Effects of Angelica Polysaccharide on telomere length in mice with benzene-induced aplastic anemia
Runjie Sun,Xing Cui,Qingsong Wang,Yanyu Zhang,Xiaoqi Sun
1Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jinan,China;
2Department of Hematology,Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jinan,China;
3First Clinical College of clinical,Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jinan,China.
Abstract
Keywords:Aplastic anemia,Telomere,Bone marrow failure,Angelica polysaccharide
Background
Aplastic anemia(AA)is a rare life-threatening disease of bone marrow failure[1].This causes a deficiency of all the three types of blood cells such as: red blood cells,white blood cells,and platelets.Individually their deficiencies are known as anemia,leucopenia,and thrombocytopenia,respectively,and collectively it is known as pancytopenia.Other reasons behind development of AA can be exposure to chemicals,drugs,radiation,infection,immune disease,and heredity;in about half the cases,the cause is unknown[2].In addition,exposure to chemicals like benzene can also lead to development of AA.
At each end of a chromatid,in a chromosome,there exists a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences called telomere.One of the main function of telomere is to protect the ends of the chromosome from deterioration or from fusion with neighboring chromosomes,and it is of vital importance to maintain chromosome stability [3].It was observed that about one third of the patients with AA had telomere shortening,and the degree of telomere shortening was related to the length of the course of disease.The shorter the telomere,the more likely it was to develop into late malignant clonal complications.Furthermore,telomere erosion in acquired marrow failure mainly affected the granulocytes and it was also seen that patients with short telomeres were predominantly those who did not respond well to immunosuppression[4-6].It was speculated that presence of ‘stressed’hematopoietic stem cell resulted in telomere shortening,which over-proliferates in response to marrow failure.In some in vitro studies,it was demonstrated that telomeres are highly susceptible to oxidative stress,similar evidence was presented in other study by Richter and Zglinicki,showing that oxidative stress-mediated DNA damage is an important determinant of telomere shortening[7].
AP,which is isolated and purified from the root of Danggui (Angelica Sinensis),It can rapidly reconstitute hematopoiesis and increase platelet production in mice[8].In the present study,we investigated the changes of telomere length and the level of BFU-Es and CFU-Es in mice with benzene-induced AA; conducted a follow-up of the therapeutic effects of AP.
Materials and methods
Grouping of animals
Healthy BALB/c SPF mice (male,6-8 weeks old,weight 18-20 g,n = 120) were obtained from the Experimental Animal Center of Shandong University(Qualified number:37009200006508,Shandong,China).These mice were used according to the guidelines of the Jinan Military General Hospital Animal Care and Use Committee and the studies were performed with approval from the committee.Totally 120 mice were randomly divided into three groups by random number table method,normal group(n=24)and modeling group (n=96).Group 1: normal control; 24 healthy mice were fed under the same conditions without any treatment.Group 2: AA control (48 mice); according to the Liu’s method[9],inhalation of benzene at a concentration of 14.6 mg/l air was carried out in a tightly closed plastic jar(volume 0.05 M3) for 2.5 months,2.5 h/d,6d/wk.After that,of the 48 mice,24 mice were put to death for the measurement,and remaining 24 mice received 1 ml distilled water as daily p.o.dose for 2 weeks after the establishment of AA models.It was found that three of these 24 mice treated with distilled water died within 2 weeks.Group 3: treated AA (48 mice);benzene inhalation procedure was similar to Group 2,but given AP (10mg/kg body weight) was given ip.per day for 6 weeks after the establishment of AA models.Out of 48 mice in Group 3,four mice were found dead within 2 weeks after treatment with AP.
Reagent
AP was purchased from Beijing Biochem Co.,Ltd.China.
Peripheral blood cells and BMC count
An amount of 20 μL blood was taken from the orbital vein of these mice and was diluted with the diluent(recommended by manufacturer)on day 1 and 14 after the establishment of AA models,before analysis with the HS-18 fully automatic blood cell analyzer.For estimating bone marrow cells (BMC) count,24 mice from each group were sacrificed,and the femurs of each mouse were removed.The BMC suspension was prepared according to Till’s method [10],and the number of BMC was counted.
