湿疹对幼儿生长发育的影响探讨
李菲 刘龙魂 殷致富

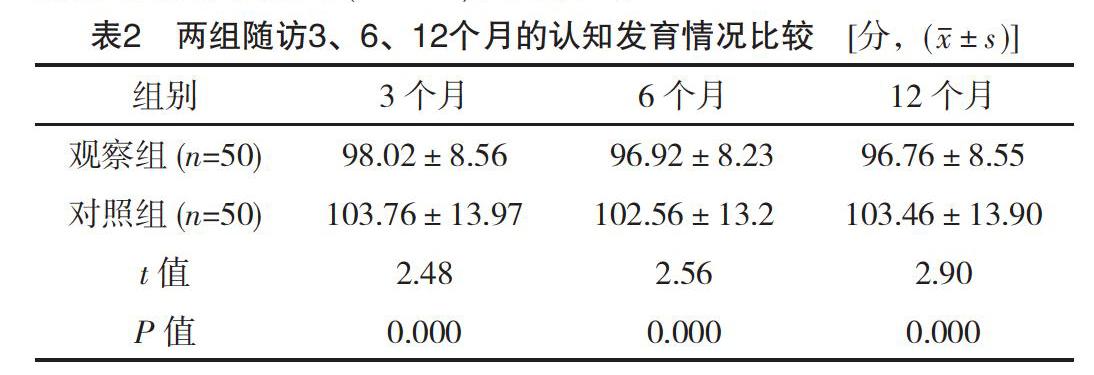
【摘要】 目的:探讨湿疹对幼儿生长发育的影响。方法:将笔者所在医院2017年9月-2018年2月收治的50例湿疹幼儿设为观察组,将同期接受健康检查的50例健康幼儿设为对照组,观察组幼儿予以糖皮质激素乳膏+润肤剂外用治疗,饮食回避,对照组幼儿常规饮食,两组幼儿随访12个月,比较两组幼儿随访3、6、12个月的年龄别体重Z评分(WAZ)、年龄别身高Z评分(LAZ)、认知发育情况。结果:对照组随访3、6、12个月的WAZ、LAZ、发育商评分均高于观察组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:湿疹的发生对幼儿生长发育具有一定的阻碍作用。
【关键词】 湿疹; 幼儿; 生长发育; 体格发育; 认知发育
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2019.19.072 文献标识码 B 文章编号 1674-6805(2019)19-0-03
Effect of Eczema on the Growth and Development of Young Children/LI Fei,LIU Longhun,YIN Zhifu.//Chinese and Foreign Medical Research,2019,17(19):-160
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the effects of eczema on the growth and development of young children.Method:A total of 50 cases of eczema children admitted to our hospital from September 2017 to February 2018 were set as observation group.50 healthy children who received health check during the same period were set as control group.The children in the observation group were treated with Glucocorticoid Cream combined moisturizer and diet avoidance,the control group children were given regular diet,and the two groups of children were followed up for 12 months.The weight-for-age z-score(WAZ),length-for-age z score(LAZ) and cognitive development were compared between the two groups of children at 3,6 and 12 months.Result:The WAZ,LAZ and developmental quotient scores at 3,6 and 12 months were higher in the control group than those in the observation group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:The occurrence of eczema has a certain hindrance to the growth and development of young children.
【Key words】 Eczema; Young children; Growth and development; Physical development; Cognitive development
First-authors address:Tangxia Hospital of Dongguan City,Dongguan 523710,China
濕疹在我国临床较常见,是指由多种内外因素引起的一种皮肤炎性反应,发病后临床症状主要表现剧烈的皮肤瘙痒,延误治疗或治疗不当会造成较严重的皮损[1]。婴幼儿由于胃肠道发育不完善,为发生湿疹的主要群体[2]。长期临床观察发现,幼儿发生湿疹后,除皮损症状外,可伴随出现呕吐、腹胀、腹泻等多种胃肠道症状,阻碍机体对营养物质的消化和吸收,另外,严重的皮肤瘙痒会影响睡眠,继而可能会增加幼儿发生营养不良性相关疾病的风险[3]。为进一步明确幼儿湿疹与生长发育之间的关系,本研究选取50例湿疹幼儿和50例健康幼儿作为研究对象,分析和探讨湿疹对幼儿生长发育的影响,现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
研究对象为笔者所在医院2017年9月-2018年2月收治的50例湿疹幼儿设为观察组,湿疹的诊断以中华医学会皮肤性病学分会免疫学组制定的《湿疹诊疗指南》(2011年版)为参考,除外早产儿、小于胎龄儿、出生低体重儿、唇腭裂及严重出生缺陷儿如心、肝、肾疾病等。同期来笔者所在医院接受健康检查的50例健康幼儿设为对照组。观察组,男28例,女22例;年龄1~3岁,平均(1.40±0.50)岁。对照组,男24例,女26例;年龄1~2.5岁,平均(1.35±0.30)岁。两组幼儿的性别、年龄等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),有可比性。本研究在获取幼儿家属知情、同意后实施。
1.2 方法
观察组幼儿予以糖皮质激素乳膏(芙美松,浙江仙琚制药股份有限公司生产,国药准字H20050610)+润肤剂外用治疗,采取高蛋白饮食回避如牛奶、鸡蛋、虾、蟹、海鱼.对照组幼儿常规饮食,不回避高蛋白食物。比较两组幼儿随访3、6、12个月的体格发育情况、认知发育情况。

