信息熵多属性约简的煤粉尘图像特性机理
王征 汪梅



摘 要:为研究无明确特征模式的煤尘颗粒图像特性,以某煤矿煤样为研究对象,按国标标准运用粉尘采样器对粉尘溢散源处颗粒物进行多点采样。采用多决策属性约简模糊粗糙集3个阶段即提出隶属度模型、实现属性约简、确定最大信息熵阈值分割对颗粒形态特征机理进行分析。首先建立粉尘图像各像素点对应的模糊类别隶属度模型,利用多分段函数确定隶属度;分析煤粉尘图像灰度特征并将其作为条件属性,确定条件属性的模糊依赖度,获取最优值并提取模糊属性约简,进行目标及背景区域的模糊下近似和模糊上近似划分;最后建立煤粉尘颗粒的信息熵模型,存储信息熵并实现对分割阈值的提取。结果表明:依据模糊属性约简的互异重要度可实现多属性约简;并确定煤粉尘图像模块区域的最大信息熵分割阈值。所建立模型可删除冗余属性,选择出对分类更为重要的属性,并通过属性约简完成特征选择分类。
关键词:安全科学与工程;图像灰度特征;信息熵;模糊类别隶属度;多属性约简
中图分类号:TD 76 文献标志码:A
DOI:10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2019.0421 文章编号:1672-9315(2019)04-0713-07
Abstract:To investigate imagery characteristics of coal dust particles without clear characteristic mode,coal samples from a coal mine were taken as research objects,and the dust sampler was used to conduct particles multi point sampling at dust spill source according to the international standard.The multi decision attribute reduction fuzzy rough set,including three stages of the membership model,realizing attribute reduction,and determinating maximum information entropy threshold segmentation,are adopted to analyze the particle morphology characteristics.The corresponding fuzzy degree membership model was established for dust image pixels and meanwhile the membership coefficient was determined by multi segment function.In additon,the gray feature of coal dust image was