]. Excessive production of ROS stimulates apoptosis through the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and translocation of JNK to the mitochondria. Thus, based on these findings, the anti-inflammatory effect of the methanolic extract of C. excavata is proposed to occur partially through the stimulation of the production of anti-inflammatory mediators by macrophages and the anti-oxidative effects of its phenolic contents.
In skin injuries, such as burns, TNF-α expression was positively correlated with the expression of BAX and negatively correlated with BCL-2 protein[33]. Therefore, in healing conditions, the expression of TNF-α and BAX gene decreases while that of the BCL-2 gene increases. There is a direct association between the expression of the pro-apoptotic BAX protein, anti-apoptotic BCL-2 protein, and rate of wound healing[34]. The regulation in COX-2 expression is also important for effective wound healing as shown in the fetus, where down-regulation of COX-2 expression facilitates scarless wound healing[35]. In rat wound, the methanolic extract of C. excavata promotes healing, as shown by decreased expression in TNF-α, and BAX and COX-2 genes and increased expression of the BCl-2 gene.
In conclusion, the methanolic extract of C. excavata decreased TNF-α and IL-6 and increased IL-10 release in J774A.1 cells and in healed rat wound tissue. In addition, the extract down-regulated BAX and COX-2 and up-regulated BCL-2 gene expressions, suggesting apoptosis-inhibition effect. Thus, the methanolic extract of C. excavata effectively promotes wound healing via the inhibition of the production of inflammatory mediators and apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the University of Malaya PPP Grant no. PG059-2013A.
Authors’contributions
NA and AR conceptualized and designed the experiment. SFAA conducted the experiments. SFAA and YA interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript draft. NA, AR, SFAA and YA read and approved the final manuscript.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2020年5期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2020年5期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Emerging mosquito-borne arboviral infection Zika - An epidemiological review
- Crebanine N-oxide, a natural aporphine alkaloid isolated from Stephania hainanensis, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells
- Piperlongumine inhibits cell growth and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells
- Pear pomace water extract reduces adiposity in vivo and in vitro by activating the AMPK-dependent pathway
- Diversity of Phlebotomine sand flies (Diptera: Psychodidae) in mountainous and plain areas of an endemic focus of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran
