Relationship between granulomatous lobular mastitis and methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism
Qing-Ran Lei,Xin Yang,Chun-Mei Miao,Jin-Chang Wang,Yue Yang
Qing-Ran Lei,Xin Yang,Chun-Mei Miao,Jin-Chang Wang,Yue Yang,Department of Breast,The First People's Hospital of Kunming,Kunming 650031,Yunnan Province,China
Abstract BACKGROUND Variations in the methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase(MTHFR)gene have been reported as risk factors for numerous conditions,including cardiovascular disease,thrombophilia,stroke,hypertension and pregnancy-related complications.Moreover,it was reported there is an association between breast cancer and mutations in MTHFR-C677T.However,whether there is an association between MTHFR gene polymorphism and granulomatous lobular mastitis or not has been rarely investigated.AIM To analyze the association between MTHFR gene polymorphism and granulomatous lobular mastitis.METHODS Fifty-one patients with granulomatous lobular mastitis admitted to The First Hospital of Kunming were selected as study samples.Their hospitalization time ranged from February 2018 to February 2019.The 51 patients were included in the experimental group,and another 51 women who underwent physical examination at The First Hospital of Kunming in the same period were included in the control group.Deoxyribonucleic acid and MTFR genetic polymorphism testing were performed in each group.The association between MTHFR gene polymorphism and granulomatous lobular mastitis was observed.RESULTS There were significant differences in genotype frequency and allele frequency of C/C and C/T between the experimental group and the control group(all P <0.05).However,there was no significant difference in frequency of T/T genotype between the two groups(P > 0.05).In addition,there was no significant difference in genotype frequency and allele frequency of A/A,A/C and C/C between the two groups(P > 0.05).CONCLUSION MTHFR gene C677T locus polymorphism is closely related to granulomatous lobular mastitis.
Key Words:Methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase;Gene polymorphism;Granulomatous lobular mastitis;Association;C677T;Factor
INTRODUCTION
Granulomatous lobular mastitis is a chronic inflammatory response caused by granulomatous changes around lobules and ducts of the breast.It often occurs in young women,and the disease course is long.If patients are not treated effectively,they are likely to relapse.In addition,the rate of misdiagnosis is high because the clinical manifestations are similar to those of plasma cell mastitis.The diagnosis error leads to delayed treatment and tremendous physical and emotional damage in patients[1].Although some research reported that granulomatous lobular mastitis is associate with methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase(MTHFR)gene,the research is limited and the relationship is not clear[2].Thus,we examinedMTHFRgene polymorphism in 51 patients with granulomatous lobular mastitis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials at baseline
Fifty-one patients with granulomatous lobular mastitis who were admitted to The First Hospital of Kunming from February 2018 to February 2019 were included in the experimental group.Another 51 women who underwent physical examination in our hospital in the same period were included in the control group.The average age of the experimental group and the control group was 32.19 ± 3.28 years and 32.26 ± 3.30 years,respectively.Data at baseline were analyzed by statistical software.APvalue <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Methods
Two milliliters of blood specimen was collected from the patients’ upper arm.Deoxyribonucleic acid(DNA)was extracted and following DNA extraction,samples were tested forMTHFRA1298C and C677T gene polymorphisms.Then,200 μL of blood specimen was drawn,and 200 μL of GB buffer and 20 μL of Proteinase K mix were added.The sample was left at room temperature 2-5 min,and then 350 μL of BD buffer was added.After centrifugation at 12000 rpm for 30 min,500 μL of PWB buffer was added to the CG2 adsorption column.Then,600 μL of PWB rinsing liquids were added,and an equivalent amount of rinsing was added repeatedly followed by centrifugation for 2 min.The waste was discarded.The CG2 adsorption column was left for 2 min at room temperature.The remaining rinses were dried in adsorption columns that were then transferred to centrifuge tubes with 1.5 mL volume.Fifty microliters of elution buffer TB was added and left for 2 min at room temperature.The sample was centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 2 min,and the solution was collected.
Kits manufactured by Kuangyuan Molecular(Suzhou,China)were used forMTHFRgene polymorphism detection.Fluorophore solution(5 μL)was placed into each reaction hole,and the samples,including positive samples 1-A,1-B and 1-C,were added to each reaction hole.The above steps were repeated,and the samples,including positive samples 2-A,2-B and 2-C,were added to each reaction hole.Then,1 μL of purified water was dripped into the holes.The above reaction plates were centrifuged and brought to a standstill.Quantitative polymerase chain reaction device manufactured by Beijing Keyu Xingye Science and Technology Development Co.Ltd(Beijing,China)was set to the heating mode.The fluorophore was activated at 95°C for 10 min,and the samples were denatured at 95°C for 15 min.Complete integration of samples and fluorescence were acquired at 95°C for 40 min.The steps of denaturation and integration were repeated 40 times and then the samples were cooled down.VIC and FAM signals were acquired and recorded at 60°C.Reaction plates were embedded in the device.Scale reading was conducted,and data were acquired.