analyzed and used as conditional attribute so that the fuzzy dependence of conditional attribute can be determined to obtain its maximum value and extract the fuzzy attribute reduction.At the same time the fuzzy lower approximation and the upper approximation in the target and its background regions were divided.Finally the information entropy model of coal dust particles was established with the information entropy stored and its corresponding segmentation threshold extracted.The results show that multi attribute reduction can be realized according to the mutual importance of fuzzy attribute reduction;and the maximum information entropy segmentation threshold of coal dust image module area is determined.The established model,therefore,can delete the redundant attributes,select more important classification attributes,and complete the feature selection classification through attribute reduction.
Key words:safety science and engineering;image grey feature;information entropy;fuzzy membership;multi attribute reduction
0 引 言
近幾年,随着国家与有关专家对大规模煤炭开采所引发的煤矿环境污染等问题的重视,以图像信息为基础的煤尘识别技术凭借其高效的视觉化、智能矿山系统等优势,在国内外矿山已获得更深入的研究[1-3]。图像视觉特性信息技术在解决煤矿安全可靠性不高的同时,也为现场恶劣环境难适应及煤尘爆炸危害难预测等问题的解决提供了有效的途径。但粉尘的检测机理十分复杂,其决定因素很多,导致煤尘检测结果具有很大随机性。因此,在粉尘颗粒物特性参数检测中,运用了不同研究方法进行分析。电感应法由脉冲数目确定颗粒的数量,由电位差变化幅度测量颗粒的体积。但该方法获得的是颗粒尺寸的二次信息,须通过转换获得颗粒的实际尺寸信息[4]。对于密度不大且形状为球形的粉尘颗粒,运用光散射法,通过光强分析,可获得粒子直径及浓度,但对于形状不规则的煤尘颗粒,若运用光散射法,由于煤矿的地质结构和综放面煤层强度系数不同,且煤尘对光的吸收和散射存在差异,因此检测结果会出现偏差[5-7]。
