Phytomedicines as therapeutic interventions for hepatic encephalopathy
Joshua Ahiasi-Mensah,Xin He,2*,Nannan Huang,Peng Hu
1 School of Chinese Materia Medica,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,China;
2 School of Chinese Materia Medica,Guangdong Pharmaceutical University,Guangzhou,China.
Abstract
Keywords: Hepatic encephalopathy,Neuropsychiatric,Neuroinflammation,Phytomedicines,Phytochemicals
Background
In the absence of other known brain anomalies,Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) describes a spectrum of neuropsychiatric abnormalities in patients with liver insufficiency.Overt hepatic encephalopathy or minimal hepatic encephalopathy forms the broad umbrellas by which Hepatic encephalopathy is classified [1].Disorientation or asterixis,according to the International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN),marks the setting in of overt hepatic encephalopathy (grade II-IV).Overt hepatic encephalopathy is described by neurological and psychiatric abnormalities detectible by bedside clinical tests,whereas covert hepatic encephalopathy,require specific psychometric tests to identify,as these patients show normal mental and neurological status on clinical work [2,3].HE is a ranking contributor to global mortality rate.It is also the most pervasive liver-associated disorder especially,if complicated by ascites.The intensification of HE typically results in hepatic coma,which eventually leads to death [4].The invasion of the brain by neurotoxins from the blood is responsible for HE.Currently,ammonia,alterations in neurotransmitters such as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA),and the imbalance of specific amino acids in plasma have been identified as pathological factors for HE[5].The World Health Organization,puts the global prevalence of liver HE at 4.5% - 9.5% of the general population,estimating that more than 50 million of the population of the world suffer from chronic liver disease [6].A study to compare the prevalence of HE from some Sub-Saharan African countries like Central African Republic,Gabon,Malawi,Uganda,and Cote d’Ivoire revealed an average prevalence of 10%[7].
The practice of natural medicine employs the utilization of biological agents and their products to reverse and or mitigate human ailments.Many complementary and alternative techniques are,therefore utilized in natural medicine [8,9].Existence in nature,the absence of synthetic additives and a no or limited processing procedure are the primary criteria of a therapeutic agent of natural medicine.Global perception and acceptance of the use of natural therapeutic agents have witnessed positive ratings[10].The increased interest in the use of natural medicine has beckoned its regulation in most jurisdictions in the world.Notably,natural medicine practitioners need to acquire licenses to practice successfully in most northern American regions.The comfort meted out to patients has led to an increase in the patronage of natural medicine.Nutraceuticals provide vital tools for the treatment of ailments in naturopathy [11].One major organ whose disease has been tried and tested with natural remedies is the liver,and typical among these diseases is HE.
Treatment of HE has seen much success using different pharmacological interventions.Man has resorted to the use of natural therapeutic agents for liver ailments for a long time.This chronicles from Ayurveda to the Chinese,European and then to the other systems of traditional medicines[1].
In recent times,phytomedicinal regimens for treatment of HE has gained ground in all the continents across the globe.A drastic change in the fundamental concepts and practices has encapsulated the therapeutic assessment of herbal products in liver[12].Through the judicious coordination of the proficiencies of the traditional systems of medicine with that of the modern concept of evidence-based medicinal evaluation,standardization of herbal products and randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials to support clinical efficacy,this has been achieved in the 21stcentury.Traditional healers globally,utilize various plants for the purposes of treatment and treatment of liver disease [13].A wide variety of plants have been assessed for their therapeutic effects for liver impairments,including HE [14].Some of the plants are located in varying geographical locations on the various continents.
Modern attention to natural therapies and alternative medicines has triggered more research in traditional herbal medicine.The systematic assessment of traditional medicines from plant source for combatting numerous diseases has received tremendous attention in the past decade [15].Herbal drugs are widely prescribed even when their biologically active constituents are not fully identified[16].Largely,this is due to their apparent negligible adverse reactions and less expensive costs albeit,very effective.The treatment of liver impairments by the application of natural remedies has a long history.Noteworthy,constituents in combinations have confirmed anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,antifibrotic,anticarcinogenic,or antiviral properties though,most recommendations have no confirmations from evidences [17,18].Unsatisfactory defines the state of matter on the investigations done on a large number of plants and formulations.To show this,in many of these investigations,evaluations were made for the therapeutic values evaluated in averse to a number of chemically-induced subclinical levels of liver impairments in rodents [19].The reasons for such deductions are scarcity of toxicological studies checking traditional remedies,lack of standardization of the herbal drugs,and limited number of randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials [20].Meaningful impacts can be given to the recovery processes of a diseased liver by natural products,herbal extracts inclusive.Medicinal plants such as Gancao(Glycyrrhiza glabra Fabaceae),Vernonia amygdalina,Shifeiji (Silybum marianum Asteraceae),Picrorhiza kurroa,andPhyllanthusspecies (amarus,niruri)Yuganzi (Phyllanthus emblica Phyllanthaceae) have shown themselves in most times potent and are therefore,used widely for remedying liver disorders[8,21,22].These effects are achieved through antioxidant-related properties.The ability of plant products to be as hepatoprotective agents is well documented.There are several medicinal combinations in the traditional medicinal system which are popularly harnessed as tonics for the treatment of hepatic and neuronal impairments.Over the years,the field of pharmacognosy and herbal medicine have received much attention in all the five continents,especially in Asia and Africa.In this review,we discuss some selected plants with hepatoprotective and neuroprotective effects that are used in treating HE in some local communities in the world.
Current Treatments for Hepatic encephalopathy
The current knowledge of the multifactorial factors involved in the pathogenesis of HE such as inflammation,oxidative stress,sarcopenia,the role of the gut microbiota,cerebral abnormalities,complications of lactate and bile acids etc.,require that treatment options,encompass seeking solutions to the underlying complications contributing to HE,restoring normal metabolic homeostasis,ensuring the regeneration of hepatocytes,antibiotics agents suppressing the production of ammonia in the gut through the inhibition of mucosal glutaminase,and liver transplantation[23].While,concurrently managing the complications from HE itself.Personalized treatment options should be adequately encouraged and looked at to ensure the best of care to patients.Table 1 enumerate the current trends and as well as the experimental candidates.
Phytomedicinal Remedies for Treatment of Hepatic encephalopathy
Various herbal plants have proven to be potent sources of therapeutic agents for treatment of diverse abnormalities,including HE [23].These herbal plants are found in different places over the world.The very diverse phytochemicals which are present in these particular herbal plants,ensure that they are found useful in the treatment of a number of disease conditions.Table 2 therefore,shows a number of plants which are utilized in Traditional Chinese medicine in treating the various pathogenic factors of HE.
