Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Hugan Tablets(护肝片) in the Treatment of Drug-Induced Liver Injury
SHA Jing-yu (沙靖昱), LV Jian (吕 健), SUN Meng-hua (孙梦华),XIE Yan-ming (谢雁鸣), SUN Lin-xi (孙粼希)
1. Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
ABSTRACT Objective:To systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) in the treatment of drug-induced liver injury.Methods:Totally seven Chinese and English databases, including CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, CBM, PubMed, EMbase, Web of Science were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) for the treatment of drug-induced liver injury , which were published from the date of establishment to April 20, 2019. The meta-analysis software RevMan 5.3 software and Excel were used to build a database into combine and analyze the studies that met the standards and to draw a forest plot.Results:Forty five RCTs were included with 7478 patients. The quality of included studies was uneven. Meta-analysis showed that the outcome index of liver injury rate was divided into seven subgroups. Hugan Tablets (护肝片) were used in the treatment of anti-tuberculosis drugs was superior to the conventional western medicine treatment group (RR=0.27, 95% CI[0.22, 0.33],P<0.00001). Which was also better than the without Hugan Tablets (护肝片) treatment group (RR=0.32, 95% CI[0.20, 0.52],P<0.00001).For the role of drug-induced liver injury in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, the Hugan Tablet + conventional treatment group is better than the conventional treatment group (RR=0.16, 95% CI [0.03, 0.88],P=0.03).The effect of drug-induced liver injury in the treatment of hypertension was superior to the conventional western medicine treatment group (RR=0.07, 95% CI[0.03, 0.14],P<0.00001). The effect of drug-induced liver injury during the treatment of hyperlipidemia was not statistically significant (RR=0.57, 95% CI[0.33,1.00],P=0.05). There was no statistical difference between the two groups in the effect of drug-induced liver injury during the treatment of coronary heart disease (RR=0.09, 95% CI[0.01, 1.61],P=0.10). There was no significant difference between the two groups in the treatment of cerebral thrombosis for drug-induced liver injury (RR=0.11, 95% CI[0.01, 2.01],P=0.14). The effect of anti-hyperthyroidism on liver injury was better than that of conventional western medicine treatment group (RR=0.45, 95% CI[0.25, 0.82],P=0.009).Outcome index of total effective rate was divided into two subgroups. The effect of drug-induced liver injury caused by the type of drug was not mentioned was superior to the conventional western medicine treatment group (RR=0.78, 95% CI[0.70, 0.88],P<0.0001). There was no significant difference between the two groups in the liver injury caused by antipsychotic drugs (RR=0.97, 95% CI[0.81, 1.16],P=0.72).Conclusion:When used in the treatment of tuberculosis and psychiatric drug treatment, combineduse of Hugan Tablets(护肝片) can significantly reduce the incidence of drug-induced liver damage, and can significantly improve clinical symptoms caused by liver damage. In the treatment of hypertension, the addition of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) can significantly reduce the incidence of drug-induced liver injury, improving the safety of medication.In the treatment of drug-induced liver injury caused by which drug is not mentioned, Hugan Tablet has a therapeutic effect. Slight adverse reactions were reported, including rash, headache, palpitations,hypoglycemia, flushing, fatigue, nausea, bowel sounds, flatulence, diarrhea, and gastrointestinal discomfort.All studies reported minor adverse reactions that were well tolerated by patients and recovered without treatment after discontinuation. Oral administration of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) has positive effects on druginduced liver injury, but this conclusion still needs further evidences delete. It is necessary to adopt a larger sample, more design, and accord with the international standards to improve the quality of evidence.
KEYWORDS Hugan Tablets (护肝片); Drug-induced liver injury; Meta-analysis; Systematic review;Randomized controlled trial
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) refers to direct toxic effect on the liver by various prescription or over-the-counter chemical drugs, biological agents,traditional Chinese medicines, natural medicines,health products, dietary supplements and their metabolites and even excipients[1], It also refers to liver injury induced by idiosyncracy of the body,including allergic (immunity-specific) and metabolic(metabolic-specific), which can be clinically manifested as a variety of acute and chronic liver diseases. Patients with mild symptoms can restore to normal after stopping the drug, while severe cases can endanger life. Based on epidemiological surveys, the annual incidence of DILI in Iceland was 19.1/100,000, and the annual incidence of DILI in France was 13.9/100,000. The United States collected 5,404,705 eligible patients through the GPRD medical database between 1994 and 1999,among which 128 cases of DILI were found The estimated annual incidence of DILI was 2.4/100,000.A Chinese multi-center retrospective survey of sixteen large general hospitals covering thirteen regions across the country showed that 1492 adult patients with acute DILI were admitted between 2000 and 2005[1]. According to the above data, the incidence of DILI varies greatly in different research methods,different regions and countries. DILI is often ignored or misdiagnosed due to lack of specific diagnostic markers or being be masked by the primary disease,so the actual incidence may be higher.
