Transmission of cryptococcosis by liver transplantation: A case report and review of literature
Gustavo de Sousa Arantes Ferreira, Andre Luis Conde Watanabe, Natalia de Carvalho Trevizoli,Fernando Marcus Felippe Jorge, Carolina de Fatima Couto, Priscila Brizolla de Campos,Gabriel Oliveira Nunes Caja
Gustavo de Sousa Arantes Ferreira, Andre Luis Conde Watanabe, Natalia de Carvalho Trevizoli,Fernando Marcus Felippe Jorge, Carolina de Fatima Couto, Priscila Brizolla de Campos, Gabriel Oliveira Nunes Caja, Department of Liver Transplantation, Instituto de Cardiologia do Distrito Federal, Brasilia 70673900, Brazil
Abstract BACKGROUND Cryptococcosis is a fungal infection caused by the yeast-like encapsulated basidiomycetous fungus of the Cryptococcus neoformans (C.neoformans) species complex.These fungi are ubiquitous in soil and bird droppings, and infection by them is an important global health concern, particularly in immunosuppressed patients, such as organ transplant recipients and those infected by the human immunodeficiency virus.The fungus usually enters the body through the respiratory tract, but extremely rare cases of infection acquired by transplantation of solid organs have been reported.CASE SUMMARY We report a case of disseminated cryptococcosis in a liver transplant recipient,diagnosed 2 wk after the procedure.The patient initially presented with fever,hyponatremia and elevated transaminase levels, manifesting intense headache after a few days.Blood cultures were positive for C.neoformans.Liver biopsy showed numerous fungal elements surrounded by gelatinous matrix and sparse granulomatous formations.Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain showed multiple small lesions with low signal in T2, peripheric enhancement and edematous halo, diffuse through the parenchyma but more concentrated in the subcortical regions.Treatment with amphotericin B for 3 wk, followed by maintenance therapy with fluconazole, led to complete resolution of the symptoms.The recipients of both kidneys from the same donor also developed disseminated cryptococcosis, confirming the transplant as the source of infection.The organ donor lived in a rural area, surrounded by tropical rainforest, and had negative blood cultures prior to organ procurement.CONCLUSION This case highlights the risk of transmission of fungal diseases, specifically of C.neoformans, through liver graft during liver transplantation.
Key words: Cryptococcosis; Liver transplantation; Cryptococcus neoformans; Case report;Immunosuppression; Fungal infection
INTRODUCTION
Cryptococcosis is a fungal infection caused by the yeast-like encapsulated basidiomycetous fungus of theCryptococcus neoformans(C.neoformans) species complex.This fungus is ubiquitous in soil and tree bark and is found in particularly great concentrations in the nitrogen-rich environment that is present in the droppings of birds, bats and other vertebrates.It can also be found in up to 50% of domestic dust samples[1].There are two pathogenic species:C.neoformansandCryptococcus gattii(C.gattii).Approximately 95% of reported cryptococcal infections are caused byC.neoformansserotype A, with the remaining 5% caused by other serotypes or byC.gattii[2].
The fungus presents as an oval or globular yeast at microscopy, with a diameter of 3 mm to 8 mm, and is characteristically surrounded by a mucopolysaccharidal capsule[1].The capsule has a high content of melanin, produced as a result of the action of the phenoloxidase enzyme.Brain tissue is rich in substrates for phenoloxidase action, which may at least in part explain the tropism of Cryptococcus for the central nervous system (CNS)[1].Cryptococcus has several characteristics that underlie increased virulence, including thermotolerance and variations in composition of its cell wall and capsule.There are reports of infection by Cryptococcus in dogs, cats, horses, sheep, snakes, and porpoises.Birds appear to be relatively resistant to this infection, possibly due to their high body temperature[3].
The most common site of symptomatic cryptococcosis is the CNS, which is affected in about 80% of patients with the disease, and usually presents as a subacute or chronic meningitis with or without hydrocephalus, or less commonly as cerebral cryptococcomas, which may be confused for brain neoplasms in imaging evaluation[1].The most common symptoms are headache, fever and confusion, but ataxia,amaurosis and cranial nerve palsies may also occur[8,9].Signs of meningeal irritation are present in about 50% of patients[10].The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion may occur as a complication of cryptococcal meningitis and can cause severe hyponatremia[11].There are reports from endemic areas in Brazil whereC.gattiiis the main causative agent of meningeal cryptococcosis, butC.neoformansremains the most common agent throughout the world[12].
