基于非格点MonteCarlo方法模拟高分子在表面上吸附
施双飞 孙立望 李洪

摘 要: 高分子链在表面吸附过程已经成为了物理、生物、医学等领域的重要课题。通过研究高分子链在表面上的吸附作用,可以指导改善物理化学器件性能,改变生物领域某些如蛋白质吸附、药物合成等相关过程。高分子链在表面上的吸附构象性质与高分子链链内作用力以及表面吸附作用强度有关。本论文采用非格点Monte Carlo模拟方法研究其在不同作用力下的吸附过程以及构象性质。模型采用软排斥表面,研究了高分子单链在均质表面上的吸附行为,及其临界吸附点。
关键词: Monte Carlo模拟; 非格点; 构象; 吸附
中图分类号:TP391 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-8228(2019)11-01-03
Abstract: The research on the adsorption process of polymer chains on the surface plays an important role in the fields of physics, biology and medicine. The study on the adsorption of polymer chains on the surface, can lead to the improvement of physical and chemical device performance, and change some processes in the biological field such as protein adsorption and drug synthesis. The adsorption conformation properties of the polymer chain on the surface are related to the unit force of the polymer chain and the adsorption strength of the outer surface of the chain. In this thesis, the adsorption process and conformational properties under different forces are studied by off-lattices Monte Carlo simulation. With the soft repellent surface model, the adsorption behavior of the polymer single chain on the homogeneous surface is studied, and its critical adsorption point is discussed.
Key words: Monte Carlo simulation; off-lattice; conformation; adsorption
0 引言
高分子鏈可以以化学吸附或物理吸附两种方式吸附在表面上,并随着几何限制、表面吸引力、溶液质量的不同,其最终稳定后的高分子链的构象也会不同。在化工界,对高分子吸附行为的研究有着重要应用,例如电子器件的保护涂层、高分子纳米材料[1]、工业使用的润滑剂[2]、胶体悬浮液的稳定性[3-4]和粘附性。因此研究高分子在临近表面时表现的吸附行为具有重要意义[5-8]。
1 模型
本文用Lx*Ly*Lz的三维连续空间模拟均质单链高分子的运动环境,其中x和y方向为周期性边界,在z方向z=0处存在一个无限大的不可穿透软排斥表面,该表面对高分子存在吸附作用。本文将单体直径归一化设置为[σ],开尔文温度T=1,玻尔兹曼常数[kB=1]。
1.1 模型建模
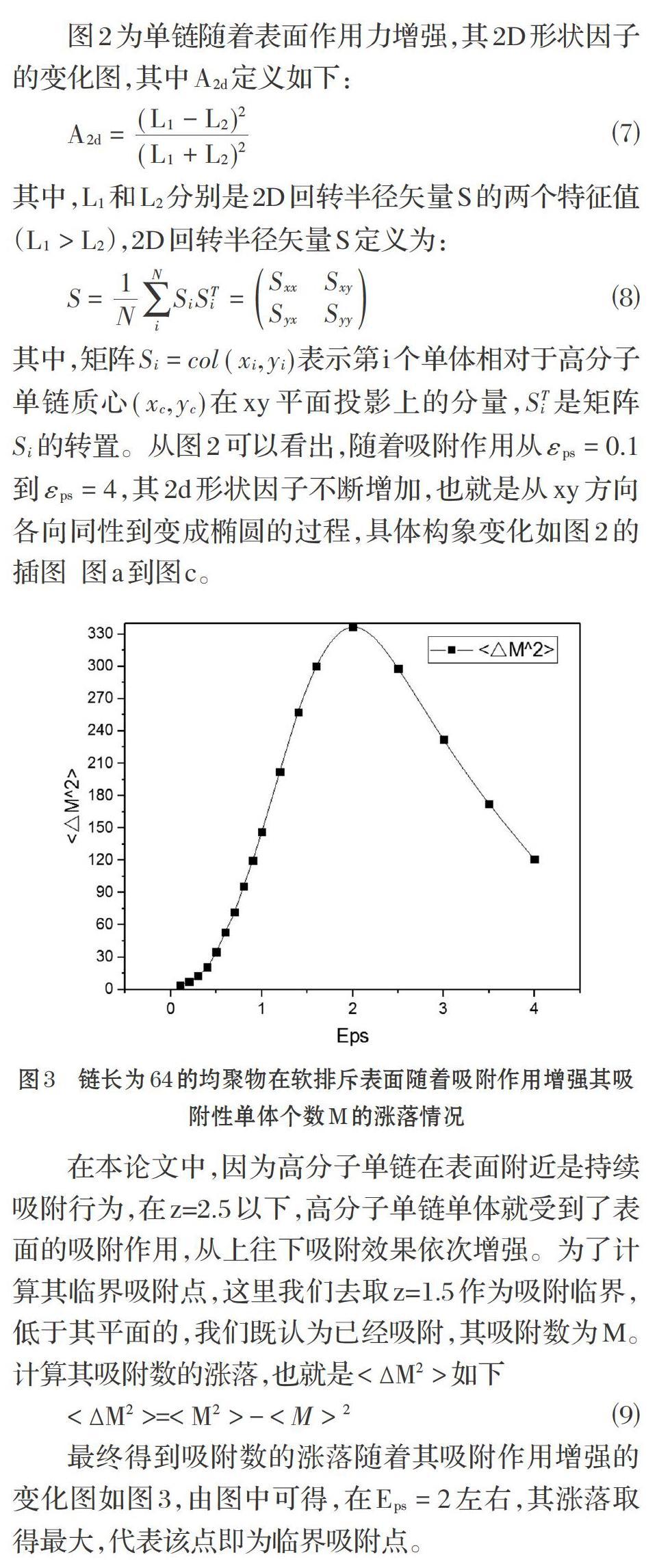
3 结论