By 2018, more than 1,100 drugs with potential liver toxicity have been marketed worldwide[1]. The general treatment principles include the immediate discontinuation of relevant or suspicious drugs (the key to treatment), the promotion of drug removal for liver injury, drug treatment, liver transplantation,etc. In principle, medication should be streamlined as much as possible. Traditional Chinese medicine(TCM) can relief symptoms, improve patients'quality of life, and reduce recurrence rates in the treatment of DILI. Hugan Tablets (护肝片), as a distinctive Chinese patent medicine, has been found in early clinical and experimental studies. Kuihua Hugan Tablets (葵花护肝片) which is composed of Radix Bupleuri (Chai Hu), Herba Artemisiae Scopariae (Yin Chen), Radix Isatidis (Ban Lan Gen), Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis (Wu Wei Zi),Pulvis Fellis Suis (Zhu Dan Fen), and Phaseolus Radiatus L. (Lv Dou). It was extracted came from modification of Yinchenhao Decoction (茵陈蒿汤)and Xiaochaihu Decoction (小柴胡汤) in Treatise on Cold Pathogenic Diseases (《伤寒论》). It has the functions of relieving liver and regulating qi,strengthening spleen and digesting food, enhancing the detoxification function of the liver, reducing the blood concentration of serum transaminase,protecting liver cells, promoting the metabolism rate of chemical drugs by the liver and improving the symptoms of patients with drug-induced liver damage. On the one hand, due to the increasing incidence of DILI, more and more attention has been paid to it. On the other hand, the importance of rational clinical use of drugs has become increasingly prominent. However, the effectiveness and safety of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) in the treatment of drug-induced liver injury are stil unclear without comprehensive evidence-based study. In this study, a rigorous research and selection of literature was conducted, and a systematic review of clinical studies was cited to evaluate Hugan Tablets'(护肝片) clinical effectiveness and safety. The study result could be used as an evdience for rational drug use in clinical medication.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Screening Criteria of Literature
Inclusion criteria
Studies that meet the following conditions were included: a. The types of experimental studies were randomized controlled trials (RCTs); b. The study subjects were clearly diagnosed with druginduced liver injury, or meet drug-induced liver injury after administration; c. Intervention measures: the experimental group was treated with Hugan Tablets(护肝片), or combined with Hugan Tablets (护肝片)on the basis of the control group; the control group was treated with conventional Western medicine or took one or two Western medicine except Hugan Tablets (护肝片) based on conventional treatment; d.The primary outcome indicators: liver damage rate,total effective rate was decreased or decreased to normal range of physical and chemical examination of liver function (total effective rate = (effective +markedly effective) / total cases×100%); e. The secondary outcome indicator was the occurrence of adverse reactions.
Exclusion criteria
a. Reviews, short reports, and documents that cannot be obtained in full text; b. Repeated publication of articles and repeated data; c.serious errors or missing data in the experiment;d. Complicated with toxic hepatitis in the study; e.Others liver diseases in the study, such as patients with alcoholic, autoimmune or liver cancer and liver transplantation; f. Study objects who were given other ways of administration besides oral administration; g. Studies with traditional Chinese medicine, Chinese patent medicines, Chinese materia medica extracts, acupuncture, moxibustion,auricular pressure and other traditional Chinese medicine treatment in the intervention measures.
