The contribution of bacteria to organic matter in coal-measure source rocks
Qingsong Cheng·Min Zhang·Guanghui Huang·Wenjun Zhang
Abstract On the basis of GC–MSanalysis,a suite of nine coal-measure source rocks(Ro 0.51%–0.63%)from the southern margin of Junggar basin was found to contain many biomarkers for bacterially-generated hydrocarbons:hopane,sesquiterpene,C23+monomethyl alkanes(even carbon predominance),and C24+ alkyl cyclohexane.Rock–eval and microscope analysis indicate that vitrinite(especially desmocollinite and homocollinite)plays a signif icant role in the generation of hydrocarbons in coalmeasure source rocks.Vitrinite performs this role by absorbing ultramicroscopic organic matter,generally in the form of resins or bacterial plastids.C23+monomethyl alkanes(even carbon predominance)and C24+ alkyl cyclohexane series compounds are derived from bacterial metabolitesof higher plants.Theultramicro organic matter adsorbed by vitrinite source rocks in the study area is probably ultramicro bacterial plastids.Because the organic matter of higher plants with low hydrogen content hasbeen transformed into organic matter rich in hydrogen by bacteria,the hydrocarbon generation capacity of source rocks isgreatly improved.In other words,in coal-measuresource rocks,bacteria play an important role in hydrocarbon generation.
Keywords Coal-measure source rocks·Organic matter type·Bacteria·Monomethyl alkanes·Alkyl cyclohexane
1 Introduction
Лoмoнocoвf irst proposed that coal is related to oil and gas generation(Ma1958).Craig(1917)f irmly believed that the coal bearing strata can generate oil.Dai(1979)suggested that the coal can form liquid hydrocarbon.Over the last several decades,the discovery of many coal-formed oil f ields has yielded widespread consensus that coal-measure source rocks play a signif icant role in oil generation(Liu 1985,1988;Huang 1991,1995,1999;Wilkins and George 2002;Cheng 1994,2004;Yang et al.2014;Zhou et al.2017).More recently,much research has centered on hydrocarbon-generating materials in coal-measure source rocks and the ability of coal to generate and expel oil.Studies of coal-measure source rocks generally focus their analyses on the content of hydrogen rich components(alginite,sporophyte,cutinite,etc.)in organic macerals(Hunt 1991;Snowdon 1991;Mukhopadhyay et al.1991;Zhong and Chen 2002).Hydrogen index(Killops et al.1998;Suggate et al.1993,2002;Sykes and Snowdon 2002)studies of the oil generating potential of coal employ a variety of experimental techniques such as thermal simulation,infra-red spectrum,elemental analysis,nuclear magnetic resonance(Wilkins and George 2002).Research from the Chinese Academy of Sciences(CAS)for the formation of oil by organic matter hassuggested that humic coal,which was the main source of higher plants,inhibits the formation of commercially viable oil f ields(CAS 1979).Many different properties of the original organic matter in the sediments form the internal cause and basis for determining whether the organic matter proceeds down the oil-generation pathway or the coal-generation pathway.The reduction environment is only the external cause and condition of the transformation,for it cannot drive all forms of organic matter down the pathway of petroleum bitumen generation.This causal relationship is illustrated in theformation of petroleum asphalt:higher plant residues have an H content(approx.6%by mass)that isinsuff icient for petroleum genesis,regardless of the reduction environment.Instead,petroleum asphalt isderived from animal and lower plant residues which are primarily composed of fat,protein,sugar,and wax molecules and consequently have a much higher H content(10%–14%).Recent studies show that the CAStheory does not preclude the coal-based formation of oil f ields.
Generally speaking,the reduction environment promotes the preservation of organic matter,which is conducive to hydrocarbon generation in the later stage of organic matter.While organic matter can be preserved in an oxidizing environment via absorption into coal,bacteria thrive in an oxidizing environment and can metabolize higher plant residues under the principle of material balance,the organic matter of poor hydrogen in higher plants were used by bacteria.Although there is a loss of some material energy in the process,most of the material was converted into the organic matter of the bacteria rich in hydrogen.Therefore,bacteria promote oil production in coal.Coal-measure source rocks in the southern margin of Junggar Basin were taken as the research object.Through the analysis of macerals,rock pyrolysis and GC–MS,the signif icance of bacterial activity in the diagenetic stage of coal derived source rocks was identif ied.
