Protective effects of Pulsatilla chinensis Regel against isoproterenol-induced heart failure in mice
Huimin Zhang,Congping Su,Wei Wang*,Sen Li,Shuzhen Guo*
1 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing,China;
2 School of Life Sciences,Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing,China.
Abstract
Keywords:Pulsatilla chinensis(Bunge)Regel,Heart failure,Network pharmacology,PDE1,PDE5
Background
Heart Failure (HF),the end stage of various cardiac diseases,is a kind of complex clinical syndrome characterized by impaired ventricular structure and ejection or filling function,which increases the risk of death [1].It was reported that the 5-year mortality of HF was approximately 50% globally which was higher than that of various types of cancer [2].In recent years,considerable advances have been obtained in the treatment of heart failure through surgery,transplantation and neurohormonal drugs.However,the strong side effects and a considerable economic burden greatly limited their clinical application.Correspondingly,Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) were historically recorded as the main approach for the treatment of palpitation and cardiac obstruction(heart failure)with multiple targets,low cost and low risks[3].
TCM researches consistently suggest that the gradual formation and development of toxic-heat and blood stasis on the basis of qi deficiency play a vital role in the onset of heart failure.Moreover,TCMs with the effect of clearing heat and removing toxicity have been widely used in the clinical treatment of heart failure [4].The dried roots of Baitouweng(Pulsatilla chinensis (Bunge) Regel,PR),has been clinically used in the treatment of heat toxin and blood dysentery for more than 1000 years due to its heat-clearing,blood-cooling and detoxification effects[5,6].Emerging evidences indicate that PR has many biological activities including anti-inflammation,anti-oxidation,anti-tumor,vasodilation,anti-ulcerative colitis,etc [7,8].But little is known about the efficacy of PR on HF treatment.Thus,we investigate whether PR exhibits the cardioprotective activity in isoproterenol (ISO) induced HF mice and its potential action targets based on the network pharmacological prediction.
Materials and methods
Preparation of PR water extract
The medicinal materials of PR were extracted twice with 10 times water with two hours for each time.The extract was then filtered,and the filtrate was combined and concentrated under reduced pressure to a thick paste with a relative density of 1.48 g/mL.
Animals
All studies were conducted in line with the China Physiological Society’s Guiding Principles in the Care and Use of Animals and with the approval of the Animal Care Committee of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine.40 male C57BL/6 mice weighted 16±1 g were housed in the SPF level conditions(certification number SCXK (Jing) 2012-0001) at Beijing University of Chinese Medicine with the temperature of 22 ± 1°C,humidity of 55 ± 5% and a 12 h light/dark cycle.The mice were provided with free water and diet.All the animals were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co.Ltd.(Beijing,China).
Heart failure model establishment and grouping
After one-week acclimation,the mice were randomly divided into five groups according to the random number table method (n=8 each): control group,model group,PR group,digoxin group,and fosinopril group.The HF models were established by intraperitoneal injection of isoprenaline (day 1: 20 mg/kg/d; day 2: 10 mg/kg/d; day 3 - day 14: 5 mg/kg/d,sigma,101722747,USA) [9].At the same time,PR group,digoxin group and fosinopril group mice were separately intragastrically treated with PR water extract (8.25 g/kg/d),digoxin (0.165 mg/kg/d,Xinyi,H3102067804,China) and fosinopril (5.5 mg/kg/d,China-USA Squinn,H19980197,China) for 14 consecutive days.Control and model group were intragastrically treated with equal volume of distilled water.
Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular function
After two-week treatment,echocardiography was conducted by Vevo2100 ultrasound imaging system(Visualsonics,Canada) with probe (MS-400),a center frequency of 30 MHz and a standard frame rate of 449 fps.Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and removed chest hair.The ejection fraction (EF) and the fractional shortening (FS) were calculated by measuring the left ventricular internal diameter in systole (LVIDs) and left ventricular internal diameter in diastole(LVIDd),respectively.
Morphological observation and the calculation of heart weight index
At the end of the experiment,mice body weights were measured,and the hearts were rapidly obtained from the sacrificed mice.Heart weights were recorded after cold phosphate buffer solution (PBS) flushing and filter paper blotting.Heart shape was photographed by a high-definition digital camera(Nikon,D100,Japan).Heart weight index (HWI) was defined as the ratio of heart mass to tibia length.
Histopathological Examination
The hearts fixed in 10% neutral formalin were dehydrated and cleared with gradient ethanol and xylene,and embedded in paraffin.The 5μm sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE) solution to record overall pathological changes under a microscope[10,11].