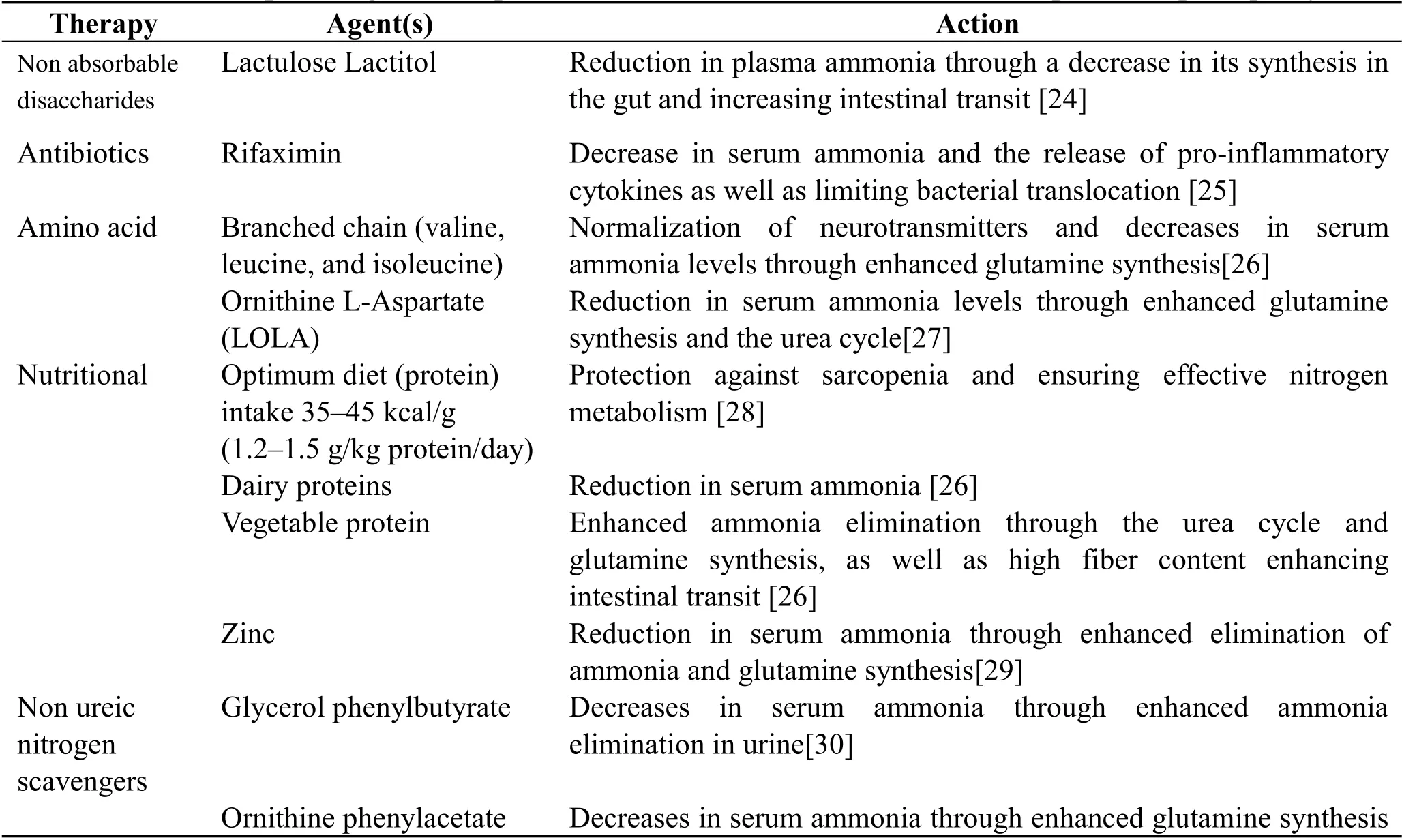
Table 1 Therapeutic agents and potential candidates for the treatment of Hepatic encephalopathy

Therapy Agent(s) Action(OP) as well as a reduction in neuroinflammation[31]Polyethylene glycol(PEG)Reduces the levels of plasma ammonia[32]Human albumin dialysis Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System(MARS)Focus on inflammation and reduction in the concentrations of plasma creatinine,bilirubin and ammonia[33]Reduction in levels of ammonia through portosystemic shunting Probiotics Varying Reduction in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and plasma ammonia levels through reduction in intestinal pH and changes in the composition and function of the microbiome[34]Dopamine agonist Radiological approaches Spontaneous shunts occlusions Bromocriptine Improve dopaminergic neurotransmission[35]Experimental/Research Minocycline Reduction in the levels of ammonia in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid[36]Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflamm atory Drugs(NSAIDs)Ibuprofen Normalization of the glutamate-NO-cGMP enzyme pathway and prevention of neuroinflammation[37,38]Indomethacin Inhibits the synthesis of potent bias positive allosteric modulators(ALLO and THDOC)of the GABAA receptor[39]Others Sildenafil Inhibits phosphodiesterase 5 leading to increase in cGMP with resultant effect on the glutamate-NO-cGMP pathway improving cognitive and learning deficits[40]Fecal Microbiota Transplantation(FMT)Adjusts favorably the gut microbiota[41]Ro 15-4513 Attenuates neurosteroids induced potentiation of GABA-evoked currents[42]AST-120 Exhibits a bias adsorbent profile for ammonia[43]

Table 2 Herbal Formulations for the Treatment of Hepatic encephalopathy
Vernonia amygdalina Del
V.amygdalina(Asteraceae) is shrub or small tree of 2-5 m.It is commonly known as bitter leaf.Its leaves are petiolated,elliptical,and about 6 mm in diameter.With a marked odor,the leaves are green,and distinctly taste bitter [21,44].The plant is widely distributed in Nigeria (especially in the southeastern and southwestern parts of the country) and Ghana.The leaves serves as ingredient in soups while tonic drink for the prevention of certain ailments are made from its juice [45].A wide array of phytochemicals is present inV.amygdalina.Extracts fromV.amygdalina,have been shown to exhibit good ethnomedical and pharmacological properties,including a profound hepatoprotective action [21,46].A comparative quantitative phytochemical study in Ghana by Asante et al.[8],showed the action of anthraquinones,tannins,alkaloids,terpenoids,saponins,cardiac glycosides and reducing sugar in both young and old leaves with flavonoids present in only the young leaves.This explains why most Ghanaian communities prefer the use of the young leaves to the old ones.
In vivo histological study of liver damage inPlasmodium bergheiinfected ICR mice indicates hepatic rejuvenation.In the case of the mice treated with 200mg/kg,there was no evidence of hepatic necrosis,Kupffer cell hyperplasia,haemosiderosis or periportal mononuclear cell infiltration [8].Biochemical analysis in the same study also shows improved hepatic enzymatic activity such as Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) and Alanine transaminase (AST),total bilirubin,and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) compared with control groups.V.amygdalinais known to exhibit anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting prostaglandin E2 (PDGE2),thromboxane (TXA),cytokines and nitric oxide [47].These inflammatory molecules are known to mediate the pathophysiology of HE [44].Though V.amygdalina has been used to treat HE,cirrhosis and hepatitis in some local communities in Africa,there is little or no pharmacologic evidence available to support the mechanism of action of the drug in humans.
