旅游环境承载力研究综述
杨秀平 翁钢民
[摘 要]旅游环境承载力的研究对加强旅游目的地的管理、提升目的地相关主体的满意度、促进目的地可持续发展具有重要意义,旅游环境承载力问题的研究成为旅游管理领域的研究热点。文章从旅游环境承载力的概念、指标体系、计量模型、应用研究和管理工具等5个方面梳理了近年来国内外学者的研究,提出旅游环境承载力问题的研究方向和侧重点,指出:(1)针对旅游相关主体偏好的区间性特征、界定基于多主体需求的旅游环境承载力概念体系,从旅游环境承载力的供给指标与主体对旅游环境的需求要素角度构建指标体系;(2)提高旅游环境承载力计量模型的科学性与精确性,分析系统内部与系统之间的动态匹配机理、测度模型,模拟特定主体的行动轨迹与旅游环境承载力的波动轨迹;(3)结合时代特征,关注典型区域,并展开应用研究;(4)对旅游环境可持续承载进行优化,分析可持续承载“潜力”转化为可持续承载“实力”的系统性管理举措。
[关键词】旅游环境承载力;旅游可持续发展;人一地关系;旅游影响
[中图分类号]F59
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1002-5006(2019)04-0096-10
Doi: 10.19765/j .cnki.1002-5006.2019.04.013
引 言
旅游承载力(tourism canying/bearing capacity)又被称为旅游容量,当今国内外学者关于此问题的研究多集中在旅游环境承载力、旅游环境容量方面[1],相关文章多发表在旅游、生态、环境、地理等主题的学术期刊,虽有学者质疑两者的差异,但多数学者坚持旅游环境容量与旅游环境承载力是同义语。20世纪60年代,旅游环境承载力问题受到学者的关注;20世纪90年代后,随着可持续发展理念研究的深入,旅游环境承载力相关问题逐渐成为旅游资源开发与规划领域研究的热点问题。旅游环境承载力相关问题的研究凭借其独特的理论与广阔的应用前景,阐释着“人一地”系统的相互作用机制以及人类活动产生的生态与环境效益。
21世纪旅游发展迅猛,旅游产业已成为部分国家或地区国民经济的战略性支柱产业;旅游者规模空前增大,旅游活动成为百姓常态化的生活方式。根据《世界旅游经济趋势报告(2019)》的分析,2018年全年全球旅游总人次达121.0亿人次,全球旅游总收入达5.34万亿美元,预计2019年全球旅游总收入将达到5.54万亿美元,相当于全球GDP的6%,高于全球经济增长速度;从我国来看,2018年国内旅游为55.4亿人次,中国公民出境旅游1.48亿人次,入境游客1.42亿人次,实现旅游收入约5.99万亿元,预计2019年国内旅游人数60.6亿人次,将实现旅游总收入6.52万亿元①。大众旅游时代的到来,旅
游者出游率的提升,导致旅游旺季客流的大规模集中,当外界“刺激”(旅游环境需求量)超出旅游环境承载力时,旅游环境系统将逐渐呈现逆向变化嘲。世界旅游组织指出,把旅游活动限定在旅游环境承载力范围内,是保证旅游目的地可持续发展的需要。在此背景下,国内外学者对旅游环境承载力的相关问题进行着基础性和前沿性研究、从事着本土化适应性的尝试,以期对民众出行进行合理引导。
近年来,旅游环境承载力相关问题的研究逐步深入,文章从旅游环境承载力的概念、指标体系、计量模型、应用研究与管理工具5个角度对旅游环境承载力相关研究进行梳理,提出今后旅游环境承载力研究的重点方向与研究内容,解决旅游发展中旅游者大量涌入导致旅游环境压力增大的系列现实问题,为实现旅游目的地的可持续发展提供科学依据。
1 旅游环境承载力概念的研究
