High expression of squamous cell carcinoma antigen in poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the stomach:A case report
Lin Wang,Lei Huang,Lei Xi,Shi-Chang Zhang,Jie-Xin Zhang
Lin Wang,Shi-Chang Zhang,Jie-Xin Zhang,Department of Laboratory Medicine,The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University,Nanjing 210029,Jiangsu Province,China
Lei Huang,Department of Laboratory Medicine,Nanjing Medical University,Nanjing 210029,Jiangsu Province,China
Lei Xi,Department of Pathology,The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University,Nanjing 210029,Jiangsu Province,China
Abstract BACKGROUND Squamous cell carcinoma antigen(SCCA)is regarded as a specific indicator of epithelial malignancies and is widely used in the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma(SCC).However,the expression of SCCA in gastric adenocarcinoma has not been studied in detail.CASE SUMMARY A 52-year-old man was admitted to our hospital for a 2.5 cm × 2.5 cm ulcer at the antrum-body junction with dull pain and fullness in the upper abdomen for 2 mo.His pre-surgery serological testing results showed 0.51 ng/mL SCCA(reference interval,<1.5 ng/mL)and 9.9 ng/mL carcinoembryonic antigen(reference range,<4.7 ng/mL).He underwent radical distal gastrectomy and Roux-en Y anastomosis and was diagnosed with poorly differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma(Lauren classification:Diffuse)by pathological examination of the resected lesion.Immunohistochemistry showed that SCCA was highly expressed in the cytoplasm of cancer cells.After surgery,the patient received an S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for six cycles containing tegafur,gimeracil,and oteracil potassium.He showed no sign of recurrence or metastasis within 24-mo follow-up.CONCLUSION This is a frontal report of SCCA overexpression in poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the stomach.
Key Words:Squamous cell carcinoma antigen;Gastric adenocarcinoma;Protease inhibitor;Immunohistochemical staining;Differentiation;Case report
INTRODUCTION
Gastric cancer(GC)is a common malignancy and the second leading cause of cancer related death[1].Gastric adenocarcinoma,arising from the glands of the most superficial layer or the mucosa,accounts for more than 90% of all GC cases[2].The survival rate of GC is dismal,and the 5-year survival rate is generally between 30%-40%,except in Japan and Korea[3].Although the addition of trastuzumab to first line chemotherapy has improved the overall survival of some advanced patients,only 20%of patients benefit from this strategy[4,5].Researchers are still devoting to identify new effective therapeutic targets.
Squamous cell carcinoma antigen(SCCA)is a tumor marker for squamous cell carcinoma(SCC).It is overexpressed in neoplastic tissues of epithelial origin,such as cervical[6],esophageal[7],and head and neck SCCs[8].Elevated serum SCCA is often associated with therapeutic resistance and poor prognosis[9].However,SCCA expression has not been studied in depth neither in serum nor in tissue of GC patients.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 52-year-old man presented to our hospital complaining of dull pain and fullness in the upper abdomen for 2 mo,especially after eating.He reported no fever,diarrhea,hematemesis,black stool,or other discomfort.
History of present illness
The patient’s symptoms started 2 mo ago.He took domperidone but had no relief.
History of past illness
The patient had tuberculosis 20 years ago,and he had habits of drinking alcohol 150 mL per day and smoking 20 cigarettes per day for over 30 years.
Physical examination
Upon admission,the patient’s temperature was 37.0 °C,heart rate was 80 bpm,respiratory rate was 18 breaths per min,and blood pressure was 120/80 mmHg.Physical examination showed tenderness in the upper abdomen.
Laboratory examinations
Routine blood examination showed mild erythrocytopenia(4.19 × 1012/L).Serum carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA)level was 9.9 ng/mL(reference range,<4.7 ng/mL),and other serum tumor markers were normal,including CA19-9,CA724,SCCA,and α-fetoprotein.
Imaging examinations
Endoscopy showed a congestive mucosa in the gastric fundus with edema and an irregular ulcer approximately 2.5 cm × 2.5 cm in dimension at the antrum-body junction(Figure 1).Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography further revealed irregular thickening and enhancement of the wall of the gastric antrum near the pylorus(Figure 2).No abnormalities were found in the esophagus,duodenum,liver,pancreas,kidney,or bladder.