Saponaria officinalis L.Saponaria officinalis(Caryophyllaceae),is popularly known as the soapwort plant.The roots and leaves are used for the treatment of scrofula and skin diseases,sap to increase bile flow and treat scabies,hepatic eruptions,the roots as a blood purifier,diuretic,and diaphoretic[48].This,therefore,shows the utility of the various parts ofS.officinalisin traditional medicine.In some local African communities,extract from the root ofS.officinalisis harnessed for remedying both acute and chronic hepatic derangements like chronic hepatitis B,alcohol-induced hepatitis,cirrhosis,hepatic encephalopathy [49].The presence of cyanogenetic glycosides terpenoids,lignoids,flavonoids and curcuminoids has been seen on the screeningS.officinalisphytochemically[50,51].
In a paracetamol-induced liver toxicity in rat model,the potency and efficacy ofS.officinalisroot extracts(methanol) for its hepatoprotective activity was studied [52].The percentage protection based on important liver markers SGPT,SGOT,ALP,total serum bilirubin and total protein levels,showed very good efficiency.The study showed that the effect of the highest dosage of 500mg/kg being comparable to efficacy as the standard drug Liv 52 (Positive),with the significant restoration of altered biomarker enzymes with percentage protection 66.67%,60.63%,65.93%,64.24% and 60.98% of liver(AST,ALT,ALP,total bilirubin and total protein)levels.The percentage protection produced by the chloroform extract ofS.officinalison AST,ALT,ALP,total bilirubin and total protein levels were 16.19%,15.47%,17.18%,15.63% and 14.63%,31.82%,31.09%,34.74% 31.25% and 30.49%,56.17%,54.53%,61.55% 57.29% and 53.66% respectively[53].The hepatoprotective action produced by the methanol extract ofS.officinalison AST,ALT,ALP,total bilirubin and total protein levels were shown to be comparatively higher than the ethanolic extract ofV.amygdalinaon albino rats[54].
Niuzhangzi(Antrodia cinnamomea Polyporaceae)
Antrodia cinnamomea(Polyporaceae),habited mostly in Taiwan,is parasitic fungus and a medicinal mushroom.A.cinnamomeais employed in remedying varying ailments,example,liver diseases,abdominal pain,diarrhea,and hypertension [55].The Taiwanese people,have since time immemorial,utilized this to teat liver diseases arising from alcohol consumption abuse.Collecting wild fruiting bodies ofA.cinnamomeahowever,is a difficult task [56].The chemical constituents ofA.cinnamomeahave had a wide reportage.Maleic/succinic acid derivatives,polyphenols,flavonoids,benzenoids,diterpenes,triterpenoids,steroids,and polysaccharides have been isolated fromA.cinnamomea,and they have been showed to possess potent remedying effects [56,57].In ethanol-induced acute liver injury in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats,potential hepatoprotective activity was shown byA.cinnamomeafruiting bodies [58].Again,in a chronic alcohol consumption model study in rats,Huang et al.[59] observed that,the fruiting bodies effects ofA.cinnamomeacaused a down regulation in the gene expression of acetyl-CoA carboxylase,SREBP-1c,3-hydroxy-3-methoxyglutaryl-CoA reductase,fatty acid synthase and malic.From other studies also,histopathological examination results,further augment the proof of the remedying effects of ethanolic extract ofA.cinnamomeafruiting body of in alcohol-induced liver injuries- hepatocyte necrosis and inflammatory cell infiltration [60].
Again,in an ethanol-induced liver fibrosis model,Lu et al.[61],has reported the hepatoprotective potential of the fruiting bodies ofA.cinnamomea.It was revealed that the ethanolic extract,ensured a down regulation in the expression of hepatic mRNAs,i.e.,tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α,matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9,Kruppel-like factor(KLF)-6 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1.The effects ofA.cinnamomeamycelia against ethanol-induced liver injury in male SD rats was investigated by Lu et al.[56].Oral administration ofA.cinnamomeawas shown to suppress the elevation levels of AST,ALT,ALP,and TB in rats.In the prevention of ethanol-induced acute liver injury and free radical generation in rats,it was further revealed that a triterpenoid enriched fraction of the ethanolic extract ofA.cinnamomeamycelia,proffered the most significant effect [46].In a CCl4 induced liver injury model in mice Hsiao et al.[62],examined the hepatoprotective potential of the water extract of fruiting bodies ofA.cinnamomea.AST and ALT were revealed to be significantly declined in theA.cinnamomeaaqueous extract orally administered group.In another study,the water extract ofA.cinnamomeaimproved the effects of hepatic superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) [63].Again,in vitro study,1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radicals were scavenged to an appreciable level by the water extract ofA.cinnamomeafruiting bodies[63].
Chenxiang(Aquilaria agallocha Roxb.Malvaceae)
Aquilaria agallocha(Malvaceae) typically grow in forest zones up to about 80 feet tall with a thick stem of 3-4 feet in diameter.It is native to Southeast Asia.The bark is papery thin and was sometimes used for writing.Leaves are thin-like leather,shiny,and up to 3-inch long [64].The plantAquilaria agallochahas several pharmacological effects.It has hepatoprotective,anticancer,antioxidant,anti-inflammatory,antidiabetic,analgesic,antihistaminic,antipyretic,laxative,antidiarrheal activities.Aquilaria agallochaalso has an antihistaminic,anxiolytic,antimicrobial,sedative,antibacterial,ulcer,and anticonvulsant activities [47,65].It has been proven that the hepatoprotective role of ethanolic extract ofA.agallocha(AAE) leaves in PCM-induced hepatotoxicity in Sprague-Dawley(SD)rats are relatively high due to higher antioxidant properties.It contains a high amount of terpenoids,flavonoids and glycosides and actively maintained the enzymatic activities of AST,ALP,ALT,LDH,CHL,thereby preventing PCM-induced histopathological changes in the liver[8].
Xiantaoxianrenzhang(Opuntia ficus-indica L.Cactaceae)
Opuntia ficus-indicahas long been a house-trained crop plant essential in agricultural economies distributed in the arid and semiarid areas of the world[66].It is believed to have originated from Mexico.It is often used in livestock feed as a vegetable forage resource during water shortage and shortage of herbaceous plants [67,68].Most scientific medicinal research studies involve the leaves(cladodes) rather than the fruit.Reports have shown that a variety of medicinal plants,contain phenolic compounds such as phenolic acid,proanthocyanidins,tannins,diterpenes,and flavonoids.Through the prevention of the decomposition of hydroperoxides into free radicals as well as,the inactivation of free radicals,the mentioned phenolic compounds exert their antioxidant actions.Rajaratnam et al.[69] and Naoi et al.[70],have reported the inhibition of hydrolytic and oxidative enzyme activity,anti-inflammatory,and free radical scavenging effects of flavonoids.The hepatoprotective potential of aqueous extract from cactus cladodes in CCl4-induced toxicity in wistar male rats examined showed decreases in AST and ALT levels.In the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria,cytochrome P450 metabolizes CCl4 with the resultant formation of CCl3O-,a reactive oxygen species (ROS) which initiates lipid peroxidation and enhanced marker enzymes such as ALT,ALP and AST [71].In ethanol-attenuated liver,a marker of lipid peroxidation- malonaldehyde (MDA) was increased.Again,in the hepatocytes,reduced glutathione (GSH)is ordinarily present for the detoxification of free radicals.GSH depletion,has been seen to positively correlate to increases in the sensitivity of cells to diverse aggressions,leading to tissue disorder and injury[72].