Measurements
The expression of C677T and A1298CMTHFRgenes were observed at different loci.The transcript sequences for C677T and A1298CMTHFRgenes were as follows:Mutant type C/C and wild type C/C;mutant type C/C and heterozygous C/C;mutant type C/C and mutant type T/T;heterozygous A/C and wild type C/C;heterozygous A/C and heterozygous C/T;heterozygous A/C and mutant type T/T;wild type A/A and wild type C/C;wild type A/A and heterozygous C/T;wild type A/A and mutant type T/T[3,4].
Data processing
The results in this study are presented using “%”.SPSS 20.0 statistical software(Armonk,NY,United States)was used,and chi-square test was performed to compare the differences between the two groups.P< 0.05 indicated that the differences between the two groups were significant.
RESULTS
Genotypic and allelic frequencies of MTHFR C677T
There were significant differences in C/C and C/T genotype frequency between the experimental group and the control group(allP< 0.05).However,the difference in T/T genotype frequency was not significant between the two groups(P> 0.05).There were significant differences in allele frequency between the two groups(allP< 0.05,Table 1).
Genotypic and allelic frequencies of MTHFR A1298C
The differences in A/A,A/C and C/C genotypic and allelic frequencies ofMTHFRA1298C were not significant between the two groups(P> 0.05,Table 2).
DISCUSSION
Granulomatous lobular mastitis is very common in breast-feeding women.Mostly,it occurs in women within 6 years after giving birth[4,5].However,the disease pathogenesis on granulomatous lobular mastitis is unclear.According to some experts[6-8],it is associated withMTHFRgene,to be specific,MTHFRC677T.Generally,autoimmune disease and malignant diseases have genetic susceptibility,which may be due to gene mutations.Accordingly,the present study discussed the relationship between granulomatous lobular mastitis andMTHFRgene polymorphism.
MTHFRgene polymorphism may cause decreased thermostability and bioactivity of an enzyme.C677T and A1298C are two important loci to test the relevant diseases in the clinical practice.C677T is associated with autosomal recessive inheritance.Similarly,A1298C mutation may also cause decreased thermostability and bioactivity of an enzyme.Comparatively,the effect of A1298C is less serious than that of A1298C[9,10].Reduced enzymatic activity ofMTHFRresults in high homocysteine level and abnormal folic acid levels,which in turn has an adverse effect on DNA formation and causes chromosome disorder[11,12].
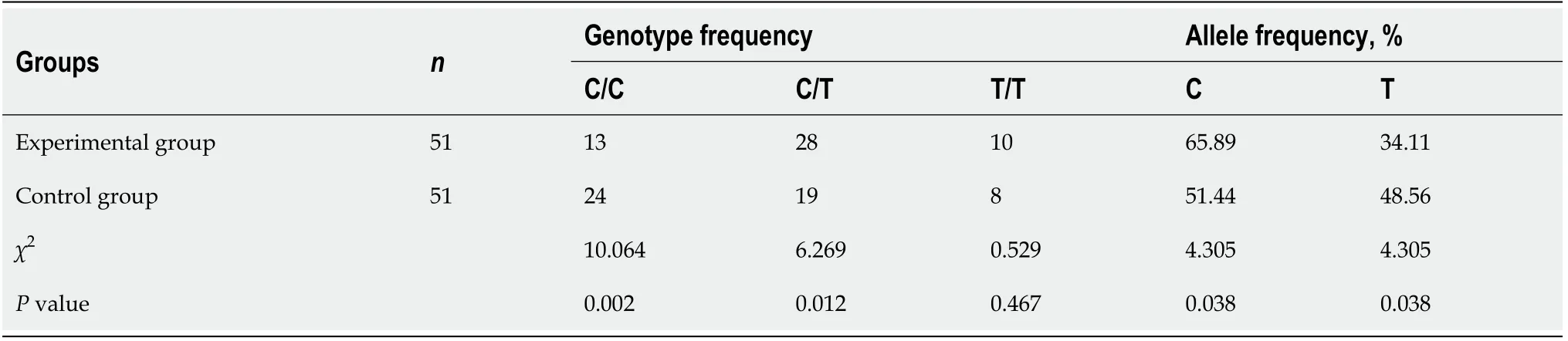
Table 1 Differences in methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase C677T between the two groups
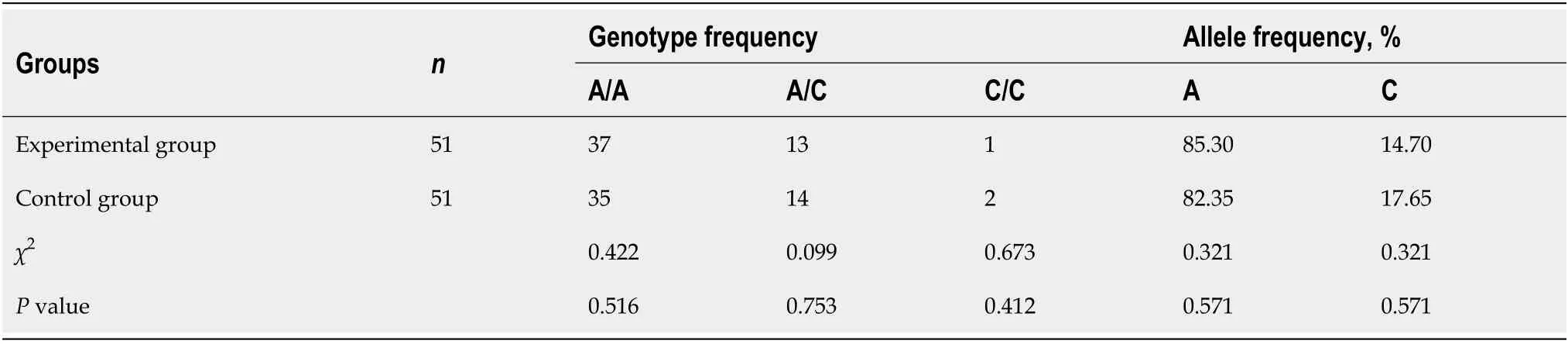
Table 2 Differences in methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase A1298C between the two groups
In the current study,there were significant differences in C/C and C/T genotype frequency between the experimental group and the control group(allP< 0.05).However,the difference in T/T genotype frequency was not significant between the two groups(P> 0.05).In addition,the differences in A/A,A/C and C/C genotypic and allelic frequencies ofMTHFRA1298C between the two groups were not significant(P> 0.05).Nevertheless,there were significant differences in allele frequency between the two groups(allP< 0.05).The results suggest that theMTHFRgene is a susceptible factor for granulomatous lobular mastitis,and it causes specificity of genetic loci.Of them,loci C677T may cause diseases but A1298C may not[13].