学者们对旅游环境承载力的探讨围绕“人一地”关系展开,以“地”为中心的理念认为旅游环境承载力的研究重点考虑人类开展旅游活动空间场所和地域背景下的基础要素;以“人”為中心的理念认为旅游环境承载力的研究应关注以旅游者为代表的相关主体的感受。20世纪60-70年代,旅游环境承载力概念的探讨侧重于“使用量”[3]“利用强度”[4]与“旅游者满意度”[5-6]等的定性分析;20世纪80-90年代以后,伴随着国内学者对旅游环境承载力研究的起步,学者们在前期“使用量”“利用强度”[5,7-11]等相关研究的基础上,热衷于目的地旅游者数量极限值或临界值的界定,旅游环境承载力研究的侧重点集中在旅游者的“最大承载数量”[12-17],旅游环境承载力成为目的地旅游可持续发展的重要判据[15]。进入21世纪,旅游环境承载力的研究在强调其“增长极限——旅游者最大承载数量”[18-19]“使用水平与利用强度”[20-22]的同时,旅游环境相对承载力的研究有助于目的地旅游环境承载力问题的横向比较[21];有学者提出在旅游发展中应注重多主体对旅游环境需求与目的地旅游吸引物承载力之间的匹配、考虑相关主体利益的协调[22-24],部分学者把旅游影响研究纳入旅游环境承载力的研究范畴[25-26],旅游环境可持续承载问题的研究体现了国内外学者对旅游社会责任的认同[27-29]。
综上,国内外学者对旅游环境承载力概念的界定虽有所差异,但相关研究已达成4点共识:第一,以可持续发展思想为指导;第二,以探究旅游目的地开发限度为直接目的;第三,旅游目的地自然、经济、社会等要素没有遭到破坏;第四,注重旅游者满意度的提升。可持续发展强调“惠众”“公平”“可持续”,现有概念多围绕旅游者这一主体展开,不利于和谐旅游环境的构建。缺乏对相关主体旅游环境需求的考虑,导致研究成果难以有效地应用到旅游目的地的管理实践,在特定背景下旅游环境承载力研究对相关主体关注的缺位,将导致相关主体的利益被掠夺,导致目的地旅游开发的粗放性和旅游管理的短视性。
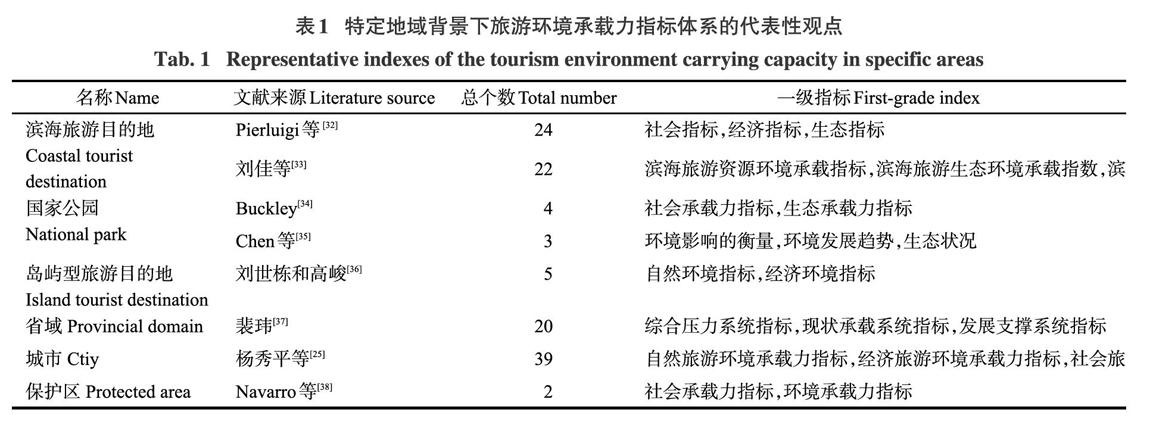
2 旅游环境承载力指标体系的研究
旅游环境承载力测评指标体系经历了从单指标向多指标的发展过程,旅游环境承载力研究的初始阶段多选取以自然环境为主的旅游目的地,此时指标体系的构建多以单指标为主,通过对相关文献[23,30-31]的追溯,单指标的研究未构成明确的发展阶段且很快进入指标多元化阶段。随着研究视角、旅游目的地类型及其他因素的影响,指标体系涵盖了生态、经济、社会、文化等方面,指标体系的多元化为其计量模型的丰富奠定了基础。值得一提的是,在指标体系构建中,结合滨海旅游目的地[32-33]、国家公园[34-35]、岛屿型旅游目的地[36]、省域[37]、城市[25]、保护区[38]等特定地域背景,对指标体系进行了细化,如表1所示;相对旅游环境承载力指标体系的提出[21],为区域旅游环境承载力的比较奠定了基础。由此可见,基于不同的旅游目的地构建差异化的旅游环境承载力指标体系,并结合具体的旅游目的地进行灵活调整,是今后旅游环境承载力指标体系构建的重点。
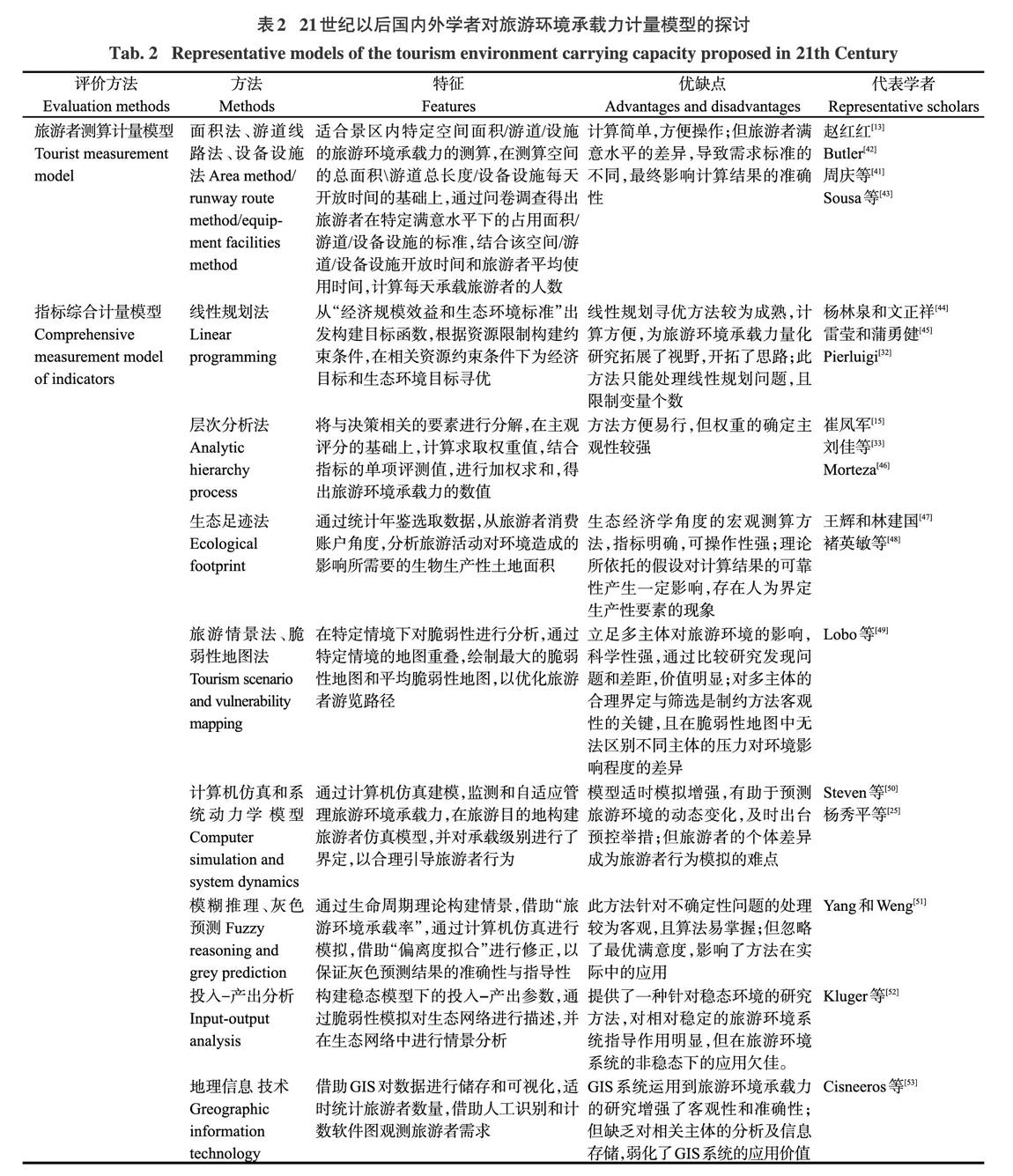
3 旅游环境承载力计量模型的研究
旅游环境承载力的评价方法具有多学科交叉的特点,分为对旅游者的测算模型与对指标体系的综合计量模型。部分学者提出应用“木桶原理”中的“短板理论”确定旅游环境承载力数值[39],在问卷调查的基础上[40],结合周转率提出面积法[13,41]、景点线路法[42]、设备设施法[43]等方法;进入21世纪,综合指标计量模型占据主导地位,比较有代表性的有线性规划法[44-45]、层次分析法[17.46]、生态足迹法[47-48]、旅
游情景法和脆弱性地图法[49]、计算机仿真和系统动力学模型[25,50]、模糊推理和灰色预测[51]、投入一产出分析[52]、地理信息技术[53]等,从旅游业的季节性变动和旅游地生命周期角度,分析了旅游环境承载力的动态变化,相关计量模型的比较见表2所示。
现有旅游环境承载力计量模型的研究成果关注精确数值的限定;部分学者尝试寻找其波动范围,但受单一主体需求的影响,阈值随着外界条件的改变而调整,承载力随着技术、参数、产品和消费的结构而变动[49]。在“管理目标”或“理想状况”的具体标准缺位的情况下,尽管旅游环境承载力相关问题的研究强调科学性、客观性,但其计量模型却融入了一定的主观性因素;对旅游环境需求主体考虑单一,影响计量方法的准确性。旅游环境供给方表示旅游环境的容纳能力,旅游环境的需求标准和需求量造成对旅游环境的压力,计量模型的研究需要综合考虑旅游环境的供给方和多主体对旅游环境的需求状况。从现有国内外学者对旅游环境承载力计量模型的分析看,亟须对旅游环境需求主体进行合理界定,结合地域背景分析旅游环境的供给能力,量化分析差异情景下的决策者偏好。上述问题的成功解决是量化方法应用的前提。