2 Sample and analysis methods
Nine Jurassic coal-measure source rocks were collected from a shallow mountain zone of the Sangong River valley.The area belongs to the Fukang fault zone in the North Tianshan foreland thrust belt,near the southern margin of the Junggar basin.The western end of the Fukang fault zoneisadjacent to thesouthern Fukang sag,and theeastern extent is adjacent to the southern Jimsar sag(Fig.1).This region is a favorable oil and gas accumulation structure(Yang et al.2004).The Jurassic source rocks in the study area are mainly developed in the Badaowan formation(J1b)and Xishanyao formation(J2x).These source rocks are a set of swamp facies and shallow lacustrine facies deposits,with high organic matter abundance,and theorganic matter type is predominantly type III(Fu et al.2011).

Fig.1 A simplif ied map of geological structure in the study area
All samples were pulverized to 100 mesh and subjected to bitumen extraction using a Soxhlet apparatus for 72 h with copper.The extracted bitumen samples were fractionated into saturated compounds,aromatic compounds,NSOs(Heteroatom compounds containing nitrogen,sulfur and oxygen atoms)and asphaltenes via open column chromatograph.The saturated hydrocarbonswere analyzed by GC–MS(Agilent 6890N/5995MSD gas chromatography-massspectrometry).The chromatographic column was an HP-5MS quartz elastic capillary column(30 m×0.25 mm i.d.,f ilm thicknesses 0.25μm).
The pre-injection heating procedure was as follows.The samples were heated to an initial temperature of 50°C.After 2 min at this constant temperature,the samples were heated from 50 to 100°C at a rate of 20°C/min,and then at 3°C/min to 310°C,maintaining a constant f inal temperature for 15 min.The injection mode was pulse without shunt,the temperature of the injector was 300°C,the carrier gas was helium,and the f low rate was 1 mL/min,the ionization energy was 70 eV,and the detection method was full scan(SCAN)/multi ion detection(SIN).
The basic geochemical information of the sample is shown in Table 1.Vitrinite occupies an absolute predominance in organic macerals.‘‘Exinite+Sapropelinite’’was only 0.51%–16.8%.The research samples are typical coalmeasure source rocks(Ro 0.51%–0.63%).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Differences in organic matter types

Table1Thebasicgeochemicalinformationofthesamples TI A(%)V22 V21+(%)S E+(%)-39.60-15.90-56.10-29.30-66.15-66.55-3.85-6.55-34.50 0.00 0.10 0.00 0.15 0.15 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.10 50.40 18.00 68.00 18.40 17.60 22.40 1.20 2.00 40.20 16.80 6.00 6.00 2.00 1.60 8.80 0.20 0.80 9.00;V22homocollinite;V3vitrodetrinite;I inertinite;I(%)V3(%)V1(%)V(%)TMC(%)D(%)HI(mg/g)S1+S2(mg/g)TOC(%)Tmax(°C)Lithology Stratum Sample 1.60 0.00 2.40 10.20 29.60 28.00 0.80 2.00 0.00 5.60 5.20 2.00 6.40 9.20 4.00 2.60 2.60 10.80 6.40 1.60 5.60 1.40 22.40 31.20 0.40 1.80 0.60 62.40 24.80 75.60 26.20 49.20 57.60 4.20 6.40 51.60 80.80 30.00 84.00 37.20 79.20 94.40 5.20 8.80 59.80 15.99 19.97 19.74 9.70 8.01 13.34 4.00 6.46 12.77 185.28 203.15 197.30 111.43 95.73 153.47 38.60 74.59 149.16 140.46 21.41 178.11 14.73 55.91 80.50 0.55 2.39 49.55 72.90 8.90 74.90 12.60 57.90 50.10 1.14 3.07 32.20 431 431 432 434 428 432 451 438 385 Coal CMS Coal CMS Coal Coal Mud Mud Coal J1b J1b J1b J2x J2x J2x J2x J2x J2x J03 J05 J06 J09 J11 J12 J14 J15 J17 totalorganicmacerals;V vitrinite;V1telinite;V21desmocollinite CMS carbonaceousmudstone;Mud mudstone;D degradationrate;TMC E exinite;S sapropelite;A amorphousorganicmatter;TI organicmattertypeindex
According to the Chinese petroleum industry standard(SY/T 5125-2014),vitrinite is dominant in the organic maceral of the samples(Table 1,Fig.2a),and TI(organic matter type index)values are less than 0,which is typical type III organic matter.Figure 2b shows that TICoal<TICarbonaceous<TIMudstonce,indicating that the organic matter type of mudstone is better than carbonaceous mudstone and coal.The calculation formula of the TI is as follows:
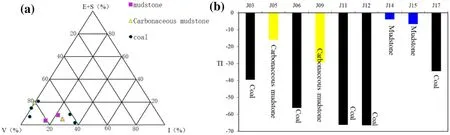
Fig.2 a Trilinear diagram of organic macerals in the study area;b distribution map of organic matter type index.V:vitrinite;I:inertinite;E:exinite;S:sapropelite;TI:organic matter type index
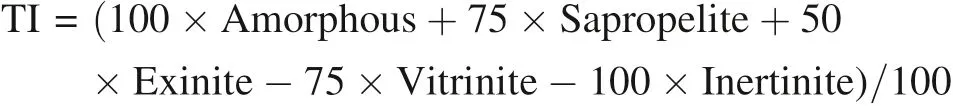
It can be seen from the TIformulathat the vitrinite isnot used as a hydrocarbon generation material.
