不同术式治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱癌的临床研究
王永顺 王永刚 祁岳鸿


[摘要] 目的 探討经尿道钬激光膀胱肿瘤切除术治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱癌患者的临床疗效及安全性。 方法 选择我院2013年8月~2015年9月收治的91例NMIBC患者随机分为观察组(n=46)和对照组(n=45)。对照组给予TURBT治疗,观察组给予HOLRBT治疗。观察比较两组患者术中出血量、手术时间、膀胱冲洗时间、尿管留置时间及住院时间等围术期指标,HGF、TSGF及FIB水平变化,术后并发症及复发情况。 结果 观察组术中出血量(27.61±4.28)mL、手术时间(26.32±3.74)min、膀胱冲洗时间(1.85±0.28)d、尿管留置时间(3.78±0.74)d、住院时间(6.20±1.12)d,均明显低于对照组的(49.45±6.34)mL、(30.89±3.67)min、(2.67±0.32)d、(4.92±1.05)d、(7.69±1.19)d(t=-19.218,P=0.000;t=-5.883,P=0.000;t=-12.998,P=0.000;t=-5.975,P=0.000;t=-6.148,P=0.000)。术后,两组HGF、TSGF、FIB水平均显著降低(t=10.564,P=0.000;t=18.150,P=0.000;t=47.004,P=0.000;t=32.128,P=0.000;t=12.583,P=0.000;t=20.986,P=0.000),且观察组HGF、TSGF水平均显著低于对照组(t=-15.559,P=0.000;t=-23.752,P=0.000),FIB水平高于对照组(t=10.755,P=0.000)。观察组术后发生肾盂积水等并发症1例,发生率为2.17%,明显低于对照组的15.56%(P=0.030);术后复发率6.52%,明显低于对照组的22.22%(χ2=4.579,P=0.032)。 结论 HOLRBT治疗NMIBC临床疗效显著,可有效改善患者围术期指标及血清学指标水平,缩短手术及住院时间,并发症少,复发率低,安全性高,值得推广应用。
[关键词] 非肌层浸润性膀胱癌;经尿道钬激光膀胱肿瘤切除术;经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术;膀胱穿孔;复发
[中图分类号] R694 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2019)12-0046-04
Clinical study of different surgical treatments for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
WANG Yongshun1 WANG Yonggang2 QI Yuehong1
1.Department of Urology,Xi'ning NO.1 People's Hospital in Qinghai Province,Xi'ning 810000,China;2.Department of Outpatient,Huangyuan County Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Qinghai Province,Huangyuan 812100,China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the clinical efficacy and safety of transurethral holmium laser tumor resection for patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Methods A total of 91 patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer(NMIBC) admitted in our hospital from August 2013 to September 2015 were randomly divided into observation group(n=46) and control group(n=45). The control group was treated with TURBT and the observation group was treated with HOLRBT. The perioperative indexes such as intraoperative blood loss, operation time, bladder irrigation time, urinary catheter indwelling time and hospitalization time, the changes of HGF, TSGF and FIB levels, postoperative complications and recurrence were compared and observed between the two groups. Results The intraoperative blood loss(27.61±4.28)mL, the operation time(26.32±3.74)min, the bladder irrigation time(1.85±0.28)d, the catheter indwelling time(3.78±0.74)d, and the hospitalization time (6.20±1.12)d in the observation group were significantly lower than(49.45±6.34)mL, (30.89±3.67)min, (2.67±0.32)d, (4.92±1.05)d, (7.69±1.19)d in the control group(t=-19.218, P=0.000; t=-5.883, P=0.000; t=-12.998, P=0.000; t=- 5.975, P=0.000; t=-6.148, P=0.000). After operation, the levels of HGF, TSGF and FIB were significantly lower in the two groups(t=10.564, P=0.000; t=18.150, P=0.000; t=47.004, P=0.000; t=32.128, P=0.000; t=12.583, P=0.000; t=20.986, P=0.000). And the levels of HGF and TSGF in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group(t=-15.559, P=0.000; t=-23.752, P=0.000), and the FIB level in the observation group was higher than that of the control group(t=10.755, P=0.000). One case of complications such as hydronephrosis occurred in the observation group, and the incidence rate was 2.17%, which was significantly lower than 15.56% of the control group(P=0.030). The recurrence rate was 6.52% in the observation group, which was significantly lower than 22.22% of the control group(χ2=4.579, P=0.032). Conclusion HOLRBT has a significant clinical effect in the treatment of NMIBC, which can effectively improve the perioperative and serological levels of patients, shorten the time of surgery and hospitalization, with fewer complications, low recurrence rate and high safety. It is worthy of popularization and application.