Hematological examination
The tails of the mice from the three groups were cut and blood samples were collected before and after benzene inhalation and following AP administration.Blood cells (RBC,WBC,and platelets) were counted in the peripheral blood samples.On completion of the experiments,mice were sacrificed and femur smears were prepared for differential counting of BMCs.Figure 1 shows the difference among the marrow hematopoietic tissue of these three groups.
Culture of BFU-Es and CFU-Es from mouse bone marrow
113 mice were killed by decapitation and femora and humeri were dissected under sterilized condition.The BMCs were washed with Iscove’s modified Dulbecco’s medium (IMDM; Sigma),then a suspension of mononuclear cells (MNCs) was prepared and adjusted to a concentration of 106 cells/ml.A methyl cellulose system was used to perform an in vitro cultivation [11].Transferred the cultivation system into a flat-based culture flask,and incubated at 37°C under 5% CO2 in air.After incubation,colonies of colony-forming unit-erythrocytes (CFU-Es) and burst-forming units-erythrocyte (BFU-Es)were counted at day 3 and 7,respectively,and the colonies were collected.
Measurement of telomere length
Relative telomere length was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method as described previously [12],this method is further referred as Tel-PCR.For the PCR assay,2 μL of each DNA dilution was prepared in a total reaction volume of 20 μL using the 2 x SYBR Premix Ex Taq [Takara Biotechnology(Dalian)Co.,Ltd.China].
All sequences were obtained from Sangon Biotech Co.,Ltd (Shanghai,China).Telomere sequences were amplified in an ABI 7300 real-time PCR system(Applied Biosystems,Foster City,California,USA)using the following conditions: Activation of Taq polymerase was done at 95°C for 10 min;35 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 sec,and annealing/extension was done at 54°C for 2 min.The conditions for the amplification of the36B4gene were as follows:95°C for 10 min; 40 cycles at 95°C for 15 sec,and 58°C for 1 min.The ABI Prism 7300 SDS Software was used for data analysis.The telomere length(x)for each sample was based on the telomere to single copy gene ratio (T/S ratio),which was based on the calculation of the ΔCt[Ct(telomeres)/Ct(36B4)](Table 1).
Telomere length was expressed as the relative T/S value,which was normalized to the average T/S value of reference sample [2-(ΔCtx-ΔCtr) = 2-ΔΔCt ],which was used for standard curve construction,as the reference sample,and as the validation sample.The results obtained from different plate runs were used to make comparisons,the results of each plate were approved only if the relative T:S ratios of the validation reference sample fell within a 3%variation.Laboratory personnel conducting the telomere length assay were blinded to the clinical outcomes of the mice prior to statistical analysis(Table 1).

Table 1 The final telomere primer concentration and sequence
Statistical analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was made to compare the experimental results among three groups of mice and q-tests were applied for the paired comparison between two groups each.
Results
Hematological criteria confirmed that AA mouse models were successfully established,which was confirmed by significant reductions of RBC,WBC,and platelet counts in peripheral blood of AA mice (P<0.01),and significantly increased non-hematopoietic tissues of bone marrow in comparison with normal control.However,a notable recovery appeared after treatment with AP (Figure 1).The data of marrow hematopoietic tissue capacity showed that ASP could also ameliorate the bone marrow hyperplasity (Figure 2).
Mice were randomly chosen from the three groups(1,2,3) for the colony cultivation and counting of bone marrow BFU-Es and CFU-Es (Table 2).Compared to normal control group,the colony counts of BFU-Es and CFU-Es from bone marrow of AA mice were found to be significantly lower (P<0.01).Furthermore,when microscopically observed,it was found that depressed growth and proliferation of erythroid progenitor cells were evident in AA mice.After treatment with AP,counts of BFU-Es and CFU-Es restored to 66.8% (17.5/26.2) and 77.25%(59.1/76.5) of the normal levels,respectively (Table 2).
After application of ionizing radiation,a significant decrease in telomere length was observed (P<0.01).Whereas,after treatment with AP,the length of telomere was restored upto 76.34% (0.71/0.93) of thenormal levels.It was also found that the telomere length in treated AA mice group (Group 3) was distinctly higher than the AA mice group (Group 2,P<0.01).And after treated with AP,the peripheral blood cell and BMMNC counts improved obviously than the AA mice group(Figure 1).