But when using pyrolysis parameters to classify the types of organic matter,the results show that coal is type II2organic matter and better than coal-measure mudstone(Fig.3).According to Fig.3,we can speculate that in the coal-measure source rocks,besides the amorphous,sapropelite and exinite,other macerals also contribute to hydrocarbon generation.
Similar phenomena are evident in samples from other locations,such as coal-measure source rocks in Xihu depression(East China Sea basin)(Zhu et al.2012)and Ardjuna Basin(Horsf ield et al.1988).In addition,Horsf ield et al.(1988)and Jasper et al.(2009)found coal has a higher HI than mudstone under the same maturity condition,but the two main components of higher plants,lignin and cellulose,have a comparatively low H content of 6%by mass(CAS 1979).Therefore,the parent material of coal is not rich in hydrogen.Where does the abundant hydrogen in coal come from?What is the hydrocarbon generating capacity of other macerals except for the amorphous,sapropelite and exinite?

Fig.3 Correlation diagram of pyrolysis parameters Tmax-HI and Tmax-D in the study area
3.2 Difference of hydrocarbon generating capacity of macerals
Different methods of organic material type classif ication yield different results,suggesting that other macerals contribute to hydrocarbon generation.Vitrinite correlates more strongly with TOC and‘‘S1+S2’’than‘‘E+S’does(Fig.4).This shows that vitrinite contributes more to hydrocarbon generation in coal-measure source rocks than saprolite and exinite do.In addition,Fig.5 shows that‘‘V21+V22’’correlates more strongly with TOC and‘‘S1+S2’’than ‘‘V1+V3’’does.This indicates that desmocollinite and homocollinite are the main hydrocarbon generating material in vitrinite.Here,we can answer the previous question:the vitrinite group in the coal measures source rocks has important hydrocarbon generation contribution,and the desmocollinite and homocollinite are the main hydrocarbon generating material.
Desmocollinite and homocollinite are important hydrocarbon generating parent materials in coal-measure source rocks(Junggar Basin).Several studies have also attributed this role to ultramicro-resinite which occupies voids in vitrinite.Robinson(1987)conducted an electron microscopic observation of the terrigenous source rocks in Indonesia,and proposed that vitrinite adsorbs ultramicro resinite,since vitrinite is partly f luorescent and its ref lectivity isoften low.Desmocolliniteisthemost important oil generating component in Turpan-Hami basin,has the characteristics of early hydrocarbon generation,hydrocarbon generation material isthe ultramicro-resinite f illed in it(Zhao1994,1997a,b;Cheng 1994;Liu et al.1996).In addition,the mudstone of the Meishan formation of the Ya13-1 gas f ield in China(Zhang 1992),the river delta facies hydrocarbon source rock in the Indonesia basin(Thompson et al.1985),and the middle Miocene marine source rock in the Surma Basin of Bangladesh(Alam and Pearson 1990)were considered that the hydrocarbon generating material is an ultramicro-resinite adsorbed in the desmocollinite.Simoniet(1977)has reported that the deep sea drilling has yielded signif icant quantities of the resinite,indicating that the ultramicro-resinite has a strong transport capacity.The study of coal in Shuicheng(Guizhou Province,Southern China)shows that the content and hydrocarbon generation characteristicsof desmocollinitehave an important inf luence on the hydrocarbon generation.The hydrocarbon potential and hydrocarbon generation mode of desmocollinite are different from that of Turpan-Hami basin,which may be related to the type and content of the ultramicro lipoid(Sun et al.1999,2000).The source rocks of this desmocollinite-adsorbed ultramicro-resinite are mostly continental or marine facies source rocks with allochthonous deposits.Whether or not the ultramicroresinite is a hydrocarbon generating material in the desmocollinite can be determined by examining the biomarkers present in them.