4 旅游环境承载力的应用研究
国内外学者对旅游环境承载力的研究与不同类型的旅游目的地结合,使应用领域的选取呈现了“点、线、面”的特点,并出现了向特定区域扩展的趋势。基于不同的研究视角承载力理论得以广泛应用,学者们通过限制旅游者流量和流向来保护自然资源、保障旅游者的体验和经历[54]。但在实践环节,旅游环境承载力的研究多通过一些可以量化的指标,突出其在旅游规划中的“数字”特征。国内外学者对旅游环境承载力的应用研究始于旅游区(点),学者结合海滨沙滩[32-33,43,53]、岛屿[36,46]、山体岩石[39,55]、洞穴[49]、主题公园与国家公园[24,56]、沙漠[57]等特定旅游资源特征进行分析,在实地调研的基础上获得一手数据资料,旅游者测算评价法成为特定空间、游道、设备设施承载力的主要测算方法;研究对象拓展到单体旅游城市[25,58],接着延伸到特定区域[59-62]。旅游城市与特定区域旅游环境承载力的研究多基于统计年鉴等获取数据进行测算。探讨量化方法在不同地域背景下的适应性,不断地提升研究成果的理论化程度、从本土特征的研究中探索并构建本土化的学科基础理论。但特定区域旅游环境可持续承载的量化研究较少,削弱了应用研究的系统性。
5 旅游环境承载力管理工具的研究
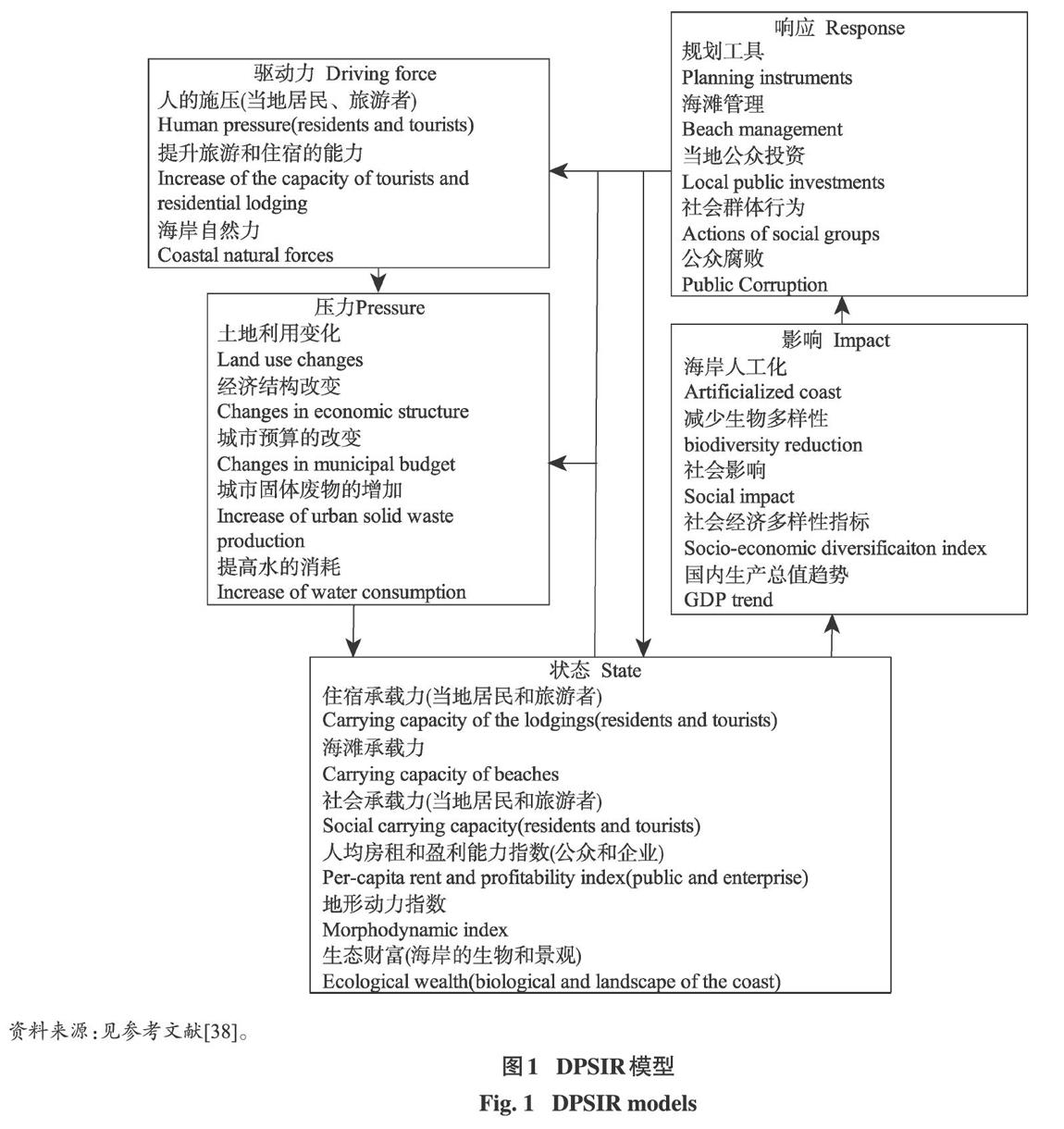
因国情的差异,国内外管理工具的发展路径相差很大。国外学者呼吁制定国家法律保证管理工具作用的发挥,国内学者更多强调旅游目的地改进性的管理举措。国外常见的管理工具有可接受改变的极限理论(limits of acceptable change,LAC)、旅游者体验和资源保护理论(visitor experience andresource protection,VERP)、旅游者活动管理程序(visitor activities management process, VAMP)、旅游者影響管理(visitor impact management,VIM)、游憩机会谱系(recreation opportunity spectrum,ROS)、最优化旅游管理模型(tourism optimizationmanagement model,TOMM)等;针对国外学者提出的管理工具[63],张骁鸣进行了其适应范围的对比研究[64];Navarro提出应用较为广泛的驱动力一压力一状态一影响一响应模型(driving force-pressure- state-
impact-response,DPSIR),指出旅游者的到来对旅游目地的转变具有驱动性,表现为旅游者的涌入对旅游目的地产生“人”的压力,压力促使旅游目的地系统发生改变,对旅游目的地产生影响,导致旅游目的地主动与被动的响应[38],见图1所示。国内,清华大学对LAC理论及衍生工具进行了相关研究;但在我国特殊国情下,受复杂性、长周期、高花费等影响,学者们多结合特定的旅游目的地,从经济学、管理学、地理学等角度提出的具体管理举措,且多注重定性分析;部分学者围绕旅游环境承载力预警系统进行研究,提出了预控管理举措[57],为国内管理工具的研究开辟了新的路径。
旅游环境承载力的研究强调“测定——评价——管理举措”的系统性。国外,管理工具提供的理论框架在旅游目的地广泛应用,鉴于旅游承载力应用领域的特殊性,此类管理工具在方法的非定量性、分析的严谨性上有待商榷;国内学者对管理工具的研究多表现为“套路式”的相关举措,旅游目的地实质性的系统管理相对较少。未来研究倾向于在理解旅游环境承载力内涵的基础上,寻找较为合理的管理工具,从而达到有效调控的目的。
6 旅游环境承载力相关问题的研究展望