Extreme necrotic alterations,as well as other noteworthy alterations such as inflammatory infiltration of lymphocytes,microvesicular steatosis,increase in sinusoidal space,dilation of central vein and increase in the fat droplet,has been revealed in a histopathological study of CCl4 induced liver model[73].Recovery with the observed alterations has been seen to be effected by the treatment of ethanolic extract ofA.indicatuber,evident by the recovery features such as the typical pattern of the central vein,radiating pattern of cell plates and absence of fat droplets.Again,ethanolic extract ofA.indicatuber,has been observed to significantly decrease serum markers ALT,ALP,AST,MDA,GSH[22].
Haizao(Phoenix dactylifera L.Arecaceae)
Phoenix dactylifera(Arecaceae),commonly referred to as date palm is regularly used in the northern parts of Nigeria,Middle-Eastern countries,and Arabia for liver-related ailments treatment with clinical symptoms such as jaundice[74].Earlier investigations have shown that the fruit's extract protects the liver from toxins and alcohol damage.The hepatoprotective potential of methanolicP.dactyliferafruit extracts in TAA-induced toxicity in male rats was quite auspicious [75].Reports indicate that the methanolic fruit's extract of the plant displayed substantial hepatoprotective capability because of the reduction in the levels of the hepatocellular enzymes of the test groups in comparison to the TAA-induced (control)group [76].The potentials of the extract to upset the rise in serum bilirubin and ALP induced by TAA suggests its prospect in reversing the plasma membrane damage.Qualitative evaluation of the plant extract showed the existence of tannins,flavonoids,saponins,terpenoids,carbohydrates,steroids,proteins,and glycosides [21].Membrane-stabilizing capabilities of flavonoids have been reported.Therefore,it is wise to conclude that the membrane-stabilizing effect ofP.dactyliferaextract could be due to the presence of flavonoid in it.However,the biochemical mechanism of the hepatoprotective effect of theP.dactyliferawas not investigated in this study.The bioactive compound in fruit extract β-sitosterol was assumed to be responsible for its action.Also,flavonoid was proposed to be responsible for the hepatoprotective role via cytochrome P450 aromatase inhibition[77].Similarly,Ferreira et al.[78],recently documented the hepatoprotective property of aqueous flesh and pits of dates extracts(P.dactyliferaL.)against CCl4-induced toxicity in rats.There are many other medicinal plants with similar biological properties to the above-discussed ones.Globally,some plants have been utilized medicinally to remedy liver impairments.Some of these plants are Pugongying (Taraxacum officinale Asteraceae,Heizhongcao (Nigella sativaL.Ranunculaceae),Allium hirtifoliumBoiss.,Qincai(Apium graveolensL.Apiaceae),Cibo (Berberis vulgarisL.Berbericidaceae),Yangji (Cynara scolymus Asteraceae),Jinzhanhua (Calendula officinalisAsteraceae),Suanyepoluomenshen(Tragopogon porrifolius Asteraceae).Others are Dasuan (Allium sativumL.Amarylidaceae),Daamiqin(Ammi majusL.Apiaceae),Prangos ferulaceaL.,Ouxiazhicao (Marrubium vulgare Lamiaceae),Ouzhoulongyacao(Agrimonia eupatoriaL.Rosaceae),Xigua (Citrullus lanatusThunb.Cucurbitaceae) andPrunus armeniacaL.Noteworthy,they all seem to have the same or similar phytochemical constituents.This could be a pragmatic reason why a variety of plants are employed for the remedying of HE in different continents across the globe.
Biochemistry of phytochemicals
Polyphenols exist in different plant parts,including leaves,roots,stem,bark and fruits,with flavonoids being the largest group [8].The excessive production of ROS by mitochondria and NADPH oxidase,and consequent reduction in antioxidant activity in cells inevitably,results in oxidative stress.This is an important stage in the neuronal involvement in HE and some neurodegenerative diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis[79].The disruption of the microanatomy of the blood-brain barrier by the actions of Free radicals have been reported.This is ensured through the oxidation of protein,RNA and DNA,peroxide membrane lipids,membrane damage and inducing proteins crosslinking in astrocytes.A similar reaction occurs in the endothelium of cerebral microvasculature,thereby increasing vascular permeability of ammonia [80].Noteworthy,the number of hydroxyl groups in the phenolic rings of A and B,the presence of 2,3-unsaturation and a 4-carbonyl in the C ring,determine the antioxidant activity of flavonoids.Flavonoids make a donation of a hydrogen molecule from one phenoxyl radical to mop up single superoxide,oxygen,hydroxyl and peroxyl radicals by releasing extra hydrogen atom.The diol group complexes with transition metal ions such as ferric iron,copper,to prevent the synthesis of ROS,which is known to cause cytoplasm and mitochondria damage.Flavonoids are,therefore,suitable membrane stabilizers[81,82].
Naoi et al.[70],demonstrated the flavonoid NOB’s overall ability to decrease serum ammonia which is a crucial molecular agent of hepatic encephalopathy.As dietary components,NOB and other related polymethoxylated flavonoids generally,depict commendatory pharmacokinetic profiles [13,81].Again,studies investigating the efficacy of NOB in treating the metabolic disorder without substantial toxicity has shown satisfactory results [83].In employing varying diet-specific mechanisms,the study also revealed broad ammonia-lowering activities of NOB in mice.The co treatment of NOB together with RC and HPD feeding seemed not to stimulate significant CPS1 induction,although transcriptional activation of CPS1 via C/EBP induction appears to operate under HFD.Furthermore,contrary to NOB’s ability to similarly ensure a reduction in serum ammonia at both ZT6 and ZT18,in HFD and HPD,the high ammonia levels in the respective diets were more strongly diminished by NOB [84].Thus,NOB fundamentally stabilizes the circadian ammonia rhythm in HFD and HPD to RC levels,by functioning to reverse the surged ammonia difference between the active and inactive phases.Noteworthy,varying molecular and cellular mechanisms,may underlie such mechanistic and functional plasticity due to the fact that NOB and other flavonoids,remarkably modulate diverse cellular pathways [85,86].Posttranslational modifications (PTMs) for CPS1 protein activity has received much attention recent mechanistic studies besides,the transcriptional regulation and the allosteric cofactor NAG [87].Also,an ability to attenuate HPD-induced bacterial production of ammonia by amino acid deamination and urea hydrolysis,has been attributed to NOB.