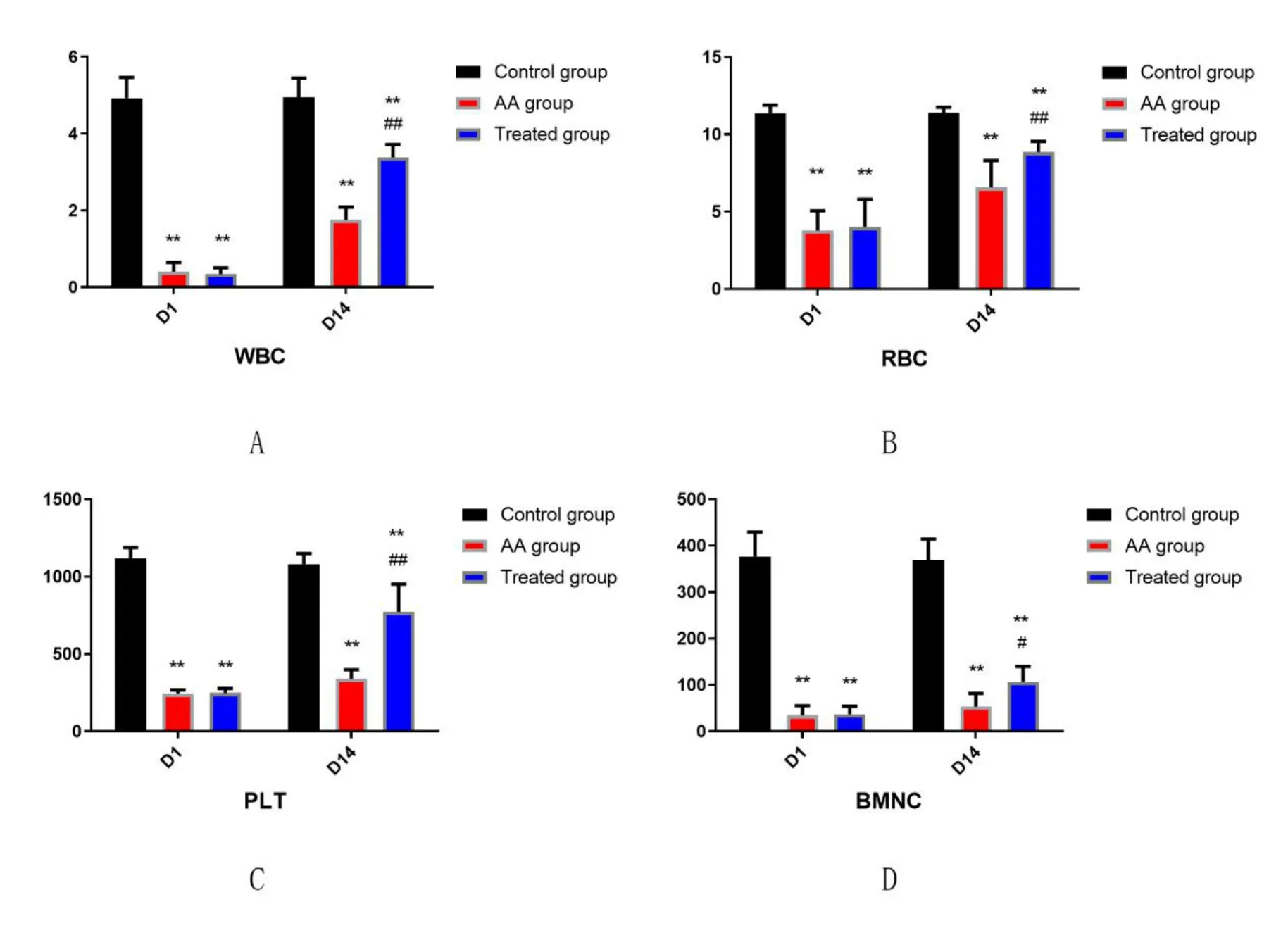
Figure 1 Cell counts(x±SD)in three groups of mice
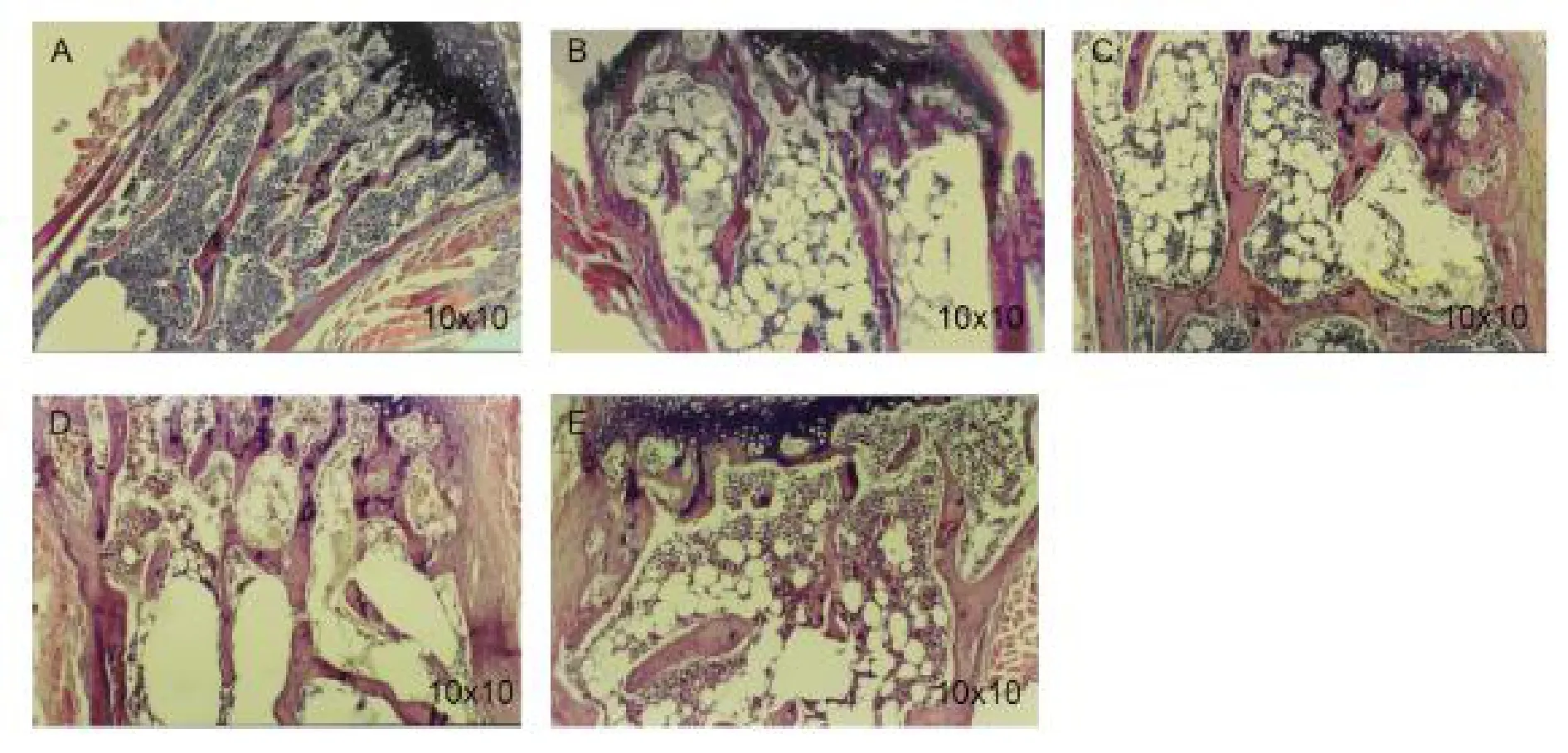
Figure 2 Marrow hematopoietic tissue of three groups of mice
Table 2 The colony counts (x ±¯;number/2x105 nuclear cells)of erythroid progenitor cells from bone marrow in three groups of mice

Table 2 The colony counts (x ±¯;number/2x105 nuclear cells)of erythroid progenitor cells from bone marrow in three groups of mice
Note: *P <0.01,**P <0.05,compared with the Normal control group;△P <0.01,△△P <0.05,compared with the AA mice group.
