miRNA-675-5p与食管鳞癌上皮间质转化的相关性研究
张倩 孙永红 文世民
[摘要] 目的 探討miRNA-675-5p表达水平与食管鳞癌(ESCC)上皮间质转化(EMT)的相关性。 方法 采用实时定量PCR技术检测miRNA-675-5p在ESCC组织及配对癌旁正常组织中的表达差异,并分析其表达水平与患者临床分期的相关性。脂质体转染ECA109细胞,分为miR-675-recursor组、miR-675-5p-inhibition组和NC组,上调及抑制miRNA-675-5p表达水平,分析改变目的基因表达后对ECA109细胞株迁移侵袭能力的影响,蛋白印迹实验检测干扰表达每组细胞中EMT相关蛋白E-cadherin、N-cadherin、Vimentin表达水平,评估其对ECA109株EMT过程的影响。 结果 与癌旁正常组织比较,miRNA-675-5p在ESCC组织中表达显著升高(P < 0.05),不同分期患者miRNA-675-5p表达比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。与NC组比较,miR-675-recursor组细胞迁移侵袭能力明显增强,miR-675-5p-inhibition组细胞迁移侵袭能力受到显著抑制(P < 0.05)。此外,与NC组比较,miR-675-recursor组E-cadherin蛋白表达降低,N-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白表达升高;miR-675-5p-inhibition组E-cadherin蛋白表达升高,N-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05)。 结论 miRNA-675-5p表达与ESCC患者TNM分期相关,miR-675-5p能促进ESCC细胞间质转化从而增强侵袭能力;下调表达能逆转ESCC细胞EMT过程,降低迁移侵袭能力。
[关键词] 食管鳞癌;ECA109细胞;miRNA-675-5p;上皮间质转化
[中图分类号] R735.1 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)02(a)-0018-05
[Abstract] Objective To investigated the correlation between the expression of miRNA-675-5p and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Methods Real-time quantitative PCR was used to detect the differential expression of miRNA-675-5p in ESCC and normal adjacent tissues, while the correlation between its expression level and clinical stage of patients was analyzed. Liposomes was transfected into ECA109 cell, and divided into miR-675-recursor group, miR-675-5p-inhibition group and NC group. The expression of miRNA-675-5p was up-regulated and inhibited, while the effect of changing the expression of the target gene on the migration and invasion of ECA109 cell lines was analyzed. The expression levels of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and Vimentin in EMT-associated proteins in each group of cells were detected by western blot experiments, while the effect on the EMT process of ECA109 strain was evaluated. Results Compared with normal adjacent tissues, miRNA-675-5p expression was significantly increased in ESCC tissues (P < 0.05), and comparison of miRNA-675-5p expression in patients with different stages, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Compared with the NC group, the miR-675-recursor group had significantly enhanced cell migration and invasion ability, and the miR-675-5p-inhibition group had significantly reduced cell migration and invasion ability (P < 0.05). In addition, compared with the NC group, the expression of E-cadherin protein in the miR-675-recursor group was reduced, while the expression of N-cadherin and Vimentin proteins were increased; the expression of E-cadherin protein in the miR-675-5p-inhibition group was increased, while the expression of N-cadherin and Vimentin proteins were reduced (P < 0.05). Conclusion The expression of miRNA-675-5p is related to the TNM stage of ESCC patients. miR-675-5p can promote the interstitial transformation of ESCC cells and thus enhance the invasion ability; down-regulated expression can reverse the EMT process of ESCC cells and reduce the migration and invasion ability.
