Analysis of drug use law and mechanism of prostate cancer based on data mining and network pharmacology
Yao Yang , Ying Chen , Zhen-ning Yang , Guo-wei Zhang
Analysis of drug use law and mechanism of prostate cancer based on data mining and network pharmacology
Yao Yang1, Ying Chen1, Zhen-ning Yang2, Guo-wei Zhang1
1College of Chinese Medicine, Hebei University, Baoding, Hebei province, China.2Heibei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China.
: Excavate the medication rule of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of prostate cancer, and predicting the biomolecular level mechanism of high-frequency drug compatibility.: Relevant documents in CNKI, Wanfang Medical Network and VIP Chinese Biomedical Periodical Database Pubmed, EMbase were collected and collated systematically. Frequency statistics, association rule analysis and new party mining were carried out using TCMISSV2.5. BATMAN-TCM was used to analyze the interaction relationship and related pathways between high-frequency drug targets.: Huangqi () was the single drug most used of the 102prescriptions included in the standard. There are 6 pairs of combinations with high confidence in association rule analysis. System entropy cluster analysis resulted in 20 core drug combinations and 9 new prescriptions. Through KEGG pathway analysis of HuangqiFuling ()Gancao ()Dihuang (), it was found that the number of potential targets of the neural active ligand receptor rented pathway and purine metabolism pathway was the largest.: Prostate cancer is mainly treated with deficiency-tonifying drugs, which are combined with drugs for promoting blood circulation, removing blood stasis, clearing heat, promoting diuresis, detoxifying and resolving hard mass. The mechanism of action of high-frequency traditional Chinese medicine may be realized by interfering with the neuroactive ligand receptor interaction pathway and purine metabolism pathway.
prostate cancer, medication law, mechanism of action, data mining, network pharmacology
This article found that deficiency-tonifying drugs, which are combined with drugs for promoting blood circulation, removing blood stasis, clearing heat, promoting diuresis, detoxifying and resolving hard mass are commonly used to treat prostate cancer. Core herbs may play their role by interfering with the neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction pathway and purine metabolic pathway.
Background
In the latest global cancer statistics report, the incidence of prostate cancer ranks second among global male malignancies [1]. Its incidence has obvious ethnic and regional differences, and it is one of the many malignant tumors in Europe and the United States. At present, the incidence of prostate cancer in China is also significantly increased [2]. According to China cancer statistics in 2015, the growth rate of prostate cancer has surpassed that in Europe and the United States [3]. By 2018, prostate cancer ranks first in the incidence of male genitourinary tumors, far greater than bladder cancer [4]. At present, modern medical treatment methods for prostate cancer include waiting for observation and treatment, surgical treatment, radiotherapy, and endocrine therapy. As an auxiliary means of modern medical treatment, traditional Chinese medicine has obvious advantages in reducing toxicity and increasing efficiency, alleviating clinical symptoms, improving patients' quality of life, and prolonging survival [5-7]. Comply with the development trend of large data, apply data mining technology and network pharmacology, realize the distracted clinical data to the systematic regular experience data, and then to the accurate drug action pathway and target analysis, better serve clinical and basic research [8]. This study collects the literature on CNKI, Wanfang Medical Network, VIP Chinese Biomedical Periodical Database, Pubmed and EMbase, screening and arranging medical records, using traditional Chinese medicine inheritance system to obtain Chinese medicine prescription and new prescription, application Network pharmacology, predicting the mechanism of action of core drug pairs, providing scientific theoretical support and new treatment ideas for the treatment of Chinese medicine for this disease.

Figure 1. Inclusion of medical record extraction process
Data Sources and Methods
Selection of Published Studies
CNKI, Wanfang Medical Network and VIP Chinese Biomedical Periodical Database were used to identify literature published from January 1, 2000 to February 1, 2019. The search terms used were prostate cancer, and Traditional Chinese medicine. The rest of the conditions are default. The keywords "prostate cancer" and "traditional Chinese medicine" were entered in the PubMed and EMbase databases. The search results were 127, 71, 62, 23, and 17 related documents. The literature extraction process is shown in Figure 1.
Inclusion criteria
(1) Clinical study of traditional Chinese medicine prescription for the treatment of prostate cancer, patients have no other major diseases; (2) Clearly provide clinical prescriptions of traditional Chinese medicine practitioners;(3) There are clear symptoms and complete drug composition in the literature。
Exclusion criteria
(1) Repeated studies; (2) External treatment, Chinese and Western medicine combined treatment, drug records are unknown or single Chinese medicine and other literature;(3) Non-clinical research such as basic research, review, and theoretical discussion on cell and animal experiments.
Data process
According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the modified prescriptions are eliminated, and a total of 102 prescriptions are obtained. Then these prescriptions were entered into the TCMISSV2.5 by two researchers, and the data was proofread by professionals to establish a Chinese medicine database. Drug names, classifications, and symptom names are all based on the 2015 edition of Chinese Pharmacopoeia, Chinese Pharmacy (Adult Higher Education Pharmacy Professional Textbook) and TCM Syndrome Differentiation Diagnostics to ensure the scientific nature of data analysis [9-11].
Data analysis
Frequency statisticsIn the “Basic Information Statistics” project, the drugs’ frequency, property flavors attributive channel, and the types of symptoms are sorted from large to small, and the results are derived.
Association rule analysis In the “Group Formula” project, the number of support degrees is set to 12, the confidence level is 0.6, and the drug use pattern and rule analysis results are respectively derived, and a network display of core drugs is obtained.