Pulmonary disease is the second most common manifestation of cryptococcosis,presenting as pulmonary consolidations, nodular or cavitary infiltrates, miliary pattern, or rarely as pleural effusion, and may be unilateral or bilateral[1].Symptoms of pulmonary disease include coughing, fever, pleuritic chest pain, and hemoptysis,but it can be asymptomatic in up to 30% of patients[1,13].
Cutaneous cryptococcosis can present as nodular lesions with a central umbilication, mimicking molluscum contagiosum, or as areas of swelling and erythema, similar in aspect to bacterial cellulitis.The most common sites for cryptococcal skin lesions are the lower extremities (65% of cases) and the trunk(26%)[14].Subcutaneous abscesses are a rare manifestation of cryptococcosis, described mainly in solid organ transplant recipients[15].
Cryptococcal peritonitis is clinically similar to spontaneous bacterial peritonitis,and usually occurs in cirrhotic patients[16].Hepatic cryptococcal infection is rare but may occur in disseminated disease, usually manifesting as cholestatic jaundice that may rapidly progress to liver failure and death[17].Disease affecting more than one organ is considered as disseminated cryptococcosis.Vertical transmission of cryptococcosis during pregnancy is extremely rare[1].
The diagnosis of cryptococcosis can be made by direct microscopy of sputum,bronchoalveolar lavage, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood, urine, or organ biopsy.The use of India ink is helpful in the identification of fungal elements, having a 50%-80%sensitivity.Fungal culture can also be obtained from the same kind of samples, and colony growth is usually observed in 48 h to 72 h using mediums such as Sabouraud agar or blood agar, and having a sensitivity of 70%-90%.A latex agglutination test can be used to detect Cryptococcus antigens in serum and CSF, having a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 98%.Titers above 1:8 strongly suggest active cryptococcosis,and titration can be used as a parameter to assess the response to antifungal treatment.Serum antigen does not cross the blood-brain barrier, and therefore does not interfere with titers detected in the CSF.Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay can also be used for the detection of both antigens and antibodies to Cryptococcus, with even greater sensitivity.Analysis of the CSF usually shows pleocytosis with lymphocytosis, an increase in protein content, and a decrease in glucose[1,2].Imaging of the brain in patients with cryptococcosis affecting the CNS can show leptomeningeal enhancement, encephalomalacia, infarcts, cerebellitis, hydrocephalus, transverse myelitis, or the presence of cryptococcomas.In these patients, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is more sensitive than computerized tomography (CT),which can be normal in 50% of patients[10,18,19].Analysis of the ascitic fluid in patients with cryptococcal peritonitis is highly variable but seldom shows significant pleocytosis and usually shows an increase in lymphocytes[16].
Recommendations for the treatment of cryptococcosis vary according to the site of infection and the immunological status of the host.Amphotericin B (0.7 mg/kg daily)in combination with flucytosine or fluconazole for 2 wk to 10 wk is the recommended induction treatment for cryptococcal meningitis, followed by a maintenance treatment of 12-24 mo with daily fluconazole or itraconazole.Refractory cases should be treated with higher doses (3-6 mg/kg daily) of amphotericin B for another 6-10 wk.High doses of fluconazole (800-2000 mg daily) can be used if amphotericin B is not tolerated or unavailable.Intrathecal infusion of amphotericin B has multiple side effects and should only be used in refractory cases[20].Voriconazole and posaconazole can also be treatment alternatives for these patients.Echinocandins appear to have no efficacy against Cryptococcus.Intermittent lumbar punctures can be of great importance in the first weeks of the treatment to alleviate intracranial hypertension, which is a significant source of mortality in cryptococcal meningitis.
There is no consensus in the current literature regarding persistent inflammatory lesions in the brain during treatment.The complete regression of these lesions can take a long time, and analysis of the CSF is of limited value to assess the presence of Cryptococcus in the brain parenchyma.If the lesions persist after the full treatment course has been completed, and the patient remains asymptomatic and with negative cultures, the suspension of the antifungal drugs appears to be safe, as long as adequate clinical and imaging follow-up can be obtained[21].