Search Strategy
Eligible data from seven major Chinese and English databases, including Chinese Journal Fulltext Database (CNKI), Wanfang Date (Wanfang),VIP Database for Chinese Technical Periodicals(VIP), Chinese Biomedical Literature Database(CBM), Public Medine (PubMed), EMBASE database and Web of Science were retrieved by the researchers. The retrieval content was randomized controlled clinical study on Hugan Tablets (护肝片) for the treatment of drug-induced liver injury,which was published from the date of database establishment to April 20, 2019 with no publication language restrictions. In order to conduct a more comprehensive literature review, the Chinese search formula was made as: "huganpian (护肝片)"and "yaowuxinggansunshang (药物性肝损伤)" or"yaowuxingganyan (药物性肝炎)" or "gansuanhai (肝损害)"; "gansunshang (肝损伤)" or "jiakang (甲亢)"or "kangjiangshanbing (抗精神病)" or "kangjiehe (抗结核)" or "tangniaobing (糖尿病)" or "gaoxueya (高血压)"; "gaozhixuezheng (高脂血症)" or "guanxinbing(冠心病)" or "naoxueshuan (脑血栓)". The English search formula was "Huganpian" and "DILI, DILI",without any other restriction.
Evaluation Methods
Literature screening
After two people cross-screened the literature,two researchers independently completed the data inclusion, extraction and cross-checking. The disagreement was resolved through discussion and consultation with the third researcher.Through checking repeated literature, preliminary screening (title + abstract) of relevance, exclusion,and preliminary inclusion of literature for full-text evaluation, the researchers then decided which literature should be included.
Literature data management and extraction
The main author, year, research object(experimental group, control group, total number of cases), intervention measures (dose of western medicine type), course of treatment, main outcome indicators, adverse reactions. were summarized into tables to observe research results, rigor of research conclusions, and heterogeneity between studies.The above-mentioned literature data management and extraction were planned to be summarized qualitatively and listed in table.
Methodological quality evaluation of the included studies
The quality of the literature is evaluated according to Risk of Bias risk assessment tool of the Cochrane. The quality evaluation included the following main contents: a. the generation of random sequences; b. the allocation and hiding; c. the implementers and participants were double-blinded;d. blinding in outcome assessment; e. incomplete outcome data; f. publication bias; g. other bias. Based on the bias of each item, high-risk, low-risk, and uncertain risk judgments were made to evaluate the methodological quality of the included studies[2].
Statistical analysis
Qualitative analysis mainly adopted descriptive methods. The descriptive analysis was conducted for the indicators that calculated by scientific and accurate mathematical models in the literature and the series of values involved were performed for descriptive analysis. Quantitative analysis (Meta-analysis):RevMan 5.3 software package provided by Cochrane was used. Relative risk (RR) was used for calculating data, and mean difference (MD) or standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% CI were used for data measurement. Ifwhich means that the homogeneity between studies is better, then a fixed effect model was used; if I2>50%, which means that there is significant statistical heterogeneity, then a random effect model was used. If the source of heterogeneity can be identified, further heterogeneity analysis will be performed according to the factors that may cause heterogeneity. In this study, if there were ten or more studies included in an outcome indicator,funnel plot would be used for bias analysis publication.
Subgroup analysis
The data of all subjects were divided into multiple groups and then being compared between groups, which can be used to explore heterogeneous sources, or to explore specific types of DILI or specific types of intervention. The data can be divided into two or more subsets according to the types of drugs that cause DILI in the study subjects.According to the study subjects, the characteristics of conventional Western medicine are divided into two or more subsets.
RESULTS
Literature Search Results
A total of 541 related papers were initially retrieved and imported into the literature management software NoteExpress5.0. After removing repeated ones, 253 literature were collected, After reading the title. We found out abstract, 107 papers were selected for full-text evaluation. During the full-text evaluation,there were five papers in English, which could not be obtained by searching the English database,and the source journals were Chinese journals, so it was considered to be Chinese literature, and the corresponding Chinese documents were downloaded.In addition, two papers were not available in full text.Finally, forty five papers were included, all of which were in Chinese. The literature selection process was shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Literature Screening Process and Results
Basic Characteristics of Included Literature
The database search obtained 541 records,and finally included forty 5 Chinese RCTs. Among them, with 4 papers did not mention which type of drug caused liver injury[3,4,43,46], 1 paper of liver injury caused by anti-hyperthyroidism drug[5], one paper of liver injury caused by anti-psychiatric drugs[6], 22 papers of liver injury caused by anti-tuberculosis drugs[7-23,41,42,44,45,47]. 3 papers of type 2 diabetes mellitus treated combined with Hugan Tablets (护肝片)[24-26], 9 papers for treating hypertension[27-35],3 papers for treating hyperlipidemia[36-38], 1 paper for treating coronary heart disease[39], 1 paper for treating cerebral thrombosis[40](Table 1).