MULTIDISCIPLINARY EXPERT CONSULTATION
The patient should undergo radical distal gastrectomy.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The pathological examination of the distal stomach showed poorly differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma(Lauren classification:Diffuse),mostly signet-ring cells,and lymph node metastasis(pT3aN3aM0)(Figure 3).Immunohistochemical staining showed that the tumor cells were positive for CK-L(focal +++),CEA,SCCA(>90%,+++),and E-cadherin but negative for CD68,Her-2,p40,p63,CK5/6,CK7,CAM5.2,CK20,and Ki-67(Figure 4).
TREATMENT
The patient underwent radical distal gastrectomy and Roux-en Y anastomosis.A 4 cm× 3 cm × 2 cm mass was found in the greater gastric curvature that had penetrated the serosa,and multiple enlarged lymph nodes were found in the lesser gastric curvature.After surgery,he orally took 50 mg BID of tegafur,gimeracil,and oteracil potassium capsules for six cycles.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
During the follow-up period of 24 mo,the patient regularly came to our hospital for reexamination and he had no sign of recurrence or metastasis.
DISCUSSION
GC is one of the most common gastrointestinal malignancies worldwide,most of which are adenocarcinoma.Due to the high incidence of recurrence after resection and chemotherapy resistance,the 5-year overall survival rate of GC is less than 50%.Treatment of GC patients is extremely challenging due to patients being commonly treated in a uniform fashion irrespective of disease subtype.Existing traditional clinicopathologic criteria are inadequate for guiding individualized therapy[10].With the deepening of studies at the molecular level,some new GC subtypes based on molecular characteristics have been proposed,providing a roadmap for patient stratification,treatment options,and drug selection[11].Understanding the pathogenesis of GC and finding potential therapeutic targets to improve medical management and survival from this deadly disease are urgent tasks.
Here,we report a case of SCCA overexpression in gastric poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma.The specificity of this overexpression was further confirmed by its absence in gastritis tissue and well differentiated adenocarcinoma(Figure 5).SCCA,a member of the ovalbumin serpin(ov-serpin)/clade B serpin family,was originally isolated from SCC tissues of the uterine cervix by Katoet al[12]in the 1970s and used as the earliest marker to diagnose SCC.It has two subtypes with an identical 45-kDa molecular weight:SCCA1(Serpin B3)and SCCA2(Serpin B3);Both contain a key reactive center loop for interaction with the target protease and function as irreversible'suicide' inhibitors for cellular proteases through reactive center loop cleavage[13].This patient has been shown to have no sign of recurrence up to 24 mo.It seems that he has a better prognosis compared with other patients in the same TNM stage[14,15].Pettyet al[16]found that SCCA leads to entirely opposite outcomes in two non-small cell lung cancer subtypes-squamous carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
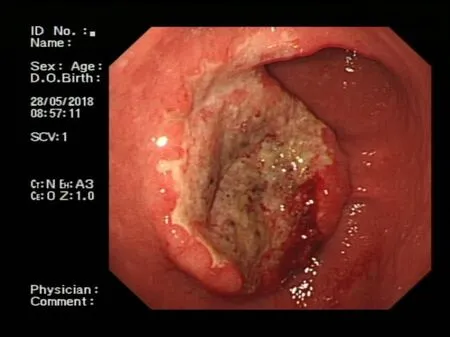
Figure 1 Endoscopic findings of the patient.Endoscopy showed a large,irregular,raised ulcer 25 mm × 25 mm in dimension at the antrum-body junction.

Figure 2 Findings from preoperative abdominal computed tomography.Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography revealed irregular thickening and enhancement of the wall(arrow).

Figure 3 Histological characteristics.Hematoxylin and eosin stain indicated poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with signet ring cells(200 × magnification).