New formulation analysisIn the “New formulation Analysis” project, the correlation degree is set to 8 and the penalty degree is 2. The cluster analysis and the unsupervised entropy hierarchical clustering algorithm are used to obtain the core drug combination and the new prescription, and the results are derived separately.
Mechanism of action Use the BATMAN-TCM system for KEGG pathway analysis, set the “Score cutoff” to 80, and set the “Adjust P-value” to 0.1 to construct a target-path-disease correlation map [12].
Results
Frequency of herbs
The statistics involved a total of 163 Chinese herbal medicines, of which the most used was Huangqi (), which occurred 38 times; followed by FulingGancaoThe top 20 frequencies used are shown in Table 1, and the frequency of use is 10 times or more.
Property flavors attributive channel
Among four natures,the drugs warm in nature was the highest, the frequency was 201, accounting for 31.5%, followed by the drugs cold in nature; the sweet herbs, belonged to the five flavours, was the most commonly used, the frequency was 409, accounting for 42.9%, followed by bitter herbs and acrid herbs. From the point of medicinal herb’s meridian tropism, the drug belongs to the spleen meridian is the most used, the frequency is 302, followed by the liver meridian and kidney meridian, accounting for 18.7%, 17.2%, and 15.0%, respectively (Table 2).
Syndrome type
In the frequency statistics of Syndrome type, the deficiency of the spleen and the kidney type was the most, occurred 19 times, followed by combination of blood stasis and toxin, damp-heat-stagnation-type. The distribution of the syndromes with frequency ≥ 5 is shown in Table 3.

Table 2. Distribution of property flavors attributive channel in prescriptions for treatment of prostate cancer

Table 3. Distribution of main symptom types of prostate cancer (Frequency ≥5)
Prescription Composition Rules analysis
Through analysis, 11 pairs of commonly used drug combinations were obtained, and the most frequently used drug pairs were Huangqi and Fuling, appearing 21 times; followed by Fuling and Dihuang, appearing 16 times; Huangqi, Gancao and Baizhu (), Fuling appeared 14 times (Table 4). In the drug combination with higher confidence, it shows that the Gouqizi (), Huangqi, Baizhuand Fuling are common drug combinations. Analyze the medication rule of the obtained drug combination, in descending order (Table 5). The core drug network is shown in Figure 2.
New formulation analysis