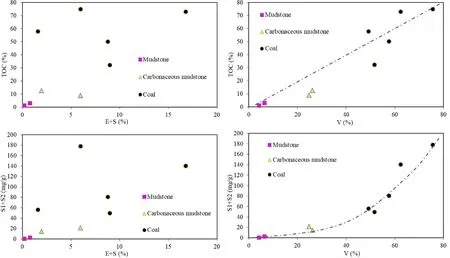
Fig.4 Correlation diagram of maceral and‘‘S1+S2’’and total organic carbon(TOC).V:vitrinite;E:exinite;S:sapropelite
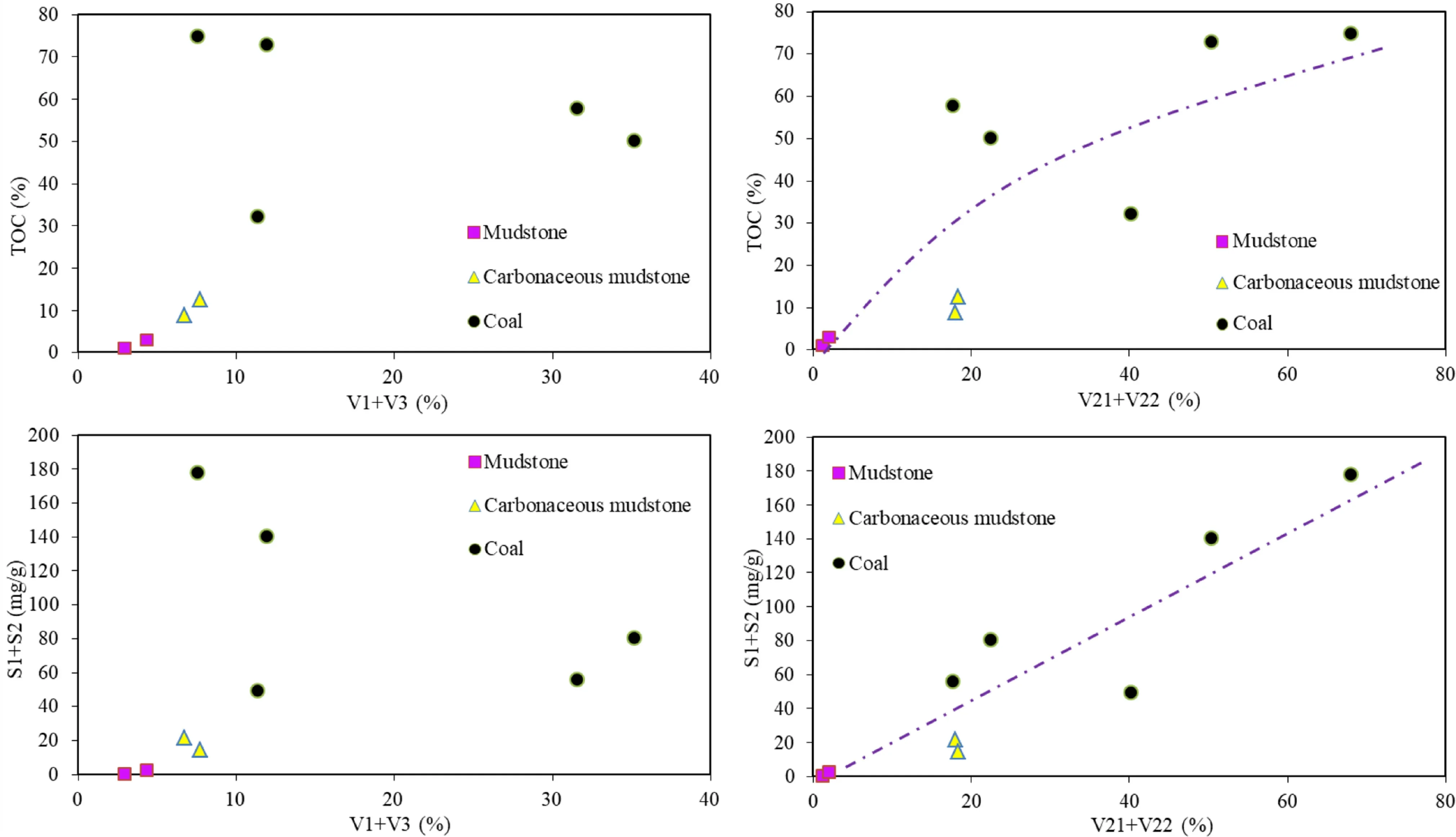
Fig.5 Correlation maps of‘‘telinite+vitrodetrinite’’,‘‘desmocollinite+homocollinite’’with‘‘S1+S2’and TOC respectively.V1:telinite;V21:desmocollinite;V22:homocollinite;V3:vitrodetrinite
3.3 Steroid and terpenoid biomarkers
Sterane is generally converted from sterols,sterone,and steric acids in the cell walls of eukaryotes.Algae are mainly C27sterols and C28sterols,fungi contain mostly C28sterols,and terrestrial plants are dominated by C29sterols(Lu and Zhang 2008).Triangular C27–C28–C29sterane showed that sterane in the coal-measure source rocks of the study area mainly came from the input of higher plants(Fig.6).C29Sterane 20S/(20S+20R)and C29Steraneββ/(αα+ββ)can be used to evaluate the maturity of source rocks(Mackenzie et al.1980).C29Sterane 20S/(20S+20R)and C29Steraneββ/(αα+ββ)correlation diagrams show that all samples were in the immature and low maturity stage(Fig.6).