Figure 4 Immunohistochemical staining characteristics.A:Immunohistochemical(IHC)staining showed strong squamous cell carcinoma antigen expression(+++)mainly in the cytoplasm of tumor cells(200 × magnification);B-D:IHC staining showed that the tumor cells were negative for p40,p63,and CK5/6(200 × magnification);E and F:IHC staining showed that the tumor cells were positive for E-cadherin and carcinoembryonic antigen(200 × magnification).
In this case,the patient’s serum SCCA was within the reference range by flow immunofluorescence assay.In fact,the current sensitivity of serum SCCA is unsatisfactory(44%-69% in cervical squamous carcinoma).More importantly,whether extracellular SCCA is a result of passive release from dead cells or active secretion from live cells is still debatable.Uemuraet al[17]confirmed that SCCA(1 or 2)synthesized by squamous carcinoma cells is mainly retained in the cytoplasm,and only a small amount is secreted.
SCCA upregulation is also observed in adenocarcinoma of the lung[18],Barrett’s esophagus[19],breast[20],pancreas[21],and chronic inflammatory diseases of the skin(psoriasis,specific dermatitis,and eczema)as well as in respiratory inflammatory diseases(pulmonary tuberculosis,asthma,and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).A large retrospective study found upregulated SCCA in patients with uremia,azotemia,diabetic nephropathy,and nephrotic syndrome[22].SCCA regulates the differentiation of the normal squamous epithelium.It enhances tumor growth by promoting cell resistance to apoptosis and amplifies invasive potential by triggering epithelial-mesenchymal transition[23].SCCA also inhibits chemotaxis and cytotoxicity of natural killer cells to suppress the immune system[24].Turatoet al[25]demonstrated that SerpinB3 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma stem cell phenotypeviamiR-122.
Immunohistochemical markers of gastric SCC commonly used in pathology department include keratin CK,p63,and p40(ΔNp63).Humanp63gene is composed of 15 exons and 2 independent promoters.Two proteins are encoded by this gene:(1)Full-length protein p63 with trans-activation domain transcribed from exon 1;and(2)P40 without trans-activation domain starting from exon 3.P63 is often expressed in the basal layer of epithelial tissue and plays an important role in the formation of the normal epithelium.Both p63 and p40 are expressed in various benign and malignant tumors of squamous cell origin,which often leads to a pathological diagnosis of SCC.Our data showed that the tumor cells in this patient were negative for CK5,CK6,CK7,CAM5.2,CK20,p63,and p40 but positive for SCCA,CEA,and E-cadherin,indicating that SCCA is an independent marker in gastric poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma cells.Such evidence underlines the“non-squamous”property of SCCA and clearly highlights the diverse biological functions of SCCA both inside and outside the cell.