Evaluation of Methodological Quality of Included Studies
The results of the methodological quality evaluation of the included studies were shown in Figure 2 and the specific results were shown in Table 2. A total of 45 RCTs included in this study,15 RCTs[10,13-17,19-21,23,41,42,44,45,47]did not mention the course of treatment and there was a certain bias; six RCTs[4,7,8,11,32,38]reported the correct random grouping method. 4 RCTs[42-47]did not mention randomness.One RCT[45]was grouped by visiting time. The previous study only reported random grouping, but the specific method was not described. All studies did not report the implementation of hidden allocation, and bias could not be judged. Besides, neither mentioned blinding method nor bias could not be judged. The data included in the literature was relatively complete,so the data was evaluated as low risk. By comparing the methodology and results of the literature, 3 RCTs[4,39,46]mentioned adverse reactions in the abstract, but the results were not listed, which was determined as high bias in selective report. 20 RCTs[7-9,11-13,15,17-23,28,32,39,42,43-45]did not mention adverse reactions. There was some bias, and data were provided for the rest; all studies were determined to be low risk if no other bias was mentioned.





Figure 2. Methodological Quality Evaluation Results of the Included Studies
Meta-Analysis
Liver damage rate
Effects of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on liver damage caused by antituberculosis drugs: A total of 20 studies were included in the conventional western medicine treatment group[7,8,10-14,16-19,21-23,41,42,44,45,47].After the heterogeneity test, there was no heterogeneity between the studies (P=0.64, I2=0%).Meta-analysis was performed through applying a fixed-effects model. The results showed that the treatment group of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) for liver injury was superior to the conventional treatment group (RR=0.27, 95% CI [0.22, 0.33], P<0.00001)(Figure 3). 3 studies were included in the group that not taking hepatoprotective drugs[9,15,20]. After the heterogeneity test, there was no heterogeneity between the studies (P=0.59, I2=0%). Meta-analysis was performed by applying a fixed-effects model. The results showed that the treatment group of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) for liver injury was superior to the treatment group without taking hepatoprotective drugs (RR=0.32, 95% CI [0.20, 0.52], P<0.00001)(Figure 4). Heterogeneity tests showed statistical heterogeneity among the included studies. For the values of the two groups, the average of the experimental group was smaller than that of the control group, suggesting that the addition of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) can significantly reduce the incidence of drug-induced liver damage during the treatment of tuberculosis.
Effect of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on druginduced liver injury during the treatment of type 2 diabetes: 3 studies[24-26]were included. After heterogeneity testing, there was no heterogeneity among the studies (P=0.83, I2=0%). Meta-analysis was performed through applying a fixed-effects model.The results showed that the treatment group of the Hugan Tablets (护肝片) + conventional treatment for liver injury were superior to the conventional treatment group (RR=0.16, 95% CI [0.03, 0.88], P=0.03) (Figure 5). The average of the experiment group was smaller than that of the control group, suggesting that in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, the addition of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) can significantly reduce the incidence of drug-induced liver damage.
Effects of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on DILI during the treatment of hypertension: 9 studies[27-35]were included. After heterogeneity testing, there was no heterogeneity between the studies (P=0.60,I2=0%). Meta-analysis was performed by applying a fixed-effects model. The results showed that the treatment group of the Hugan Tablets (护肝片) +conventional treatment for liver injury was superior to the conventional treatment group (RR=0.07, 95% CI[0.03, 0.14], P<0.00001) (Figure 6). The mean value of the experiment group was smaller than that of the control group, suggesting that in the treatment of hypertension, the addition of Hugan Tablets (护肝片)can significantly reduce the incidence of drug-induced liver damage.