[Key words] Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer; Transurethral holmium laser cystectomy; Transurethral resection of bladder tumor; Bladder perforation; Recurrence
膀胱癌(bladder cancer)是临床泌尿系统中常见恶性肿瘤,发病多与吸烟、长期接触芳香胺类化学物质等相关,患者临床中以血尿、排尿障碍、尿路阻塞等为主要症状[1]。非肌层浸润性膀胱癌(non-muscle invasive bladder cancer,NMIBC)占所有膀胱癌患者的75%以上,具有发病率高、复发率高等特点,严重威胁患者生存期限及生活质量[2]。因此,早发现、早诊断、早治疗尤为关键,可有效减少患者浸润转移及复发风险[3]。
临床中,NMIBC的治疗以手术为主,膀胱内灌注化疗为辅[4]。经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术(transurethral resection of bladder tumor,TURBT)是临床常规术式,但该术式破坏肿瘤层次,对肿瘤组织切除不彻底,影响术后肿瘤病理结果及临床分期的判断,增加肿瘤复发概率;患者出血及膀胱穿孔等并发症发生率较高,物理效应容易导致肿瘤扩散转移,临床疗效欠佳[5]。有数据显示,TURBT治疗NMIBC,1年内复发率为20%~60%,5年内复发率高达31%~75%[6]。近年来,随着泌尿外科微创手术的不断发展及钬激光技术的广泛应用,经尿道钬激光膀胱肿瘤切除术(transurethral holmium laser resection of bladder tumor,HOLRBT)在膀胱癌的治療中发挥重要作用,安全性较高,成为临床研究热点内容[7]。我院于2013年8月~2015年9月共收治NMIBC患者91例,采用HOLRBT进行治疗,评估其临床疗效,旨在为此类患者的临床治疗提供科学理论依据,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选自2013年8月~2015年9月于我院就诊的91例NMIBC患者,所有患者采用随机数字法分为观察组(n=46)与对照组(n=45)。观察组:男25例,女21例;年龄55~81岁,平均(64.26±7.45)岁;肿瘤直径4~32 mm,平均(21.35±3.28)mm;单发肿瘤31例,多发肿瘤15例;肿瘤部位:膀胱侧壁28例,膀胱后壁9例,膀胱顶部7例,膀胱三角区2例。对照组:男26例,女19例;年龄57~79岁,平均(63.94±7.28)岁;肿瘤直径6~29 mm,平均(20.47±3.48)mm;单发肿瘤33例,多发肿瘤12例;肿瘤部位:膀胱侧壁26例,膀胱后壁、膀胱顶部各8例,膀胱三角区3例。两组患者性别、年龄、肿瘤直径、肿瘤个数和肿瘤部位等因素均无统计学差异(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2 纳入与排除标准
