Safety and Risk Management of Cosmetic Products
Jiang Ligang
Proya Cosmetic Co., Ltd., China
Abstract
Key words
cosmetic; safety; critical control point; risk management
In the past three decades, China's economy has developed rapidly, with residents' incomes increasing, information exchange smoothing, and the living standards of developed coastal areas being close to that of developed countries.The domestic cosmetics industry market has increased year by year, and now China has become the world's second largest consumer of cosmetics.With regard to the cosmetics market, from the multinational companies manipulating the mainstream market, to the gradual rise of domestic enterprises, and then the small and micro enterprises are booming, the future competition will be more intense.From the national level, the country frequently introduces cosmetics management regulations.Today, the strictness of Chinese cosmetics regulations is already world-class.From the capital level, the cosmetics industry has digested a good deal of labor employment, and has contributed huge tax revenue to the country.It has also attracted the favor of capital, and several cosmetics companies have successfully listed.
Thanks to China's rapid development of 4G technology, Internet+, and popularized WeChat communication tools and online payment methods, it has brought about a great fusion of knowledge and information flatting , so cross-border innovation, beauty tools, microelectronics technology, genetic engineering, enzymatic synthesis, chiral synthesis, and medical aesthetics have changed the cosmetics industry quickly.However, due to product safety issues, there have been many consumer victimization incidents.At the same time, from the perspective of the whole world trend, personalized niche beauty brands are emerging rapidly in a short period of time, and their operators are often cross-border.They have no experience working in the cosmetics industry.They are easy to ignore quality management or lack of understanding of regulations.This leads to product safety issues that ultimately have a significant negative impact on the business itself.
Product safety is the key to the survival of cosmetics manufacturers, and product safety and risk management is an important key point to determine product safety.It is an important guarantee for cosmetics companies to improve economic efficiency and ensure the core competitiveness of enterprises.
The author discusses the various factors affecting product safety from three stages of cosmetics: research and development, production and sales.This article focuses mainly on cosmetic safety.
Product safety and risk management in the research and development stage
There are three main parts of product safety and risk management in the research and development phase: Raw material selection, formulation screening and evaluation, risk assessment of safety risk substance.
Raw material selection
Cosmetic is a chemical industrial product made from a variety of raw materials.The common materials in cosmetics such as heavy metals, methanol, dioxane, asbestos, phenol, hydroquinone, acrylamide monomer, diethylene glycol, nitrosamines, secondary alkane (alcohol) amines, pesticide residues, Sudan Ⅲ and other substances may be brought into cosmetics through raw materials.
Excluding deliberate additions, many safety incidents in the cosmetics market in recent years have been related to the improper selection and control of cosmetic raw materials.Preventing and controlling the unsafe factors of raw material is the primary prerequisite for cosmetic safety and risk management.
Operators should make sure each ingredient is thoroughly evaluated for safety in the selection of cosmetic ingredients.Investigating the raw material producers is essential, and the raw materials used in each product need to be provided with complete raw material safety information, as shown in Table 1.

If some data is incomplete, the R&D department needs to verify the safety of raw materials through literature index or related experiments, mainly for eye irritation, skin irritation, skin sensitization, reproductive toxicity, phototoxicity, cytotoxicity, etc.It can be referred to the 2015 edition of theSafety Technical Specifications for Cosmetics.

Table 1.Safety information of raw materials provided by supplier
Formulation screening and evaluation
In terms of formula design, it is always important to remember that cosmetics and medicine are different.Medicine is based on a risk-benefit balance.It is effective while allowing side effects, but the patient will discontinue using after the symptoms disappear.Cosmetics should not be at risk during normal daily use; take safety as the first core, while stability, efficacy and usability should be developed with full consideration of safety.When necessary, we can ensure the product by shortening the shelf life, weakening the efficacy and consider convenience for safety.
For product safety, testing can be carried out within the company, and human experiments must meet the relevant national regulations and ethical requirements in advance.Product irritancy and safety were evaluated by human skin patch test (48H test, repetitive patch test, cumulative patch test), and ZEIN.