Based on the mutual information method, a total of 137 correlations between the two drugs in the prescription were obtained, and the list of correlation coefficients was derived. A total of 17 pairs of drugs with correlation coefficient ≥0.038 were obtained. The specific results are shown in Table 6. A total of 20 core drug combinations were extracted, which is the basis of the new prescriptions combination.The 9 new prescriptions aiming at different syndromes respectively. The results are shown in Table 7 and 8.
Mechanism of action
Based on the above data mining results, the four medicinal herbs of Huangqi, Fuling, Dihuang, Gancaowere selected for KEGG pathway analysis. As a result, there were 258 kinds of diseases enriched by 4 herbs, including prostate cancer, and the number of potential targets was 7. See Table 9 for a list of diseases with a target number ≥ 7. There are a total of 152 potential signal pathways, and the number of potential targets is ≥12. The specific results are shown in Table 10. The potential targets, signaling pathways and disease network are shown in Figure 3

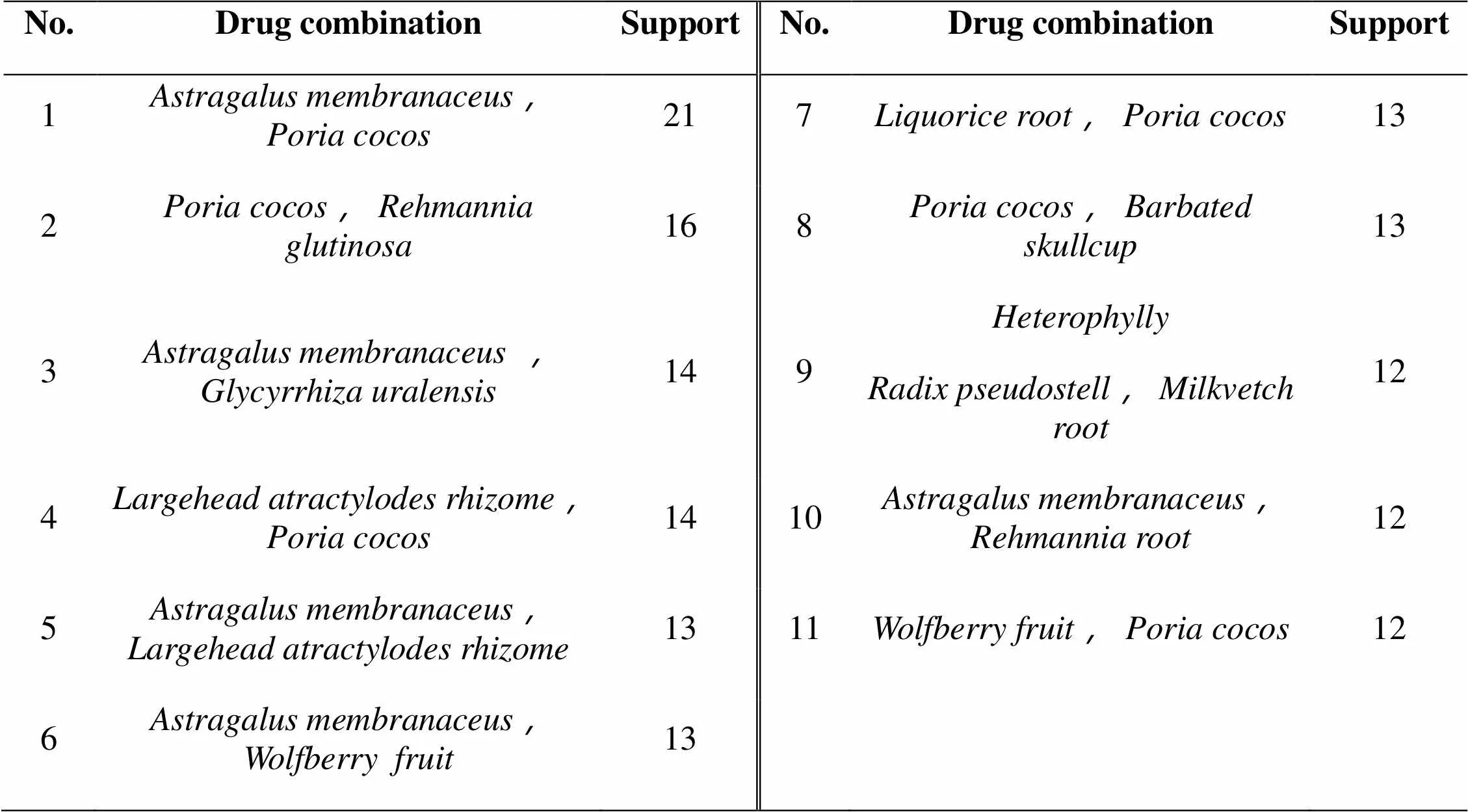
Table 4. Drug combination in prescription for prostate cancer (Support ≥12)
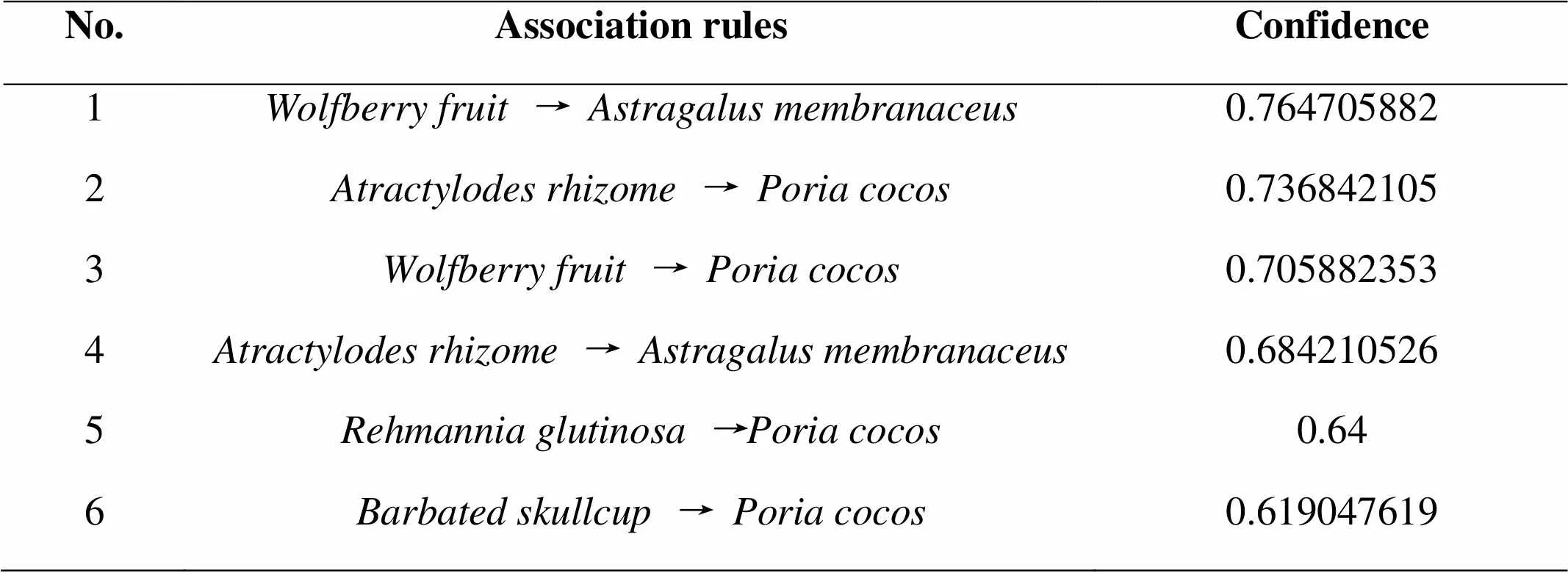
Table 5. Association rules of drugs in prescriptions for treatment of prostate cancer (Confidence ≥0.6)

Figure 2 Core drug network showcase
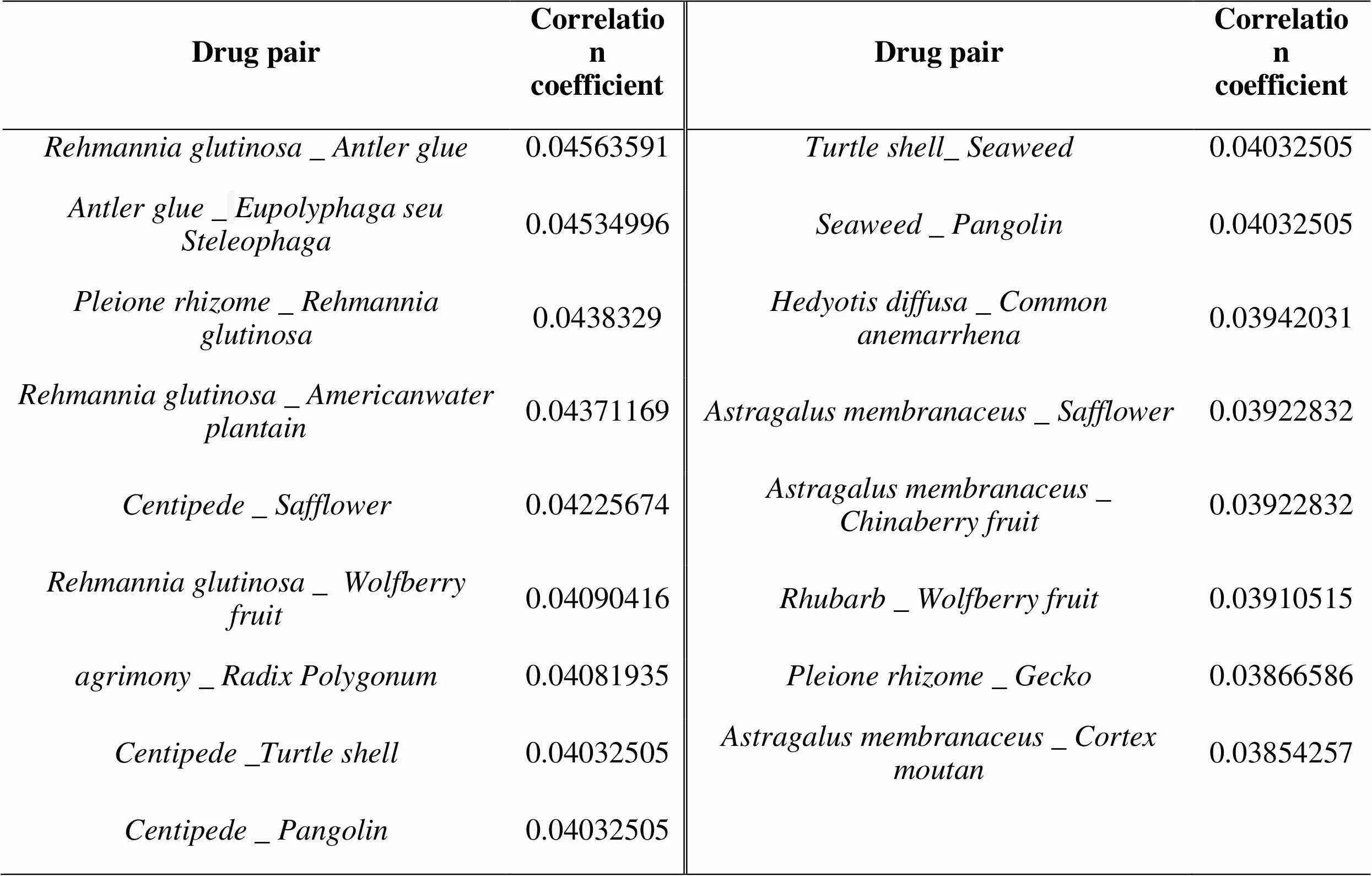