纳入标准:①符合非肌层浸润性膀胱癌的诊断标准[8],并经膀胱镜活检确诊;②初次发病;③TNM分期Ta或T1期;④所有患者均知情同意。排除标准:①既往膀胱手术者;②近半年发生脑血管意外者;③合并其他恶性肿瘤、血液系统疾病或免疫系统疾病者;④严重心、肺、肝、肾等重要脏器功能障碍者。
1.3 手术方法
所有患者术前常规检查血常规、肝肾功能、血糖、血清PSA、肿瘤标志物、心电图及胸片等,抗生素预防感染。观察组给予HOLRBT治疗。嘱患者截石位,硬膜外麻醉,通过尿道将膀胱操作镜置入膀胱。明确肿瘤发生位置,0.9%氯化钠冲洗,膀胱持续灌注。钬激光光纤通过操作孔置入膀胱,参数为输出能量1~2 J,功率20~40 W,频率15~20 Hz。切割起始位置在肿瘤基底附近,光纤靠近瘤体,切割至肌肉层;推出1 cm继续行推进式切割,水流配合掀起肿瘤组织,一并切除瘤体周围2 cm的正常黏膜组织,激光汽化切割。术后留置F22三腔气囊导尿管。对照组给予TURBT治疗,术前0.9%氯化钠灌注使膀胱半充盈状态。嘱患者截石位,硬膜外麻醉,F27Olympus连续灌洗电切镜直视下进入膀胱,电切功率140 W,电凝功率60 W,电切环切除瘤体及瘤体周围2 cm的正常黏膜组织,电凝止血,留置双腔导尿管。所有患者术后吡柔比星膀胱内灌注,50 mg/次,1次/周,治疗8周;随后1次/月,治疗24个月。同时常规抗感染治疗。
1.4 观察指标
观察比较两组患者术中出血量、手术时间、膀胱冲洗时间、尿管留置时间及住院时间等围术期指标,尿道狭窄、肾盂积水等术后并发症发生情况。所有患者随访1年,观察比较复发情况。
手术前后,分别采集3 mL晨起静脉血,常温静置20 min,离心10 min,离心速率3000 r/min,取上清液于-80°C保存,酶联免疫吸附测定患者多肽生长因子(hepatocyte growth factor,HGF)、肿瘤特异性生长因子(tumor supplied group factors,TSGF)及血浆纤维蛋白原(plasma fibrinogen,FIB)水平变化情况。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 20.0对数据进行统计学处理。计量资料采用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间比较采用独立样本t检验;计数资料采用[n(%)]表示,组间比较采用χ2检验或Fishers检验,等级资料比较采用Mann-Whitney Test检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
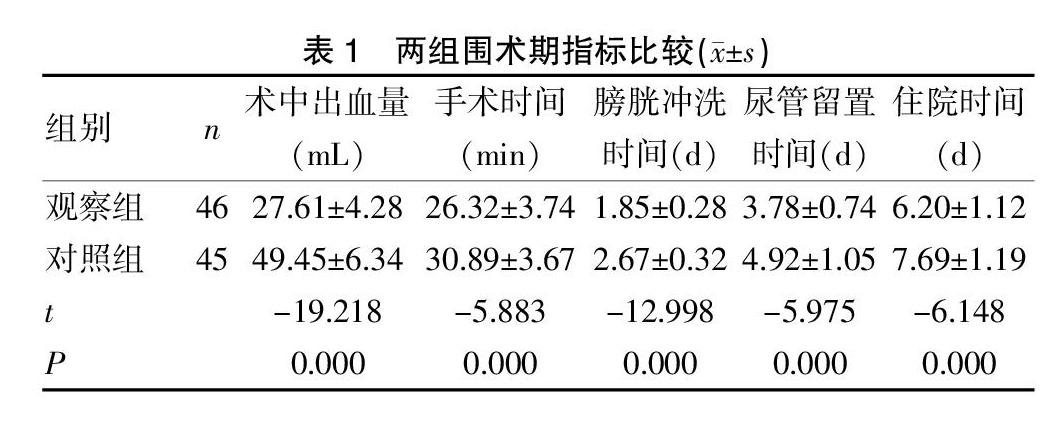
2.1 两组围术期指标比较
观察组术中出血量(27.61±4.28)mL、手术时间(26.32±3.74)min、膀胱冲洗时间(1.85±0.28)d、尿管留置时间(3.78±0.74)d、住院时间(6.20±1.12)d,均明显低于对照组的(49.45±6.34)mL、(30.89±3.67)min、(2.67±0.32)d、(4.92±1.05)d、(7.69±1.19)d,差异具有统计学意义(t=-19.218,P=0.000;t=-5.883,P=0.000;t=-12.998,P=0.000;t=-5.975,P=0.000;t=-6.148,P=0.000)。见表1。

