Breeding of New Japonica-indica Hybrid Rice Combination Chunyou 284
Xinwei SONG Jianrong LIN Mingguo WU


Abstract Chunyou 284 is a medium-japonica hybrid combination, as well as an indica-japonica subspecific hyrbid with super-high yield, which was developed from Chunjiang 23A, a thermo-sensitive CMS line with very early anthesis time, and C84, an indica-japonica intermediate type restorer line with wide compatibility. This combination has the advantages of high yield potential, early maturity, excellent comprehensive agronomic traits and wide adaptability. It was approved by Jiangsu Provincial Crop Variety Approval Committee in June, 2018. The breeding process, main characteristics, cultivation techniques and seed production points of the combination were introduced.
Key words Japonica-indica hybrid rice; Chunyou 284; Super high yield; Breeding
From the present situation and development trend of rice heterosis utilization, the heterosis utilization of indica-japonica intersubspecific hybrid rice and the further improvement of cultivar plant type will become the main direction of hybrid rice development in the future[1-2]. In recent years, the heterosis utilization of indica-japonica intersubspecific hybrid rice has developed rapidly in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China. The Ningbo Academy of Agricultural Sciences and the China National Rice Research Institute have greatly improved the yield potential of indica-japonica hybrid rice by increasing the genetic difference between parents and have bred intersubspecific hybrid rice with strong heterosis such as Chunyou 58, Chunyou 84, Chunyou 927, Yongyou 2640 and Zheyou 18[3-7], which are showing good development momentum in Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui, Hubei, Jiangxi, Fujian, Hunan and other places. The F1 hybrids are characterized by typical intersubspecific hybrid rice with strong vegetative growth, high biological yield, strong stalks, strong lodging resistance, high absolute yield and high yield potential.
However, at present, among the intersubspecific hybrid rice that is used in production, some combinations suffer from problems such as high light sensitivity and long total growth period, and some even cannot be planted in Zhejiang Province. China National Rice Research Institute has successfully bred a medium-japonica hybrid combination Chunyou 284, as well as an indica-japonica subspecific hyrbid with super-high yield, from Chunjiang 23A, a thermo-sensitive CMS line with high stigma exsertion rate and extra early anthesis time, and C84, an indica-japonica intermediate type restorer line with wide compatibility. This combination has the advantages of high yield, high yield potential, early maturity, excellent comprehensive agronomic traits and wide adaptability. Chunyou 284 was approved by Jiangsu Provincial Crop Variety Approval Committee in June, 2018. It is a promising new intersubspecific hybrid rice combination.
Breeding process
Chunjiang 23A is a medium-japonica CMS line, which was developed by China National Rice Research Institute with Chunjiang 16A which is a Dian-type japonica rice CMS line as the cytoplasmic donor and Chunjiang 23B which is a japonica restorer line (Chunjiang 16B/(Peiai 64S/Bing 95-255//Chunjiang 016)) as the male parent through crossing and successive selection and backcrossing for many generations. It passed the sterile line identification by Jiangsu Provincial Crop Variety Approval Committee in April, 2014[8]. The restorer line C84 is an indica-japonica intermediate type restorer line with wide compatibility, bred by China National Rice Research Institute from japonica restorer (G070×Chunhui 58) with wide compatibility and indica restorer CH172 with wide compatibility through hybridization[9]. In autumn of 2005, the hybrid combination (G070×Chunhui 58)×CH172 was prepared; in spring of 2006, generation-adding propagation of the hybrid combination (G070×Chunhui 58)×CH172 was carried out in Hainan; in autumn of 2006, 850 strains of the F2 generation were planted in Hangzhou, and 35 plants with thick and strong stalk and larger spikes were chosen; in spring of 2007, the 35 strains of the F3 generation were planted in Hainan, and 49 plants with thick and strong stalk and larger spikes were chosen; in autumn of 2007, the 49 strains of the F4 generation were planted in Hangzhou for the screening of agronomic traits and the identification of resistance and rice quality, by which 18 plants with thick and strong stalk, good disease-resistance, large spikes and high yield were chosen; in spring of 2008, 18 strains of the F5 generation were planted in Hainan, and 3 strains with thick and strong stalk, good disease resistance, large spikes, and high, stable and uniform yield were chosen for the determination of fertility recovery capability using japonica rice sterile line Chunjiang 12A and indica rice sterile line II-32A; in autumn of 2008, testing F1 and mating parents were planted in Hangzhou, and based on the fertility and seed setting rate of testing F1, the restorer line C84 with good agronomic traits, strong lodging resistance, large spike and wide compatibility were bred. In spring of 2012, seeds production was performed using Chunjiang 23A and C84 in Hainan. In 2014, the combination was taken to take part in the regional trial of Zhejiang successive cropping late indica hybrid rice and designated Chunyou 284. Subsequently, it performed outstanding in the regional trial of Jiangsu medium-japonica hybrid rice in 2015, and was taken to take part in the continuing trial in 2016 and the production trial in 2017. Finally, it was approved by Jiangsu Provincial Crop Variety Approval Committee in 2018 (Sushendao 20180008).