Because of the widespread use of animal experiments is cruel and complicated, and human correlations are doubtful as well.With the development of technology, the use of animal replacement methods to assess product safety and efficacy will eventually become the trend of the future.Because animal replacement experiments are more scientific, quantitative, efficient, stratified, and humane, it can facilitate the establishment of structure-activity relationships, doseeffect relationships, and time-effect relationships that cover raw materials, formulations, and product processes, with toxicity predictions, toxicity grading, and integrated assessments, raw material screening, threshold determination, formulation optimization and more.There are already many more mature animal replacement methods.For cosmetics that may be mistaken into the eye, eye irritation replacement tests can be operated, such as chicken chorioallantoic membrane blood tests; Allergic tests can be performed using capsaicin receptor assays, direct peptide reaction assays (DPRA) and human cell line activation assays (h-CLAT), mouse local lymph node assays (LLNA: DA) for skin sensitization, and Chick Embryo Chorioallantoic Membrane test (EC50 method), orin vitrostimulation test using a reconstructed skin model (eg Episkin et al).
For some small-scale cosmetics companies, in order to evaluate the irritancy, cooperation with thirdparty testing organizations is an important method for formula screening and evaluation.There are 28 cosmetics administrative licensed to health and safety testing institutions in China, and 196 domestic nonspecial-purpose cosmetics inspection agencies which can carry out microbiological, sanitary chemistry and toxicology testing projects; 7 cosmetics administrative licensed institutions for human body safety inspection can carry out human body safety inspection items and sunscreen effect human body test items; Many import and export commodity inspections, drug inspection institutes, quality and technical supervision bureaus, and a growing number of private third-party testing agencies can evaluate the safety of formulations.
Through the safety assessment, it is possible to screen out safe and effective formulas and then enter the statutory testing process before filing.(note: On December 16, 2013, the State Food and Drug Administration issued theNotice on Adjusting the Registration of Cosmetics Registration (No.10, 2013), proposing that the risk assessment of domestic non-special-purpose cosmetics can confirm the safety of the products.The relevant toxicological tests of the product may be exempted.)
However, considering the current situation of domestic SMEs, in most enterprises, when the synthesis and source of raw materials is not clear, it is still recommended to use experimental methods to ensure that listed products meet safety standards.