上述研究鉴于技术手段以及研究角度的局限,并没有系统地分析粉尘颗粒物特性表现。随着研究手段不断发展,以图像信息为基础的粉尘识别技术具有直接观察在不同粒度下的粉尘颗粒形状的优势。Grasa等针对图像区域内灰度相似性及不连续性提出将粉尘图像按不同特性进行区域划分,并对颗粒目标点的特性参数测量及特征提取,这对研究人员进一步研究煤尘图像具有一定参考价值[8]。Baldevbhai等提出在图像空间中对不同图像信噪比运用模糊聚类算法,由于对图像的对比度分布性能敏感性好,可产生很好的分割效果,但该方法忽略图像的细节信息,对灰度值差异不大的图像目标间或灰度值存在相互重叠区域的情况,分割效果不佳[9]。以上研究成果更多地考虑到图像灰度的空间分布信息,大大提高了图像分割的准确度,但是终究无法达到理想状况,面对各种图像分类,运用某种单一算法缺乏通用性。因此,采用合理的研究手段对图像空间信息下煤尘颗粒物表现出来的微观特性进行有效解释是必须讨论的问题[10-13]。
结合图像空间学和微观学研究发现,煤尘颗粒物特性信息属于非线性和不确定性建模问题,图像识别的难点在于对冗余特征剔除的准确度。文中从微观角度对煤尘颗粒物的图像特性机理展开研究。多属性约简为这类问题提供了新的解决思路。基于图像灰度特征空间区域信息划分,考虑了分类属性重要度的选择,以图像像素点的模糊类别隶属度、图像灰度特征对应的模糊依赖度入手,构建属性约简信息熵数学模型,依据所构建模型对煤尘颗粒特性信息表征进行合理解释,为后期重叠颗粒分离进行了先期理论和试验验证,对煤粉尘颗粒识别提供依据[14-17]。
1 属性约简图像特征空间模型机理分析
1.1 决策信息系统属性约简的建立
将样本图像设为对象,各种特征设为条件属性,类别结果设为决策属性,可形成决策表。对有用特征的提取过程实质就是对决策表中属性的约简过程。通过离散化处理获得的决策表可作为用逻辑关系处理的一组公式,并对公式和规则进行判别是否具有矛盾性以此确定其相容性,属性约简是以决策表的相容性为基础[19-20]。
根据图像中对象或区域的颜色、形状、纹理和空间位置等重要的图像信息特征来进行分析和检索,获取图像的有用信息,实现对图像的识别。图像特征的选取通过反复试验,在极大似然分类精度原则下从10多种特征中确定了用于分类的6个特征,经比较确定为一组对分割精度较为敏感的有效特征信息。设灰度均值、灰度方差、对比度、纹理均值、粗糙度、均匀度6个特征信息表示条件属性A.由于这些特征值为连续值,因此通过相应算法进行离散化处理。通过获取有效特征信息,确定目标类别属性即决策属性C,实现对图像的识别[21-22]。
1.2 属性约简算法描述
通过下述算法可实现对决策表的属性约简。
输入:决策表T={U,A∪C,V,f},其中U表示论域,A,C分别对应为条件属性集和决策属性集。
输出:决策表的相对属性约简。
3 实验结果与分析