Terpenoids found in plants likeP.dactyliferascavenges for hydroxyl and peroxy radicals,singlet oxygen and nitric oxide to prevent the excess formation of ammonia which has neurotoxic effects [88].Compassing the lipid membrane bilayers,they ensure the trapping of radicals at the conjugated polyene chain and in the terminal ring moiety,and lipid peroxide products are consequently eliminated from the membrane [89].In vitro and in vivo studies,the antioxidizing ability of phytochemicals,especially tannins and,flavonoids has been proposed to contribute to neuroprotection.Noteworthy,the required structure for neuroprotective ability does not sometimes associate with that for antioxidant function.For neuroprotection,the orthodihydroxy substitution in the B ring of flavones is not necessary [9].The hydroxyl substitution in position 3 on the C ring and position 5 on the A ring is however,required for the neuroprotective activity of quercetin [89].The involvement of antioxidant-independent mechanism in neuroprotection is therefore,backed by these results.
The activities of ROS-scavenging enzymes,such as superoxide dismutase,catalase,glutathioneS-transferases,glutathione peroxidase,glutathione reductase and NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) are augment by polyphenols.This is mediated by activation of cell signalling pathways.Several reports show that a pragmatic role is played by ROS in the inflammatory process,by releasing inflammatory signalling peroxiredoxin 2 (PRDX2) and activates macrophages to in turn,release Interleukin-6.The synthesis and release of inflammatory TNF-α,IL-6,inducible nitric oxide synthase and MCP-1 are suppressed through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory transcription factors by stilbenoids,lycopene and curcumin,derivatives of flavonoid [90].In vivo models in albino rats,the activity of cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase,arachidonic acid-metabolizing enzymes,prostaglandins and leukotrienes synthesis,were curtailed by flavonoids,resveratrol and curcumin through modulating the second messenger systems[91].
Neuroprotective Mechanism of Phytochemicals in Hepatic encephalopathy
Phytochemicals proffer hepatoprotective and neuroprotective effects in the liver and brain respectively,and regulate apoptosis signalling,mitochondrial functions,ATP synthesis,mitochondrial biogenesis and degradation by autophagy.Complex I is protected by anthocyanins and resveratrol.Mitochondrial fission/fusion pathways in cells transfected with amyloid precursor protein (APP) are also modulated by the duo.Mitochondrial fragmentation and cytotoxicity induced by Aβ in cells is inhibited by [9].Liquiritigenin again,induces mitochondrial fusion.The expression of mitofisin-1 and -2 (Mfn1 & Mfn2),fusion-mediating optic atrophy protein 1 (Opa1),fission regulating dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) and mitochondrial fission protein 1 (Fis1),are enhanced by resveratrol,and it also,protect PC12 cells against rotenone-induced cytotoxicity[3,92,93].
The integrity of neurons is preserved by the increase in mitochondrial biogenesis by phytochemicals.The proliferator-activated receptor PGC-1α and NRF-1 & -2,regulates mitochondrial biogenesis whereas,mtDNA replication and transcription is controlled by mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM).GC-1α activates NRF-1 & 2 transcription factors and estrogen-related receptor α and induces expression of nuclear DNA-encoded mitochondrial protein [94].PGC-1α activity is post-transcriptionally regulated by phosphorylation and acetylation in astrocytes.Resveratrol has been reported to upregulate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK),enhance mitochondrial biogenesis in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes via PGC-1α,and preserve neuronal cells[95].
Histopathological hallmarks of hepatic encephalopathy include neuronal cell shrinkage,chromatin condensation and nucleosomal degradation.Inhibition of membrane permeabilization and preservation of cells from apoptosis induced by MPTP,was effected by black tea extract,quercetin,resveratrol,rosmarinic acid and astaxanthin[96].They also,ensured the prevention of amyloid aggregates and ischemia by vascular endothelium rejuvenation.
Nucleotide translocator (ANT) and cyclophilin-D form a pore at the inner mitochondrial membrane of neurons.This has therefore,been identified to be a burst of superoxide synthesis.Sesamolin,astaxanthin and lipophilic derivatives of ferulic acid have been reported to prevent the formation of this pore.Again,at the outer mitochondrial membrane,the aldehyde and alcohol derivative of ferulic acid prevented the opening of the pore.Equally suppressed were the efflux of apoptogenic cytochrome and calcium,the formation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) and apoptosis in the liver [11].Phytochemicals,like curcumin,has also been reported to suppress phosphorylation of voltage-dependent anion channel by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3),directly interact with voltage-dependent anion channel,inhibit oxidative modification of the thiol residues in ANT and membrane protein,and prevent the pore opening in hepatic mitochondria[96].
Using several prosurvival MAP-K pathways,including PI3K/Akt and PKC,phytochemicals activate prosurvival signal pathways[64].Through the alteration of the phosphorylation state of target molecules and modulation of gene expression,these pathways affect cellular function,synaptic plasticity and memory formation.Noteworthy,for MAP-K cascades,known to trigger prosurvival ERK and also apoptosis-inducing N-terminal kinase as well as p38 MAP-Ks,oxidative stress is a known significant trigger.The activation of ERK via transcriptional upregulation of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL,and inhibition of Fas-mediated apoptosis,enhances cell survival and obstructs the formation of the death-inducing signalling complex [97].The binding of bilobalide derived from leaf ofGinkgo biloba,naringenin,hesperetin,luteolin,quercetin,resveratrol and ametoflavone to the ATP-binding site on enzymes and receptors to activate PI3K/Akt and PKC,thereby protecting neurons from premature cell death and improve cognitive and memory functioning have been reported.On the other hand,Flavonoids,ensure the inhibition of oxidative stress-induced apoptosis,activate upstream MAP-K and prevent N-terminal kinase activation [1].The protection of neurons in vivo and in vitro through the activation of PI3K/Akt pathways by resveratrol,curcumin and salvianolic acid derived from traditional Chinese herb Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhizaB.Labiatae) has also been seen.In neurons in the hippocampus,Adamu et al.[98],reported activation of Akt and down-regulation of proapoptotic proteins such as cellular apoptotic signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)by hesperetin.Again,Akt activates NF-κB to upregulate the expression of prosurvival IAP and Bcl-2 protein family,phosphorylates longevity transcription factor Forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) and inhibitors of NF-κB (IκB).In vivo and in vitro,the PI3K/Akt- or ERK-CREB-BDNF cascade were activated by resveratrol,hesperetin,caffeic acid and curcumin,leading to neuron preservation,memory functioning promotion and reversal of depression-like behavior.Also,through inactivation of GSK-3β by phosphorylated Akt,MPP+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis is suppressed by resveratrol[99].