Before listing, it is necessary to carry out hygiene and safety testing (including microbiological testing, hygienic chemical testing and toxicological testing) in accordance with the requirements for cosmetic administrative licensing or filing inspection.For the convenience of retrieval, the test contents are listed in Table 2 and Table 3.

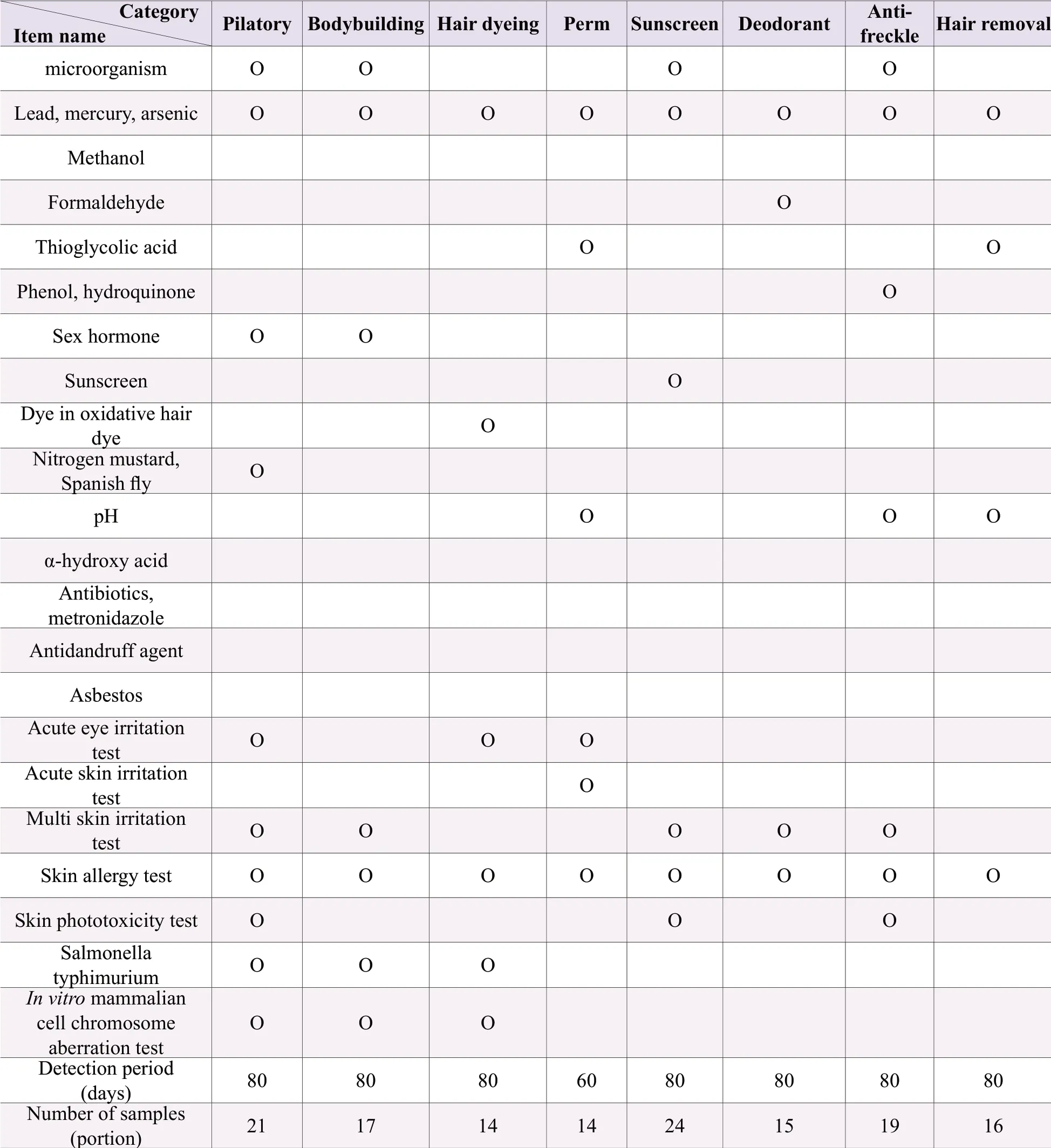
Table 2.The test items, test period and required sample quantity of special cosmetics
Note: “O” needs testing.Samples have more than two independent small packages or separate in a sample package (such as powder cake, eye shadow, blush, etc.), and only have one product name, with different raw material components, should be tested separately; Samples have non-independent small packages or without separate parts, and with the same raw materials except for the coloring agent in each part shall be tested according to the method of use of the instructions; Those with an ethanol content of ≥75% don't need to be measured for microbial indicators; products that do not have microbial inhibitory components in the product formula (such as physical hair removal products, pure plant hair dye products, etc.); Products with a combined ethanol or isopropyl alcohol content of ≥10% need methanol test; Besides sunscreen products, other products containing sunscreens (excluding titanium dioxide and zinc oxide) ≥0.5% should test sun-screener; Products that claim to contain alpha-hydroxy acids or that do not claim to contain alpha-hydroxy acids, but have a total amount of ≥ 3% should test alphahydroxy acid and pH value; Products that claim anti-acne, anti-mites, anti-pimple, etc.need to be tested for antibiotics and metronidazole; Products that claim to be used for anti-dandruff purposes need to be tested for anti-dandruff agent project; For products containing talcum powder, asbestos should be additionally tested; For hair dye products that are used in combination with two or more doses, the corresponding sanitary chemistry items shall be tested separately according to the dosage form; Instant washable skin products do not require multiple skin irritation tests but only acute skin irritation tests; In addition to hair care, sunscreen and ecchymoses, products containing sunscreens (excluding titanium dioxide and zinc oxide) ≥0.5% should conduct skin photoxicity test; Perform a Salmonella typhimurium or reverse mutation test or in-vitro mammalian cell gene mutation test; The smearing temporary hair dye product does not carry out Salmonella typhimurium and in-vitro mammalian cell gene mutation test.For products containing two or more doses of hair dye products, toxicological tests shall be carried out according to the methods used in the instructions; the quantity to be inspected is for products with a net weight of 25 grams per package.If the quantity is less than 25 grams, the number of samples needs to be increased.This quantity includes the samples of the sealed samples provided by the imported cosmetics at the time of approval by the SFDA.The seal samples and inspection reports should be collected at the same time.Domestic special-purpose cosmetics are not used.