Then the curtain fell before it once more, and the Prince, after many ceremonies, was presented with a raven which perched upon his wrist, and was conducted slowly back to the iron gate
Treatment for pulmonary cryptococcosis consists of fluconazole (200 mg to 400 mg daily) for 6-12 mo.
In solid organ transplant recipients afflicted with cryptococcosis, an important adjuvant for antifungal treatment will involve reduction of the immunosuppressive drug regimen to the lowest possible levels, in order to increase host cellular immunity against the fungus[3].
Incidence of cryptococcosis in solid organ recipients has been estimated at 0.3% up to 5%, being the third most commonly occurring invasive fungal infection in this population[8,22].Mortality ranges from 15%-20% but may be as high as 40% when infection of the CNS is present[23,24].Among solid organ transplant recipients, lung and liver recipients appear to the be the most vulnerable to cryptococcosis, but mortality is higher in heart transplant patients[25,26].The onset of the disease after the transplant usually ranges from 8-21 mo but may occur many years after the procedure[6,8,27,28].Patients who develop cryptococcosis more than 24 mo after transplantation are more likely to have CNS disease than those with early-onset disease[29].
Since many antifungals, such as fluconazole, are inhibitors of the cytochrome P450 enzymes, a reduction of about 40%-50% in the dose of tacrolimus may be warranted in order to maintain therapeutic drug levels[4].
Cirrhosis is an independent risk factor for the development of cryptococcosis,particularly for cryptococcal peritonitis, and the possibility that early-onset disease after the transplant actually represents an increase in the symptoms of preexisting disease must be considered[30-32].If adequately treated before the transplant,cryptococcosis is not a contraindication for liver transplantation[33].There are some reports on the transmission of Cryptococcus by organ transplantation, and early (less than 4 wk after the procedure) post-transplant cryptococcosis warrants consideration of donor transmission[6,34,35].There are well recorded cases of transmission by corneal[36,37], lung[38], kidney[39-41]and liver transplants[42-44].
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
At 14 d after the surgery, a 57-year-old male returned to the emergency room complaining of fever and malaise.
History of present illness
The patient reported fever (39 °C), chills and loss of appetite that had started 5 d after hospital discharge.
History of past illness
A 57-year-old male diagnosed with cryptogenic cirrhosis - with hepatic encephalopathy being the main manifestation of the disease - underwent liver transplant in a Brazilian tertiary care hospital.At the time of transplantation, the patient’s model for end-stage liver disease score was 14 and Child-Pugh classification was class B (8 points).Prior to the procedure, the patient had been admitted to the hospital several times for hepatic encephalopathy and suffered two major episodes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.Investigation for viral hepatitis and autoimmune disease had negative results, and there was no previous history of significant alcohol consumption.The patient worked as a farmer in a rural area located in the North of Brazil, had no comorbidities, and suffered from frequent and severe symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy in spite of optimal clinical treatment.He had a previous CT scan of the brain, with no abnormal findings, and both an ultrasound and a CT scan of the abdomen, which were unremarkable except for portal hypertension and liver cirrhosis.
The patient was submitted to orthotopic liver transplantation with a graft obtained from a cadaveric donor (53-year-old male), in whom brain death had been caused by a hemorrhagic stroke that occurred 3 d before organ procurement.The donor worked as a lumberjack in the rural area of the North region of Brazil and was reported as being previously healthy, having normal biochemical tests, and no evidence of ongoing infection at the moment of organ procurement.He had positive results for serological tests for anti-HBs and anti-HBc but negative result for the serological test for HBsAg;these findings suggested a resolved hepatitis B infection.The transplantation procedure was uneventful, with a total ischemia time of 9 h and 9 min, no intraoperative complications, and no need for blood product transfusions.The patient was discharged from the intensive care unit 3 d after the procedure and from the hospital 8 d after the transplant.
The patient had no significant comorbidities, other than the recent transplant.He had no pulmonary, neurological or genitourinary symptoms.His immunosuppressive drug regimen consisted of tacrolimus, mycophenolate and prednisone, with a blood level of tacrolimus of 11.4 ng/mL.