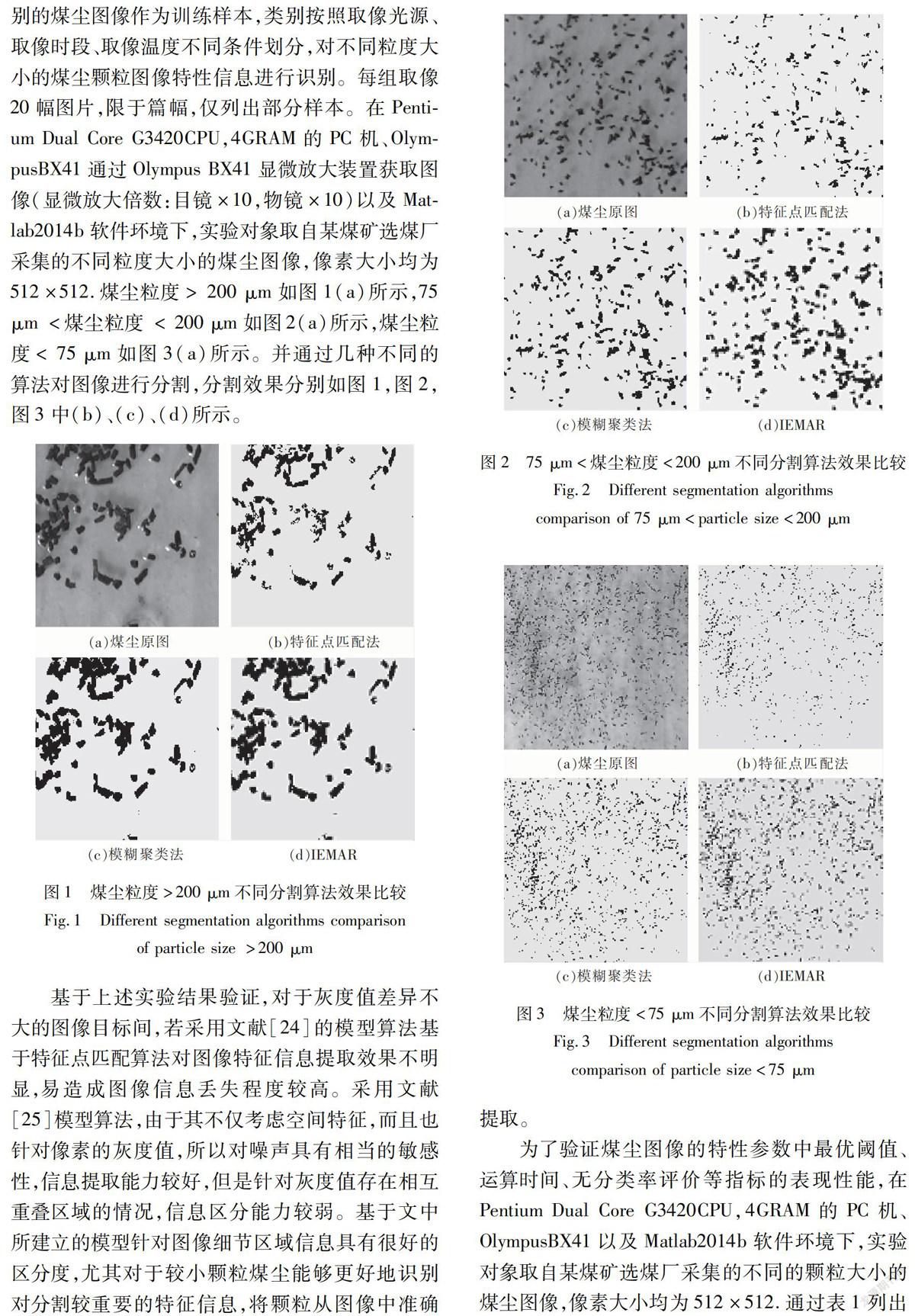
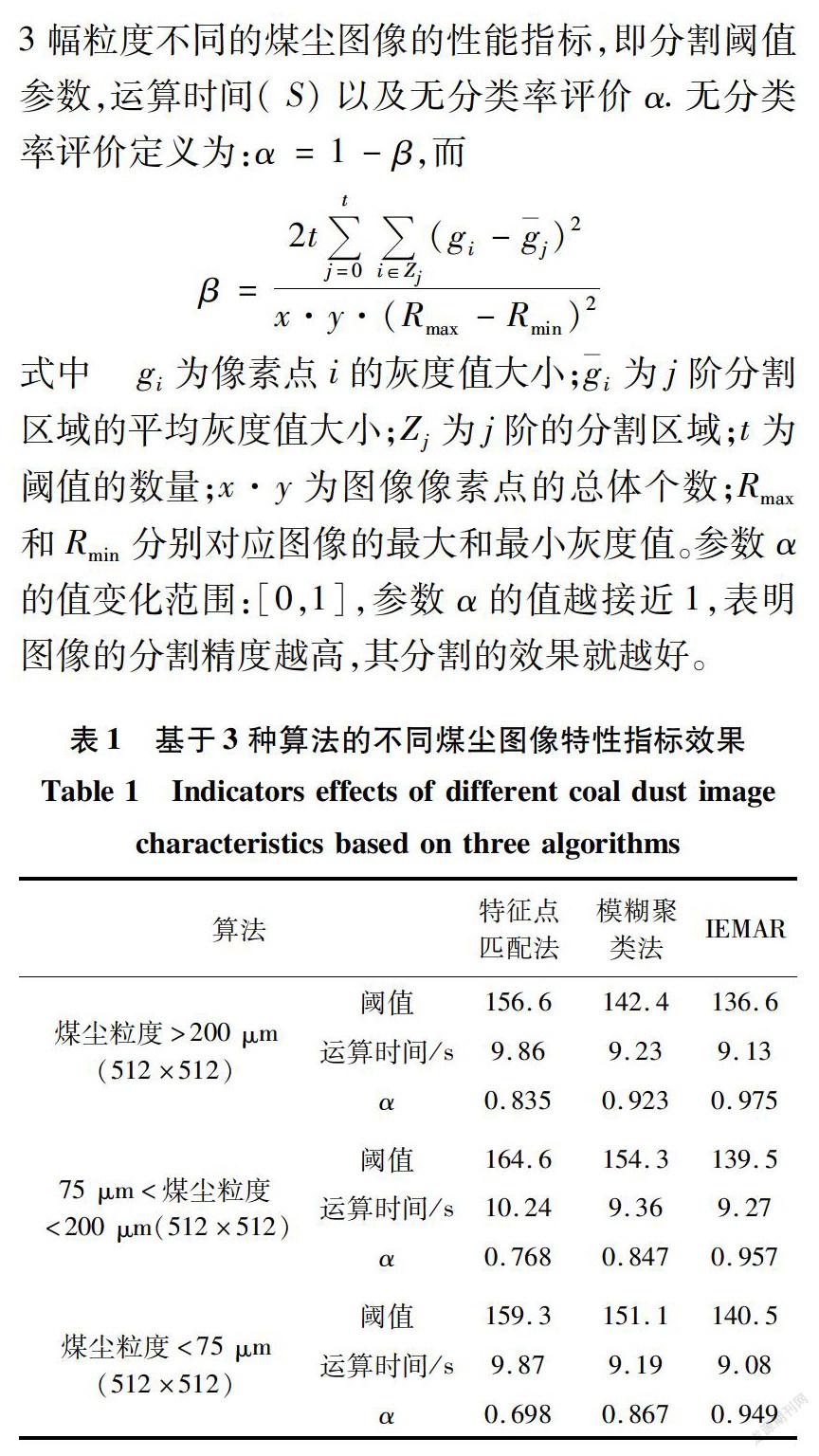
为了验证文中提出的信息熵多属性约简模型及其性能反应的合理性,首先采用文献[24]、文献[25]及IEMAR算法对比展示,依据30组不同类别的煤尘图像作为训练样本,类别按照取像光源、取像时段、取像温度不同条件划分,对不同粒度大小的煤尘颗粒图像特性信息进行识别。每组取像20幅图片,限于篇幅,仅列出部分样本。在Pentium Dual Core G3420CPU,4GRAM的PC机、OlympusBX41通过Olympus BX41显微放大装置获取图像(显微放大倍数:目镜×10,物镜×10)以及Matlab2014b软件环境下,实验对象取自某煤矿选煤厂采集的不同粒度大小的煤尘图像,像素大小均为512×512.煤尘粒度> 200 μm如图1(a)所示,75 μm <煤尘粒度 < 200 μm如图2(a)所示,煤尘粒度< 75 μm如图3(a)所示。并通过几种不同的算法对图像进行分割,分割效果分别如图1,图2,图3中(b)、(c)、(d)所示。
从表1可以得出,文中提出算法与其他同类方法相比,融合了信息系统中的模糊性和粗糙性形成的模糊分类规则,具有更强的泛化能力,而且提高了搜索效率,并在一定程度上使得图像分割的有效性和鲁棒性得到保证。从权衡分割精度同计算效率的角度考虑,文中算法是一种实用有效的图像分割算法。无论在阈值还是分割性能指标上都拥有显著的优势,能满足精确分割的要求,这也为煤尘图像处理的后续研究提供精确数据。
4 结 论
1)属性约简数据库模型对连续数值离散化处理后消失的属性有序关系可提供很好的借鉴。分析表明属性约简模型的建立极大程度上降低了因属性的有序关系消失而导致连续值属性信息丢失造成的影响。而模型结构的半序关系在一定程度上可使得信息的丢失量降低。
2)煤尘图像的有效获取受到多种因素的影响,比如监控环境中空间、湿度、气流等,目前的研究多关注的是外在环境参数的影响规律,忽略了包含内在因素等其他因素的影响效应,有待进一步研究。
3)煤尘粒度、粒度分布和煤尘浓度是煤尘爆炸的关键因素,而对煤尘图像进行图像特性机理分析是研究煤尘粒度、粒度分布和煤尘浓度,解决煤尘检测问题的关键。目前对煤尘颗粒群的宏观问题研究较多,后期研究可考虑对微观尺度下的煤尘颗粒研究,以期提高识别精度。
参考文献(References):
[1] 王国法,赵国瑞,任怀伟.智慧煤礦与智能化开采关键核心技术分析[J].煤炭学报,2019,44(1):34-41.
WANG Guo fa,ZHAO Guo rui,REN Huai wei. Analysis on key technologies of intelligent coal mine and intelligent mining[J].Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(1):34-41.
[2]韓建国.神华智能矿山建设关键技术研发与示范[J].煤炭学报,2016,41(12):3181-3189.