Table 6. Correlation degree of drugs in prescriptions for treatment of prostate cancer (Correlation coefficient ≥0.038)

Table 7. Core drug combinations in prescriptions for prostate cancer

Table 8. New prescriptions for prostate cancer

Table 9. Enrichment Analysis of compatible diseases of 4 drugs (Target number ≥7)
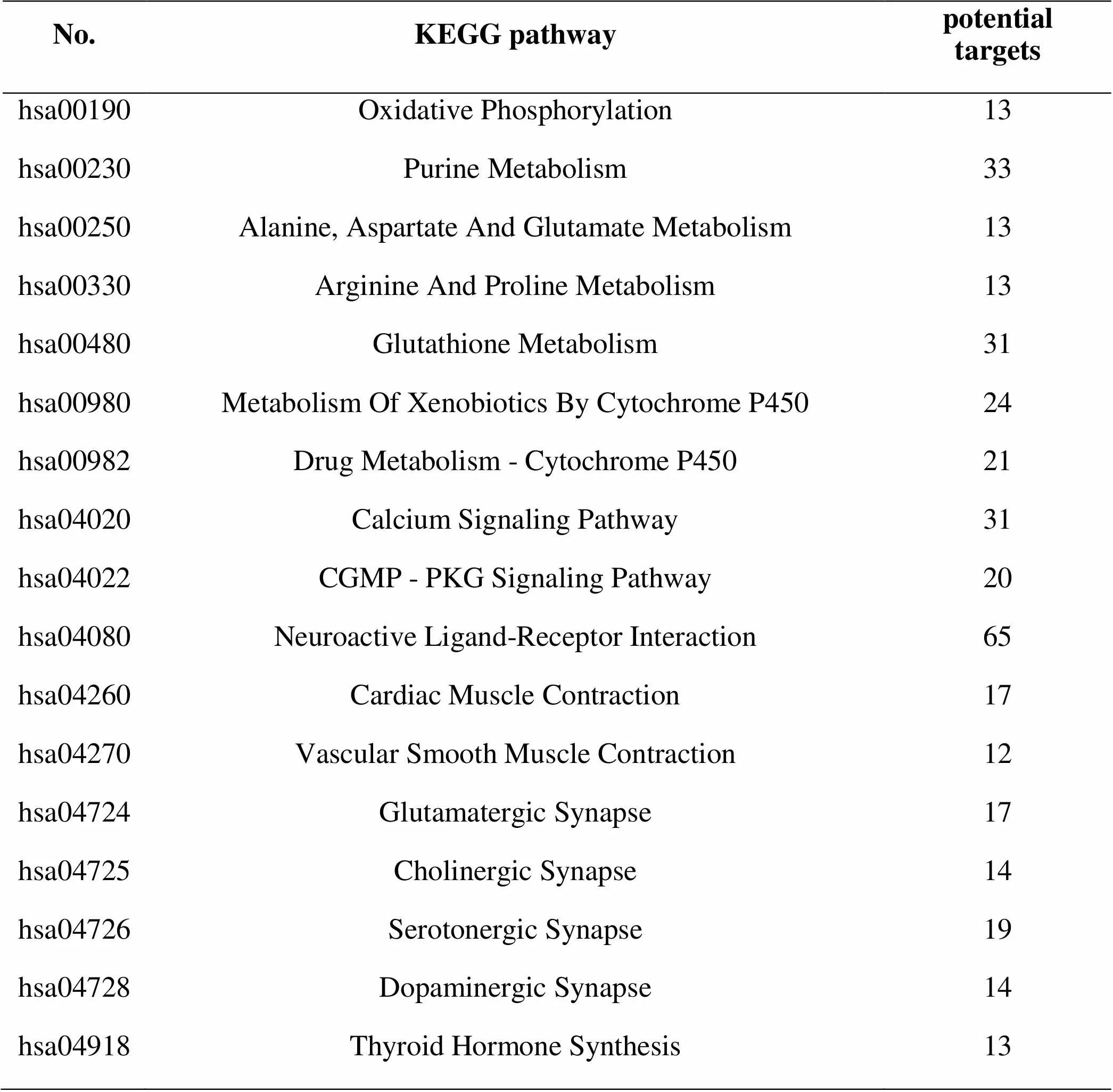
Table 10.KEGG pathway analysis (Target number ≥12)
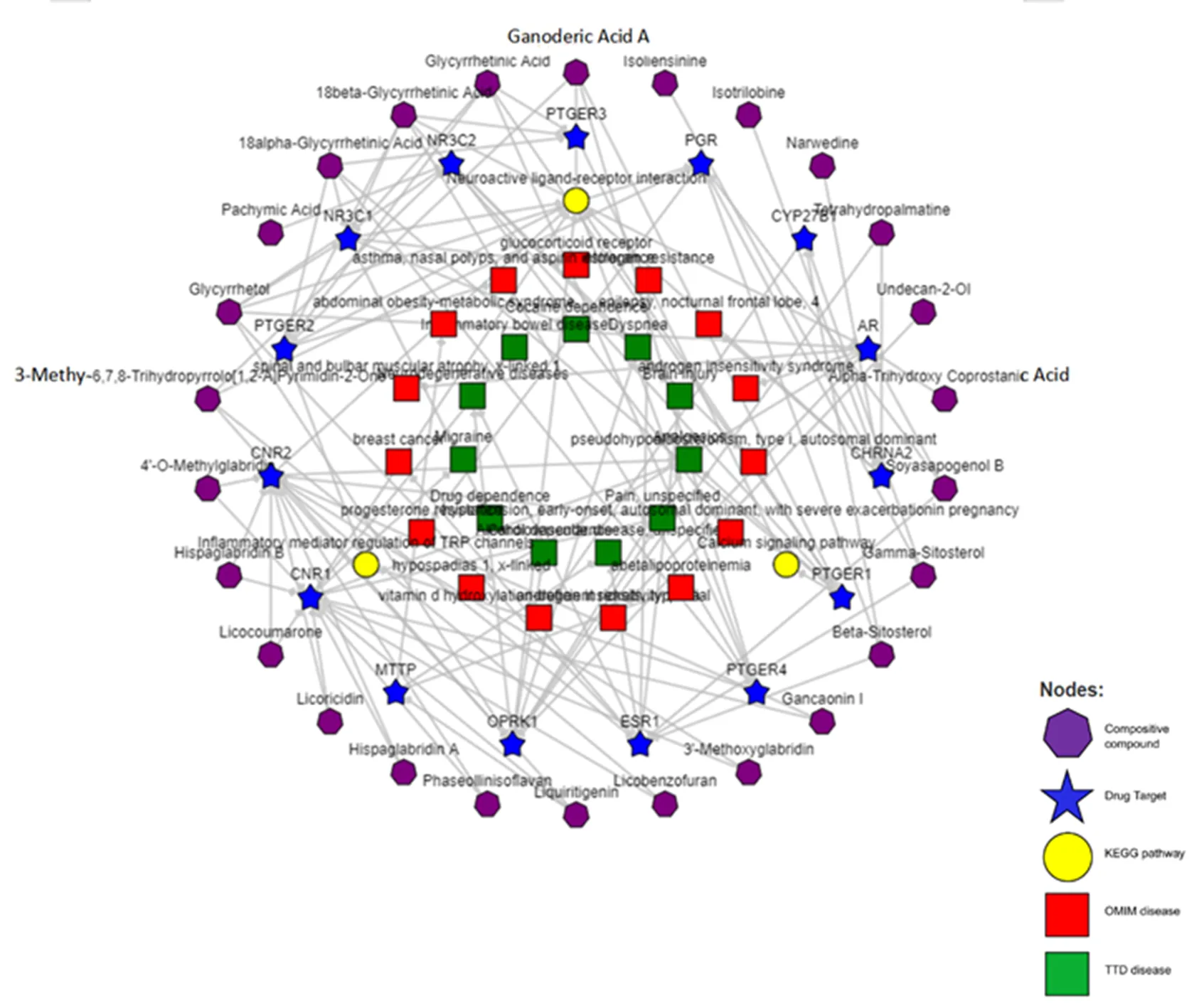
Figure 2 Visualization of Potential Targets, Signal Pathways and Disease Networks
Discusson
Prostate cancer belongs to the category of "kidney rock", " stranguria"," dysuria"," hematuria" and "lumbago" in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). The Canon of Internal Medicine said that: "Where pathogenic qi gathered , its Qi will be deficient." Yi Zong Bi Du said that, "Accumulate what is accomplished, lacking of vital qi, and then pathogenic qi gathered. Therefore, TCM thinks that the basic pathogenesis of prostate cancer is "deficiency of vital qi, combination of blood stasis and toxin" and that the core of the pathogenesis is "deficiency, toxin, blood stasis and dampness" [13]. "toxin" is the inducement, "deficiency" is the internal cause, "blood stasis" and "dampness" are both pathological products and pathogenic factors [14].