Physical examination
Physical examination was unremarkable, with absence of skin lesions, vital signs within the normal range of values, and no signs of infection in the surgical wound.Neurological examination was completely normal.The patient was admitted to the hospital for investigation.As he remained hemodynamically stable, admission to the intensive care unit was not deemed to be necessary.
Laboratory testing
Blood and urine cultures were obtained, producing growth ofC.neoformansafter 48 h in two separate blood cultures.Biochemical tests showed normal leukocyte and platelet counts, and levels of blood urea nitrogen and creatinine within the normal range.Remarkable findings were anemia (hemoglobin concentration of 8.1 g/dL;normal range: 13.5-17.5 g/dL), hyperbilirubinemia (total bilirubin of 5.3 mg/dL;normal range: 0.1-1.2 mg/dL), hyponatremia (sodium concentration of 119 mmol/L;normal range: 136-145 mmol/L), increased gamma-glutamyl transferase (referred to as GGT) (1470 UI/L; normal range: 9-48 UI/L), alanine aminotransferase (referred to as ALT) (45 UI/L; normal range: 7-56 UI/L) and aspartate aminotransferase (referred to as AST) (132 UI/L; normal range: 10-40 UI/L).A lumbar puncture was obtained,with the analysis of CSF showing values of glucose, protein and cytology all within normal range.CSF culture was negative for fungal growth.
Imaging examination
An ultrasound of the liver with doppler evaluation of the hepatic vessels was performed and gave normal results.An X-ray of the chest was also normal.An MRI of the brain was obtained, showing multiple small lesions with low signal in T2,peripheric enhancement and edematous halo, diffuse through the parenchyma but more concentrated in the subcortical regions (Figure 1).
MULTIDISCIPLINARY EXPERT CONSULTATION
A liver biopsy was obtained and investigated by histological analysis carried out by an expert in liver pathologies (Dr.ESM).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Histology of the liver biopsy showed a large number of fungal elements immersed in gelatinous matrix, in both liver parenchyma and portal spaces, with some of them surrounded by a loose histiocytic response (Figure 2).The patient was diagnosed with disseminated cryptococcosis, affecting both the CNS and the liver graft.
TREATMENT
Treatment was initiated with liposomal amphotericin B (3 mg/kg) in combination with fluconazole for 3 wk, followed by maintenance treatment with oral fluconazole(450 mg daily).Mycophenolate was discontinued and tacrolimus dosage was adjusted according to serum levels, which eventually stabilized around 8 ng/mL, with the patient taking 1 mg of tacrolimus on alternate days.The patient remained afebrile and asymptomatic after the amphotericin B treatment, showing marked decrease in total bilirubin levels (1 mg/dL) and progressive decrease in GGT levels (1162 UI/L).
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
Early disseminated cryptococcosis was also reported in the recipients of both kidneys obtained from the same donor of our liver transplant recipient; those transplants had occurred in hospitals located in different parts of the country.We concluded that the donor, while reportedly asymptomatic, had disseminated cryptococcosis that was transmitted by the grafts to the recipients.Our patient remained asymptomatic and with laboratory tests showing normal range of values for the 3.5 years of outpatient follow-up.The fluconazole dosage was progressively reduced to the current dosage of 150 mg daily.Control MRIs of the brain were obtained at 6, 12, 18 and 36 mo, all showing persistence of the brain lesions but with gradual reduction of the contrast enhancing halo around them.Liver biopsies were obtained at 4 and 16 mo, initially showing numerous granulomas containing oval fungal structures (Figure 3) and finally the absence of fungal structures, respectively.