Generally,the long chain tricyclic terpene derives from the intermediate product of algal biosynthesis(Wang et al.1994).Higher plants are the main source of C19TT and C20TT(Barners and Barbers 1983;Noble et al.1986).C24Te comes from the input of terrestrial organic matter(Grice et al.2001).High C24Te distribution of tricyclic terpenes in the coal,carbonaceous mudstone and mudstones of the study area shows that the input of the terrestrial plants is the main source of organic matter in the source rocks of the coal measures(Fig.7).
Hopane is usually indicative of the contribution of bacteria,and its precursor is bacterio hopanetetrol(Peters et al.2005).The hopane distribution characteristics of the coal,carbonaceous mudstone and mudstone in the study area each exhibited a maximum peak consistent with C30H(Fig.7).The relative content of rearranged hopanes was low,the relative content of moretane and normoretane was relatively high,and the abundance of gammacerane was low.With the increase in carbon number,the abundance of C31–C35homohopane series decreases gradually,with a high abundance of C31homohopane potentially indicating that free oxygen was present in sedimentary environments(Peters et al.2005).Generally,Ts is more stable than Tm,but in the study area Tm is much more abundant than Ts.This is likely due to acidic conditions in the ambient water,which would hinder the transfer of hydrogen ions,thereby impeding the conversion of Tm into Ts(Huang et al.1995).
Previous studies have shown that tricyclic terpenes are highly abundant in organic matter derived from algae,and the abundance of tricyclic terpenes from bacteria is low(Volkman et al.1989).In the study area,the relative content of triterpenoids in the source rock steroid terpenoids is only 1.62%–9.94%,and the relative content of the hopane is 38.92%–93.16%.The relative content of tricyclic terpene is much lower than that of hopane.
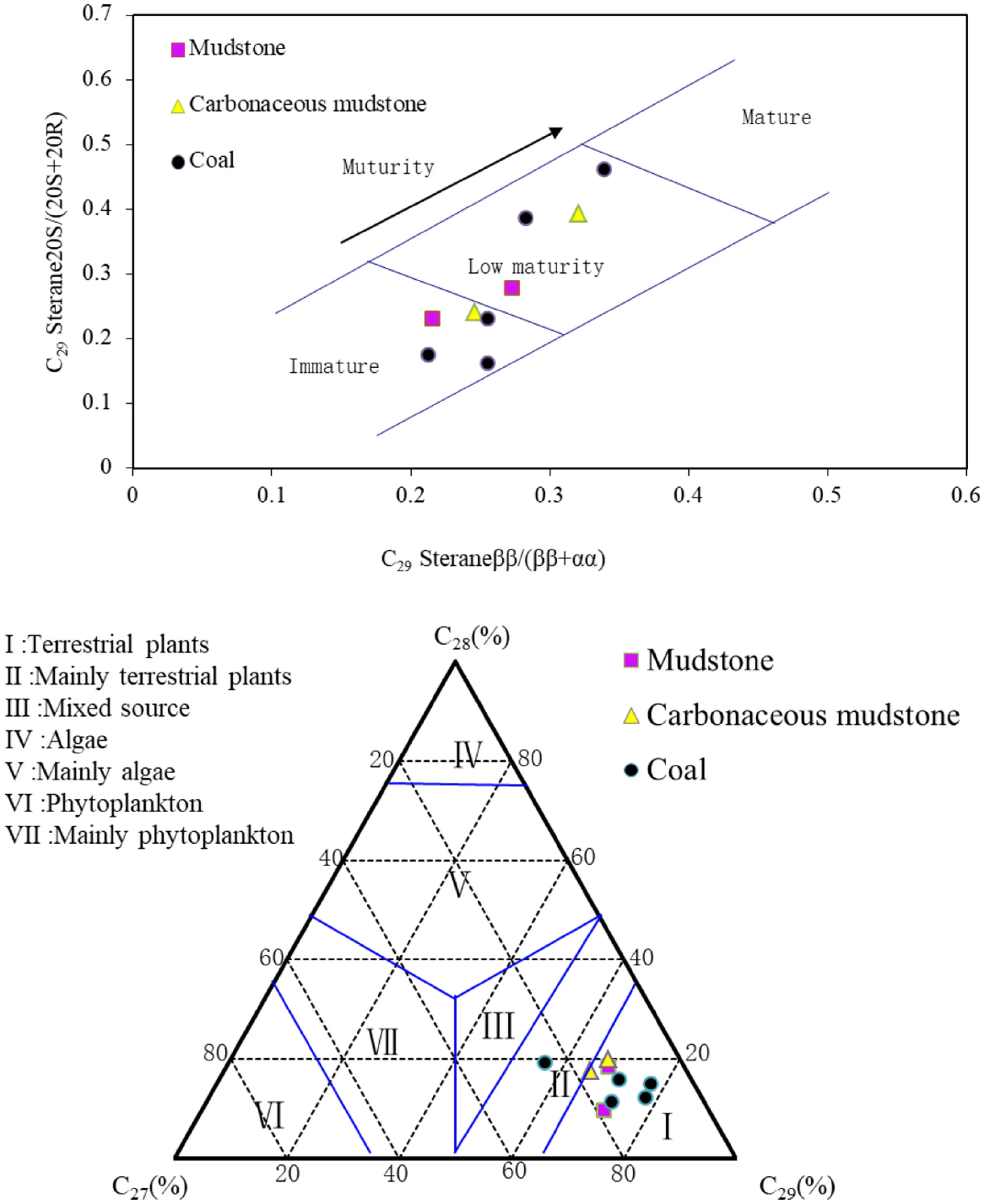
Fig.6 Correlation diagram of regular sterane in samples of the study area