[Key words] Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; ECA109 cells; miRNA-675-5p; Epithelial mesenchymal transition
我國食管癌新发患者大约23万人/年,占全世界发病人数的53%[1-2],90%以上为鳞状细胞癌。复发和转移是导致我国食管鳞癌(ESCC)患者生存率低下的主要原因[3],ESCC复发转移机制尚未明确,亟需探索新的分子标志物,预测ESCC预后及指导个体化治疗。miRNAs长度约22个核苷酸,miRNAs转录后抑制信使RNA翻译蛋白质。miR-675-5p是长链非编码RNA H19的成熟序列,位于人染色体11p15.5,胎儿时期表达量最高,分娩后组织器官中表达急速下降,最终稳定低表达[3-4]。研究发现,miR-675-5p在多种实体肿瘤中异常表达,如胶质母细胞瘤[3]、结肠癌、膀胱癌及胃癌等[5-9]中表达升高,体外实验也证实能够促进肿瘤细胞株增殖或转移。90%以上肿瘤患者死亡原因是转移,肿瘤转移的重要机制是上皮间质转化(EMT)[10],即上皮源性肿瘤细胞发生间质细胞特性转化,从原发灶逃离进入脉管,发生淋巴结或远处脏器转移。张航等[11]发现食管癌转移病灶中miR-675-5p表达水平升高,且与患者生存时间成负相关。miR-675-5p能否促进食管鳞癌复发转移,与食管鳞癌细胞EMT过程是否存在关系,值得进一步研究。
1 对象与方法
1.1 细胞株和组织
ESCC细胞株ECA109、TE-1(ATCC),人食管上皮细胞Heepic(ScienCell)。细胞均用含10%胎牛血清(Hyclone,美国)、100 mg/L青霉素和100 mg/L链霉素的高糖DMEM培养基(Hyclone,美国)培养。组织来源于2018年1~12月四川省南充市中心医院和川北医学院附属医院心胸外科行食管鳞癌切除术21例,术前均未接受放化疗及靶向治疗。切除肿瘤及癌中心5 cm以上癌旁正常组织。患者术后病理分期采取美国癌症联合会(AJCC)第8版标准。
1.2 细胞转染
ECA109细胞转染分为miR-675-recursor组、miR-675-5p-inhibition组和NC组。质粒装载miR-675-5p类似物(miR-675-recursor)、抑制片段(miR-675-5p-inhibition)、阴性对照片段(NC),片段均合成于上海吉凯公司,LipofectamineTM 2000(Invitrogen,美国)。转染前24 h用6孔板进行细胞铺板(铺板细胞数25×104个/孔),siRNA∶LipofectamineTM2000=1∶1.5,按照说明书操作,转染48 h收集细胞。重复9次。
1.3 方法
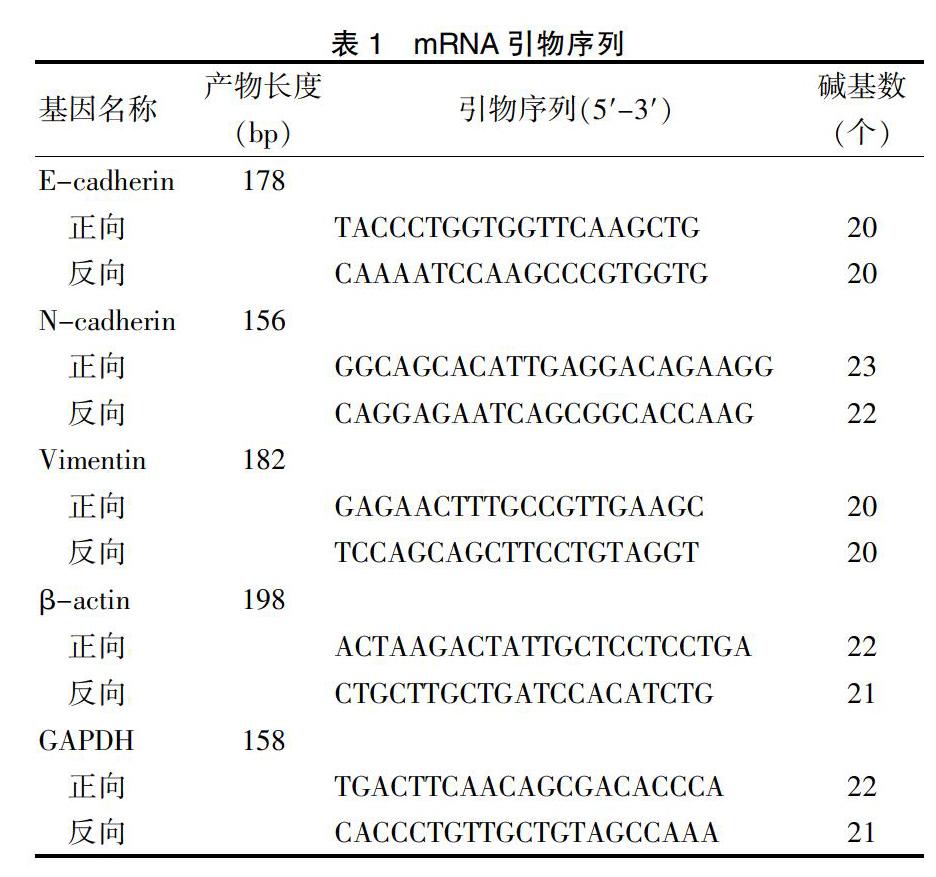
1.3.1 定量即时聚合酶链锁反映(qRT-PCR)检测目的基因表达
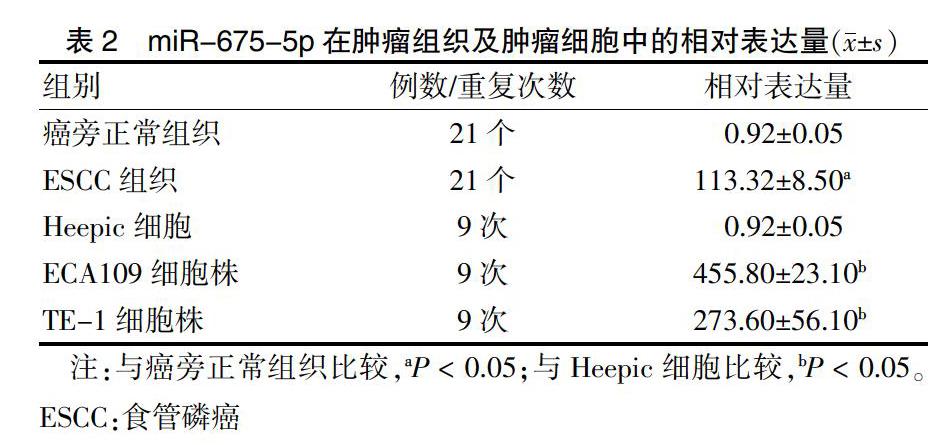