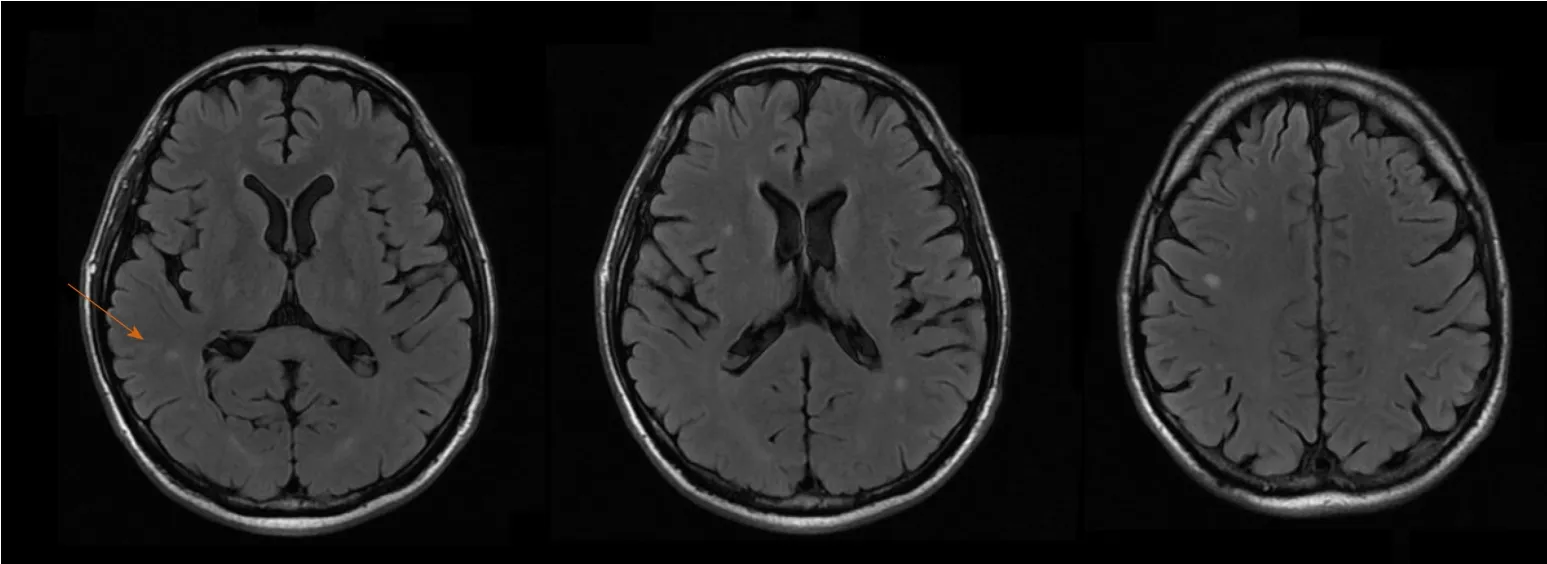
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
DISCUSSION
Diagnosis and treatment of disseminated cryptococcosis in recipients of solid organ transplantation remains a clinical challenge, given the unspecific nature of the initial symptoms, the need for reduction in immunosuppression - which may cause rejection, and the adverse reactions associated with antifungal treatment.In the case we report, diagnosis of disseminated disease was obtained by growth of Cryptococcus in blood cultures.The CSF cultures and direct microbiology tests were negative despite the presence of multiple brain lesions, highlighting the poor correlation between the presence of the fungus in the CSF and in the brain parenchyma.Serological tests were unavailable at our institution at that time.The patient also presented with severe hyponatremia, which may have been associated with CNS cryptococcosis infection, and increases the morbidity of the disease.The patient also had a marked increase in bilirubin and liver enzymes caused by fungal infiltration of the liver, which was diagnosed by liver biopsy and quickly improved after antifungal treatment was initiated.The fact that all recipients (both kidneys and liver) who received organs from the same donor reported here developed early disseminated cryptococcosis, makes transmission by the transplant the most likely means of contagion in this case.This impression is reinforced by the presence of Cryptococcus in the biopsies of all three transplanted organs.In the cases of suspected or confirmed transmission of cryptococcosis through a liver transplant previously reported in the literature, the most common outcome was the death of the organ recipient[17,31,44].Changet al[42]reported on a patient who developed hepatic and pulmonary cryptococcosis one week after a liver transplant and was successfully treated with amphotericin B.We have found no previous reports in the literature of long-term follow-up of a liver transplant recipient with disseminated cryptococcosis, which allowed us to document the complete clearance of fungal structures in the liver 16 mo after treatment was started, and the long-term persistence of brain lesions in a asymptomatic patient with no other signs of infection.