上述成果丰富了旅游环境承载力研究的相关理论,增强了人们对旅游环境系统的关照程度,扩大了旅游环境承载力理论的应用范围;更重要的是,为旅游环境承载力的深入研究奠定了坚实的基础。针对已有研究成果存在的不足,文章提出了4点展望。
6.1深入研究旅游环境承载力的概念和指标体系
基于“人”偏好的区间性特征,本文认为对旅游环境承载力概念界定,采用“可接受范围”更合理,建议从旅游相关利益主体理论出发,构建基于多主体需求的旅游环境承载力概念体系。在文献研究和专家调查的基础上,根据旅游目的地生命周期理论,探究旅游目的地不同发展阶段旅游环境需求主体的构成并分析多主体的需求特征;在主动性、重要性、紧急性等维度上分析多主体对旅游环境系统施压存在差异,借助量化方法对多主体进行分析,把多主体细分为核心主体、蛰伏主体和边缘主体,重点考虑核心主体对旅游环境的需求。对多主体进行合理分区并确定其优先级是对旅游环境承载
是核心主体)偏好的目标间的相互重要性关系,根据目标区间的偏好区域,利用进化优化算法寻优,进一步比较具有相同序值的进化个体的性能,指导算法向决策者的偏好区域搜索;最后,探讨特定“情景”下决策者偏好与相关主体偏好的变动,动态调整管理工具设定目标区间和参数值,以形成调控旅游目的地承载状况、挖掘旅游目的地可持续承载的潜力、优化其可持续承载路径、分析其可持续承载“潜力”转化为可持续承载“实力”举措的系统性研究框架。对旅游目的地合理规划的基础上,积极引导旅游环境施压主体的行为路径转变,通过对旅游环境系统施压主体需求的重新规划,解决多主体旅游环境承载状况时空错位问题,实现区域或单体旅游目的地各旅游区(点)及区内节点的协调发展,在保障旅游环境可持续承载的前提下,提升旅游目的地的综合效益,打造其整体旅游形象,实现旅游环境需求主体流量的增加和路径的延长。
参考文献(References)
[1] XIONG Ying. Progress and prospect of study on carryingcapacity of ecotourism[J].Economic Geography, 2013, 33(5):174-181.[熊鹰.生态旅游承载力研究进展及其展望[J].经济地理,2013,33(5): 174-181.]
[2] CETIN M,ZEREN I,SEVIK H,et al.A study on thedetermination of the natural park's sustainable tourism potential[J]. Environmental Monitoring&Assessment, 2018,190(3):167-172.
[3] ALAN W J.The carrying capacity of wild lands for recreation:Forest science monography[J]. Society of American Foresters,1964, 18(6): 587-594.
[4] FOWLER P A.Capacity theory in Banach spaces[J]. PacificJournal ofMathematics, 1973, 48(2): 365-385.
[5] SHELBY B.Carrying Capacity in Recreational Settings [M].Oregon: Oregon State University Press, 1987: 37-45.
[6] WALL G,WRIGHT C.The environmental impact of outdoorrecreation[J]. Department of Geography University of Waterloo,1977, 8(11): 11-18.
[7] o REILLY A M.Tourism carrying capacity concept and issues[J]. Tourism Management,1986, 7(4): 254-258.