The single medicines used most frequently are Huang qi, Fuling, Gancao, Dihuang, and Baihuasheshecao ()which was found in frequency analysis. Among four natures, the drugs were mainly distributed in warm and cold. The drugs in five flavours were mainly distributed in sweet and bitter. From the point of medicinal herb’s meridian tropism, the drug belongs to the spleen meridian, liver meridian, kidney meridian is the most used. In the frequency statistics of Syndrome type, the deficiency of the spleen and the kidney, blood stasis and toxicosis type were the most, which is also in line with the understanding of the disease by ancient physicians.
It was found in association rules that the highest confidence in the drug combination were 6 pairs, which prompted that we should pay attention to the compatibility between drugs, such as Huangqi, Fuling, Gouqizi, Dihuang, Gancao, and BaizhuForm the compatibility between drugs pair Gouqizi →Huangqi (yin-reinforcing drugs → qi-invigorating drugs)、Baizhu →Fuling (qi-invigorating drugs → drugs removing dampness and promoting diuresis)、 Banzhilian ()Fuling(heat-clearing drugs →drugs removing dampness and promoting diuresis), we can know that the prostate cancer is mainly treated with d enforcing spleen and nourishing kidney and kidney tonifying and essence replenishing drugs and combined with drugs for dissolving blood stasis and detoxication, inducing diuresis and excreting. Pachymaric acid can inhibit the proliferation and invasion of colon cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer and prostate cancer [15]. Glycyrrhizic acid inhibits the proliferation of LNCa P and DU145 cancer cells in concentration-time correlation through a mechanism of apoptosis unrelated to caspase-3 and caspase-8, which can DNA damage in prostate cancer cells [16]. Astragalus polysaccharide for injection is widely used in clinical treatment of cancer, and it is a reversal agent of drug resistance. Combination with other adjuvant drugs can improve the quality of life of cancer patients [17]. Studies have shown that scopolamine, an active ingredient of Gouqizi, has a significant inhibitory effect on the proliferation of human prostate cancer PC3 cells [18]. It can be seen that the high-frequency drug obtained from data mining is also in line with modern pharmacological research.
We obtained 10 new prescriptions by cluster analysis in new prescriptions analysis. The prescription 1 takes Maidong (Xingren(and Huanglian () as the core, aiming at prostate cancer of deficiency of Qi and Yin, which treated with drugs of nourishing Yin and clearing heat. The prescription 2 and 8 takes Dangshen ()Biejia ()and Shemei () and Biejia, Dihuang and Chuanshanjia() as the core , focusing on spleen and kidney deficiency, blood stasis and toxicity syndrome, which treated with drugs of strengthening spleen and kidney, nourishing yin and blood, removing blood stasis, clearing away heat and detoxification. The prescription 3 takes Beimu (), Gancao, and ezhu () as the core , aiming at the syndrome of blood stasis blockade, which focused on the drugs of breaking blood and promoting qi, removing blood stasis and dispersing blood stasis. The prescription 4 takes Huangqi, Fuziand Rouguias the core, aiming at prostate cancer of kidney yang deficiency type, which treated with drugs of warming and tonifying kidney yang, dispersing cold and dredging collaterals.The prescription 5 takes Yiyiren (), Taizishen (), and Zhuling()as the core , aiming at the deficiency of spleen-qi syndrome, the treatment is mainly to invigorate the spleen and invigorate qi, promote water and permeate dampness. The prescription 6 takes Muli ()ChaihuHuangqin ()as the core, focuses on soothing liver, regulating qi and activating blood circulation, softening firmness and dispersing heat for prostate cancer with stagnation of liver qi. The prescription 7 takes Niuqi (), Zaojiaoci (), and Tubiechong () as the core , aiming at liver and kidney deficiency, blood stasis blocking syndrome, which treated with drugs of nourishing liver and kidney, activating blood circulation to remove stasis, detoxifying and dispersing knot. The prescription 9 takes Zelan (), Baihuasheshecao, Chenpi (),and Banzhilian () as the core , aiming at damp-heat and stasis syndrome, which treated with drugs of clearing away damp-heat, detoxifying and removing blood stasis.