CONCLUSION
In summary,MTHFRC677T is one of the factors that induce granulomatous lobular mastitis.The relationship betweenMTHFRpolymorphism and granulomatous lobular mastitis need to be studied further in large studies.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Granulomatous lobular mastitis is a chronic disease of the breast.Its clinical and radiological features are similar to breast cancer,which makes its diagnosis and treatment complicated.To date,there is no obviously effective treatment for it because its etiology and pathogenesis remain unclear.Several potential reasons include autoimmunity,hormonal disorders,gene polymorphisms,etc.For polymorphisms,the relationship between common variants ofMTHFR,e.g.,677T and 1298C,and granulomatous lobular mastitis was not fully understood.
Research motivation
Identification of the pathogenic genes for granulomatous lobular mastitis will aid in the diagnosis of this disorder by using gene testing.In addition,it will help in the development of targeted therapy,which will allow for better clinical outcomes.
Research objectives
This study aimed to analyze the association betweenMTHFRgene polymorphism and granulomatous lobular mastitis.
Research methods
Participants were enrolled and divided into two groups,an experimental group and a control group.The experimental group included patients with granulomatous lobular mastitis.Participants in the control group were women who underwent physical examination.Blood specimen was collected forMTHFRA1298C and C677T gene polymorphisms.The expression of C677T and A1298CMTHFRgenes were observed at different loci.
Research results
The results revealed that there were significant differences in C/C and C/T genotype frequency between the experimental group and the control group(allP< 0.05).In addition,there were significant differences in allele frequency between the two groups(allP< 0.05).
Research conclusions
MTHFRgene was a susceptible factor for granulomatous lobular mastitis,and it causes specificity of genetic loci.
Research perspectives
The relationship between common variants ofMTHFRand the incidence of granulomatous lobular mastitis should be further identified in clinical practice with a large number of patients.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年18期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年18期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Special features of SARS-CoV-2 in daily practice
- Gastrointestinal insights during the COVID-19 epidemic
- From infections to autoimmunity:Diagnostic challenges in common variable immunodeficiency
- One disease,many faces-typical and atypical presentations of SARS-CoV-2 infection-related COVID-19 disease
- Application of artificial neural networks in detection and diagnosis of gastrointestinal and liver tumors
- Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma:Update on diagnosis and therapy