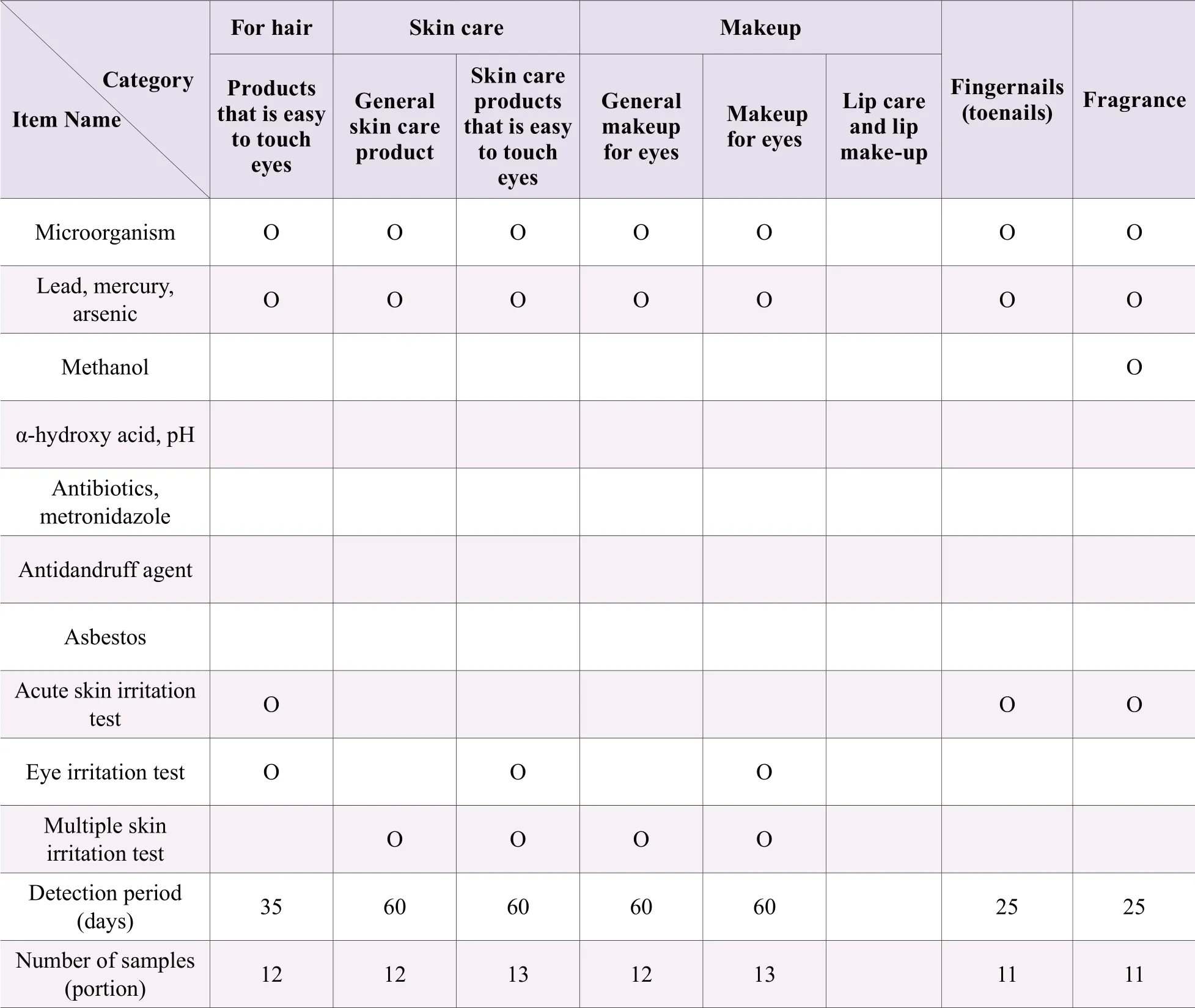
Table 3.Test items, test period and required sample quantity of imported or domestic non-special cosmetics
Risk assessment on safety risk substance
At this stage, it should be confirmed according to the actual use situation of the consumer whether the safety of the product meets the requirements.The purpose of the safety assessment during the development phase is to understand and determine the potential toxicity and possible exposure of the product components to assess and determine the danger associated with exposure to the component.