总RNA提取为超净环境,器材均无菌无RNA酶。组织冰上剪去筋膜,灭菌超纯水洗净,取黄豆大小于研磨器中倒入适量液氮研磨成组织浆,加入750 μL Trizol。后续步骤按说明书操作。总RNA浓度要求 ≥700 ng/μL,1.90 miRNA逆转录采用茎环法,引物购自锐博公司,mRNA引物由上海生物科技有限公司合成,引物序列见表1,miRNA及mRNA分别选择U6、β-actin为内参基因。qRT-PCR试剂盒SYBR TaqⅡ(TAKARA,美国,生产批号:DRR041A),逆转录及PCR均严格按照说明书进行,每基因、样本均3个复孔。优化反应程序为:95℃预变性600 s;95℃变性2 s,60℃退火20 s和70℃延伸10 s,扩增45个循环。基因表达量用2-△△ct计算。 1.3.2 蛋白质印迹法(Western blot)检测目的基因蛋白表达水平 取对数生长细胞加入裂解液进行总蛋白提取,100℃使蛋白变性,变性后蛋白进行十二烷基磺酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)、转膜、抗原抗体反应,ECL超特敏化学发光试剂盒,在荧光成像仪内对目的蛋白进行成像检测,Image Lab凝胶图像软件分析。 1.3.3 细胞迁移侵袭能力检测 Transwell:稀释Matrigel基质胶于Transwell小室上室,室温下凝固后备用。收集转染后48 h细胞制备成105 mL单细胞悬液,下室加入不含双抗的完全培养基(10%胎牛血清),上室加入200 μL细胞悬液,放置于细胞培养箱中培养24 h。固定,透明,结晶紫染色,高倍镜下随机观察16个视野并计数侵袭细胞个数,实验重复3次。 1.4 统计学方法 采用GraphPad Prism 6.0对所得数据进行统计分析及统计图表绘制。正态分布计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,采用t检验或方差分析。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。基因抑制/上调率为干扰后目的基因表达量与阴性对照组(NC)表达量的相对差异百分比。 2 结果 2.1 miR-675-5p在肿瘤组织及肿瘤细胞中相对表达量 与癌旁正常组织比较,ESCC组织miRNA-675-5p相对表达量显著升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。ECA109细胞株和TE-1细胞株miRNA-675-5p相对表达量显著高于Heepic细胞,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表2。 2.2 ESCC患者临床特征与miR-675-5p表达水平比较 不同T分期、N分期及病理分期患者miR-675-5p表达水平比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),而不同年龄、性别、肿瘤长度和神经受侵患者miR-675-5p表达水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。见表3。
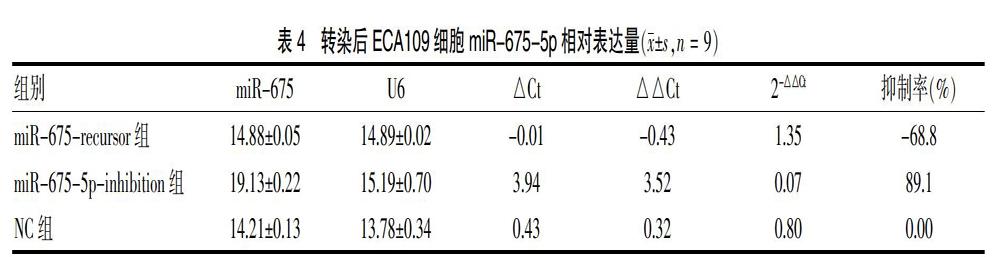
2.2 转染后ECA109细胞miR-675-5p相对表达量
绿色荧光细胞即为转染成功,转染率=绿色荧光细胞数/白色背景细胞数(同一视野下)。本实驗脂质体转染ECA109,转染效率>90%。见图2。转染48 h后检测目的基因相对表达,miR-675-recursor组、miR-675-5p-inhibition组、NC组相对表达量依次为1.350(上调率为68.8%)、0.069(抑制率为89.1%)、0.800。见表4。