Effects of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on druginduced liver injury during the treatment of hyperlipidemia: 3 studies[36-38]were included. After the heterogeneity test, the heterogeneity between the studies was statistically different. Because the control groups of two studies were statins in these 3 included studies, 1 study was excluded[38]for descriptive analysis. After the heterogeneity test,there was no inter-study heterogeneity between the 2 groups of statins (P=0.73, I2=0%). Meta-analysis was performed using a fixed-effects model. The results showed that the treatment group of the Hugan Tablets (护肝片) + statin treatment for liver injury were no statistical difference to the conventional treatment group (RR=0.57, 95% CI [0.33, 1.00],P=0.05) (Figure 7).

Table 2. Methodological Quality Evaluation Results of the Included Studies

Figure 3. Liver Damage Caused by Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs, Hugan Tablets (护肝片) versus Western Medicine Routine

Figure 4. Liver Damage Caused by Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs, Hugan Tablets (护肝片)Compared with No Liver-Protecting Drugs

Figure 5. Effect of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes on DILI
Effects of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on druginduced liver injury during the treatment of coronary heart disease Only one study[39]was included.The number of events in the experiment group was zero, and the total sample size was 60. The number of events in the control group was 5, and the total sample size was 60. The results showed no significant difference between the experimental group and the control group (RR=0.09, 95% CI [0.01,1.61], P=0.10).
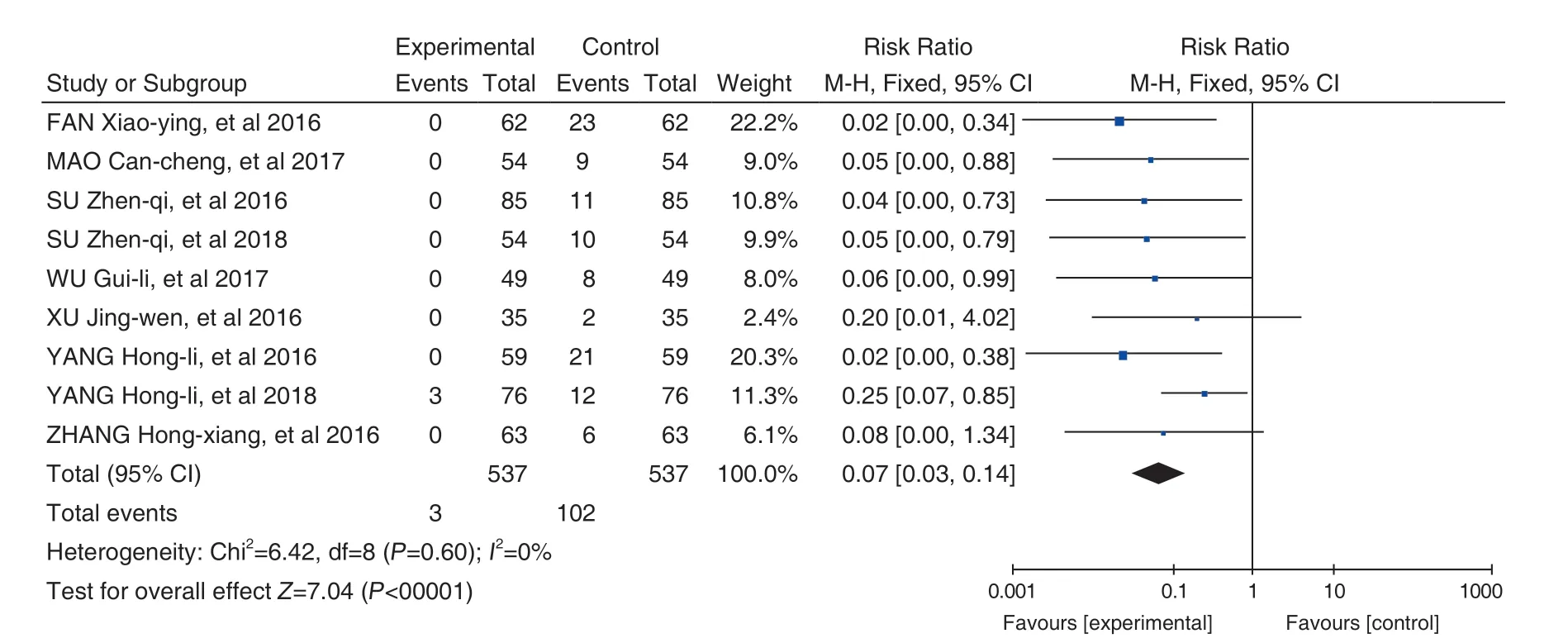
Figure 6. Effect of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on the Treatment of DILI During Hypertension

Figure 7. Effect of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on DILI in the Ttreatment of Hyperlipidemia
Effects of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on druginduced liver injury during the treatment of cerebral thrombosis Only one study[40]was included. The number of events in the experiment group was 0,and the total sample size was 50. The number of events in the control group was 4, and the total sample size was fifty. The results showed no statistical difference (RR=0.11, 95% CI [0.01, 2.01],P=0.14).