[8] PARSONS G R,KEALY M J.Randomly drawn opportunity setsin a random utility model of lake recreation[J],Land Economics,1992, 68(1): 93-106.
[9] MCINTYREG.Sustainable Tourism Development: Guide forLocal Planners[M].Madrdi: World Tourism Organization,1993:23.
[10] BUTLER R.The concept of carrying capacity for tourismdestinations: Dead or merely buried?[J]. Progress in Tourismand Hospitality Research.1996, 2(3): 283-293.
[11] CUI Fengjun, LIU Jiaming.Tourism environmental carryingcapacity theory and its practical significance[J]. Progress inGeography, 1998, 7(1): 86-91.[崔鳳军,刘家明.旅游环境承载力理论及其实践意义[J].地理科学进展,1998, 7(1): 86-91.]
[12] MATHIESON A,WALL G.Tourism. Economic. Physical andSociallmpacts[M]. New York: Longman, 1982: 184.
[13] ZHAO Honghong. On the tourism environmental carrying ofSuzhou[J]. City Planning Review, 1983, (3): 46-53.[赵红红.苏州旅游环境容量问题初探[J].城市规划.1983, (3): 46-53.]
[14] ZHANG Shibei, ZHANG Jing.A brief introduction to themethod of defining environmental carrying for tourism byatmospheric environmental planning[J]. Research ofEnvironmental Sciences,1988,1(2): 41-44.[李时蓓,张菁,从大气环境规划单方面确定旅游环境容量的方法简介[J].环境科学研究,1988, 1(2): 41-44.]
[15] CUI Fengjun. Study on the tourist environmental bearingcapacity: One of the criteria for sustainable development oftourism[J]. Economic Geography, 1995, 15(1): 105-109.[崔风军.论旅游环境承载力——持续发展旅游的判据之一[J].经济地理,1995, 15(1): 105-109.]
[16] PAPAGEORGIOUS K,BROTHERTON L A managementplanning framework based on ecological, perceptual andecononuc carrying capacity: The case study of Vikos-Aoosnational park[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 1999,56(4): 271-284.
[17] BUCKLEY R.An ecological perspective on carrying capacity[J].Annals of Tourism Research, 1999, 26(3): 705-708.
