基于线结构光源和机器视觉的高精度谷物测产系统研制
杨 刚,雷军波,刘成良,陶建峰
基于线结构光源和机器视觉的高精度谷物测产系统研制
杨 刚,雷军波※,刘成良,陶建峰
(上海交通大学机械与动力工程学院,上海 200240)
针对精准农业中谷物产量信息的高精度获取需求,设计了基于计算机视觉的谷物测产系统,由工业相机、线结构光发生器、电感式接近开关和工控机等组成。提出了基于线结构光的谷堆厚度测量方法,根据所建立的谷物几何模型计算出谷堆的体积,并采用电感式接近开关克服了传统光电式谷物测产系统存在的误触发问题。同时,研究了不同转速下结构光测量误差,建立了基于转速的线结构光测量修正模型,使得测量误差从1.1%减小为0.33%。在室内台架上进行了测产试验,试验结果表明,未使用线结构光修正模型的最大测产误差为12.73%,在使用了线结构光测量修正模型之后,相对测产误差在4.27%以内,该研究可为谷物测产研究提供理论依据。
监测;系统;机器视觉;谷物; 产量传感器;精准农业;图像处理
0 引 言
谷物测产系统是实现精准农业的关键技术之一,是实施农业精细管理的基础[1-2]。目前,国外谷物测产系统技术成熟,市场上已有商品化的测产系统出现[3-5]。与之相比国内谷物测产技术仍存在较大差距。因此,国内相关高校和企业纷纷开展了谷物测产系统的相关研究。
根据测量原理的不同,谷物测产装置主要有质量流式和体积流式2种[6]。质量流式有冲量式、γ射线式和称重式3种[7-8]。冲量式传感器具有价格便宜、安装方便等优点,然而其精度易受到机器振动的影响。陈树人等[9]通过在升运器出口处安装导流板,传感器输出电压信号值平均提高30%左右,从而提高了测产精度。周俊等[10-14]在双孔平行梁冲量传感器信号处理上采用了弹性消除振动方法,提高了传感器抵抗振动干扰的能力,田间测产误差约为10%。胡均万等[15-17]设计了双板冲量式谷物流量传感器及其差分电路,消除了车身振动对测产精度的影响,田间测产误差约为5%。射线式传感器能够结合谷物线速度测出谷物的实时质量流,具有较高的测量精度。然而,射线对人体有害,其发展受到了较大的限制[18-19]。张小超等[20-21]设计了基于称重原理的螺旋推进称重装置,室内测产试验误差小于2%。然而,称重式传感器装置结构十分复杂,难以实现产业化。
体积流式主要有基于对射式光电传感器和漫反射式光电传感器2种,具有精度高且结构简单等优势,因而得到了高校和企业的广泛关注。王要武等[22]使用对射式光电传感器测量谷物的厚度,根据谷物在刮板上谷物体积模型计算出谷物的体积,试验中体积测产误差小于3%,但没有考虑到升运器转速变化的情况,且实际测产过程中刮板上的掉落谷物会引起传感器误触发,使得测量精度下降。付兴兰等[23-24]采用漫反射式光电开关测算脉冲信号宽度,使用编码器实时测量升运器转速,可以相对准确得到谷物的厚度,田间测产误差约为3.5%。安晓飞等[25]在处理漫反射式传感器数据时提出了双阈值动态滤波处理方法,使得数据平滑度提高,变异系数降低,测产误差约为3.5%,但仍存在误触发问题。
因此,为解决光电式测产系统误触发问题,该文设计了基于线结构光源和机器视觉的谷物结构光测产系统,采用电感式接近开关代替光电开关,可以准确触发相机进行拍照,有效避免了由于掉落谷物引起的误触发问题。使用基于最近邻的图像去噪算法有效去除了图像噪点。通过修正的结构光测量模型精确地测量谷物厚度,根据容重和谷物体积模型计算出谷物质量。最后,基于自行设计的试验台对系统的准确性和稳定性进行验证。