Effects of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on drugliver injury caused by antihyperthyroidism drugs Only one study[5]was included. The number of events in the experiment group was 12, and the total sample size was 64. The number of events in the control group was 24, and the total sample size was 58. The results showed that the experiment group was better than the control group (RR=0.45,95% CI [0.25, 0.82], P=0.009). In the course of antihyperthyroidism drug treatment, by setting up a control group, it can be seen that adding Hugan Tablets (护肝片) or western medicine conventional treatment can prevent drug-induced liver damage,but the efficacy of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) was significantly better than that of conventional western treatment, which reduced the occurrence of drug-induced liver damage.
Total effectiveness rate
Effects of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on druginduced liver injury caused by the type of drug not mentioned Compared with conventional treatment of Western medicine, a total of 4 studies were included[3,4,43,46], and the heterogeneity among the studies was statistically heterogeneous.Because only one of the 4 studies has 2 main pharmacological effects: anti-hepatitis virus and anti-hepatocyte damage, descriptive analysis is needed[3]. The other 3 articles have pharmacological effects to protect liver cells and have no heterogeneity after testing (P=0.76,I2=0%). Meta-analysis was performed using a fixedeffects model. The results showed that the Hugan Tablets (护肝片) treatment group was better than the conventional treatment group (RR=0.78, 95%CI [0.70, 0.88], P<0.0001) (Figure 8). The mean value of the experimental group was smaller than that of the control group, suggesting that Hugan Tablets (护肝片) has therapeutic effects in the treatment of DILI.

Figure 8. Effect of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on DILI Cause by Which Type of Drug Is Not Mentioned

Figure 9. ADRs: Outcome Indicatoor-Liver Loss Rate
Effect of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on liver damage caused by antipsychotic drugs One study[6]was concluded. The number of events occurred in the experiment group was 31, with a total sample size of 35. 30 events occurred in the control group with a total sample size of 35. The results showed no statistical difference between the experimental group and the control group (RR=0.97, 95% CI [0.81, 1.16], P=0.72).
Incidence of adverse reactions
3 papers[5,40,47]did not report adverse reactions.19 papers did not mention adverse reactions[7-9,11-13,15,17-23,32,39,42,44,45]. 23 papers[3,4,6,10,14,16,24-31,33-38,41,43,46]mentioned adverse reactions. One paper[46]could not extract data. A total of 22 reports of adverse reactions were included in all studies. All studies reported minor adverse reactions, such as rash,fatigue, poor appetite, bloating, abdominal pain,diarrhea, etc., which patients can tolerate and disappeared without treatment after treatment. The analysis was as follows.
The outcome index was the liver damage group. A total of 18 studies were included. After the heterogeneity test, there was no heterogeneity between the studies (P=0.73, I2=0%). It was used the fixed effect model. The results showed that the results of the 2 groups were statistical significance(RR=0.37, 95% CI [0.25, 0.54], P<0.00001). The adverse reactions of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) in treating drug-induced liver injury were less than those in the control group (Figure 9).

Figure 10. ADRs: Outcome Indicatoor-Total Efficiency
The outcome index was the total effective rate group. Four studies were included. After the heterogeneity test, there was no heterogeneity between the studies (P=0.38, I2=0%). The fixed effect model was used. The results showed that there was no statistical difference (RR=0.27, 95% CI[0.07, 1.05], P=0.06) (Figure 10).
Publication Bias
In this study, the liver damage rate outcome indicators of liver injury caused by anti-tuberculosis drugs were all greater than or equal to ten. For the above outcome indicators, funnel plot was used to analyze the publication bias. The funnel chart analysis results showed that the study distribution was asymmetric, suggesting that there might be publication bias or poor methodological quality.The reasons may be due to the small sample size of the included studies, the preferred publication of positive results, and the inclusion of studies in Chinese (Figure 11).