Hazard identification: Analyze physical and chemical properties (including known or suspected impurities); how ingredients are produced and used; the target population or sub-population of the product; the ingredient and its related compounds, the toxicity of formulation, clinical and epidemiological data including ingredient evaluation results and reports from authoritative organizations.Each component needs to establish a corresponding Toxicological Profile of Substance and calculate the Margin of Safety.
Exposure measurement: Identify the target group; Determine product use situation and exposure pathways; Exposure time and frequency (survey data on consumer behavior and habits); whether it is exposed to multiple products at the same time; Estimates of extreme exposure and actual exposure; Estimation of the amount of use and absorption of human body.
Dose-response relationship assessment: Safety level (e.g.no adverse reaction levels observed); Threshold level; the form of the dose-response curve; the reversibility of the reaction.
Risk characterization: Calculation of the exposure of the human body to the concerned component of attention; Determine the appropriate unobserved adverse reaction level (NOAEL) by weighing all safety data; Compare the level of adverse reactions and exposure amount to determine the margin of safety (MOE); Consider the uncertainty of the safety data and then determine if there are enough exposure limits to support the safety of consumer product research testing or product launches.
Risk management: further reduces risks through product packaging and labeling.
Consideration should be given to the toxicity of the individual components of the cosmetic and to the assessment of the combined toxicity of the mixture effect; It is important to note the normal use of cosmetics and to measure foreseeable special uses, such as the swallow of lip gloss and the special use for children; The impact of cosmetics on people of different ages and in special status should be measured, such as infants, children, the elderly and pregnant women; A regulatory compliance check (List of Banned, Restricted and Approved Substances in the Appendix to the CMR component) is required and appropriate warning labels are provided; Need to be evaluated based on the latest toxicological research progress, risk assessment methods and official guidance; The toxicity and risks of cosmetic components, finished products and impurities need to be assessed and measured simultaneously.Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the risk assessment process of safety risk substance.
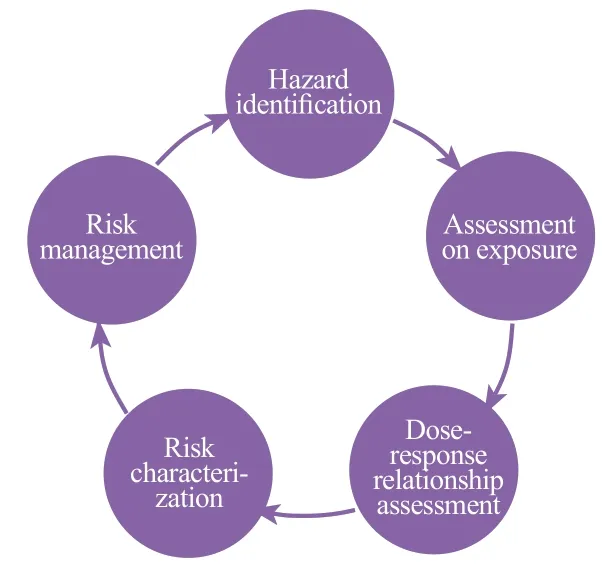
Figure 1. Risk assessment process of risk substances
Further, according to the official implementation of the EU Cosmetics Regulations (EC NO1223/2009) on July 11, 2013, all cosmetic products entering EU market must offer product safety report.The specific requirements are shown in Figure 2:
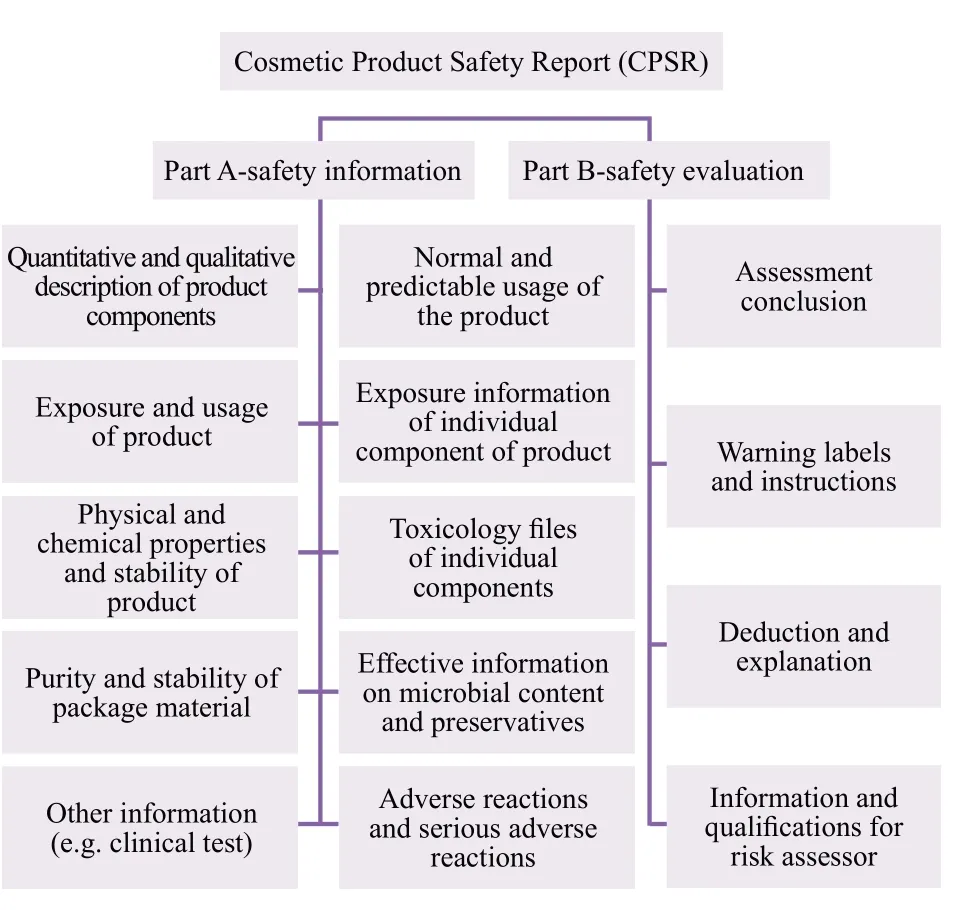
Figure 2.Content of safety report of cosmetic products in European Union
Product safety and risk management in the production stage
Product safety and risk management during the production phase can be divided into four key points: Raw materials storage; weighing and preparation; paste production and packaging; product inspection; warehousing and delivering.
The focus of product safety; management and risk control during the production; phase is: Personnel, systems, suppliers and materials, production management.
For the staff, it is necessary to carry out various training, not only for the new employees, but also the current staff, transfer workers, third-party service personnel, interns.All personnel who are exposed to the production process should be included in the training.The training includes job operation skills, health management requirements, quality knowledge, good manufacturing practices (GMP), and production safety knowledge.The training methods include on-the-job training, internal off-the-job training, lectures from externally invited experts, professional institution training, and supervision department training.The appropriate training methods are selected according to different training contents.The final training results should be tested in the mode of assessment and can be used for oral examination, written examination, and operational assessment.Different work contents can be assessed by different methods.In addition to the above training content, regular retraining should be carried out for some special skills: GMP requirements, quality and health management requirements; Key skills related to the position, key quality control points, and qualification certification for the position; Quality and safety operations, environmental health and safety, safety protection, etc.
The management of the supplier should begin when the candidate supplier develops.The candidate supplier shall be initially reviewed by the Purchasing Department, and the technical capability assessment shall be submitted after the initial review.According to the technical capability assessment, we should screen out some non-compliant suppliers, and carry out quality assessment and risk assessment for the remaining suppliers.As long as there are conditions, we should try our best to conduct on-site audits.The approved supplier can submit a formal sample, and the supplier who passed the evaluation of the official sample enters the list of qualified suppliers, and all the evaluation records in the process are archived and traceable.
ABC classification should be conducted separately for suppliers and producers, and annual or overyear quality audits should be conducted according to importance.
