BEGO短种植体在骨量不足后牙区种植修复的应用研究
黎锐锋 汪祥 张泳 阳冬青 王佩
【摘要】 目的 评价BEGO短种植体在骨量不足后牙区种植修复的应用效果。方法 选取因后牙缺失采用BEGO系统种植修复的患者60例, 随机分为对照组和实验组, 每组30例。实验组采用短种植体, 对照组采用常规种植体。Ⅰ期手术全部采用埋入式种植, 3~6个月行Ⅱ期手术, 2~3周内完成永久固定修复。对比两组种植体冠-种植体高度比(C/I)、12~18个月后种植体存留率、X线检查边缘骨吸收、患者满意度。结果 实验组患者植入42枚种植体, Ⅱ期手术时均获得骨结合。Ⅱ期修复后, 上磨牙区一枚植体负重1个月时松动取出, 其余经12~18个月随访观察, X线片检测种植体周骨组织稳定, 骨吸收为(0.54±0.36)mm, C/I为(1.14±0.51), 种植成功率为97.62%, 患者满意度评分为0.9分。对照组患者植入48枚种植体, Ⅱ期手术时均获得骨结合。Ⅱ期修复后, 上磨牙区一枚植体负重2个月时松动取出, 其余经12~18个月随访观察, X线片检测种植体周骨组织稳定, 骨吸收为(0.58±0.38)mm, C/I为(1.02±0.42), 种植成功率为97.92%, 患者满意度评分为1.0分。两组种植体存留率比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组边缘骨吸收水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组患者满意度评分比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 在骨量不足后牙區, 通过植入BEGO系统短种植体, 可以避开复杂手术, 降低风险, 缩短修复所需时间, 并有较高的成功率, 值得在临床应用推广。
【关键词】 BEGO短种植体;骨量不足;后牙;种植修复
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.08.003
【Abstract】 Objective To evaluate the application effect of BEGO short implants placed in posterior region with constrained bone for implant restoration. Methods A total of 60 patients who were implanted and repaired with BEGO system due to missing posterior teeth were randomly divided into control group and experimental group, with 30 cases in each group. The experimental group received short implants, and the control group received conventional implants. All patients received submerged dental implants at stage Ⅰ operation. Stage Ⅱ operation was performed in 3-6 months, and the permanent fixation was completed in 2-3 weeks. The crown-implant ratio (C/I), implant retention rate after 12-18 months, X-ray marginal bone absorption and patient satisfaction were compared between the two groups. Results Patients in the experimental group were implanted with 42 implants, and osseointegration was obtained during stage Ⅱ operation. After the stage Ⅱ restoration, one implant in the upper molar area was loosened and taken out when it was loaded for 1 month. The rest were followed up for 12-18 months. X-ray showed that the bone tissue around the implant was stable, the bone absorption was (0.54±0.36) mm, the C/I was (1.14±0.51), the implant success rate was 97.62%, and the patient satisfaction score was 0.9 points. Patients in the control group were implanted with 48 implants, and osseointegration was obtained during stage Ⅱ operation. After the stage Ⅱ restoration, one implant in the upper molar area was loosened and taken out when it was loaded for 2 months. The rest were followed up for 12-18 months. X-ray showed that the bone tissue around the implant was stable, the bone absorption was (0.58±0.38) mm, the C/I was (1.02±0.42), the implant success rate was 97.92%, and the patient satisfaction score was 1.0 poin. There was no statistically significant difference in implant retention rate between the two groups (P>0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in marginal bone absorption level between the two groups (P>0.05). There was no statistically significant in satisfaction score between the two groups (P>0.05). Conclusion Implanting BEGO short implants in posterior region with constrained bone can avoid complex surgery, reduce risk, shorten time required for repair and the success rate is high. It is worthy of clinical promotion and application.