Sesquiterpene is the f irst to form in the early stage of diagenesis,under the action of microorganisms.This degradation proceeds via a ring-opening mechanism formed a product with the double ring structure of the functional group.During later diagenesis,a number of isomers are formed by the functional group and rearrangement evolution(Alexander et al.1984).We can see that the relative content of hexane and sesquiterpene,representing bacterial origin,account for 77.22%–93.59%(Table 2).Tricyclic terpene and sterane,representing algae and higher plant sources,account for 6.41%–32.78%,with an average of 13.78%.It can be seen that the biomarker compounds from bacteria in the study area are dominant.
3.4 Alkyl cyclohexane and monomethyl branched alkanes
On the basisof GC–MSanalysis,ninecoal-measure source rocks from the Junggar Basin in northwestern China were found to contain a series of monomethyl branched alkanes(MMAs,m/z=85)with a range of C14–C36distribution,and a series of alkyl cyclohexanes(m/z=82)with a range of C14–C27distribution.In the study area,the MMAs are predominantly iso-alkane(2-methyl alkanes)and anteisoalkanes(3-methyl alkanes),and the iso-alkanes are predominantly even-carbon.Among the alkyl cyclohexanes,some C24+compounds are present(Fig.8).

Fig.7 m/z191 mass chromatogram of coal-measure source rocks in the study area
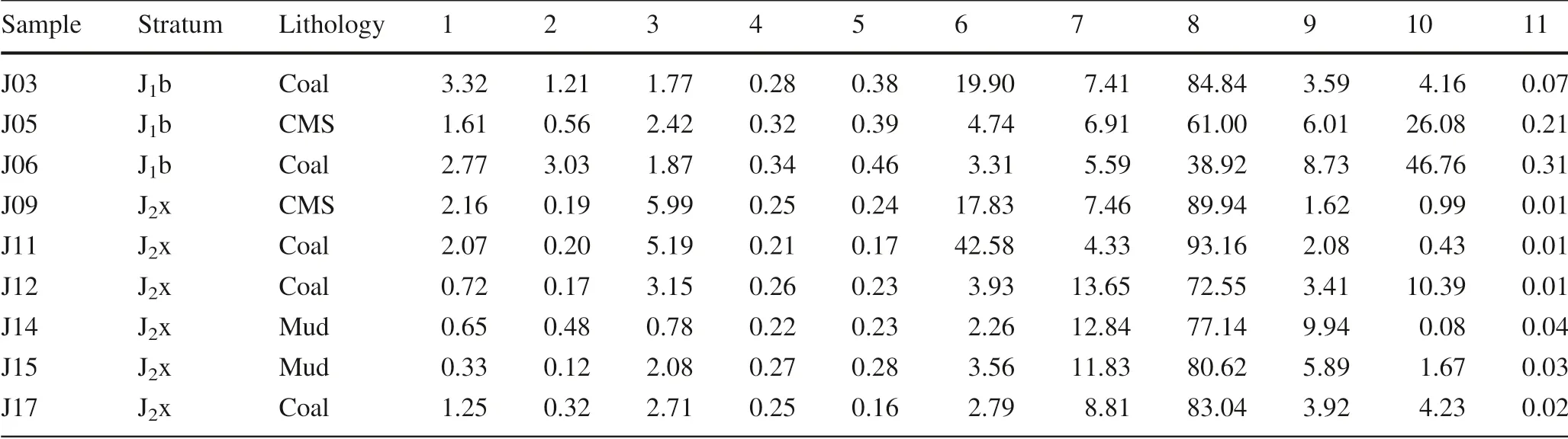
Table 2 Biomarker parameters of coal-measure source rocks in the study area
MMAs were f irst detected from cyanobacteria by Han et al.(1970),and further studieshaveshown that two-thirds of all cyanobacteria species can produce MMAs(Shiea et al.1990).MMAs are commonly found in Precambrian crude oil,with carbon numbers ranging from iC16to iC21,andit is derived from cyanobacteria(Klomp 1986;Fowler and Douglas 1987).2-methyl twenty-one alkane(iC22)is considered to be a bacterial bioinput in high salinity environments(Connan et al.1986).Although most of the terrigenous higher plants do not form MMAs,the epidermal wax of some higher plants is an important source of long chain(C23+)MMAs(Eglinton et al.1962,1967;Kolattukudy 1969;Rogge et al.1994).MMAs are relatively abundant in tobacco plants of Solanaceae family(Rogge et al.1994;Kavouras et al.1998;Grice et al.2008;He et al.2009),as well as mint and lavender plants in the Labiate family(Maffei 1994;Reddy et al.2000).The isoalkane in higher plants have the predominance of odd carbon,while the anteiso-alkanes have the predominance of even carbon(Huang et al.2011).Algae,such as Chlorella,arealso theparent material sourcesof long chain MMAs,but they do not have a carbon dominant distribution(Ji et