Prediction for PR targets
As a system biology research method,network pharmacology has been employed to predict the pharmacological targets and mechanisms in TCM,based on "disease-gene-target-drug" interaction network [12,13].A similarity-based bioinformatics analysis tool for molecular mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine (BATMAN-TCM) platform(http://bionet.ncpsb.org/batman-tcm/) has been previously developed by our lab,and was used to predict PR targets for cardiovascular disease in this study.
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR(qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from mice heart tissues,using TRIzol Reagent (Ambion,15596026,USA),according to the manufacturer's protocol.Total RNA was used for the preparation of cDNA by reverse transcription.The expression of gene was detected by using SYBR Select Master MIX(Applied Biosystems,4472908,USA).The primer sequences were listed in Table 1.The gene expression level was calculated by 2-(ΔCT).
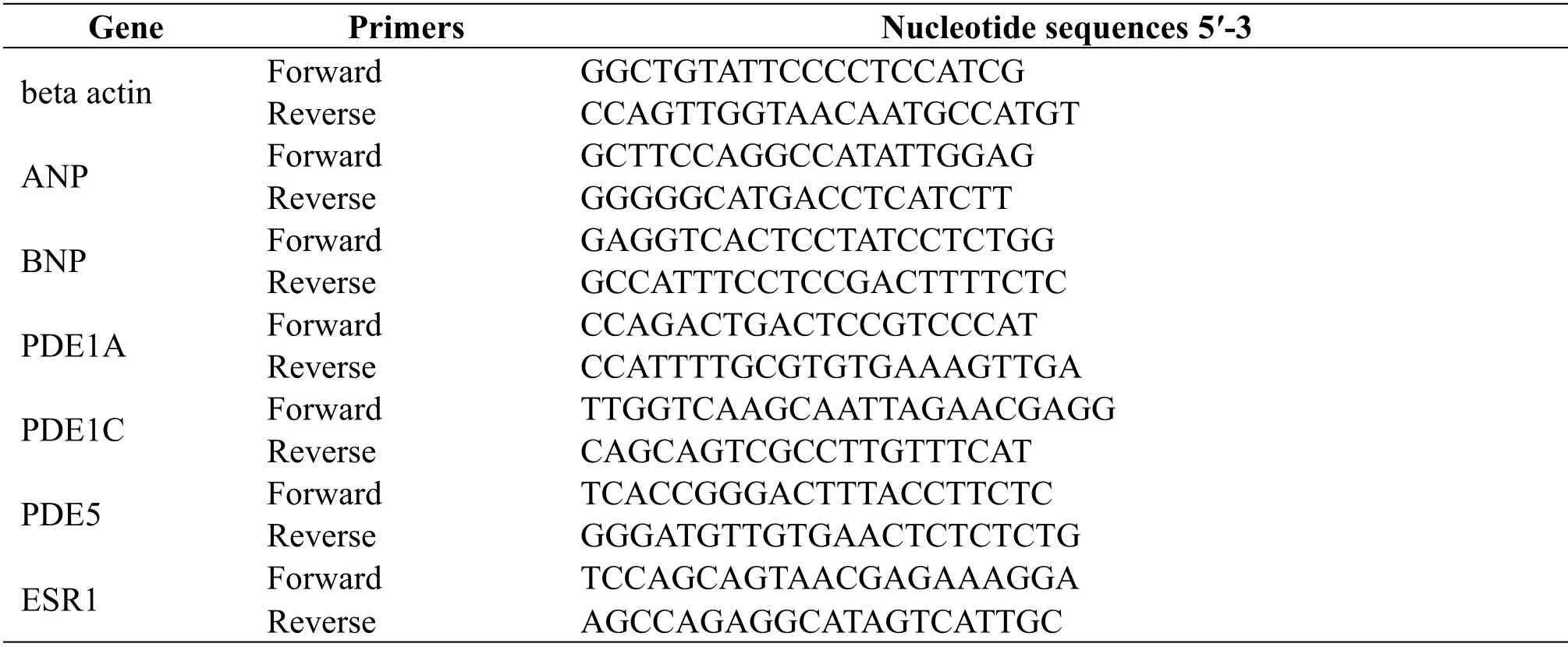
Table 1 Nucleotide sequences of primers used in real-time PCR
Immunohistochemical(IHC)staining assays
5 μ m sections of the paraffin embedded heart were defatted in xylene and hydrated with gradient ethanol,followed by incubation with antigen retrieval solution and 3% H2O2for 30 min.Next,the sections were incubated with the primary antibody (PDE1C and PDE5; BEIJING BIOSYNTHESIS BIOTECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD.) at 4°C overnight as previously described [10,11].On the second day,the sections were incubated for 1.5 h with the corresponding secondary antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology,7074S,USA) followed by the DAB and hematoxylin staining.The slices were photographed and analyzed separately using Image-pro plus(IPP).