Grouping After the establishment of AA models(d)n Bone marrow hematopoietic tissue capacity(%)BFU-Es CFU-Es Telomere length Normal control 24 90.38±6.70 26.2±4.3 76.5±5.1 0.93±0.15 AA mice 1 14 24 20 52.75±11.30*23.63±9.32*15.7±2.8*14.8±3.4*40.5±4.4*43.3±3.9*0.52±0.08*0.55±0.15*Treated AA mice 1 14 24 21 51.63±8.23*30.25±8.21*15.3±3.1*17.5±3.5*△△41.0±3.7*59.1±4.1*△0.53±0.11*0.71±0.11*△△
Discussion
Recently studies have found that AP has multiple biological activities,which can enhance the immunity,repair the damaged hematopoietic progenitor cell,anti-oxidation and anti-tumor[8,13,14].Moreover,the mechanism to recover the hematopoietic function or clinical side effects associated with AP has not been found.
One of the major factor responsible for mortality following acute radiation exposure is damage to the hematopoietic system [15].Furthermore,death due to chemicals in addition to various syndromes is assigned to inhibition of the immune system,i.e..
In this study mice were exposed to benzene inhalation and treated with AP,which resulted in a very effective stimulation and recovery of hematopoietic cells.We found that AP could promote the number of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells (BMMNC),peripheral blood counter,and the area of hematopoietic tissue effectively,and also could promote the colony formation of BFU-Es and CFU-Es.
Various human diseases associated with aging,such as cardiovascular disease and infections,etc also accelerate telomere shortening[16,17].Furthermore,shortened and lengthened telomeres also increase individuals' risk of cancer[18,19].Similarly,changes in telomere length may be closely linked to cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer's [20].It has also been observed that rate of telomere shortening with age is accelerated due to several human syndromes characterized by mutations in the telomerase genes.These include some cases of dyskeratosis congenita,aplastic anemia,and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Telomere length was related to the risk of relapse,clonal evolution,and overall survival of severe aplastic anemia [21].27 telomere length along with absolute reticulocyte and lymphocyte counts,is likely to be critical in therapy decision making [22].In addition,hematopoietic cells with short telomeres are dysfunctional,mediate chromosomal instability,and are prone to malignant transformation and bone marrow failure[23].
In brief,maintaining the adequate telomere length is pivotal for hematopoiesis,and excessive loss of telomere permeates the pathogenesis of bone marrow failure,malignancy,and fibrotic disease.Short telomeres not only inhibit cell proliferation but also predispose to chromosomal instability,and this shortening of telomere is closely related with the immune dysfunction.After treatment with AP 14 days,the length of telomere was restored upto 76.34%(0.71/0.93) of the normal levels,however,the length of telomere of AA mice group was 59.14%(0.55/0.93)of the normal levels.It was also found that the telomere length in treated AA mice group was distinctly higher than the control AA mice group (P<0.01).
The therapeutic efficacies tally with the findings of the present study that AP can protect the telomere length and differentiation of hemopoietic stem/progenitor cells,accelerate the recovery of BFU-Es and CFU-Es of AA mice,and then improve the bone marrow failure.And in the future study,we will test the activity of the telomerase and the level of shelterin proteins treated with AP,to find the AP how to protect the length of telomere.
Conclusion
Through a series of studies,we confirmed that AP can significantly increase the peripheral blood cell and BMMNC count of AA mice,and protect the telomere length and differentiation of hematopoietic stem /progenitor cells ,accelerate the recovery of BFU-Es and CFU-Es in AA mice,and thereby improve bone marrow failure.Its mechanism of action and pharmacology Learning needs further study.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2020年1期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2020年1期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Letters for “Prospects for the future of clinical efficacy evaluation of traditional Chinese Medicine—Emphasis on original theory and clinical practice”
- Prospects for the future of clinical efficacy evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine
——Emphasis on original theory and clinical practice - Phytomedicines as therapeutic interventions for hepatic encephalopathy
- Protective effects of Pulsatilla chinensis Regel against isoproterenol-induced heart failure in mice
- Effects of Alpinia oxyphylla on oxidative stress and expression of p47phox in diabetic nephropathy rats