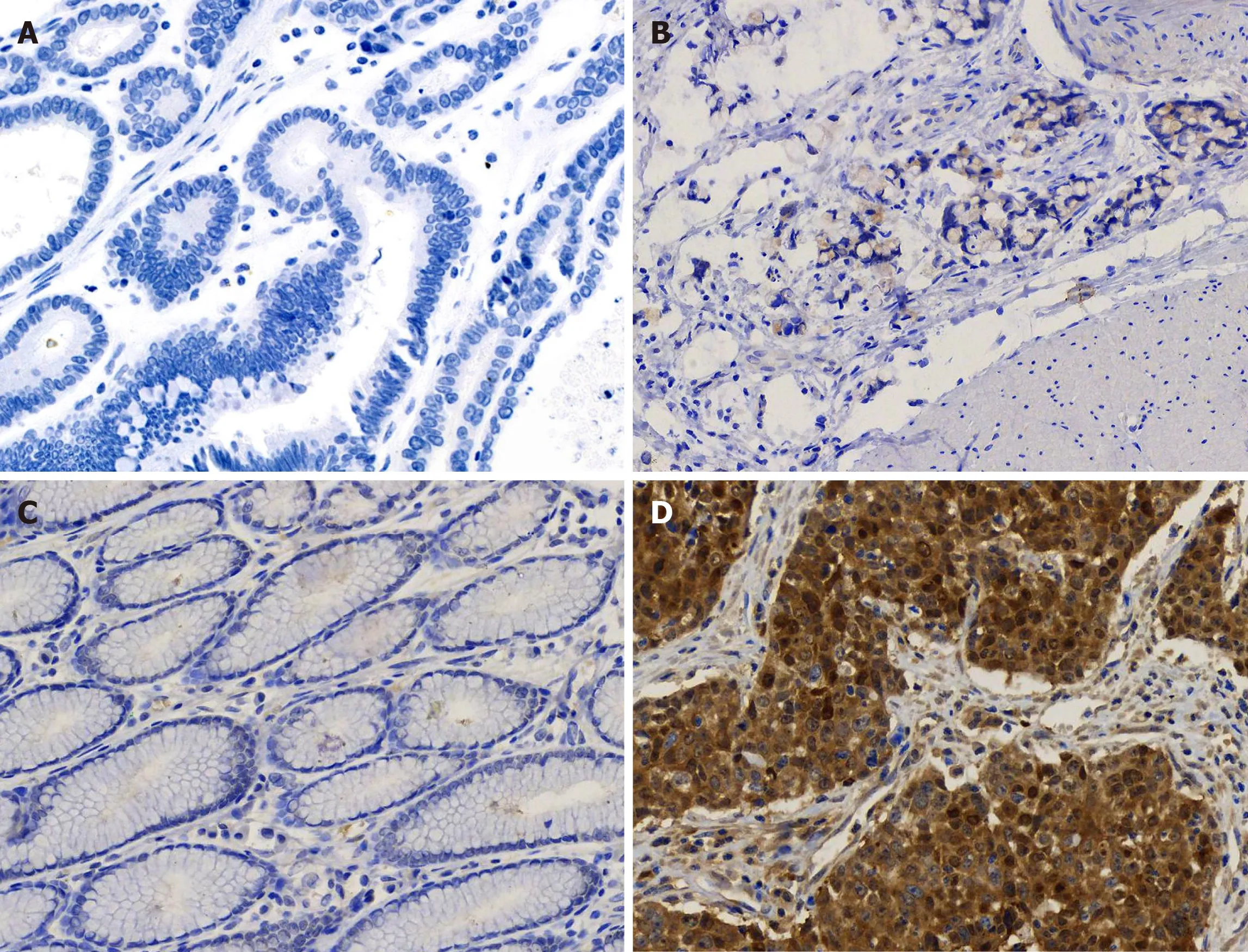
Figure 5 Immunohistochemical staining for squamous cell carcinoma antigen in gastritis and gastric cancer tissues.Paraffin-sections from gastritis and gastric cancer tissues of multiple patients were simultaneously stained for squamous cell carcinoma antigen(SCCA).A:Negative SCCA expression(-)in well differentiated gastric cancer(200 × magnification);B:Weakly positive SCCA expression(+)in poorly differentiated gastric cancer(200 × magnification);C:Negative SCCA expression(-)in chronic gastritis(200 × magnification);D:Strong SCCA expression(+++)in gastric squamous cell carcinoma(200 × magnification).
CONCLUSION
We herein report a case of poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the stomach with abundant SCCA protein.Our data further enriches the knowledge that SCCA mRNA was detected in GC cell lines[26].This patient was still alive 24 mo after surgery in a stable condition.To our knowledge,no data are currently available on the correlation between SCCA and the prognosis of GC,and SCCA has not yet been considered as a subtype marker for gastric tumor.Further in-depth study will focus on the correlation of serum level and tissue abundance of SCCA with clinical evaluation of gastric tumor(including grade,stage,recovery,metastasis,and recurrence)to evaluate the significance of SCCA in clinical laboratory.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Professor Xu ZK and Professor Wang J for expert advice on the manuscript.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年19期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年19期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Parathyroid adenoma combined with a rib tumor as the primary disease:A case report
- Displacement of peritoneal end of a shunt tube to pleural cavity:A case report
- Localized primary gastric amyloidosis:Three case reports
- Bochdalek hernia masquerading as severe acute pancreatitis during the third trimester of pregnancy:A case report
- Intravesically instilled gemcitabine-induced lung injury in a patient with invasive urothelial carcinoma:A case report
- Intraosseous venous malformation of the maxilla after enucleation of a hemophilic pseudotumor:A case report