Main characteristics
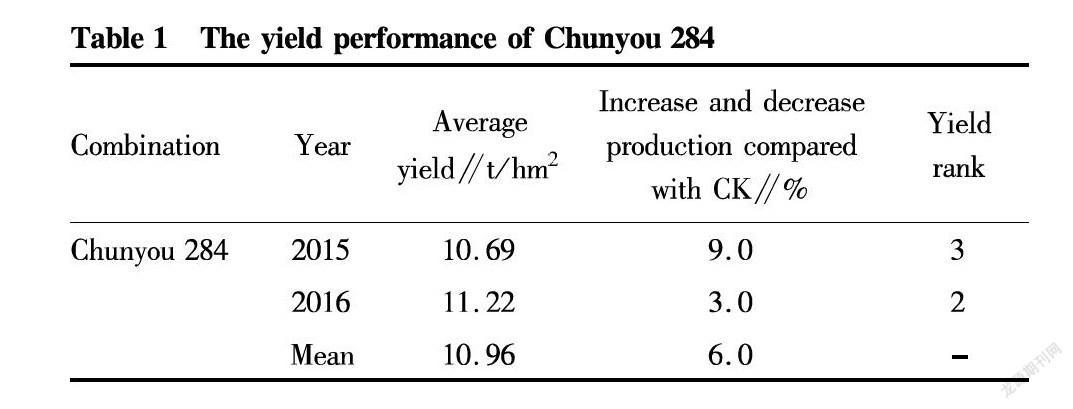
Yield performance
In the regional trial of Jiangsu medium-japonica hybrid rice in 2015, Chunyou 284 showed an average yield of 10.69 t/hm2, which increased by 9.0% compared with Jiuyou 418 (control check); and in the regional trial of Jiangsu medium-japonica hybrid rice in 2016, the average yield was 11.22 t/hm2, which increased by 3.0% compared with Yongyou 2640 (CK). In the production trial of Jiangsu medium-japonica hybrid rice in 2017, Chunyou 284 exhibited an average yield of 10.68 t/hm2, which increased by 4.7% compared with Yongyou 2640 (CK).
Main agronomic traits
Chunyou 284 has the characteristics of vigorous vegetative growth, thick and strong stalk, compact plant type, long and straight top third leaf, dark green leaf color, strong lodging resistance, large spikes, strong cold tolerance at the late period and good colouring. According to the regional trial information of Jiangsu Province in 2015-2016, Chunyou 284 was early maturing, and had a whole growth period of 147.2 d, which was 3.1 d shorter than the CK; and its plant height, number of effective panicles, number of grains per panicle, seed setting rate and 1 000-grain weight were 106.1 cm, 2.53 million panicles/hm2, 213.2 grains/panicle, 85.5% and 25.9 g, respectively.
Quality traits
According to the detection results of Rice and Its Products Quality Supervision and Inspection Center, Ministry of Agriculture of the Peoples Republic of China (Wuhan) in 2016, the head rice rate, length-width ratio, chalkiness degree, gel consistency, amylose content and taste score of Chunyou 284 were 65.3%, 2.5, 73.0%, 15.8%, 30.0 mm, 23.6% and 67, respectively.