1 谷物测产系统设计
基于图像处理的谷物测产系统结构如图1所示,主要由工业相机(型号为大恒MER-131-210U3X)、线结构光发生器(型号为FU650AB-GD16)、电感式接近开关(型号为PML1816-N,PNP型)和工控机(型号为Intel NUC7i5BNK,图中未画出)组成。考虑到需要测量谷物堆积的厚度,将结构光发生器与相机置于同一高度,如图1a所示。考虑到相机前方窗口尺寸、相机与刮板距离以及相机的视角限制,经过调整发现,结构光发生器和相机之间的距离在30~40 mm之间最佳。由于在使用过程中,需要调整接近开关的位置以获得位置居中的图像,将接近开关安装装置设计成可调整的结构,以便调整接近开关在竖直方向的位置,如图1b所示。线结构光发生器安装位置如图1c所示,测产传感器安装位置如图1d所示。在实际测量时,传感器和接近开关分别安装在升运器两侧。
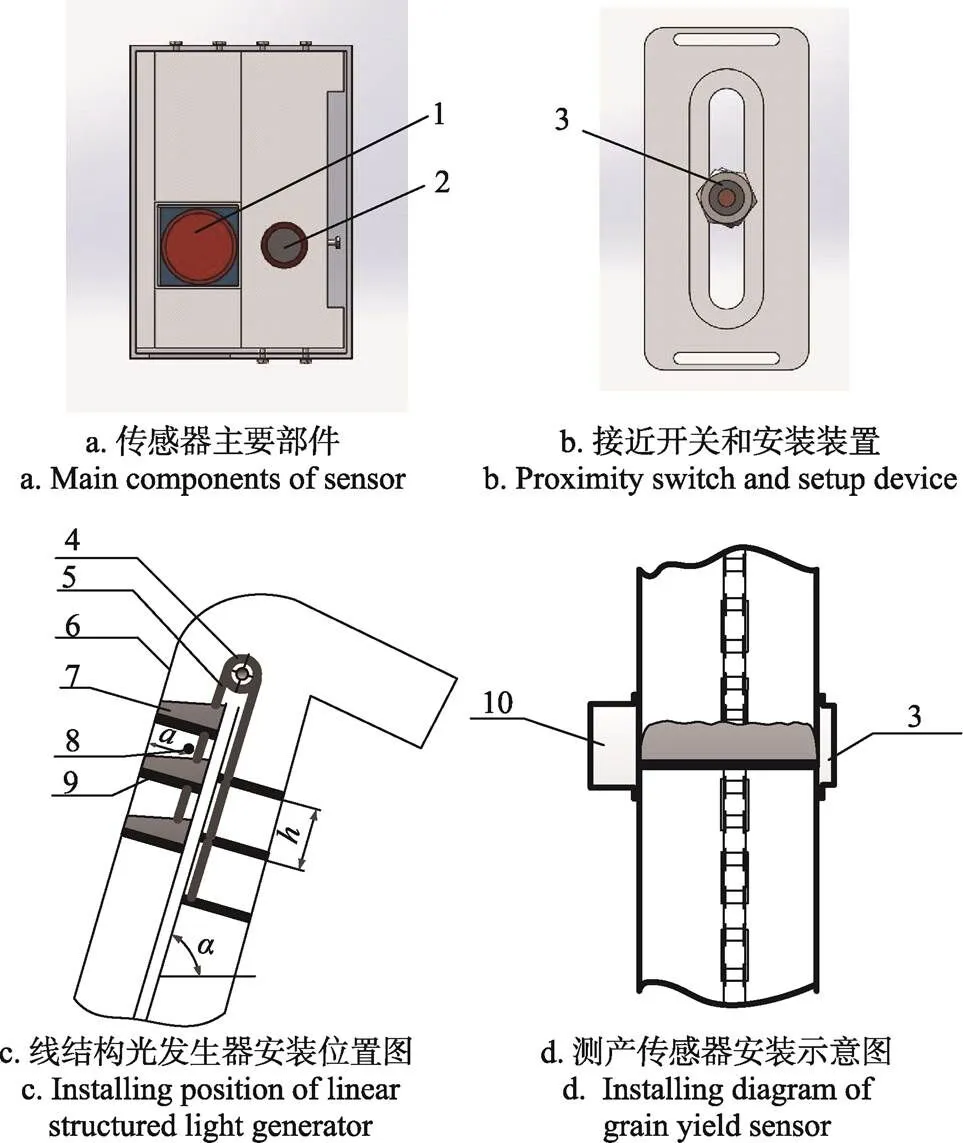
1. 工业相机 2. 线结构光发生器 3. 接近开关4. 链轮 5.链条 6. 升运器 7. 谷物 8. 线结构光发生器安装位置 9. 刮板 10. 相机和线结构光发生器
1. Industrial camera 2. Linear structured light generator 3. Proximity switch 4. Chainwheel 5. Chain 6. Elevator 7. Grain 8. Installing position of linear structured light generator 9. Scrapper 10. Camera and structured light generator.
注:表示线结构光发生器与升运器外侧的距离,mm;为2刮板之间的距离,mm;为升运器与水平面的夹角,(°)。
Note:is the distance between the structured light generator and the outer edge of the elevator, mm;is the distance between two scrappers, mm;is the angle between the elevator and the horizon, (°).
图1 测产传感器的组成及安装图
Fig.1 Composition of yield sensor and its installing diagram
2 谷物测产系统工作原理
2.1 谷物堆积体积计量模型
联合收割机上目前已广泛应用的输粮装置主要有螺旋式、刮板式、斗式和抛扔式4种。本文研究的测产系统主要针对刮板式输粮装置,因此对刮板尺寸和刮板上谷物堆积体积模型进行介绍。通过试验观察发现,谷物在刮板上的形状如图2a所示,刮板平面尺寸图如图2b所示。
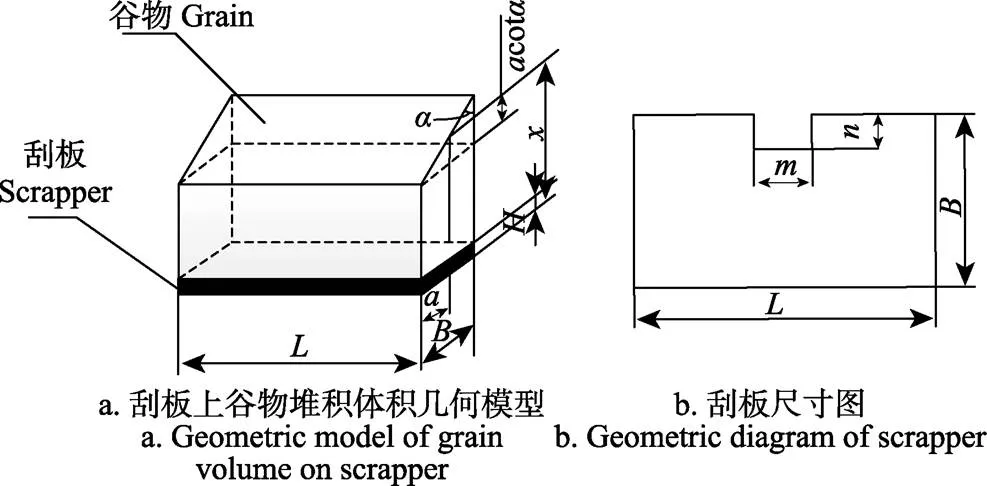
注:L、B和H分别表示刮板的长,宽和厚度,mm; m和n分别表示刮板上链条区域的长度与宽度,mm;x表示刮板厚度和结构光发生器处谷物厚度之和。
令表示刮板厚度和结构光发生器安装处谷物厚度之和,以下简称谷物厚度。刮板上谷物的瞬时体积可以表示为