Figure 11. Evaluation of Publiction Bias for Liver Damage Caused by Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs
DISCUSSION
Effectiveness
Hugan Tablets (护肝片) is composed of Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis (Wu Wei Zi), Radix Bupleuri (Chai Hu), Herba Artemisiae Scopariae (Yin Chen), Radix Isatidis (Ban Lan Gen), Pulvis Fellis Suis (Zhu Dan Fen), and Phaseolus Radiatus L. (Lv Dou). It has the effects of relieving liver qi, clearing heat and nourishing the liver, relieving dampness and detoxifying, and strengthening the spleen and digesting food. Modern pharmacological studies have found that Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis (Wu Wei Zi) extract, schisandrin B and pentasitol, etc.can improve liver mitochondria and block calciuminduced membrane permeability transition, prevent fatty changes, and significantly reduce serum ALT activity. Prevents apoptosis in the state of high oxidative stress, thereby reducing liver fibrosis,increasing liver cell activity[48], enhancing liver function, to a certain extent reducing the damage of drugs to liver cells and enhancing the body's immunity. Radix Bupleuri (Chai Hu) contains saikosaponin, saikosol, and α-spinasterol, which can promote liver cell DNA synthesis, directly protect biofilms, improve the body's ability to resist nonspecific stimuli, and other liver-protective effects,promote bile excretion, and reduce bile[49]. Bile acid,bile pigments and other choleretic effects, lower cholesterol levels and lower blood lipids. The extract of Herba Artemisiae Scopariae (Yin Chen) includes 6,7-dimethoxycoumarin (Amylin), caffeic acid, Yin Chen chromone, methyl Chen Chan ketone, etc.have promoted bile secretion and excretion in the test[48]. Certain hepatoprotective effects can reduce liver cell swelling, fatty lesions and necrosis to varying degrees. The qingdanone in Radix Isatidis(Ban Lan Gen) can reduce the damage to liver cells and remove oxygen free radicals in liver cells. The structure of phytosterols contained in mung bean is similar to that of cholesterol. The two compete for esterification enzymes, making them unable to esterify and reducing the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine. It can also promote cholesterol alienation or prevent cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver. Reduces serum cholesterol levels. Radix Isatidis (Ban Lan Gen) and Pulvis Fellis Suis (Zhu Dan Fen) can improve the body's immunity and antiallergic effects. The results of this study showed that when Hugan Tablets (护肝片) is used in the treatment of tuberculosis. During antihyperthyroidism drug treatment, the addition of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) can significantly reduce the incidence of druginduced liver damage and can significantly improve the clinical symptoms caused by liver damage;In the treatment of hypertension, the addition of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) can significantly reduce the occurrence of drug-induced liver damage and improve the safety of medication. In the treatment of drug-induced liver injury caused by the type of drug not mentioned, Hugan Tablets (护肝片) has a therapeutic effect. Hugan Tablets (护肝片) has obvious advantages in improving drug-induced liver damage when used alone; When combined with western medicine, the improvement of druginduced liver damage is significantly better than that of western medicine alone. Other symptoms such as quality of life and life satisfaction, and other relevant biochemical indicators and safety, due to too few included studies, and most of them are of low quality, exact results have not been obtained.In addition, because all studies did not follow up and report primary outcome indicators, it was not possible to determine whether the incidence of death events was effective.
Safety
The results of this study showed that a total of twenty three papers reported adverse reactions,and values of twenty two papers were extracted.There were thirty-three cases in the Hugan Tablets(护肝片) group and ninety four cases in the control group. For Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on drug-induced liver damage caused by anti-tuberculosis drugs[40],adverse reactions in the Hugan Tablets (护肝片)group reported one case of rash; Hugan Tablets(护肝片) for drug-induced liver injury during the treatment of type 2 diabetes[23,24], adverse reactions in the Hugan Tablets (护肝片) group reported two cases of hypoglycemia. Adverse reactions of the digestive system reported three cases of flatulence and bowel sounds, three cases of diarrhea; For Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on drug-induced liver injury during the treatment of hypertension[28,29], adverse reactions were reported in the Hugan Tablets (护肝片) group: five cases of headache, four cases of palpitations, and three blushes; Hugan Tablets (护肝片) combined on drug-induced liver injury during the treatment of hyperlipidemia[35-37], the Hugan Tablets (护肝片) group reported adverse reactions:four cases of dizziness, palpitations and other adverse reactions, three cases of gastrointestinal discomfort, three cases of fatigue reactions, two cases of nausea. For Hugan Tablets (护肝片) on drug-induced liver injury[3,42]caused by the type of drug not mentioned: one case of rash, one case not mentioned symptoms. All studies reported minor adverse reactions, such as rash, fatigue, poor appetite, bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc.,which patients can tolerate and disappear without treatment after drug withdrawal.