Resistance performance
Based on the disease identification of Chunyou 284, the loss rate from leaf blast was grade 5, and the comprehensive index of rice blast was 5.0. The comprehensive evaluation was as follows: Chunyou 284 is moderately resistant to rice blast, susceptible to bacterial blight and sheath blight, and moderately susceptible to stripe blight.
Suitable plan ting areas
Chunyou 284 has wide adaptive range, and is mainly suitable to be planted as single cropping rice in Subei and Suzhong areas of Jiangsu Province.
Xinwei SONG et al. Breeding of New Japonica-indica Hybrid Rice Combination Chunyou 284
Main Points of Cultivation Techniques
Sowing at an appropriate date to raise strong seedlings
Chunyou 284 can be sown in early and middle May as single cropping late rice. The seed quantity for raising seedlings can be controlled in the range of 120.0-150.0 kg/hm2, and the sowing quantity for field planting can be in the range of 12.0-15.0 kg/hm2. Dry land and wet land for seedlings are both suitable. Adequate fertilizer and sparse sowing are required for raising strong seedlings with tillers. The seedling age should be controlled at about 25 d.
Transplanting at an appropriate date, rational close planting
Because Chunyou has large spikes with close seeds, the number of effective spikes is a key factor for high yield of Chunyou 284. To increase the number of effective spikes, field planting can be carried out according to a planting distance of 20.0 cm×26.7 cm, 1-2 seedlings for each cluster.
Scientific nutrient and water management
Chunyou 284 needs more fertilizer, generally requiring pure nitrogen at 240-270 kg/hm2. Fertilizing methods: Base fertilizer should be applied heavily, and top dressing should be conducted early, according to the strategy of “heavy early, light in middle stage, supplement later”. Base fertilizer should be dominated by organic matter, supplemented by proper phosphorus and potassium fertilizers. Early application can promote early tillering, and spike fertilizer can be applied appropriately to ensure large spikes. The ratio of N, P and K is 1∶0.5∶1. For water management, rice should be transplanted in shallow water, and irrigated frequently to promote tillering. In later period, alternate irrigation of wetting and drying can be adopted, and water cut-off cannot be too early.
Pest control
Before sowing, the seeds should be treated with medicament to prevent seed-borne diseases such as bakanae disease. During rice seedling stage, the focus should be put on the control of rice thrips and small brown rice planthoppers. During the middle and late stages, sheath blight, rice stem borers, rice planthoppers, rice leaf rollers, rice blast, rice false smut should be comprehensively controlled. Special attention should be paid to the prevention and treatment of rice smut. Particular attention should be paid to the prevention and control of rice blast and bacterial blight.
Main Points of Seed Production Techniques
Choosing seed production field
The spatial isolation of the field for seed production should be larger than 100 m, and the time isolation must be more than 20 d.
Timely and sparsely sowing to cultivate strong seedlings with tillers
According to the characteristics and features of Zhejiang, the male parent C84 of the first stage should be sown on June 12, and that of the second stage should be sown on June 19; the female parent Chunjiang 23A should be sown on May 29. All these are to ensure the flower synchronization of the parents. The sowing quantity of the female parent for field planting should be in the range of 22.5-30.0 kg/hm2, and that of the male parent should be in the range of 4.5-6.0 kg/hm2. Nutrient and water management during the seedling stage must be strengthened, and rice seedlings for transplanting must be 1-2 tillers.
Transplanting in the suitable period, rationally setting row ratio
The seedling age should be at 25-30 d when transplanting. The row ratio of the female parent to the female parent is appropriately at 2∶10. Multiple plants of the male parent should be planted in double rows, and the female parent should also be planted with multiple plants. The planting spacing should be 16.7 cm×18.3 cm.
Rationally applying fertilizer, scientifically managing water, well controlling pests and diseases
Base fertilizer should be applied adequately; top dressing should be carried out early; and phosphorus and potassium fertilizers should be applied at an appropriate ratio. For water management, there should be deep water in the regreening stage, and shallow water in the tillering stage, and the rules of alternated wetting and drying, watering for booting, pellicular water for flowering and flowing water for raising rice should be followed. Meanwhile, pests and diseases should well controlled, including rice stem borers, sheath blight and brown back rice planthoppers.