al.2009;Qian et al.2017).Prior studies have suggested that the distribution in relative abundances of iso-alkanes and anteiso-alkanes is related to the organic matter of coal or coal measures,and that the exceedingly high abundances of iso-alkanes and anteiso-alkanes are almost unexceptionally distributed in coal strata(Johns et al.1966;Philp 1987;Huang et al.1993;Wang et al.1995a).The MMAs in the source rocks of Shahejie formation of the Banqiao sag(Dagang Oilf ield)possess a strong even-carbon predominance in iso-alkanes and a weak odd-carbon predominance in the anteiso-alkanes.At the same time,the trace of sporophyte is degraded by bacteria(Wang et al.1995b).In addition,Sun and Zhang(2015)detected a series of iso-alkanes with a weak evencarbon predominance in the carbonaceous mudstone of the third section of the Oligocene Shahejie formation in the eastern sag of the Liaohe basin,and the source rocks contain a large number of compounds derived from bacteria.Based on these studies,we conclude that the iC23-+iso-alkanes(with a strong even-carbon predominance)in the coal-measure source rocks in the study area are derived from the contribution of bacteria.

Fig.8 Distribution of monomethyl-branched alkanes and alkyl cyclohexanes in coal measures source rocks in the study area.‘white circle’’denotes iso-alkanes;‘‘black circle’’denotes the anteiso-alkanes;‘‘black triangle’denotes alkyl cyclohexanes
Further evidence for the bacterial generation of hydrocarbons can be seen from the distribution of alkyl cyclohexanes in coal-measure source rocks from the study area(Rubinstein et al.1979;Hoffmann et al.1987).Alkyl cyclohexane series,which are mostly short-chain homologues below C21,have been shown to be formed by the cyclization of algae or bacterial fatty acids under the catalytic conditions of clay minerals,and this process was observed in lower Paleozoic source rocks from the Tarim Basin(Zhu and Zhou 1989).The distribution of iso-alkanes and alkyl cyclohexanes shows that C24+alkyl cyclohexanes are a bacterial metabolic product of long chain terrigenous compounds such as fatty acids and alkanols,which can be used as a marker for the detritus of bacterial lipids(Duan et al.2001).The distribution of iso-alkanes and alkyl cyclohexanes shows that there are abundant bacterial metabolites in the coal-measure source rocks.