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with the SPSS program package (SPSS version 20.0) and all of the data were expressed as the mean±SEM.Comparisons among groups were performed using one-way ANOVA.The value ofP< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Effects of PR on cardiac function in ISO-induced HF mice.
As shown in Table 2,EF and FS were significantly decreased in HF model group (P<0.05) compared to that of the control mice.After treatment for two weeks,the EF and FS was enhanced significantly in PR group(P<0.05)and digoxin group(P<0.01).These results suggested that PR has the potential to improve ISO-induced left ventricular enlargement and cardiac function.The effect was similar to digoxin group and better than fosinopril group.
Effects of PR on heart morphological and pathological alterations in ISO-induced HF mice
It was demonstrated that heart weight index (HWI)was positively correlated with the severity of left ventricular dysfunction.The HF model mice showed higher HWI than the control mice (P<0.01,which could be significantly reversed after PR treatment for 14 days (P<0.05) (Figure 1A).Consistently,PR,fosinopril and digoxin treatment of HF mice attenuated the increase in myocardial cross-sectional diameter compared to control(Figure 1B).
As shown in Figure 1C,HE staining revealed that the myocardial fibers were neatly arranged and structurally intact in the hearts of control group mice.But the myocardial fiber lost its normal arrangement and became thicker and discontinuous in the hearts of HF model mice.Supplementation with PR or digoxin to HF mice for 2 weeks resulted in an improvement of myocardial fiber architecture and arrangement,reflected by decreased thickness and increased regularity of cardiomyocyte.
Table 2 Echocardiographic results(±s).

Table 2 Echocardiographic results(±s).
#P <0.05,vs.the control group.*P <0.05,vs.the model group.**P <0.01,vs.the model group.
Group Sample EF(%) FS(%)control 8 60.60±11.81 32.11±9.91 model 8 46.96±9.67# 23.17±5.92#PR 8 59.54±10.82* 31.45±7.43*digoxin 8 61.07±10.31** 32.11±7.13**fosinopril 8 55.68±11.15 28.72±7.83

Figure 1.Effects of PR on the morphology and pathology of ISO-treated hearts.
Effects of PR on the expression of ANP and BNP in ISO-induced HF mice.
ANP and BNP were usually regarded as the HF biomarkers.As illustrated in Figure 2A,ANP and BNP gene expressions in myocardium of ISO-induced HF mice were significantly upregulated (P< 0.05)compared with control group,and PR and positive drugs showed significant reverse effect on expression of both ANP and BNP(P<0.05).
Detection of potential PR targets related to cardiovascular disease by BATMAN
The BATMAN- IPP system(http://bionet.ncpsb.org/batman-tcm) can be used to analyze the significance level of the disease target enrichment and score the correlation between the active ingredient and the target [14].The potential targets of PR intervention on cardiovascular diseases in the database were predicted.Based onP<0.05 and score cutoff=20,the significance analysis and corresponding targets on the treatment of cardiovascular diseases were derived.The screening results show the following four target genes: PDE1A,PDE1C,PDE5 and ESR1.
Effects of PR on the target genes in ISO-induced HF mice
qRT-PCR results showed that the mRNA levels of PDE1A (P<0.05),PDE1C,PDE5 (P<0.05) and ESR1 in hearts were significantly up-regulated by intraperitoneal injection of ISO for 14 consecutive days,while simultaneous administration of PR could inhibit the increased expression of PDE1C and PDE5,which is consistent with the BATMAN prediction.In contrast,the expression of PDE1A and ESR1 gene in myocardium of PR group were upregulated (Figure 2B).
IHC was used to further identify the PDE1C and PDE5 expression locations in heart tissues,and the results indicated that PDE1C and PDE5 were mainly deposited in the myocardial tissue space,which was further confirmed by calculation of intergrated option density(IOD)values(Figure 3).

Figure 2.The effect of PR on gene expression in myocardium.

Figure 3.The effect of PR on the expression of PDE1C and PDE5.
Discussion
In this study,echocardiography,HWI,HE,BATMAN,qRT-PCR and IHC were used to explore effects of PR on myocardial function and structure in ISO-induced HF mice.The results showed that after ISO stimulation for 14 days,the cardiac function in the model mice was significantly decreased characterized by disarranged and hypertrophic cardiomyocytes,and upregulated expression of PDE1C and PDE5 in myocardium.After PR intervention for 2 weeks,the cardiac function was improved,and the expression of PDE5 in myocardium was significantly downregulated,but the expression of PDE1C was not changed markedly.