Artificial supplementary pollination
Generally, the total dosage of gibberellin 920 is 90-120 g/hm2, which is applied twice. The first time is at the time when 10% of the male and female parents reach the heading stage, and the dosage is 45-75 g/hm2. The second time is carried out 1-2 d later, and the dosage is 45g/hm2. Meanwhile, at the rupturing stage of the female parent, 1/2 of the flag leaves should be cut out; and at the peak flowering stage, artificial pollination should be well done.
Roguing strictly, harvesting timely
At the seedling stage and field stage, roguing must be done strictly. Before initial heading stage, unusual plants should be removed completely; and after artificial pollination, the male parent must be cut out timely, and the plants should be harvested at the right time, to ensure the purity and quality of seeds.
Conclusions
Chunyou 284 has the characteristics of vigorous vegetative growth, thick and strong stalk, compact plant type, long and straight top third leaf, dark green leaf color, strong lodging resistance, large spikes and strong cold tolerance at the late period. Because its female sterile line Chunjiang 23A has the characteristics of high stigma exsertion rate and extra early anthesis time, Chunyou 284 has high outcrossing rate, which can significantly increase seed production and reduce hybrid rice seed production cost, which has a very positive significance for the promotion and application of Chunyou 284. Chunyou 284 has a short growth period and can be planted as a medium-japonica hybrid in Jiangsu, Anhui and other places. It can also be planted as successive cropping late rice in Jiangxi, Hunan, Zhejiang, Fujian and other places.
References
[1]LIN JR, SONG XW, WU MG, et al. Super hybrid rice breeding technology innovation and variety cultivation[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(2): 207-218. (in Chinese)
[2]SONG XW, LIN JR, WU MG. Advances and prospects of heterosis utilization in indica-japonica hybrid[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(1): 1-9. (in Chinese)
[3]WU MG, LIN JR, SONG XW, et al. Breeding of indica-japonica hybrid rice combination Chunyou 58 with super high yield[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2007, 22(5): 17-19. (in Chinese)
[4]MENG TY, LI XY, LI C, et al. Plant-type characteristics of high-yielding lines of Yongyou japonica/indica hybrid rice with medium maturity[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2016, 2: 170-180. (in Chinese)
[5]ZHENG XX. Characteristics, yield components and high-yield cultivation techniques of indica-japonica hybrid rice Yongyou 2640[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019, 2: 208-210, 232. (in Chinese)
[6]WU MG, LIN JR, SONG XW, et al. Breeding of new japonica-indica hybrid rice combination Chunyou 84[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2014, 29(2): 19-21. (in Chinese)
[7]WANG YL, WANG JJ, ZHANG LX, et al. Characteristics and cultivation techniques of hybrid rice Zheyou 18[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 1(4): 364-366. (in Chinese)
[8]SONG XW, WU MG, LIN JR, et al. Breeding and utilization of medium-japonica CMS line Chunjiang 23A[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, z1: 9-11. (in Chinese)
[9]LIN JR, SONG XW, WU MG. Biological characteristics and heterosis utilization of four indica-japonica intermediate type restorer lines with wide compatibility[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2012, 26(6): 652-662. (in Chinese)
- 农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Analysis of the Southern China Tilapia Production and Economic Benefits of Different Breeding Patterns in 2018
- Dynamic Monitoring and Control Measures of Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E.Smmith) in Low Latitude Plateau Sugarcane Areas
- Control Effects of a New Sex Pheromone Trap and Biological Agents on Sesamia inferens Walker and Argyroploce schistaceana (Snellen)
- Comparative Study on Grain Cadmium Content and Yield in Different Rice Varieties
- Simulation Experiment of Air Temperature Variation in Multi-film Covering at Night
- Identification of Growth-promoting Bacteria from Rhizosphere of Pastures and Their Effects on Growth of Lotus corniculatus L.