Through BATMAN-TCM on-line analysis system of the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine, we found that prostate cancer was included in the diseases enriched by four drugs, and the potential targets were 7. Erectile dysfunction is closely related to prostate cancer. Because of the relationship between prostate and vascular bundle anatomy, erectile dysfunction occurs in almost all patients after radical prostatectomy [19]. Zhang Hui have carried out the clinical trial, of which treatment group was treated with Yishen Tongluo Decoction (25g Shudihuang (), 15g Tusizi (), 15g Xianmao (), 15g Zhiyanghuo (), 15g Danshen (), 9g Nanchaihu (), and 2 Wugong ()) [20]. The effect was remarkable after 4 weeks’ treatment. The number of potential targets of neuroactive ligand receptor interaction pathway and purine metabolic pathway was the largest in the pathways enriched by the four drugs. Neuroactive ligand receptor interaction signaling pathway is the aggregation of all ligands related to intracellular and extracellular signaling pathways in the plasma membrane, which is most closely related to neurological function in physiology [21]. The study found that the incidence of depression in cancer was as high as 35.1% [22]. It can be inferred that the neurological symptoms of prostate cancer such as anxiety and depression may be cured by this pathway . Total astragalus extract (TAE) inhibits the proliferation and collagen synthesis of HSC-T6 cells induced by oxidative stress in vitro, which is related to the significant inhibition of TAE on the production of O 2. - in xanthine (X) - xanthine oxidase (XO) system and non-enzymatic system [23]. Several research found that appropriate dose of glycyrrhizin and dexamethasone had protective effect on podocyte injury induced by purinomycin [24].
Chinese herbal decoction is often used in adjuvant treatment of prostate cancer at different stages of treatment in clinic [25]. The holistic concept and syndrome differentiation in Traditional Chinese medicine assist the treatment of prostate cancer, which can integrate traditional Chinese and Western medicine to enhance synergy. It shows bright prospects in improving clinical symptoms and alleviating physical and mental pain of patients.
In this study, we systematically summarized its medication rules and predicted the potential targets and signaling pathways of high-frequency drug compatibility through collating the clinical research literature of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the treatment of prostate cancer, providing a new direction for the study of drugs for prostate cancer. However, the data are limited so that still needs to be verified by treatment according to pattern differentiation and experimental research, so as to clarify the medication rule and mechanism of TCM the treatment of prostate cancer more scientifically.
Knowledge
Number of support degree
Refers to the frequency of occurrence of a drug pair or combination of drugs (symptoms or combination of symptoms) in the selected prescription (medical case) (this parameter ≤ the total number of prescriptions (medical cases)). Can be adjusted according to the actual amount of data.
Confidence
A on the left and B on the right of "→", meaning the probability of drug B appearing when drug A appears. (after the occurrence of A, the closer this parameter is to 1, the higher the probability of the occurrence of B.) This parameter can be adjusted according to the actual situation.
Relevance
This is an important parameter in the entropy clustering algorithm (this parameter must be less than the total number of prescriptions (medical cases). At the same time, it cannot be designed too high, generally within 20, otherwise the operation is too much and the response is very slow). A simple understanding is that a prescription or prescription is composed of several drugs, and one drug must have a certain correlation with another drug. According to the mathematical algorithm of the improved mutual information method, the correlation between drugs and drugs can be quantitatively described. Note on relevance design: Correlation design is too low, and a lot of reliable information will be lost. For example, the design is “3”. Only the drug combinations ranked in the top 2 are used for cluster calculation, and many information is lost. However, the correlation design Too large, although retaining a lot of information, but affecting the speed of operation, at the same time, a lot of useless information interferes with the clustering results.
Penalty degree
Penalty is a parameter used to reduce the interference of negative data information (this parameter must be less than the correlation). There is a positive correlation and a negative correlation between the drug and the drug. The so-called positive correlation is that the relationship between drugs and drugs is clinically meaningful and allowed to be applied, such as Zhimu and Phellodendron, frankincense and myrrh, etc. These commonly used drugs are closely related and often used in prescriptions. Some drugs are used in clinical contraindications, such as "eighteen anti-" and "nineteen fears". Although these drugs cannot be used in combination, they cannot be said that there is no relationship between these drugs. According to the software design algorithm, The relationship between these drugs is equally close, but the relationship is negatively correlated. In order to avoid the impact of negative correlation on data analysis, a penalty is added here to eliminate it. The penalty is designed to be "2", indicating that the two drugs are present at the same time in at least the existing prescription or prescription, thus eliminating those drugs that do not appear simultaneously in all prescriptions. Points of attention for the setting of penalty level: the penalty level cannot be set too large. If the setting is too large, a lot of information will be lost and the cluster mining result will be affected.
1. Lindsey A. Torre, Freddie Bray, Rebecca L, et al. Global cancer statistics. 2012. CA: A Cancer J Clin,2015. 65: 87-108.
2. Han SJ,Zhang SW,Chen WQ, et al.Analysis of the status and trends of prostate cancer incidence in China. Chin Clin Oncol, 2013. 18: 330-334.
3. Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Peter D. Baade, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA: A Cancer J Clin, 2016. 66: 115-132.
4. Chen WQ, Sun KX, Zheng RS, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2014.Chin J Cancer Res,2018. 30: 1-12.
5. Sun YY, Jia YJ, Chen J, et al. Research progress of traditional chinese medicine treatment of prostatecancer mechanis. J Pract Tradit Chin Internal Med, 2013. 27: 90-93.
6. Shabbir M, Love J, Montgomery B. Phase I trial of PC-Spes2 in advanced hormone refractory prostatecancer. Oncol Rep, 2008. 19: 831-835.
7. Jia YS, Chen XJ, Zhang ZJ. Overview of clinical research on treatment of prostate cancer with traditional Chinese medicine. J Tradi Chin Med, 2012. 53: 2142-2146.
8. Gong LJ. Professor Wei Zixiao's prescription rules and core prescription network pharmacology for subacute thyroiditis.Beijing University of Chinese medicine,2018.