在本篇论文中,我们采用了非格点Monte Carlo模拟方法,通过相邻单体之间使用FENE势能,非相邻单体之间使用LJ 12-6势能,单体和表面之间使用LJ 9-3势能,构建了比较符合实际情况的真实链。得到结论如下:因为论文使用的是连续性吸附能,和格点吸附链相比,稍有不同,在吸附作用很小时,高分子链先发生位置的改变,此时形状变化小,其表现为均方回转半径和均方末端距变化不大,z轴质心下降,随着吸附作用增加,高分子单链在Eps=2.0位置发生了垮塌吸附。
参考文献(References):
[1] Liu J,Wu Y,Shen J,et al.Polymer–nanoparticle interfacial behavior revisited: A molecular dynamics study[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2011.13(28):13058
[2] Teraoka I.Polymer solutions in confining geometries. Progress in Polymer Science[J].1996.21(1):89-149
[3] Meredith J C,Johnston K P.Theory of Polymer Adsorption and Colloid Stabilization in Supercritical Fluids. 2.Copolymer and End-Grafted Stabilizers[J].Macromolecules,1998.31(16):5518-5528
[4] Neyret S,Ouali L,Candau F,et al.Adsorption of Polyampholytes on Polystyrene Latex: Effect on Colloid Stability[J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,1995.176(1):86-94
[5] Cerda J J,Sintes T,Sumithra K.Adsorption of semiflexible block copolymers on homogeneous surfaces[J].The Journal of Chemical Physics,2005.123(20):204703.
[6] Luo M B.The critical adsorption point of self-avoiding walks:a finite-size scaling approach[J].Journal of Chemical Physics,2008.128(4):905.
[7] Sumithra K,Straube E.Adsorption of diblock copolymers on stripe-patterned surfaces[J].Journal of Chemical Physics,2006.125(15):114703.
[8] Sebastian K L,Sumithra K.Adsorption of polymers on a random surface[J].Physical Review E,1993.47(1):32-35
[9] Li C Y,Qian C J,Yang Q H,et al.Study on the polymer diffusion in a media with periodically distributed nano-sized fillers[J].The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2014.140(10):104902.
[10] Abraham F F,Singh Y.Comment on the Structure of a Hard Sphere Fluid in Contact with a Soft Repulsive Wall[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics,1977.67(5):2384-2385