As a traditional Chinese medicine,PR has good medicinal value and development value.In recent years,researchers have found that PR and its extracts have a variety of pharmacological effects.PR exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators and inflammatory factors [15].PR extract has anti-oxidant effect.PR extract and Pulsatilla saponin A can exert anti-cancer effects by inducing apoptosis [16-18].These mechanisms of action can play a significant role in the treatment of HF.
As a superfamily enzyme system,phosphodiesterase (PDEs) plays an important role in the hydrolysis of the second messenger substances including cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)and cyclic guanosine monophosphate(cGMP)[19,20].There are totally 11 PDE subtypes,in which PDE1,PDE2,PDE3,PDE4 and PDE5 are mainly expressed in the cardiovascular system [21].They act on the key proteins in PKA signaling pathway to further regulate β-adrenoceptor,vascular smooth muscle,and cardiomyocyte contraction proteins,which is crucial for the cardiovascular function.Among them,PDE1 is a calcium and calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase,which is expressed in the heart.PDE1 is expressed as three isoforms: PDE1A and PDE1C are in heart and vessels,whereas PDE1B is primarily found in brain.Novel PDE1 inhibitors induce vasodilation and lower blood pressure [22].PDE1C is expressed in myocardial tissues of mice,dogs and humans with heart failure [23].PDE1C is a direct transcriptional target of peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPAR α ) in the heart of mice,then reduces cAMP levels [24].PDE1C activation plays a causative role in pathological cardiac remodeling and dysfunction[25].
PDE5 is abundantly expressed in the vascular system and can reduces vascular tone by inhibiting NO-cGMP-PKG signaling pathway [26].PDE5 inhibitors can effectively treat pulmonary arterial hypertension [23].PDE5 is responsible for cGMP hydrolysis especially in the case of low calcium ion concentration [27].Accumulated evidences have shown that the increased expression of PDE5 in patients with advanced heart failure leads to the downregulation of cGMP and protein kinase G (PKG)which finally induces ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction and heart function deterioration[28].Meanwhile,overexpression of PDE5 in cardiomyocytes can aggravate left ventricular remodeling induced by myocardial infarction in mice[29].Takimoto et al illustrated that TAC-induced left ventricular hypertrophy in mice was significantly relieved after the PDE5 inhibitors treatment,which is attributed to the suppression of pressure overload triggered hypertrophic signaling pathways [30].In summary,PDE1C and PDE5 may play a key role in HF development.
Estrogen has vascular protective effects,but must be combined with estrogen receptor (ER) to function[31].Estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) is mainly expressed in the uterus and has a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP).Multiple SNP loci and prone to gene mutations can affect the function of ESR1 protein after transcriptional translation,thus losing the protection of blood vessels [32,33].According to the experimental results,we reasonably speculated that the treatment of PR may cause a change in some SNP loci of ESR1,resulting in a significant increase in ESR1 expression and loss of cardiovascular protection.The specific change mechanism needs further study.
Thus,we studied the role ofPulsatilla chinensisin improving heart failure and its mechanism.The experiment has initially proved that administration with PR to ISO-induced HF mice increased the EF and FS,and inhibited the expression of PDE5,indicating an improvement of cardiac structure and function.There are still many shortcomings in this experiment.For example,the detailed and deeper action mechanism are requiring such as further detecting the expression of cGMP,PKG and PKA.We will do more in-depth research in future experiments.
Conclusion
PR treatment may suppress cardiac hypertrophy and improve myocardial function in HF mice via inhibiting the predicted targets PDE5 expression.These results suggest the potential of using PR in preventing the development of HF.
Author Contributions Statement
HZ,SG and WW conceived and designed the experiments.HZ and CS was responsible for the experimental research and writing.SG and SL was responsible for the modification of the article language.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2020年1期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2020年1期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Letters for “Prospects for the future of clinical efficacy evaluation of traditional Chinese Medicine—Emphasis on original theory and clinical practice”
- Prospects for the future of clinical efficacy evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine
——Emphasis on original theory and clinical practice - Effects of Angelica Polysaccharide on telomere length in mice with benzene-induced aplastic anemia
- Phytomedicines as therapeutic interventions for hepatic encephalopathy
- Effects of Alpinia oxyphylla on oxidative stress and expression of p47phox in diabetic nephropathy rats