[18] YAN Boya, BI Chao. Calculation and evaluation of the tourismenvironmental carrying capacity of Xi'an[J]. Journal of North-west University: Natural Science Edition,2011,41(4):719-722.[闰博雅,毕超.西安市旅游环境承载力测算与评价研究[J].西北大学学报:自然科学版,2011, 41(4):719-722.]
[19] ZHANG Bo.A research on resident's social-psychological carryingcapacity of tourism destinations:A case on Asakusa area, Tokyo,Japan[J]. Tourism Tribune, 2014, 29(12): 55-65.[張博.旅游目的地居民社会心理承载力研究——以日本东京都浅草寺为例[J].旅游学刊,2014, 29(12): 55-65.]
[20] WOZNIAK D,MACNEILL T. The economic, social, andenvironmental impacts of cruise tourism[J]. TourismManagement, 2018, 2(1): 66-78.
[21] ZHANG Guanghai, LIU Jia. The study on the relative carryingcapacity of tourism environment in eastem coastal regions inChina[J]. Economic Geography, 2009, 21(7): 1222-1227.[张广海,刘佳.我国东部沿海地区旅游环境相对承载力研究[J].经济地理,2009. 21(7): 1222-1227.]
[22] WANG Youming. Evaluation on bearing capacity of tourismenvironment in Southern Jiangsu cities based on sustainabledevelopment[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University:Nature Science, 201l,30(5): 793-796.[王友明,基于可持续发展的苏南城市旅游环境承载力[J].辽宁工程技术大学学报:自然科学版,2011, 30(5): 793-796.]
[23] WEN Shouwen. Comparison of social bearing capacity for tourismbetween developed and underdeveloped regions[J]. EconomicGeography, 2008, (5): 887-890.[文首文,发达地区与欠发达地区旅游社会承载力比较[J].经济地理,2008, (5): 887-890.]
[24] SCHWARTZ Z,STEWART W, BACHLUND A E.Visitation atcapacity- constrained tourism destinations: Exploring revenuemanagement at a national park[J]. Tourism Management, 2012,33(2): 500-508.
[25] YANG Xiuping, WENG Gangmin, HOU Yujun, et al. Modelingand simulation of urban tounsm environment carrying potentialbased on the SD model under multiple scenarios: TakingLanzhou city as an example[J]. Economic Geography, 2018, 38(3): 208-216.[杨秀平,翁钢民,侯玉君,等,基于SD模型的多情景城市旅游环境承载潜力建模与仿真——以兰州市为例[J].经济地理,2018, 38(3): 208-216]
[26] SALERNO F,VIVIANO G,EMANUEL A C,et al.Multiplecarrying capacities from a management- oriented perspective tooperationalize sustainable tourismin protected areas[J]. Journalof Environmental Management, 2013,128(15):116-125.
[27] SAARINEN J. Traditions of sustainability in tourism studies[J].Annals of Tourism Research, 2014, 33(4), 121-1140.
[28] ALVAREZ S A.The problems of tourist sustainability incultural cities: Socio- political perceptions and interestsmanagement[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(2): 503-507.
[29] DEY J, SAKHRE S, GUPTA V,et al.Geospatial assessment oftourism impact on land environment of Dehradun, Uttarakhand,India[J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2018, 190(4):181.
[30] HUNTER C.Sustainable tourism as an adaptive paradigm[J].Annals of Tourism Research, 1997, 14(4): 850-867.
[31] THANH M, CARL S.Scenario-based planning for tourismdevelopment using system dynamic modelling:A case study ofCat Ba island, Vietnam[J]. Tourism Management, 2018, 38(7):336-354.
[32] PIERLUIGI B,FRANCESCO F,GUIDO P,et al.Urbangeomorphology in coastal environment: Man- mademorphological changes in a seaside tourist resort (Rapallo,Eastem Liguria, Italy) [J]. Quaestiones Geographicae. 2017, 36(3): 97-110.
[33] LIU Jia, LI Yingying, WANG Juan. An analysis of dynamicrelation between tourism environmental carrying capacity andurbanization level in China's coastal regions[J]. CommercialResearch, 2017, (4): 178-185.[刘佳,李莹莹,王娟,中国沿海地区旅游环境承载力与城镇化水平动态关联性分析[J].商业研究,2017, (4): 178-185.]
[34] BUCKLEY R.An ecological perspective on carrying capacity[J]. Annals of Tourism Research,1 999, 26(3): 705-708.
[35] CHEN H S,CHEN C Y,CHANG C T,et al.The constructionand application of a carrying capacity evaluation model in anational park [J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and RiskAssessment, 2014, 28(6): 1333-1341.
[36] LIU Shidong, GAO Jun. Research on tourism environmentalcarrying capacity of island tourist destination:A case study ofShanghai Chongming Island[J]. Journal of Shaanxi NormalUniversity: Natural Science Edition, 2014, 42(3): 85-90.[劉世栋,高峻,岛屿型旅游目的地旅游环境承载力研究——以上海崇明岛为例[J].陕西师范大学学报:自然科学版,2014, 42(3):85-90.]
[37] PEI Wei. Appraisal of the carrying capacity of tourism eco-environment:A case study of five provinces in Southwest China[J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University: Humanities andSocial Sciences, 2013, 45(3): 31-36.[裴玮,基于面板数据的西南地区旅游生态环境承载力评价[J].云南师范大学学报:哲学社会科学版,2013, 45(3): 31-36.]