2.3 干扰miR-675-5p表达后ECA109细胞株侵袭能力
miR-675-recursor组细胞穿膜数约为278个/HP,miR-675-5p-inhibition组穿膜细胞个数为95个/HP,NC组细胞穿膜个数为187个/HP。与NC组比较,miR-675-recursor组表达ECA109迁移侵袭能力明显增强,miR-675-5p-inhibition组细胞迁移侵袭能力显著下降,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图3。
2.4 目的基因对EMT蛋白表达影响
与NC组比较,miR-675-recursor组E-cadherin表达显著降低,N-cadherin、Vimentin表达升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);miR-675-5p-inhibition组E-cadherin表达显著升高,N-cadherin、Vimentin表达降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图4。
3 讨论
ESCC严重威胁我国人民生命健康,肿瘤复发转移是导致ESCC患者生存低下的主要原因,因此亟需明确ESCC复发转移分子机制[12]。编码蛋白质基因仅仅占基因总量的2%[13-14],非编码RNA是基因表达重要的调节因子[15]。其中miRNA最先被研究者发现具有沉默mRNA、抑制mRNA翻译蛋白质的功能,主要参与蛋白质沉默复合体形成[16]。近年来研究者发现miRNA还能催化mRNA降解,诱导mRNA不稳定性,直接抑制基因转录后翻译[17],调节肿瘤的发生发展过程。
肿瘤细胞发生EMT是获得转移侵袭能力的重要途径[18],H19可促进结肠癌细胞发生EMT,增强肿瘤细胞的转移侵袭能力。本研究发现,miR-675-5p表达水平与ESCC病理分期显著相关,猜测可能通过影响ESCC的EMT发生促进肿瘤细胞转移侵袭,细胞实验证实,目的基因可促进ESCC的ECA109细胞发生EMT,进而增强细胞的迁移侵袭能力。EMT发生的经典信号通路包括Snail/Slug、Twist、Six1、Cripto、TGF-β和nt/β-catenin等[19],多种信号通路途径可以促进肿瘤EMT发生,但不同肿瘤细胞主要采取不同种信号通路。miRNAs调节多能干细胞间质上皮转化,其中miR-200s与miR-205可抑制ZEB1和ZEB2表达激活骨形成蛋白信号通路诱导多能干细胞MET过程[20]。在ESCC中miR-675是如何诱导肿瘤细胞发生EMT,因此仍需进一步探讨其作用机制。
总之,miR-675-5p在ESCC组织及细胞中均显著高表达,且表达水平越高的患者,病理分期更晚,更易出现淋巴结转移,提示表达水平可预测ESCC患者预后,指导临床中根据表达状态对患者进行个体化治疗,下调miR-675-5p的表达可逆转肿瘤细胞EMT过程。因此,有望成为ESCC治疗的新靶点。miRNA能在血液中稳定存在,ESCC患者血液样本是否能得出同样的结论,仍待进一步证实。
[参考文献]
[1] 曹小琴,孙喜斌.食管癌发病水平及变化趋势[J].中国肿瘤临床,2016,4(21):932-936.