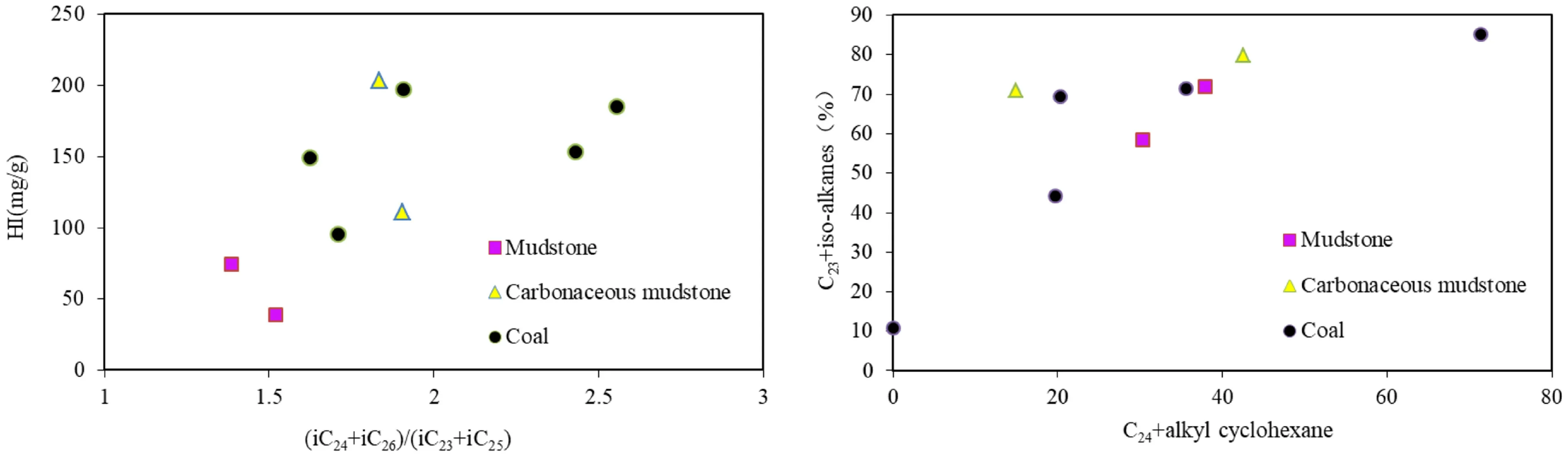
Fig.9 Correlation diagram of(iC24+iC26)/(iC23+iC25)versus HI and C24+alkyl cyclohexane versus C23+iso-alkanes
There is an abundance of bacterial biomarkers and metabolites in the coal-measure source rocks of the study area.This indicates that bacteria contribute signif icantly to the generation of organic matter within coal-measure source rocks in the study area.The relative distributions of iso-alkanes,anteiso-alkanes and alkyl cyclohexanes were correlated by comparing areas under the peaks.The relationship between(iC24+iC26)/(iC23+iC25)and HI is positive,indicating that the greater the even-carbon dominance of C23+iso-alkanes,the greater the HI value(Fig.9).Moreover,the abundance of C24+alkyl cyclohexanes is positively correlated with that of C23+isoalkanes,showing that both compound types originated from a similar source—i.e.,bacteria(Fig.9).
4 Conclusion
The classif ication of organic matter by pyrolysis parameters is more reliable than that of macerals.Because the ultramicro organic material vitrinite in coal is absorbent,it has important hydrocarbon generating ability.The ultramicro organic material adsorbed by the vitrinite of the coal-measure source rocks in the study area may be ultramicro bacterial plastids.
In the study area,the relative abundances of triterpene and sterane,which are derived from higher plants,are low,while the relative abundances of hopane and sesquiterpene series,which are derived from bacteria,are high.In addition,the products of bacterial metabolism are rich in longchain monomethyl alkanes and long-chain alkyl cyclohexanes.The high relative abundances of saturated hydrocarbon biomarkers in coal-measure source rocks indicate that bacteria contribute signif icantly to the generation of organic matter in the study area.
Because the sedimentary environment of coal-measure source rocks is oxidizing,it is benef icial to bacterial activities with higher plants as carbon sources.Bacteria transform higher plant organic matter with low hydrogen content(e.g.,cellulose and lignin)into organic matter rich in hydrogen.This signif icantly improves the hydrocarbon generation capacity of the source rocks.
AcknowledgementsThis research was f inancially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.41772124)and National Science and Technology Major Project (No.2016ZX05007001-002).
- Acta Geochimica的其它文章
- Triple oxygen isotope constraints on the origin of ocean island basalts
- The enhanced element enrichment in the supercritical states of granite-pegmatite systems
- Rare-earth and trace elements and hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of Cretaceous kaolinitic sediments from the Lower Benue Trough,Nigeria:provenanceand paleoclimatic signif icance
- Using trace elements of magnetite to constrain the origin of the Pingchuan hydrothermal low-Ti magnetite deposit in the Panxi area,SW China
- Mercury speciation,bioavailability and risk assessment on soil-rice systems from a watershed impacted by abandoned Hg mine-waste tailings
- Geochemistry of subsurface Late Quaternary ironstones in Rajshahi and Bogra Districts,Bangladesh:implications for genetic and depositional conditions