[38] NAVARRO J,CAETANO v,EMANUELA C,et al.Multiplecarrying capacities from a management- oriented perspective tooperationalize sustainable tourism in protected areas[J]. JournalofEnvironmental Management, 2013, 128(10):116-125.
[39] LIU Ling. Research about the methods of the tourismenvironment carrying capacity[J]. Journal of Anhui NormalUniversity: Natural Science, 1998, 21(3): 250-254.[刘玲,旅游环境承载力研究方法初探[J].安徽师范大学学报:自然科学版,1998, 21(3): 250-254.]
[40] WENG Jin. Analysis on the tourism environmental capacity ofShanghai Yu Garden[J]. Journal of Guilin Institute of Tourism,2000, 11(4): 17-20.[翁瑾.上海豫园旅游环境容量分析[J].桂林旅游高等专科学校学报,2000, 11(4): 17-20.]
[41] ZHOU Qing, LI Lixiong, OUYANG Zhiqin.A research ontourism environmental carrying capacity of Wengding ancientvillage[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2017,27(5): 254-257.[周庆,李立雄,欧阳志勤.原始部落翁丁古寨旅游环境承载力研究[J].中国人口·资源与环境,2017, 27(5):254-257.]
[42] BUTLER R W. Tourism and the environment:A geographicalperspective[J]. Tourism Geographies, 2000, 2(3): 337-358.
[43] SOUSA R C,PEREIRA L C C,CASTA R M, et al.Management of estuarine beaches on the Amazon coast thoughthe application of recreational carrying capacity indices[J].Tourism Management, 2017,59(4): 216-225.
[44] YANG Linquan, WEN Zhengxiang. Analysis tourismenvironmental bearing capacity in practice[J] ChinaPopulation, Resources and Environment, 2003,1 3(5): 71-74.[杨林泉,文正祥,旅游环境承载力实证分析[J].中国人口·资源与环境,2003, 13(5): 71-74.]
[45] LEI Ying, PU Yongjian. Tourism project evaluation based ontourism spatial carrying capacity constraints[J]. ManagementWorld, 2010, (8): 173-174.[雷莹,蒲勇健,基于旅游空间承载力约束下的旅游项目评估[J].管理世界,2010, (8): 173-174.]
[46] MORTEZA Z, REZA F M, SEDDIQ M M,et al.Selection ofthe optimal tourism site using the AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS in theframework of integrated Coastal zone management:A case ofQeshm island[J]. Ocean&Coastal Management, 2016,130(6):179-187.
[47] WANG Hui, LIN Jianguo. Calculation of tourism environmentalcarrying capacity on tourist ecological footprint model[J].Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2005,3 1(3): 57-61.[王輝,林建国,旅游者生态足迹模型对旅游环境承载力的计算[J].大连海事大学学报,2005, 31(3): 57-61.]
[48] Chu Ymgmin, LI Suxi,LIU Jinping.Tourism environmentalcarrying capacity of Hebei province based on Theil coeffcientand improved ecological footprint method[J].Journal ofShaanxi Normal University:Natural Scienca Edition,2014,42(4):91—95.[褚英敏,李素喜,刘金平.基于锡尔系数及改进生态足迹的河北省旅游环境承载力研究[J].陕西师范大学学报:自然科学版,2014,42(4):91—95.]
[49] LOBO H A S,TRAJANO E,MARINHO M A,et al.Projectionof tourist scenarios onto fragility maps framewodk for determin-ation of provisional tourist carrying capacity in a Brazilian showcave[J].Tourism Management, 2013,35(7):234-243.
[50] STEVEN R L,ROBERT E,WILLIAN A.Proactive monitoringand adaptive management of social carrying capacity in Archesnadonal park:An application of computer simu1ation modeling[J].Environment Management,2013,68(3):305—313.
[51] YANG X P,WENG G M.A study on the mechanism of couplingcoordination development of tourism carrying capacity andapplication research[J].Information Technology Journal,2013,12(21):6229-6234.
[52] KLUGER L C,TAYLOR M H,MENDO J,et al.Carryingcapacity simulations as a tool for ecosystcm based managementof a scal1op aquaculture systcm[J].Ecological Modelling,2016,331(9):44-55.
[53] CISNEROS M A H,SARNIENTO N V R, DELRIEUX C A,eta1. Beach carrying capacity assessment through imageprocessing too1s for coastal management[J].Ocean &CoastalManagement,2016,130(10):138—147.
[54] YEN T H,WAN L,TSUNG H C.Environmentally responaiblebehavior in ecotourism:Antecedents and implications[J].Tourism Management,2013,40(6):321—329.
[55] XU Jia.The quantification on eco—tourism environmentalcarrying capacity of Arshatu[J].Journal of Arid Land Resourcesand Environment,2014,28(10):197—202.[徐佳,对阿斯哈图景区生态旅游环境承载力进行测评研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2014,28(10):197-202.]
[56] LIANG Zengxian, DONG Guanzhi.A study on touristpsychological capacity of theme parks and its influencingfactors:An empirical study from Happy valley in Shenzhen[J].Human Geography,2011,26(2):138—143.[梁增賢,董观志,主题公园旅游者心理容量及其影响因素研究——来自深圳欢乐谷的实证[J].人文地理,2011,(3):138—143.]
[57] SONG Xiaolong,LI Longtang,WANG Yanru,et a1.Earlywarning of the tourism enviromnental bearing capacity in thedesert scenic area:A case study in Shapotou scenic area,Nomgxia,China[J].Journal of Desert Research,2019,39(2):1—8.[宋小龙,李陇堂,王艳茹,等.沙模型景区旅游环境承载力预警研究——以宁夏沙坡头景区为例[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(2):1—8.]