[2] Hesari A,Azizian M,Sheikhi A,et al. Chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of curcumin in esophageal cancer:Current and future status [J]. IJC,2019,144(6):1215-1226.
[3] 中华人民共和国国家健康委员会.食管癌诊疗规范(2018年版)[DB/OL].2018:1-69.
[4] Costa V,Lo Dico A,Rizzo A,et al. MiR-675-5p supports hypoxia induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colon cancer cells [J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(15):24292-24302.
[5] Cui J,Mo J,Luo M,et al. c-Myc-activated long non-coding RNA H19 downregulates miR-107 and promotes cell cycle progression of non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2015,8(30):12400-12409.
[6] Li S,Yu Z,Chen SS,et al. The YAP1 oncogene contributes to bladder cancer cell proliferation and migration by regulating the H19 long noncoding RNA [J]. Urol Oncol,2015, 33(427):165-174.
[7] Zhou WA-Ohoo,Ye XL,Xu J,et al. The lncRNA H19 mediates breast cancer cell plasticity during EMT and MET plasticity by differentially sponging miR-200b/c and let-7b [J]. Sci Signal,2017,10(483):678-682.
[8] Zhuang M,Gao W,Xu J,et al. The long non-coding RNA H19-derived miR-675 modulates human gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting tumor suppressor RUNX1 [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2014,448(4):121-129.
[9] Liu FT,Pan H,Xia GF,et al. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of long noncoding RNA H19 overexpression in human solid tumors:evidence from a meta-analysis [J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(50):83177-83186.
[10] Tsang WP,Ng EK,Ng SS,et al. Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer [J]. Carcinogenesis,2010,31(3):350-358.
[11] 張航.Hsa-miR-675-5p在食管鳞癌中的表达及其功能机制研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2013.
[12] Lagergren J,Smyth E,Cunningham D,et al. Oesophageal cancer [J]. The Lancet,2017,390(100):2383-2396.
[13] Matouk IJ,Halle D,Raveh E,et al. The role of the oncofetal H19 lncRNA in tumor metastasis:orchestrating the EMT-MET decision [J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(11):3748-3765.
[14] Zhang X,Hamblin MH,Yin KJ. The long noncoding RNA Malat1:Its physiological and pathophysiological functions [J]. RNA Biol,2017,14(12):1705-1714.
[15] Hosseinahli N,Aghapour M. Treating cancer with microRNA replacement therapy:A literature review [J]. J Cell Physio,2018,233(8):5574-5588.
[16] Tripathi V,Ellis JD,Shen Z,et al. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation [J]. Mol Cell,2010,39(6):925-938.
[17] Vahidian F,Mohammadi H. MicroRNAs and breast cancer stem cells:Potential role in breast cancer therapy [J]. J Cell Physio,2019,234(4):3294-3306.
[18] Chaffer CL,San Juan BP,Lim E,et al. EMT,cell plasticity and metastasis [J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev,2016,35(4):645-654.
[19] Brabletz T,Kalluri R,Nieto MA,et al. EMT in cancer [J]. Nat Rev Cancer,2018,18(2):128-134.
[20] O′Brien SJ,Carter JV,Burton JF,et al. The role of the miR-200 family in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer:a systematic review [J]. Int J Cancer,2018,142(12):2501-2511.
(收稿日期:2019-07-16 本文编辑:王晓晔)