Raw materials storage
The first pass of production is the inspection of raw materials.Enterprises should be equipped with professional laboratories for physical and chemical testing of raw materials such as pH, viscosity, specific gravity and content.Microbiological tests such as total number of colonies, pathogenic bacteria and molds should also be included.If possible, laboratories should be equipped with atomic fluorescence, AAS, ICP-MS, UV-VIS, FTIR, HPLCQQQ, GC-MS to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze impurities in the raw materials and risk substances.
Raw materials, packaging materials and products should be stored according to different material requirements and different storage conditions.To determine the raw materials during the shelf life, the raw materials that have passed the shelf life need to take an overdue assessment, especially on the color, odor, appearance, microbe, acid value, iodine value, and some other key indicators (such as active content).The original specifications can be decided according to the company's ISO documents, and the test report and decision must be based on the original records.
Weighing and preparation
In the raw material weighing and paste preparation stage, a strict preparation process should be followed.In order to facilitate memorizing, the author has compiled a short verse, as shown below:
· Prepare the material according to the item number, but also look at the batch number.
· What came first must be used first, and empty barrels should be used first.
· If there is doubt at the scene, go to the quality controller.
· If the material is defective, fill in the exception sheet first.
· Clean and safe, should be bared in mind even when you are busy.
· Protection should be done on hand, feet, eyes, mouth and nose.
· Containers and tools, clean and sterilized.
· Verify before weighing, the range should be appropriate.
· The incoming material should take gross weighing and it is confirmed that there is no profit or loss.
· The container is peeled first; the net weight and formula.
· The batch number, weight and the label should be correct.
· Record after the weighing, do not write memoirs.
· The remaining materials are wrapped and the appearance is cleaned.
· Everything is not in a hurry, and the quality is controlled.
Paste production and packaging and product inspection
The production and filling stages of the paste require two inspections, including semi-finished inspection and filling inspection.Semi-finished products are inspected in strict accordance with established specifications such as color, odor, appearance, smearing, pH, density, viscosity, preservative content, sunscreen content, active ingredient content, total number of colonies, total number of molds and yeasts, pathogenicity bacteria, heat, cold, toxic substances, etc.;
The filling package inspection is carried out according to the operation instructions, such as usability, extrusion test, net content, color difference.After the package is finished, the finished product inspection is also required.This is the last inspection process before leaving the factory.The finished product needs to be tested again for the total number of colonies, the total number of molds and yeasts, the pathogens, and the comparison standards to ensure that the paste is correct, that no foreign matter is mixed in the paste, and that the clarity of the transparent product and black spots of foreign matter impurities, etc.
Warehousing and distribution
In the warehousing process: Different products use different storage conditions, including 24-hour automatic temperature and humidity monitoring, the storage temperature of the finished product is controlled between 5-30 °C, and the relative humidity is controlled at 30% to 75% RH; The factory ERP system includes WM modules (Warehouse Management), following the principle of first in, first out.Capable companies can also introduce electronic devices to differentiate and control quality status, such as RFID chips.
A fully enclosed van should be used during transportation to provide effective protection for the finished product.Transport vehicles must be sanitized; vehicles that do not meet sanitary conditions are not scheduled for transportation.Telephones tracking for transportation should be applied for special conditions to be handled in a timely manner.
It is necessary to control the temperature of the transport vehicle and treat it especially for special circumstances.For example, if the weather forecast temperature exceeds 5-30 °C for 5 consecutive days in the distribution center of target area, we should use the constant temperature vehicle to transport the product and track the temperature during transportation.For high-heat sensitive products, such as lipstick or similar ointment products, mascara, soap-based facial cleanser should be transported by constant temperature vehicle to transport the product in high-temperature weather.For products that will freeze at low temperatures, such as lotion in glass bottles should use cold storage to keep warm and avoid freezing.

A sound quality system should establish regulations, material control, facilities and equipment, process and production control, packaging and labeling, laboratory control, with all departments working together.
Product safety and risk management in the sales stage
Product safety and risk management during the sales phase can be divided into two key points: Customer service and monitoring on customer complaints and adverse reaction.
Product entering the sales phase is not the end of safety and risk management, but a starting point for long-term development.Thanks to the modern and developed Internet, in addition to consumers' telephone complaints, cosmetic companies can also get feedback on products from different channels through comments on social platforms, so that companies can conduct long-term adverse reaction monitoring.