[58] WANG Yuming,ZHAO Zhongbua.Study on the metropolistourism capacity based on case of Shanghai[J].ChinaPopulation,Resources and Environment,2007,22(2):118一l22.[汪宇明,赵中华.基于上海案例的大都市旅游容量及承载力研究[J].中国人口·资源与环境,2007,22(2):118—122.]
[59] DU zhongchao,PU Yuqiong.The calculation and analysis onthe tourism environmental carrying capacity of the Han DynastyMausoleum scenic zone in Wuling Tableland[J].Journal ofNorthwest Normal University:Natural Science,2013,49(1):96一102.[杜忠潮,蒲玉琼.五陵塬西汉帝陵风光带旅游环境承载力测算分析[J].西北师范大学学报:自然科学版,2013,49(1):96—102.]
[60] JLANG Guiyan,ZHUO Macuo.Environment carrying capacityof eco—tourism at county levels in the south of the Qinghai—TibetPlateau[J].Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2014,28(4):202-208.[蔣贵彦,卓玛措.青海南部高原藏区生态旅游环境承载力研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2014,28(4):202-208.]
[61] CHIU H Y, CHAN C S,MARAFA L M.Local perception andpreferences in nature tourism in Hong Kong[J].TourismManagement Perspectives,2016,20(10):87—97.
[62] ZHANG Hong,HUANG Zhenfang,JU Shengli, et al.Ecological environmental bearing capacity analysis and lowcarbon tourism environment build of ancient towns:A casestudy of Zhouzhuang,Jinxi,Qiandeng[J].Chinese Journal ofAgricultural Resources and Regional Planning,2018,39(1):57—65.[张宏,黄震方,琚胜利,等.苏南古镇生态环境承载力分析与低碳旅游环境构建研究——以昆山市周庄、锦溪、千灯古镇为例[J].中国农业资源与区划,2018,39(1):57—65.]
[63] SARI S R, SUTIRTO T w,SUGIARTI R.Strengthening therole of local instotutions in protecting the environment of MountLawu areas for tourism purposes[J].Research Gate,2017,9(2):216.
[64] ZHANG Xiaoming.From theoretical framework to practicalapplication:Progress in tourism environmenta1 carrying research[J].Resources Science,2004,26(4):78—87.[张骁鸣,旅游环境容量研究:从理论框架到管理工具[J].资源科学,2004,26(4):78—87.]
A Review of Studies on Tourism Environment Carrying Capacity
YANG Xiuping1,2, WENG Gangmin2
(1. School ofEconomy and Management. Lanzhou University of Technology. Lanzhou 730050, China;
2. School ofEconomy and Management. Yanshan University. Qinhuangda0 066040, China)
Abstract: In recent years, with the rapid development of tourism and the changes in tourism demandaround the world, the environmental problems created by that industry have attracted widespreadattention. In China, the concept of tourism environment carrying capacity has become an importantbasis for formulating tourism destination planning and development policies for the tourism industry.Evaluating tourism environment carrying capacity is of great significance in the following areas:improving management in tourism destinations; enhancing satisfaction among visitors with respect totourism destinations; and promoting the sustainable development of tourism destinations. Accordingly,studies about tourism environment carrying capacity have become an area of particular interest in thefield of tourism management. In this paper, we review studies by Chinese and overseas scholarsfocused on tourism environment carrying capacity that have been published in recent years. We do sowith respect to the following five areas: the concept of tourism environment carrying capacity itself; therelated index system; measurement models; empirical research findings; and management tools. In thisstudy, we were able to identify the achievements and shortcomings of previous research into tourismenvironment carrying capacity. We also made suggestions about possible future research directionsregarding tourism environmental carrying capacity. Several conclusions emerged from the presentstudy. (1) It is necessary to conduct a deep analysis of the concept and index system of tourismenvironment carrying capacity. In view of the interval characteristics of preferences among tourismstakeholders, we defined the concept of tourism environment carrying capacity based on stakeholders'demand characteristics concerning the tourism environment system. We constructed an index systemfor tourism environment carrying capacity by adopting the perspectives of both the supply and demandfor the tourism environment system among stakeholders according to specific geographic backgrounds.(2) To enrich the econometric model analysis of tourism environment carrying capacity towardachieving harmonious development of the tourism environment system, it is essential to undertake thefollowing: focus on cross- disciplinary research; improve the scientificity and accuracy of theeconometric model; analyze the dynamic matching mechanism of the supply and demand system forthe tourism environment; create a measurement model and optimization path between that system andrelated subsystems; and simulate the action track of specific actors (for example, tourists and residents)and the fluctuating track of tourism environment carrying capacity. (3) On the basis of dynamicsimulation and optimization of changes in tourism environment carrying capacity, it is necessary toanalyze the principles and laws of spatial symmetry and nonequilibrium or polarization. In specificregions, it is requisite to examine the influence of spatial and temporal order change on tourismenvironmental carrying capacity. An emphasis should be placed on empirical research into tourismenvironment carrying capacity in tourism destinations; such research should be time sensitive and covera number of regions. (4) This paper investigates the management tools for tourism environmentcarrying capacity. It demonstrates how that capacity can be optimized to achieve sustainabledevelopment of the tourism environment system under different scenarios. This study analyzes theresearch framework for systematic management measures toward achieving sustainable carrying capacity.
Keywords: tourism environment carrying capacity; sustainable tourism; human-environment integration;tourism impact