A member of a serine-threonine kinase superfamily PKC,modulates very important physiological functions.It regulates immune responses,apoptosis,cell survival,neuronal differentiation,learning and memory.Polyphenols has been shown to activate PKC [14].Also,through the activation of Keap-1/Nrf2/antioxidant response element (ARE)pathway,Polyphenols have also been reported to regulate the expression of antioxidant enzymes.By binding to transcription regulator nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2),Keap-1 averts the signal stimulation [100].Some phytochemicals have been reported to dissociate Keap-1 from the complex with Nrf2.These are carnosol,baicalein,astaxanthin,carnosic acid,lutein,lycopene,and hydroxytyrosol.Their action induces the translocation of phosphorylated Nrf2 into the nuclei.This therefore,leads to a subsequent binding to ARE in the regulatory region of the target genes and improve expression of Phase II enzymes,such as glutathioneS-transferases,glutathione peroxidase,glutathione reductase,superoxide dismutase and NQO1 [101].Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway is activated by PKCα and PI3K/Akt signal pathways and contributes the antioxidant,anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective functions of polyphenols.
The proliferation of BDNF,GDNF and other NTFs in humans,and the subsequent amelioration of neurochemical and behavioral changes by polyphenols in animal and cellular models have been reported.Green tea catechin and coffee fruit extract increase plasma BDNF levels in humans [102,103].Also,serum BDNF and aerobic performance in physically active men were reported to be enhanced by Yinxingye(GinkgobilobaL.Ginkgoaceae) supplement.On the other hand,increased serum BDNF levels and correlative amelioration of premenstrual syndrome in women was ensured by curcumin.Therapeutic effects of flavonoids,curcumin,resveratrol,astaxanthin and piperine in animal models of ageing,depression,AD,PD,stroke and brain ischemia have been seen [70].Also,via ERK/cAMP reaction element-binding protein (CREBS) or PI3K/Akt pathways,rosmarinic,acid resveratrol,flavonoids,and oleuropein induced BDNF and GDNF expression and exhibited neuroprotection in cultured neurons and astrocytes.In animal models of PD,expression of GDNF is enhanced by Naringen and catalpol (derivatives of the herb Dihuang(RehmanniaglutinosaL.Orobanchaceae) and smilagenin and harpagoside(extracted from Xuanshen(Scrophularia ningpoensisH.Scrophulariaceae).Noteworthy,GDNF is mostly induced by non-flavonoid phytochemicals like curcumin,resveratrol and catalpol.Other the hand however,BDNF generally is induced by flavonoids in vivo and in vitro.
Trk expression and neurogenesis is upregulated by Polyphenols to proffer neuroprotection [79].In the hippocampus,TrkB and TrkA was intensified by olive polyphenols.However,in the striatum and frontal cortex,this effect was not witnessed.In animal models of depression,antidepressant-like effects were presented.In a mouse model of AD,pathological changes prevented by EGCG induced increases in BDNF,TrkA and TrkB expression[11].Again,in a rat model of depression,deoxygedunin,ethanol extracts from Huanghuacai (Hemerocalliscitrina Asphodelaceae) and citrus isolate nobiletin,promoted hippocampal neurogenesis whereas,in a mice model,increased TrkB and BDNF expression was seen[104].
The main histopathological feature in the neuronal aspect of hepatic encephalopathy,is the accumulation of plaques and neurofibrillary tangle.Alterations in the secondary structure formation of insoluble aggregate structure,oligomerization and polymerization and dysfunction of the proteolytic pathways,ensure the accumulation of abnormalmutated and altered protein [78,105].Noteworthy,neurotoxicity is lately thought to be decided by the process,rather than the end product.In view of this,the depletion of toxic oligomers and fibrils together aggregation of intermediates should be the focus of therapeutic interventions.The suppression of the synthesis of amyloidogenic monomers and formation of oligomeric and fibrillar aggregates by flavonoids has been reported [106].Also,they foster the formation of nontoxic aggregate.It was again seen that,flavonoids,through the activation of proteolytic systems,ensure the normalization of neuronal dysfunction otherwise caused by Aβ.The ability of β-secretase (BACE1) and γ-secretase to sequentially cleave APP results in the formation of amyloidogenic Aβ peptides with 40-42 amino acids.The suppression of β-secretase by some phytochemicals such as polymethoxyflavones,ferulic acid,genistein,tannic acid and galangin,have been shown to better behavioural impairment in animal models of various neurogenic disorders [11].Again,the expression of β-secretase has been seen to be reduced by rutin,luteolin,icariin,7,8-dihydroxyflavine,EGCG,curcumin,resveratrol and quercetin.APP cleavage by α-secretase into harmlessN-terminal product soluble APPα andC-terminal fragment α EGCG was fostered by curcumin,genistein and oleuropein[1].Soluble Aβ oligomer were produced by rosmarinic acid,curcumin and myricetin.On the other hand,toxic oligomers and fibrils were decreased.The hydrophobic sequences of amino acids 14-24 and 27-37 of insoluble Aβ were interacted with EGCG.This led to the breakage of the β-sheet motif,prevention of the formation of fibrils,and the conversion of large mature Aβ and αSyn fibrils into harmless,minute,amorphous protein aggregate.Inhibition of Aβ aggregation is also ensured by the binding of myricetin,honokiol and luteolin to the hydrophobic region of the amyloid pentamer[1,88].The assemblage of Aβ and αSyn into harmless spherical aggregates incompetent in seeding amyloid formation was ensured by aflavins.This therefore,led to the remodeling of Aβ fibrils into harmless aggregates.Tau protein is an ordinary,unfolded,highly soluble protein.However,imbalances between kinases and phosphatases yield hyperphosphorylated tau.The hyper phosphorylation of tau alters its conformation and renders it an aggregate-prone species: a subsequent production of neurofibrillary tangles on the back of a conversion of the monomer to oligomer and aggregation into pair helical filaments.The most harmful form,the immediate tau oligomer,is known to cause synaptic impairment in HE [90,107].The suppression of tau hyperphosphorylation by phytochemicals such as curcumin,resveratrol,altenusin and caffeic acid,inhibited the aggregation of tau into toxic oligomers[50].On the other hand,suppression of tau protein aggregation and dissolution of paired helical filaments in vitro and cells was ensured by anthraquinones [104].A proposal has been made for the aggregation of presynaptic αSyn as a pathogenic factor in α-synucleinopathies.Increases in oxidative stress,missense mutations,metal ions,phosphorylation and interaction with phospholipid membrane,induce alpha-Syn aggregation and fibrillization.The intermediate generation of the toxic oligomers is most hazardous for the αSyn neurotoxicity,just as for the cases of Aβ and tau.The suppression of αSyn oligomer formation,and assembly into aggregates by phytochemicals such as nordihydroguaiaretic acid myricetin,baicalein,kaempferol,theaflavins,rosmarinic acid,curcumin and ferulic acid has been reported [108].Also,a conversion of mature αSyn fibrils into harmless,minutes,unstructured aggregates is done by EGCG.A change in hydrophobic surface into more soluble species,through the binding of curcumin to existing toxic oligomer and fibrils has been identified [15].Impairment of the cellular proteolytic systems results in protein aggregation.Noteworthy,the two leading proteolytic systems in neurons are the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) and ALP.Dysfunction of these,is known to end in generations of proteinous inclusion body in neurodegenerative disorders [53,108,109].Unfolded ubiquitinated protein is targeted by the UPS,and the dysfunction leads to a build-up of miss-folded protein in neuropsychiatric disorders including HE.Noteworthy,concerning the pathogenesis,the part played by USP however,remains clouded.Disease-specific abnormal protein aggregates Aβ,αSyn,N-terminal fragments of mutant Huntingtin in Huntington's disease is targeted by the ALP [88].On the other hand,the ALP also targets mutant TDP43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and damaged mitochondria [110].This mechanism has been proposed to occur in HE as well.Autophagy activation has been proven to eliminate aggregate-prone proteins,control axon homeostasis and neurogenesis,and adjust the pathogenesis of HE,AD,PD and other neuropsychiatric impairments[111-113].
