乳腺癌改良根治术后上肢淋巴水肿预防行为干预远期效果评价
陈芳 堵丽丽 李娜
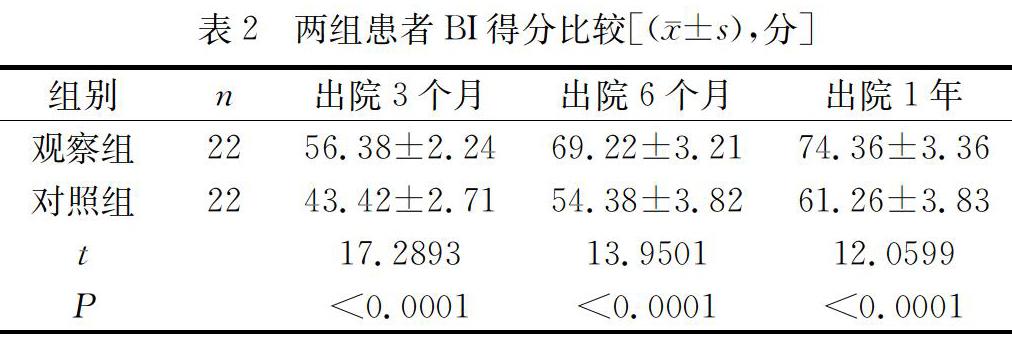

【摘 要】目的:探討对具有上肢淋巴水肿高危发病因素的乳腺癌根治术后患者实施系列预防行为干预措施对其远期效果的影响。方法:选取2016年1月至2018年10月本院外科44例行改良根治术的具有上肢淋巴水肿高危发病因素的乳腺癌患者,随机分为对照组和观察组各22例。对照组给予外科术后常规护理,观察组在常规护理基础上实施针对上肢淋巴水肿并发症的术后系列预防行为干预措施。跟踪随访1年,对比两组术后1个月、3个月、6个月、1年的上肢淋巴水肿发生率的差异和患者日常生活活动能力情况。结果:术后1个月,两组患者上肢淋巴水肿发生率比较无明显差异,无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后3个月、6个月及1年,两组患者上肢淋巴水肿发生率存在明显差异,观察组术后3个月、6个月及1年的上肢淋巴水肿发生率均明显低于对照组。出院随访3个月、6个月和1年,观察组BI得分均明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:对具有上肢淋巴水肿高危发病因素的改良根治术后的乳腺癌患者实施系列预防行为干预措施,可明显预防和减少患者上肢淋巴水肿的发生,提高患者日常生活活动能力,对患者远期治疗效果具有非常重要的临床意义。
【关键词】乳腺癌;改良根治术;上肢淋巴水肿;预防行为干预;远期效果
文章编号:WHR2019045018
[Abstract] Objective:To explore the effect of a series of preventive behavior interventions on the long-term effects of patients with radical mastectomy for upper extremity lymphedema. Methods: From January 2016 to October 2018, 44 patients with breast cancer who had high-risk factors of upper limb lymphedema were treated with modified radical mastectomy in our hospital. They were randomly divided into control group and observation group. The control group received routine postoperative care, and the observation group performed postoperative series of preventive behavioral interventions for upper limb lymphedema complications on the basis of routine care. The follow-up was performed for 1 year. The difference of the incidence of upper limb lymphedema and the activities of daily living activities of the two groups were compared between 1 month, 3 months and 6 months to 1 year. Results: At 1 month after operation, there was no significant difference in the incidence of upper limb lymphedema between the two groups (P>0.05). The incidence of upper limb lymphedema in the two groups was 3 months, 6 months and 1 year after operation. There were significant differences. The incidence of upper limb lymphedema was significantly lower in the observation group than in the control group at 3 months, 6 months and 1 year after operation. After 3 months, 6 months and 1 year of follow-up, the scores of BI in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: A series of preventive behavioral interventions for patients with breast cancer after modified radical mastectomy with high risk of upper limb lymphedema can significantly prevent and reduce the occurrence of lymphedema in the upper limbs of patients, improve the ability of patients to daily activities, and have long-term therapeutic effects on patients. Very important clinical significance.