CONCLUSION
Cryptococcosis is a relatively common fungal infection in patients that undergo liver transplantation, causing significant morbidity and mortality in this population.The most severe form of disease is disseminated cryptococcosis, with infection reaching multiple organs through the bloodstream.Treatment involves both a reduction of the immunosuppressive drug regimen and prolonged antifungal treatment.While most cases of cryptococcosis in solid organ recipients is caused by reactivation of their latent disease due to immunosuppression, in rare cases, the infection may be acquired through the liver graft, which may be suspected in cases of early infection after the transplant.Maintenance of prolonged antifungal treatment, even in asymptomatic patients, is important, since complete elimination of viable fungal elements in liver tissue may take more than a year of treatment to be achieved.
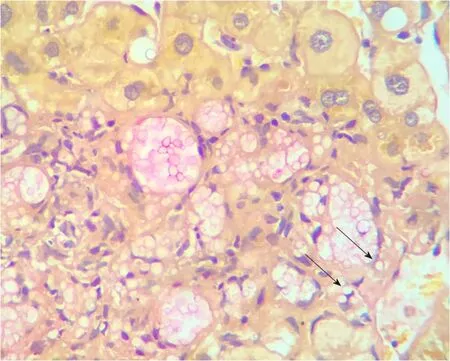
Figure 2 Liver biopsy at presentation.
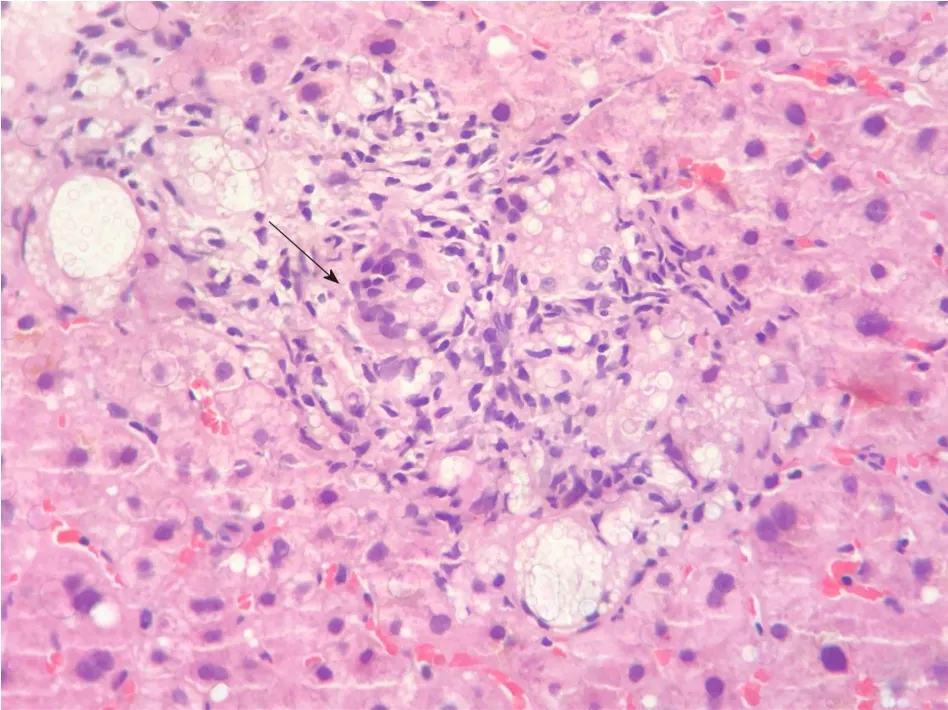
Figure 3 Follow-up liver biopsy at 4 mo.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the important contribution by Dr.Evandro Sobroza de Mello and the CICAP laboratory, in the diagnostic investigation and follow-up of the case reported, as well as in the elaboration of this manuscript.
 World Journal of Hepatology2020年5期
World Journal of Hepatology2020年5期
- World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 resolves Pringle maneuver in rats, both ischemia and reperfusion
- Drug and herbal/dietary supplements-induced liver injury: A tertiary care center experience
- Usefulness of Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer in noninvasive probing liver disease in the Vietnamese population
- Epidemiological profile of alcoholic liver disease hospital admissions in a Latin American country over a 10-year period
- Systemic review and network meta-analysis: Prophylactic antibiotic therapy for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