【Key words】 BEGO short implants; Constrained bone; Posterior teeth; Implant restoration
自20世纪60年代Branemark教授创立骨结合理论以来, 种植修复已成为牙列缺损及缺失的重要修复方法。牙齿缺失后牙槽骨会发生进行性骨吸收, 从而导致骨量不足。对牙槽骨高度不足的患者, 使用常规长度植体需采用骨增量手术, 这些手术会引起患者术中术后不适, 增加额外费用, 使修复治疗周期延长。短种植体的应用可以扩大种植适应证, 避开骨增量手术, 降低风险及费用并缩短治疗周期。本研究对BEGO短种植体进行12~18个月临床应用追踪观察, 评价其临床效果。现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1. 1 一般资料 选取2018年1月~2019年8月本院诊治的进行种植术治疗的后牙缺失患者60例, 随机分为实验组和对照组, 每组30例。实验组中, 男18例, 女12例;年龄28~63岁, 平均年龄(40.62±9.03)岁。对照组中, 男16例, 女14例;年龄25~59岁, 平均年龄(39.28±8.77)岁。两组患者一般资料比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 具有可比性。
1. 2 材料器械
1. 2. 1 植入材料 使用BEGO系统S-Line系列植体。短种植体[1]:直径为4.1 mm、4.5 mm、5.5 mm, 长度为7 mm或8.5 mm的植体。常规植体:直径为4.1 mm、4.5 mm、5.5 mm, 长度为10 mm或11.5 mm的植体。
1. 2. 2 手术器械 BEGO系统手术工具, 常规手术器械, Bien-Air种植机。
1. 3 方法 口内检查拟行种植手术区域的牙槽骨吸收量、牙龈黏膜状态、咬合空间、邻牙状况, 并做全身评估。术前拍摄锥形束CT(CBCT), 测量术区骨高度和宽度, 选择适宜的种植体型号。术区阿替卡因局部浸潤麻醉, 切开翻瓣完整暴露术区, 按BEGO种植系统要求常规备洞, 植入BEGO种植体(不进行任何骨增量或上颌窦提升手术), 上覆盖螺帽, 初稳扭力≥20 Ncm, 严密缝合, 术后7~10 d拆线。下颌3~4个月、上颌4~6个月行Ⅱ期手术, 2~3周内完成单冠或联冠永久固定修复(螺丝固位)。
1. 4 观察指标及判定标准 对比两组种植体冠-种植体高度比(crown-implant ratio, C/I)、12~18个月后种植体存留率、X线检查边缘骨吸收、患者满意度。
1. 4. 1 C/I测量方法 在全景片中, 种植体肩台至牙冠功能尖的垂直距离计为上部修复体的高度(C), 种植体肩台至种植体根尖的垂直距离计为种植体长度(I), 两数相除得出 C/I。
1. 4. 2 种植体边缘骨高度吸收测量方法 通过根尖片以种植体肩台为基准线, 记录种植体近远中牙槽骨高度, 并进行校准。牙槽骨吸收变化 HC=HL-HV(HL为完成修复当天数值, HV为随访当天数值)。
1. 4. 3 满意度评价方法 应用视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue scale, VAS)来评价患者满意度[1]。即对术中的疼痛、一般不适, 对术后的肿胀、出血、疼痛的进行VAS评分。分数越低满意度越高。
1. 5 统计学方法 采用SPSS22.0统计学软件对数据进行处理。计量资料以均数±标准差( x-±s)表示, 采用t检验;计数资料以率(%)表示, 采用χ2检验。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
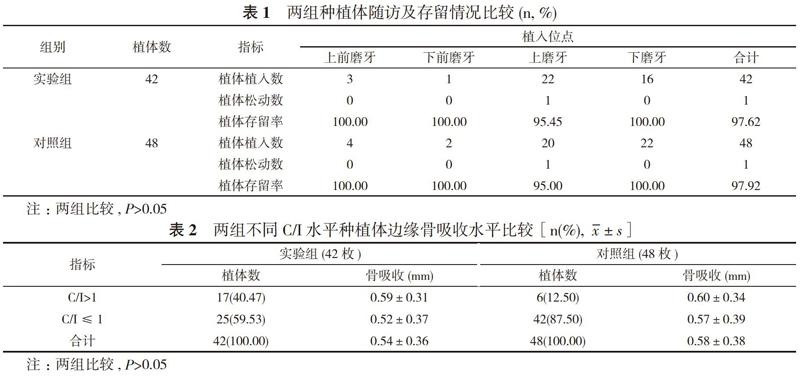
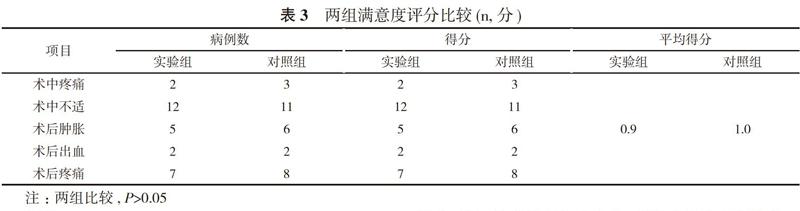
实验组患者植入42枚种植体, Ⅱ期手术时均获得骨结合。Ⅱ期修复后, 上磨牙区一枚植体负重1个月时松动取出, 其余经12~18个月随访观察, X线片检测种植体周骨组织稳定, 骨吸收为(0.54±0.36)mm, C/I为(1.14±0.51), 种植成功率为97.62%, 患者满意度评分为0.9分。对照组患者植入48枚种植体, Ⅱ期手术时均获得骨结合。Ⅱ期修复后, 上磨牙区一枚植体负重2个月时松动取出, 其余经12~18个月随访观察, X线片检测种植体周骨组织稳定, 骨吸收为(0.58±0.38)mm, C/I为(1.02±0.42), 种植成功率为97.92%, 患者满意度评分为1.0分。两组种植体存留率比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。两组边缘骨吸收水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。两组患者满意度评分比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表3。
3 讨论
3. 1 C/I与存留率 传统观点认为C/I=1是保证良好种植远期效果的最低限度, 在功能性负荷的状态下, C/I>1会存在更高的失败风险[1]。Sohn等[2]对122枚短种植体进行跟踪(最长9年), 发现C/I与种植体失败率之间无关联。Ghariani[3]发现C/I的增加并没有影响短种植体的存活率及边缘骨吸收。本研究观察结果与上述研究[2, 3]相似。
