足月妊娠水囊引产对产褥感染的影响
旷金元 吴艳 梁丽蓉
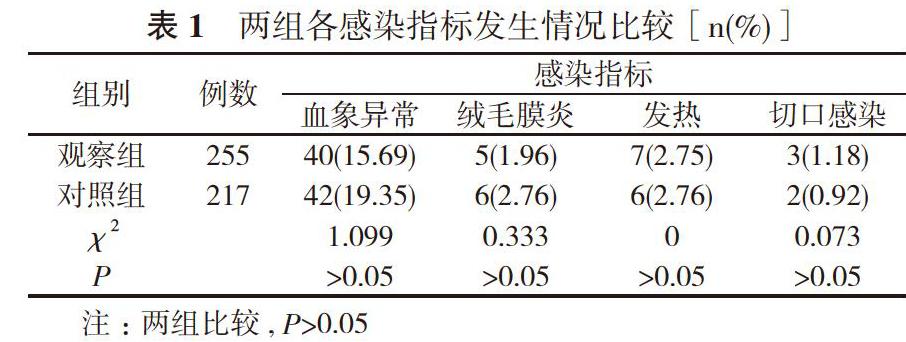
【摘要】 目的 探讨足月妊娠水囊引产对产褥感染的影响。方法 472例引产产妇, 根据引产方式不同分为观察组(255例)和对照组(217例)。对照组采用缩宫素引产, 观察组采用水囊引产或者水囊引产加缩宫素引产。比较两组感染发生情况以及各感染指标(血象异常、绒毛膜炎、发热、切口感染)发生情况。结果 观察组感染发生率为15.69%(40/255), 对照组感染发生率为19.35%(42/217), 两组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);观察组的血象异常率15.69%、绒毛膜炎率1.96%、发热率2.75%、切口感染率1.18%与对照组的19.35%、2.76%、2.76%、0.92%比较, 差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 水囊引产与单纯缩宫素引产在感染发生率方面无明显差异, 无禁忌证的水囊引产操作不会增加产褥感染的发生率, 对产褥感染没有影响。
【关键词】 足月妊娠;水囊引产;缩宫素引产;感染
【Abstract】 Objective To discuss the effect of induced labor with water bag on puerperal infection in full-term pregnancy. Methods A total of 472 pregnant women were divided by different methods of induced labor into observation group (255 cases) and control group (217 cases). The control group received oxytocin induced labor, and the observation group received induced labor with water bag or induced labor with water bag and oxytocin. The occurrence of infection and infection indicators (abnormal hemogram, chorionic inflammation, fever and incision infection) between the two groups. Results The incidence of infection in the observation group was 15.69%(40/255), which was 19.35%(42/217) in the control group, and the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). In the observation group, the abnormal rate of hemogram was 15.69%, chorionic inflammation rate was 1.96%, fever rate was 2.75%, and incision infection rate was 1.76%, which was not statistically significant with those of the control group as 19.35%, 2.76%, 2.76% and 0.92% (P>0.05). Conclusion There is no difference in incidence of infection of induced labor with water bag and oxytocin. No contraindication of induced labor with water bag will not increase the incidence of puerperal infection, and has no effect on puerperal infection.
【Key words】 Full-term pregnancy; Induced labor with water bag; Oxytocin induced labor; Infection
在妊娠的晚期, 由于母體或胎儿的疾病原因, 常需要通过引产以终止妊娠。在众多引产方法中, 水囊引产具有操作简单, 促宫颈成熟效果好, 引产效果佳等优点, 对宫颈不成熟的产妇尤为适宜[1, 2]。产褥感染作为分娩的并发症之一, 轻者影响产妇产后的恢复, 重者可导致感染性休克甚至母儿的死亡, 严重威胁着母亲和新生儿的健康。水囊引产经阴道放置宫颈扩张球囊, 多数学者认为有潜在的感染可能[3-5]。通过对2016年7月~2018年6月足月妊娠水囊引产及缩宫素引产产妇共计472例前瞻性研究, 得出水囊引产与缩宫素引产对产褥感染无明显影响。现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1. 1 一般资料 选取龙岗区第七人民医院2016年7月~
2018年6月472例足月引产产妇。平均年龄(27±7)岁, 平均产次(1.4±1.3)次, 平均孕周(39.68±1.18)周, 平均Bishop宫颈成熟度评分(4.2±1.1)分。根据引产方式不同将其分为观察组(255例)和对照组(217例), 操作前获得产妇知情同意, 并签署知情同意书。纳入标准:孕妇要求或自愿终止妊娠;孕周准确, 且37~42周;胎儿存活;单胎头位, 头盆相称;无胎膜早破;Bishop宫颈成熟度评分<6分。排除标准:急性生殖道感染;阴道分泌物常规检查洁度为Ⅱ度, 排除细菌性阴道病;24 h内有1次体温≥37.5℃;头盆不称;瘢痕子宫;低置胎盘、前置胎盘、前置血管等;具有各种妊娠并发症及合并症者, 慢性疾病的急性发作史者。