HAN Jian guo.Key technology research and demonstration of intelligent mines in Shenhua Group[J].Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(12):3181-3189.
[3]WANG Guo fa,XU Yong xiang,REN Huai wei.Intelligent and ecological coal mining as well as clean utilization technology in China:review and prospects[J].International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2019,29(2):161-169.
[4]陈建阁.交流耦合式电荷感应法粉尘浓度检测技术研究[D].北京:煤炭科学研究总院,2014.
CHEN Jian ge.Research on detection technology of AC coupled charge induction dust concentration[D].Beijing:China Coal Research Institute,2014.
[5]Okpeafoh S A,Anthony J M,Jan S.Modelling of artefacts in estimations of particle size of needle like particles from laser diffraction measurements[J].Chemical Engineering Science,2017,158:445-452.
[6]Milana I,Igor B,Milica V,et al.Size and shape particle analysis by applying image analysis and laser diffraction inhalable dust in a dental laboratory[J].Measurement,2015,66:109-117.
[7]陈继民,陈鹤天.激光在粉尘检测领域的进展与应用[J].应用激光,2018,38(3):496-501.
CHEN Ji min,CHEN He tian.The development and application of laser in dust detection[J].Applied Laser,2018,38(3):496-501.
[8]Grasa G,Abanades J C.A calibration procedure to obtain solid concentrations from digital images of bulk powders[J].Powder Technology,2001,114(1-3):125-128.