Methodological Quality
This paper performed a subgroup analysis to consider the drug-induced liver injury caused by different drugs. The degree of injury, treatment course and observation interval are all considered as grouping factors. By comparing different subgroups, the degree of liver damage caused by different drugs and the course of treatment have a significant relationship with Hugan Tablets (护肝片)in treating drug-induced liver damage. For example,liver damage caused by anti-tuberculosis drugs have a greater degree of liver damage, and the course of treatment is generally thirty daysix months;when combined with hypertension, the degree of liver damage is lower, and the course of treatment is generally seven day(four-eight) weeks. Possible problems are analyzed. The usage and dosage used in most studies are concentrated at four tablets/time, three times/d. The number of studies included in each group is different, and the weight ratio is different. As a result, a clear relationship between liver damage and dose and course of treatment cannot be obtained based on horizontal and vertical comparison. In addition, the conclusions of the above systematic reviews may also be affected by the following factors: a. Methodological quality of the included studies: In this systematic review,the quality of included studies is generally low,mainly because most studies mentioned "random",but random methods and random concealment schemes were not explained. Most studies did not report blind methods, withdrawal and lost followup. b. Differences in diagnostic criteria: Although most of the diagnoses included in the study were liver damage, inconsistent diagnostic criteria may bring selective bias of the subjects, and reduce the homogeneity of the research subjects; c. Judgment differences of the efficacy indicators: All the included studies used liver function tests as the primary effect indicators, but the criteria were different, which led to inconsistent measurement standards. There will be some misalignment bias.
Limitation and Suggestion
Hugan Tablets (护肝片) has obvious effects on the treatment of drug-induced liver injury. Due to the large number of drugs that cause drug-induced liver injury, the number of studies included in each type of drug is uneven and the number is not large.Many factors can affect the results, which reduces the reliability of the conclusions of this systematic review, so the methodological quality of the research needs to be improved. It is suggested that future research in this area should be accompanied by reasonable research design, increased research sample size, and strict implementation and process supervision. It is better to have a multi-center large-sample randomized controlled double-blind trial to further verify its efficacy to obtain reliable conclusion.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study show that in the treatment of tuberculosis, anti-hyperthyroidism drug treatment, and psychiatric drug treatment, the addition of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) can significantly reduce the occurrence of drug-induced liver damage and can significantly improve the clinical symptoms caused by liver damage; In the treatment of type two diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, and cerebral thrombosis, the addition of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) can significantly reduce the occurrence of drug-induced liver damage and improve the safety of medication. In the treatment of drug-induced liver injury caused by the type of drug not mentioned, Hugan Tablets (护肝片) has a therapeutic effect. All studies reported minor adverse reactions that disappeared without treatment after drug discontinuation. In summary, oral administration of Hugan Tablets (护肝片) has positive significance for the treatment and prevention of drug-induced liver injury, but this conclusion still lacks high-quality research evidence to support it. It is recommended that clinical trial protocols with large samples,rigorous design and meeting international standards should be used in future so as to improve the level of evidence quality.
 World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2020年2期
World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine2020年2期
- World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine的其它文章
- Systematic Evaluation (Meta-analysis) of the Efficacy and Safety of Pudilan Xiaoyan Oral Liquid (蒲地蓝消炎口服液) in the Treatment of Suppurutive Tonsillitis in Children
- Exploration on Integrative Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Strategy for Treating Patients of Lung Cancer over 80 Years Old
- Clinical Study on the Treatment Efficacy of Cerebral Hemorrhage with Xingnaojing Injection in Real World
- New Year's Message