9. State Pharmacopoeia Committee. Chinese pharmacopoeia. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2015.
10. Dou CG. Chinese Medicine. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2013.
11. Yao NL. Differential diagnosis of traditional Chinese medicine syndromes. 2nd ed. Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House, 2002.
12. Liu Z, Guo F, Wang Y, et al. BATMAN-TCM: a bioinformatics analysis tool for molecular mech ANism of traditional Chinese medicine. Sci Rep, 2016. 6: 21146.
13. LI XJ, Li YY, Mou RY, et al. Research progress on traditional Chinese medicine on treatment of bone metastasis of prostate cancer. Chin Tradi Herb Drugs, 2018. 49: 965-969.
14. Wang JX, Li XJ, Chen J, et al. Discussion of Jia Yingjie on TCM pathogenesis and treatment of prostate cancer. J New Chin Med, 2014. 46: 20-23.
15. Huang S, Pan YW, Lan H, et al. Progress of study on pharmacology of Fuling acid. Chin Tradi Pat Med, 2015. 37: 2719-2721.
16. Zhang MF, Shen YQ. Advances in pharmacologic studies on Glycyrrhizae Radix and its active components in genital system. Drug Eval Res, 2014. 37: 367-374.
17. Zhang Y, Wang L, Du MN. Research progress on treatment of tumor with Astragalus polysaccharides for injection. Drug Eval Res, 2016. 39: 1092-1094.
18. Liu XL, Sun JY, Li HY, et al. Extraction and isolation of active component for inhibiting PC 3 cell proliferation in vitro from the fruit of Lycium barbarum. Chin J Chin Mater Med, 2000. 8: 33-35.
19. Xiang XT, Zhao F, Zhao JF, et al. Research progress on erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy. Chin Androl, 2018. 32: 68-72.
20. Zhang H,Sun ZX,Chen JS,et al. Clinical Observation on Modified Yishen Tongluo Formula for 30 Cases of Erectile Dysfunction With Liver Depression and Kidney Deficiency Syndrome. J Tradi Chin Med, 2014. 55: 1207-1209.
21. Pan LZ. Toxicological Genomics Study on dependence of valeriana jatamansi jones by toxicogenomics.Southwest Jiaotong University, 2011.
22. Wang KN, Liao QL, Chen LQ, et al. Study on present situation of life quality and influencing factors in patients with prostate cancer. Chin J Androl, 2015. 29: 15-20.
23. Xu M, Zhu H, Wu YY, et al. Inhibitory effect of total extracts of astragalus membranaceus on proliferation and collagen synthesis of hepatic stellate cells induced by oxidative stress and its mechanism. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med,2006. Z1: 60-63.
24. Wang LN, Yu SY, Wu WL, et al. Study on Intervention of Glycyrrhizin and Dexamethasone on Podocytes Injury Induced by Puromycin Amino-nucleoside in vitro.Chin J Appl Clin Pediatr, 2011. 26: 1668-1670.
25. Gao Z, Shao KQ, Shen JW, et al. General situation of auxiliary treatment of prostate cancer with traditional Chinese medicine. Mod Chin Clin Med, 2011. 18: 37-39.
挖掘中药治疗前列腺癌的用药规律,并预测高频药物配伍的生物分子水平作用机制。:系统搜集与整理中国知网、万方医学网和维普中文生物医学期刊数据库,Pubmed和 EMbase中的相关文献,采用中医传承辅助平台( TCMISSV2.5)进行频次统计、关联规则分析和新方挖掘,采用BATMAN-TCM 分析高频药物靶标间相互作用关系及相关通路。结果:在纳入标准的102首处方中,黄芪为使用最多的单药。关联规则分析中置信度较高的组合有6对。系统熵聚类分析得到20个核心药物组合和9首新处方。对黄芪、茯苓、甘草、地黄进行KEGG通路分析,发现神经活性配体受体相互作用通路和嘌呤代谢通路潜在靶标个数最多。:前列腺癌的治疗以补虚药为主,配伍活血化瘀、清热利湿、解毒散结之药。高频中药作用机制可能是通过干预神经活性配体受体相互作用通路和嘌呤代谢通路实现的。
前列腺癌;用药规律;作用机制;数据挖掘;网络药理学
: Yang Y, Chen Y, Yang ZN, et al. Analysis of drug use law and mechanism of prostate cancer based on data mining and network pharmacology. TMR Modern Herbal Medicine, 2019, 2 (3): 140-150.
10.12032/TMRmhm2017A52.
Submitted: 31 May 2019,
16 June 2019,
Guo-wei Zhang, College of Chinese Medicine, Hebei University, Baoding, Hebei province, China. E-mail: xxzgw@126.com.
22 July 2019.
Abbreviation: TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of Hebei (No.H2018201179), Hebei University of Science and Technology (No. QN2016077), and Health and Family Planning Commission of Hebei (No. 20160388).
Competing interests: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Executive Editor: Jing Sun
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2019年3期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2019年3期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Erahertz spectral analysis of Xiling Zhimu with different geological conditions and plant age
- The Protective Effect of Jiujiuguiyi, a Medicine and Food Homologous Formula, on Acute Alcohol Poisoning Mice
- Mitochondrial membrane stabilization by Angelica sinensis polysaccharide in murine aplastic anemia
- Effect of Tanshinone IIA on LPS-induced inflammatory response in a ROS-NLRP3 inflammasome dependent manner in RAW264.7 cells
- Application Progress of Porous Materials in Modern Pharmaceutical