[9]Baldevbhai P J,Anand R S.Color image segmentation for medical images using lab color space[J].Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering,2012,1(2):24-45.
[10]Wasswa W,Andrew W,Annabella H,et al.Cervical cancer classification from pap smears using an enhanced fuzzy C means algorithm[J].Informatics in Medicine Unlocked,2019,14:23-33.
[11]Hassanien A E,Soliman O S.Contrast enhancement of breast MRI images based on fuzzy type Ⅱ[C]//Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications,6th International Conference SOCO 2011,2011:77-83.
[12]Khairunnisa H,Nor A,Mat I.Adaptive fuzzy intensity measure enhancement technique for non uniform illumination and low contrast images[J].Signal,Image and Video Processing,2015,9(6):1419-1442.
[13]Muhammad T,Malik J K.An intelligent mobile application for diagnosis of crop diseases in Pakistan using fuzzy inference system[J].Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2018,153:1-11.
[14]Yongyingsakthavorn P,Vallikul P,Fungtammasan B,et al.Application of the maximum entropy technique in tomographic reconstruction from laser diffraction data to determine local spray drop size distribution[J].Experiments in Fluids,2007,42(3):471-481.
[15]马 翔,楚莹莹,陈允杰.基于空间信息熵活动轮廓模型的图像分割[J].控制工程,2018,25(11):2010-2016.
MA Xiang,CHU Ying ying,CHEN Yun jie.Medical image segmentation based on active contour model of spatial information entropy[J].Control Engineering of China,2018,25(11):2010-2016.
[16]成 婷,张 扩,续欣莹.邻域粗糙集约简算法在图像特征选择中的应用[J].现代电子技术,2018,41(21):56-62.
CHENG Ting,ZHANG Kuo,XU Xin ying.Application of neighborhood rough set reduction algorithm in image feature selection[J].Modern Electronics Technique,2018,41(21):56-62.
[17]郭 健,李 智.基于ICA阈值优化耦合信息熵的边缘提取算法[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版),2018,40(9):150-155.
GUO Jian,LI Zhi.An edge extraction algorithm based on ICA threshold optimization and information entropy[J].Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition),2018,40 (9):150-155.
[18]YU Hai yan,ZHI Xiao bin,FAN Jiu lun.Image segmentation based on weak fuzzy partition entropy[J].Neurocomputing,2015,168(11):994-1010.
[19]LIN Yao jin,LI Yu wen,WANG Chen xi,et al.Attribute reduction for multi label learning with fuzzy rough set[J].Knowledge Based Systems,2018,152:51-61.
[20]LI Hua,LI De yu,ZHAI Yan hui,et al.A novel attribute reduction approach for multi label data based on rough set theory[J].Information Sciences,2016,367-368:827-847.
[21]Hadi Y,Hamid M,Mohammad A E F,et al.Determining the fragmented rock size distribution using textural feature extraction of images[J].Powder Technology,2019,342:630-641.
[22]Andrea P,Massimo P,Fabio L,et al.Dust detection and analysis in museum environment based on pattern recognition[J].Measurement,2015,66:62-72.
[23]Farid G L,Jair C,Asdr bal L,et al.Segmentation of images by color features:a survey[J].Neurocomputing,2018,292(5):1-27.
[24]陳天华,王福龙.实时鲁棒的特征点匹配算法[J].中国图象图形学报,2016,21(9):1213-1220.
CHEN Tian hua,WANG Fu long.Real time robust feature point matching algorithm[J].Journal of Image and Graphics,2016,21(9):1213-1220.
[25]李婷婷,江朝晖,饶 元,等.结合基因表达式编程与空间模糊聚类的图像分割[J].中国图象图形学报,2017,22(5):575-583.
LI Ting ting,JIANG Zhao hui,RAO Yuan,et al.Image segmentation based on gene expression programming and spatial fuzzy clustering[J].Journal of Image and Graphics,2017,22(5):575-583.