The mTOR/ULK1 is an essential deleterious modulator of autophagy,and the Beclin-1 is a constructive controller[114].Neuroprotection through mTOR-dependent or -independent mechanisms is proffered by phytochemicals,through the stimulation of autophagy.Through autophagic breakdown of αSyn and efflux,mediated by Sirt-1-dependent deacetylation of LC3 (MAP1LC3A) and its translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm,resveratrol prevented MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in mouse models of PD [115].The downregulation of mTOR/p70S6K signalling and activation of autophagy by curcumin,protected PC12 cells against A53T αSyn-induced cytotoxicity [116].In other studies,the activation of autophagy by curcumin through the downregulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway,ensured neuroprotection in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice [5,117].Amelioration of cognitive impairment was proffered,through the ability of oleuropein aglycone to induce autophagy through activation of AMPK/mTOR signal pathway,and inhibit Aβ aggregation.In cellular models of PD and AD,phytochemicals such as EGCG,resveratrol and curcumin have been seen to suppress AMPK and initiate mTOR-mediated autophagic degradation[118].
Mechanism of Hepatoprotection
The progression of the liver towards damage when exposed to toxins initiates hepatosteatosis,fibrosis and cirrhosis.Characteristically,elevated levels of various liver enzymes and altered metabolites mark the deteriorated state of the liver [115,119,120].The observation of dead hepatocytes indicate poor prognosis.Chronic antibiotics exposure,alcoholism,viruses pose marked danger to the hepatocytes.In the state of hepatocytes damage,transaminases and glutathione have been reported to be prime candidates'marker in the metabolism of bile [86].Also,measurement of serum levels of alkaline phosphatase(a key hepatic enzyme),provides an avenue to assess the clinical state of the hepatic environment [121].The replacement of healthy hepatocytes with scarred tissues affect the normal functioning of the liver.Essential function such as,detoxification,metabolism,clearance of various drugs and secretion of essential proteins are highly compromised[48,122,123].
Through a number of mechanisms,hepatoprotective herbal drugs,ensure protection against several harmful effects.In regulating several mechanisms,they help in appropriate hepatocellular functioning[2].These mechanisms include but not limited to,inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymatic activities and an increase in antioxidant level/decrease in oxidants (ROS formation).It is apparently clear that some phytochemicals have the capacity to cause the presence of microsomal enzymes either by hastening the elimination of the hepatotoxin or by suppressing lipid peroxidation caused by it [124].Hepatoprotective activities,have been identified with phytochemicals such as,flavonoids,triterpenes,saponins and alkaloids are known to possess.Ali et al.,have suggested that Flavonoid and tannins exert their antioxidant activity by scavenging the free radicals,which cause lipid peroxidation[125].
Apigenin
Apigenin,a plant flavone,has been observed to foster hepatocellular integrity.Thapa and colleagues [110],have reported its capacity to regulate downwards Nrf2-signalling,and upregulate the BCL-2 apoptotic pathway.This pathway is known for its mitochondrial biogenesis and plasma membrane stabilization.
Caffeic acid
Occurs naturally in coffee bean,green tea,wine and fruits.Caffeic acid is chemically 3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid.Through the suppression of the release of proinflammatory cytokines,it has identified itself as a potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent [126].Also,it was effective in treating major liver complications,including HE.The expression of kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1(Keap1),a hepatic carcinoma factor can be modulated by caffeic acid.This is done through its interaction with Nrf2 binding site and disallowing it from binding to Keap1[127].This has been reported to increase the expressions of vital antioxidative signals.
Catechin
Catechin is found in some particular fruits,seeds and extracts of green tea.The presence of a hydroxyl moiety at C3,C5 and C7 position of the A ring,and also at C3 and C4 of the B ring,form the order for their categorization.Catechin possesses anti-hyperlipidemic property,and this ensures it usage in a wide range of multiple clinical situations involving non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases,where dysfunctions in protein and lipid metabolisms have great influences on the pathophysiology of the liver[128,129].
Curcumin
Curcumin ensures its hepatoprotective effects through a number of ways.The inhibition of hepatic stellate cells,lipid peroxidation products,activation of Akt and pro-inflammatory cytokines,describes the varying therapeutic routes of curcumin.The expression of GSH,SOD,Nrf2 and CAT,as result of oxidative stress has been seen to be remedied by curcumin.Through the possession of the potent phenolic pharmacophore,β-diketone and methoxy group,curcumin is enabled as a free-radical scavenger over the activity of varying forms of ROS[73].
Epicatechin
Epicatechin is chemically flavan-3-ol.It is abundantly present in cocoa and other plant material.Epicatechin plays a key role in lipid metabolism in fatty liver condition and Hypercholesterolemia [109].In the event of liver impairments,it has been seen to decrease the levels of vital liver enzymes like AST,ALP and GGT which are otherwise elevated[130].
Ferulic acid
It is the most predominant phenolic acid in plants and possesses a formidable antioxidant ability to mob up and nullify the activity and effects of the free radicals like O2-.By interfering with the Smad signalling pathways and extracellular signal-regulated kinases as well as,suppressing the expression of the extracellular matrix related gene,the powerful liver anti cholestatic therapeutic effects of ferulic acid is felt [111].It usually stimulate AMPK itself,or the MAP-K signaling pathway to enhance lipid metabolism [131].Kim and colleagues [132],reported that ferulic acid regulate the expression of several physiological factors like PPAR α,CPT-1α through lipid oxidation,and is very paramount in remedying fatty liver diseases.