For products with adverse reactions, investigation and traceability should be carried out, starting from four aspects: Trace the batch number, quantity, status and supplier of the raw materials used by the product through the information when the raw materials are put into storage; Through the use of materials, the batch number, usage amount, and internal transfer can be traced; Trace the batch number and quantity of the finished product storage stage; Trace the batch number, quantity, customer information, etc.at the time of shipment.
Through the analysis and evaluation of the complaint information, the validity and grade of the complaint are judged, and the inspection information of the complaint is traced back, which is convenient for subsequent processing.
Here, we should establish a sound return and exchange system, improve the monitoring and reporting system for adverse reactions, report regularly to the local monitoring agencies, report on major group cosmetic adverse reactions in a timely manner and actively take effective measures to prevent recurrence.
Global regulations concern
On May 2, 2018, China Taiwan issued the Order No.10700045851, promulgating theAmendment to the Regulations on the Administration of Cosmetic Hygiene, and revised the name to theAdministrative Measures for Cosmetics and Health Safety, and revised the full text.It was implemented from the date of publication.According to the new regulations, there will be no more “medicine-containing cosmetics” and “general cosmeceutical products” in the future, which will be merged into “cosmetics”.All the products need to be registered in the product and related information files, and will no longer be required for inspection and registration.All cosmetics manufacturing sites must comply with GMP, establish product sources and flow information, and operators must also actively report.In addition, non-medical toothpaste and mouthwash are also included in cosmetic category.

On June 19, 2018, the UK Department of Environment, Food and Rural Affairs announced that the ban on the sale of rinse-off cosmetics and personal care products containing plastic microbeads in England and Scotland was officially in force, such as facial scrubs, soaps, toothpaste and products containing plastic microspheres such as shower gels are all prohibited from being sold.The ban is considered to be the most powerful and comprehensive ban on plastic-containing microbeads worldwide.The ban is another major step in the UK government's ban on the production of plastic microbeads followed by that launched in January.
China published theSafety and Technical Standards for Cosmeticson November 25, 2015, and implemented it on December 1, 2016.The National Institutes for Food and Drug Control organized the preparation of theReader of Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmeticsto explain in detail the relevant contents of the regulations and guide enterprises to control risks.In order to further strengthen the safety evaluation of cosmetics and improve the technical regulations of cosmetics, the Secretariat of the Expert Committee of Cosmetics Standards of the CFDA has organized theMethods for Testing Sunscreens in Cosmetics (Consultation Draft)andSkin Allergies: Local Lymph node test (LLNA: BrdU-ELISA) (Draft for Comment),Skin Allergic Reaction: Mouse Regional Lymph Node Test (LLNA: DA) (Draft for Comment),Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics(Consultation Draft).It has been opened to the public for comments.
The Chinese government's cosmetics-related regulatory authorities have been working hard to improve relevant regulations to ensure consumer safety.At present, the EU and China are generally the countries and regions with the strictest regulations on cosmetics management in the world today.In Japan and the United States, the control of cosmetics is relatively unsystematic, but it is strictly pursued afterwards.For example, Kanebo, Japan's second largest cosmetics group, was acquired after bankruptcy because of the use of sterols, so the overall security is still guaranteed; As for South Korea, Thailand and other countries or regions, the regulations are relatively loose, The importance and seriousness of the construction of laws and regulations can be seen.
The safety of cosmetics is gradually becoming the focus of attention.In order to avoid being eliminated by fierce market competition, it is necessary to enhance product quality awareness, pay attention to product safety, and establish sound product safety and risk management system.The author hopes this article can be somewhat referential and beneficial for improving the safety management of domestic cosmetics.
 China Detergent & Cosmetics2019年3期
China Detergent & Cosmetics2019年3期
- China Detergent & Cosmetics的其它文章
- Experimental Design of Cosmetics Human Efficacy Evaluation
- Application Research of Bamboo Vinegar in Daily Chemicals
- Determination of Paeonol in Detergent by High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- Fluorinated Surfactants and Fluorinated Polymer Materials (III): Personal Opinion on the Problems of PFOS
- A New Method to Improve the Product Stability and Performance of Soap-based Cleanser at Two Different Temperatures
- Innovation Reshapes the Future of Detergent Industry in China