BEGO S-Line系列种植体为柱状高度密螺纹种植体, 种植体表面经喷砂加酸蚀处理, 具有良好的生物相容性及初期稳定性[4], 根部较大挤压型螺纹设计可增加种植体周围骨密度。本研究中其短期临床效果满意, 长期骨结合效果有待进一步追踪观察。
3. 2 边缘骨吸收 种植体周围骨质稳定是种植修复成功的基础。Abrahamsson等[5]认为, 种植体-基台界面存在细菌的定植, 细菌进入种植体深部产生局部的炎症灶, 从而引起种植体周骨吸收。另一个引起种植体周骨吸收的可能原因是粘结时多余的粘结剂溢出至龈沟内, 溢出的粘结剂流至骨组织的位置, 导致了骨吸收[6]。
本研究中, 实验组与对照组的边缘骨吸收没有明显差异且吸收较少, 可能与以下因素有关:①使用的BEGO S-Line系列种植体其颈部有光滑设计, 能有效降低细菌在种植体-基台界面的定植;②种植体-基台间内六角结合内圆锥的结合方式, 可抗旋转并利于轴向传导应力, 颈部微螺纹设计利于分散咀嚼力[7-10];③所有的植体均为螺丝固位的固定修复, 不存在粘结剂残留的问题。
3. 3 满意度 短种植体作为种植技术的新发展, 可应用于骨高度不足的后牙区, 避免了复杂骨增量手术, 减少了术后并发症, 同时能够缩短治疗时间, 降低手术费用, 减少术后不适感[11-13]。本研究中短种植体经短期的临床观察, 能获得较高的成功率, 与常规植体比较患者满意度无统计学差异。
综上所述, 在骨量不足后牙区, 通过植入BEGO系统短种植体, 可以避开复杂手术, 降低风险, 缩短修复所需时间, 并有较高的成功率, 值得在临床应用推广。
参考文献
[1] 吴茴, 林野, 邱立新, 等. 口腔短种植体临床效果五-十年回顾性研究. 中国口腔种植学杂志, 2017, 22(1):47-50.
[2] Sohn DS, Kim WS, Lee WH, et al. A retrospective study of sintered porous-surfaced dental implants in restoring the edentulous posterior mandible: up to 9 years of functioning. Implant Dentistry, 2010, 19(5):409-418.
[3] Ghariani L, Segaan L, Rayyan MM, et al. Does crown/implant ratio influence the survival and marginal bone level of short single implants in the mandibular molar? A preliminary investigation consisting of 12 patients. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 2015, 43(2):127-135.
[4] 劉长虹.钛种植体表面特征对种植体周细胞功能的影响.中国口腔种植学杂志, 2008, 13(2):82.
[5] Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T, Lindhe J, et al. Soft tissue response to plaque formation at different implant systems. A compatative study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res, 1998, 9(2):73-79.
[6] Schwedhelm ER, Lepe X, Aw TC. A crown venting technique for the cementation of implant-supported crowns. Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2003, 89(1):89-90.
[7] 张翔, 徐晶, 曲哲, 等. BEGO种植系统的临床应用及疗效观察. 口腔医学, 2014, 34(5):388-390.
[8] 徐晶, 张翔, 曲哲, 等. 上颌前牙区BEGO种植体即刻修复的临床效果评价. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2014, 30(8):510-511.
[9] 张翔, 曲哲, 贺平. BEGO牙种植系统临床应用体会. 中国当代医药, 2013, 20(15):23-24,26.
[10] 徐晶, 张翔, 曲哲,等. BEGO种植系统近期临床效果评价. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2013, 29(4):223-224.
[11] 冯建国, 李慧, 张春梅, 等. BEGO种植体在改善牙缺失患者咀嚼功能与生存质量中的作用探析. 中国医学创新, 2016(24):107-110.
[12] 张翔, 曲哲, 贺平,等. 2627颗BEGO种植体临床效果观察. 口腔疾病防治, 2013, 21(10):548-551.
[13] 莫嘉骥, 乔士冲, 张枭, 等. 后牙区短种植体(≤6 mm)单冠修复3~5年临床效果评价. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2019(3):235-239.
[收稿日期:2020-01-13]