Hyperoside
The ability to ensure the up regulation of the expression of various diverse endogenous antioxidant enzymes,and equally shut formed free radicals during the metabolism of xenobiotics,make hyperoside an important phytochemical [133].Again,the normalizing detoxifying enzymes phase II ability of hpyeroside further augment its importance,as it is needed that these enzymes play a role during the first lap of oxidation.In a CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity study,its stimulation of the Nrf2 signalling pathwaypurposed for nullifying oxidants,provided an avenue for the alleviation of liver fibrosis[9,134].
Iccarin
In a rat model,iccarin has been reported to retard the buildup fibronectin and collagen in renal interstitial tissues and mesangial cells [135].It has also been reported to be identifiable with the genusEpimedium.Through the inhibition of TNF-α and IFN-γ signalling pathway,iccarin proffers its therapeutic effect identified by a number of published studies [136].In addition,through the regulation of the expression of toll-like receptor,and the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK),iccarin ensures protective hepatoprotective effect[91].
Magnolol
Isolated fromMagnolia officinalis,magnolol from is significant phenolic phytochemical.In a galactosamine-injured hepatotoxicity mice models,magnolol was seen to sustain the oxidative equilibrium.Again,upon exposure of hepatocytes to free fatty acid in vitro,Fasullo et al.[101],reported the ability of magnolin,another phenolic phytochemical fromMagnolia officinalis,to proffer alleviating effects in hepatic inflammation,insulin resistance and lipid accumulation.
Morin
Morin,is chemically 2′,3,4′5,7-penta-hydroxyflavone.It is found in fruits like jackfruit,oranges and mulberry and also in green tea,buckwheat and tartary.In metabolism,the canonical NF-Kβ signalling is inhibited by morin [89].It also stimulate the MAP-K signaling pathway,enhances lipid metabolism and prevents hepatosteatosis[137].
Naringenin
Naringenin is chemically 2,3-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one.It is a naturally flavonoid that proffers anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects [137].Naringenin,by acting as a scavenger,exhibits antioxidant effects,albeit minimal.However,even in clinical conditions where prooxidants and reactive oxygen are formed as a result of damage mechanism in hepatocytes,naringenin ensures in upregulating the Nrf2 pathway,to make sure the normal redox of the cell is intact[119].
Resveratrol
Resveratrol,a polyphenolic compound,is chemically3,5,4′-trihydroxystilbene.It is found in some distinct fruits such as grapes and some plant materials.Resveratrol has been identified to have regulatory activity over sirtuins (SIRT),a specialized mammalian [138].Lipogenesis has been seen to be regulated through the overexpression of this homolog.This has been seen to be beneficial in the treatment of non-alcoholic related fatty liver disease.Also substantial decreases in various liver enzymes,proinflammatory cytokines and transcriptional factors like nuclear factorκB,has been seen to be linked to the effects of resveratrol.On the back of the activation of IκBα,resveratrol alleviates nuclear factor-κB(NF-κB)expression[93].
Wogonoside
This is a naturally occurring flavonoid obtained from Huangqin(Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi.Lamiaceae).Wogonoside is chemically 3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(5-hydroxy-8-methoxy-4-oxo-2-phenylchromen-7-yl)oxysoxane-2-carboxylic acid.It is known for its anti-inflammatory effect.By fostering the oxidation process,wogonoside proffers hepatoprotective effect by regulating the metabolism of lipid.In different models of studies,the therapeutic effectiveness of wogonoside,has been seen to be from its abilitytoregulate AMPK signaling[139].
Conclusion and the Way forward
Conclusion
Though current and experimental therapeutic approaches are provided in Table 2.0,there is no mistaking that there are enormous therapeutic opportunities in phytomedicines in the treatment of more complex ailments like hepatic encephalopathy as shown in Table 1.0,with very minimal adverse effects and at a relatively cheaper cost.This review has shown that herbal drug formulations possess significance hepatoprotective and neuroprotective activity.Hepatic necrosis,Kupffer cell hyperplasia,haemosiderosis,periportal mononuclear cell infiltration,neuroinflammation,oxidative stress,and mitochondrial dysfunction are major pathological hallmarks of a hepatic anomaly.Again,it has shown the ability of phytochemicals from various medicinal plants in correcting these anomalies.Through varying mechanisms identified by published studies,phytochemicals ensure their therapeutic effects.This ranges from the regulation of very simple to more complex molecular pathways as well as,the promotion or inhibition of the expression of various molecular products and or factors,which have varying effects on these pathways.
Noteworthy,it can also be seen that different plants have the ability to ensure remedying effects for HE.This is possible,due to the presence of diverse phytochemicals in these plants.These diverse phytochemicals have various therapeutic effects and are able to return to order,the varying pathogenic factors (inflammation.ROS,altered neurotransmission,complications of the gut microbiota,brain edema and energy metabolism)causing hepatic encephalopathy.Again,certain herbal plants example,P dactylifera,possesses both neuroprotective and hepatoprotective phytochemiclas.This,therefore,shows the ability of a single herbal plant to give remedying effects to a number of disease conditions.The diverse store of phytochemicals in herbal plants,are able to act on varying pathogenic factors in a disease condition.Equally,a number of herbal plants share similar phytochemicals and this therefore,ensures that a number of botanicals have the ability to remedy similar disease condition.
The Way forward
Although,much need to be done to bridge the gap between basic laboratory studies and the clinical research,the contemporary understanding of the molecular interactions between phytochemicals and the various systems on which they exerts their pharmacological effects,provides an avenue for effective drug designs to reduce hepatic injury,delay brain ageing and improve cognitive functioning.Noteworthy,until recently,HE was thought to be fully reversible after liver transplantation,LT as the definitive treatment for end-stage liver diseases is LT,and this clears the underlying pathogenic factor[140].Recent studies,however,indicate that there are existing cognitive deficits which cannot be exactly explained [140,141].Post LT associated cognitive impairments have been seen in patients who have undergone LT for acute liver failure and those with cirrhosis without HE and also without any existing cerebral impairments [142].With the multifactorial proposition on the pathogenesis of HE by recent studies,and the very new findings perhaps,effective treatment might require more than one therapeutic agent.It is of great relief that herbal sourced therapeutic agents like JianPi HuaZhuo XingNao formula [143],are being put through clinical trials.Therefore the search for effective therapeutic agents must follow a strict cutting edge pharmacological and clinical procedures.With the evidences of therapeutic ability of phytochemicals from herbal plants shown,further researches utilizing human randomized controlled trials,are needed to elucidate the clear-cut part that phytochemicals can employ in ameliorating hepatic encephalopathy.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2020年1期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2020年1期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Letters for “Prospects for the future of clinical efficacy evaluation of traditional Chinese Medicine—Emphasis on original theory and clinical practice”
- Prospects for the future of clinical efficacy evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine
——Emphasis on original theory and clinical practice - Effects of Angelica Polysaccharide on telomere length in mice with benzene-induced aplastic anemia
- Protective effects of Pulsatilla chinensis Regel against isoproterenol-induced heart failure in mice
- Effects of Alpinia oxyphylla on oxidative stress and expression of p47phox in diabetic nephropathy rats
