口服HIF稳定剂与静脉补铁治疗肾性贫血的临床观察
刘素青

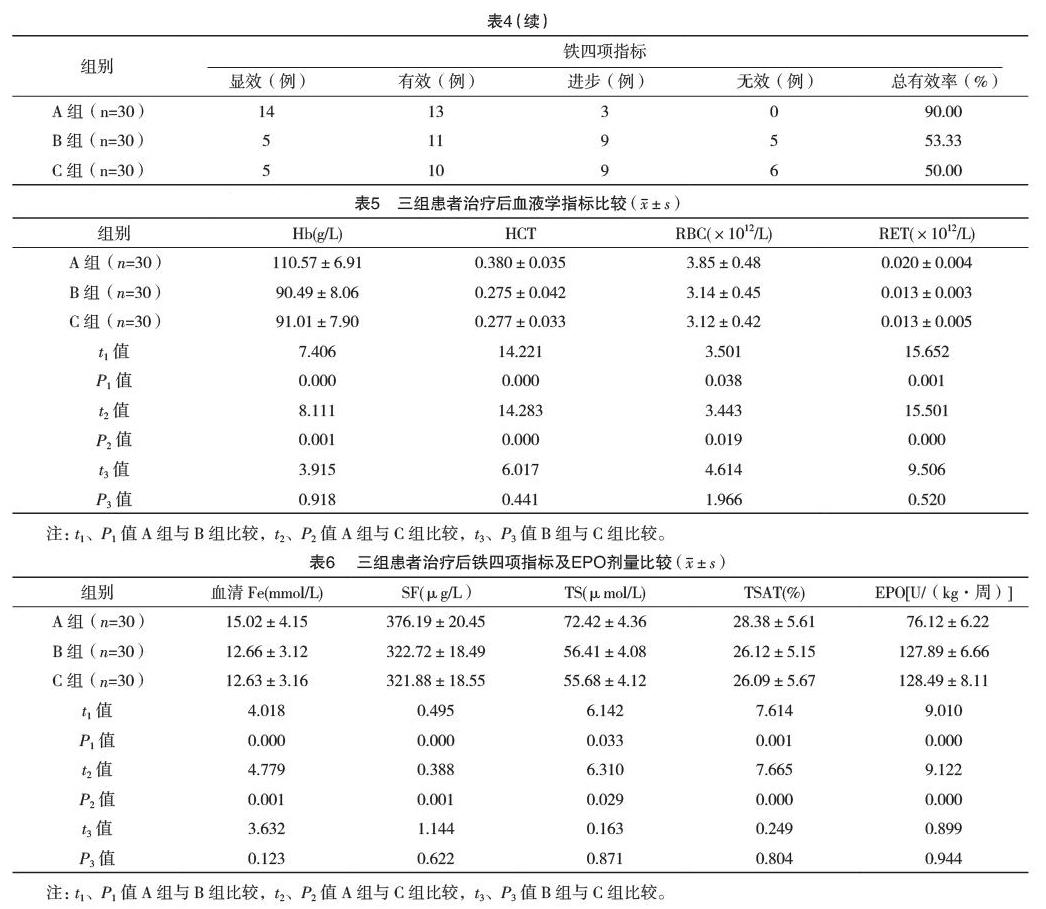
【摘要】 目的:比较口服低氧诱导因子(hypoxia - inducible factors,HIF)稳定剂与静脉应用蔗糖铁、右旋糖酐铁治疗肾性贫血的临床疗效和安全性。方法:选取2017年1-12月菏泽市立医院肾脏内科收治的慢性肾脏病并肾性贫血的患者90例,以治疗药物的不同将口服HIF稳定剂的患者30例为A组,静脉用蔗糖铁的患者30例为B组,静脉用右旋糖酐铁的患者30例为C组。在给予促红细胞生成素(EPO)基础上,持续治疗6周观察2周,总8周,比较三组患者基本血液学指标[红细胞计数(RBC)、血红蛋白(Hb)、网织红细胞计数(RET)、红细胞比容(HCT)]及铁四项指标即[血清铁(Fe)、血清铁蛋白(SF)、总铁结合力(TS )及转铁蛋白饱和度(TSAT)]。观察三组患者不良反应(血糖变化、过敏、胃肠不适、静脉炎、口腔异味等)发生情况。结果:患者临床疗效A组明显优于B、C组。治疗前,三组患者血液学基本指标和铁四项指标比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗8周后,B、C组比较血液学指标、铁相关指标比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);A组与B、C组比较,血液学指标、铁四项指标、EPO剂量比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。三组患者不良反应中过敏、胃肠不适、静脉炎、口腔异味比较差异有统计学意义(p<0.05)。结论:口服HIF稳定剂与静脉应用蔗糖铁或右旋糖酐铁都能有效改善慢性腎脏病并肾性贫血,而口服HIF稳定剂能稳定血液指标、增加总铁结合力、降低血清铁蛋白、减少EPO剂量,安全性较高,不良反应少,增加患者依从性。
【关键词】 低氧诱导因子; 蔗糖铁; 右旋糖酐; 肾性贫血
【Abstract】 Objective:To compare the clinical efficacy and safety of oral hypoxia-inducing factors(HIF)stabilizers and intravenous use of sucrose iron and dextrin iron in the treatment of renal anemia.Method:From January 2017 to December 2017,90 patients with chronic renal disease and renal anemia were admitted to the Department of Kidney Medicine of Heze City Hospital,they were divided into three groups according the different drugs.30 patients with oral HIF stabilizers as group A,30 patients with intravenous sucrose iron as group B,30 patients with ferric anhydride for venous use as group C.Based on the administration of erythropoietin(EPO),continuous treatment for 6 weeks,observation for 2 weeks,for a total of 8 weeks,the basic hematologic indicators of 3 groups of patients[ Red blood cell count(RBC),hemoglobin(Hb),reticulated red blood cell count(RET),red blood cell specific capacity(HCT)].The four indicators of iron and iron were[ Serum iron(Fe),serum ferritin(SF),total iron binding force(TS)and transferrin saturation(TSAT)] of three groups were compared.The occurrence of adverse reactions(blood pressure changes,allergies,gastrointestinal discomfort,phlebitis,bad breath and so on)of three groups were observed.Result:The clinical curative effect of group A was better than that of group B and group C.There was no significant difference between the basic indexes of hematology and the four indexes of iron(P>0.05).After 8 weeks of observation,there was no significant difference between B and C groups in hematology and iron correlation(P>0.05).Compared with group A,B and C,the hematologic indicators,the iron four indicators and EPO dose were statistically significant(P<0.05).Adverse reactions of allergies,gastrointestinal discomfort,phlebitis and bad breath in three groups were statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:Oral HIF stabilizers and intravenous use of sucrose iron or dextran iron can effectively improve the blood index of patients with chronic renal disease and renal anemia,while oral HIF stabilizers can stabilize blood index,increase total iron binding force,reduce serum ferritin,and reduce EPO dose.It has higher safety,less adverse reactions,increased patients compliance.