式中1表示刮板体积(包括链条部分)与谷物中规则长方体体积之和,m3;2表示谷物上方楔形的体积(包括链条部分),m3;3表示刮板体积,m3;4表示链条部分所占的体积,m3;可分别计算如下:

将(2)代入(1)并整理可得:

式中为与谷堆形状有关的断面模量[24],理论分析中为刮板的实际面积,即有:

式中0为与、、、、相关的常数项。由此可知,此时刮板上谷物的体积与谷物厚度成线性关系。因此可以通过对谷物厚度进行测量即可得到刮板上的谷物体积。最终可以计算得到刮板上谷物的质量为

式中表示第次采样,为谷物容重,kg/m3;m为刮板上的谷物质量,kg。由每一时刻刮板上谷物质量可求出谷物的累计产量为
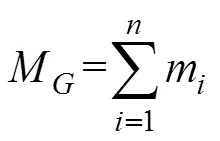
式中M为谷物累计产量,kg。为了获得准确的模型参数,需要通过试验来标定出各参数,以得到谷物产量和谷物厚度的关系式。
假设每个时刻测得的割宽为b(m),收割机的行驶速度为v(m/s),获取数据的间隔时间为Δ(s)。可以算出产量为

式中表示产量,kg/hm2。
2.2 线结构光测量原理
利用相机进行工业测量属于计算机视觉技术的应用[26-27]。计算机视觉是利用相机的二维图像来构建三维世界的研究,结构光测量技术是一种主动立体视觉测量技术[28]。若使用单目相机,通常只能获取被拍摄物体的二维信息,为了得到刮板上谷堆的三维信息,从而测量出刮板上谷物厚度,本传感器采取了线结构光测量技术,线结构光测量原理如图3a所示。

注:P为被测量物体结构光光条上的任意一点;P¢为P的像点;P0和P1分别为被测量物体上的最高点和最低点;P¢0和P¢1分别为P0和P1的像点;UOV表示相机的像素坐标系;XO¢Y表示图像坐标系;XcOcYc表示相机坐标系。
线结构光发生器和相机构成结构光传感器的主要部件。一般来说,测量过程包含3个步骤:
1)标定,包括相机内参和光平面方程的标定。
2)线结构光发射器将光束投射到被测量物体表面,使用相机采集结构光条纹图像。
3)提取结构光条纹中心,并计算特征点的三维坐标。
假设相机内参矩阵为
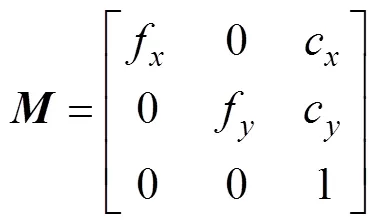
根据小孔成像模型,可得相机坐标系下特征点(x,y,z)与其对应的像素坐标(,)之间的关系为
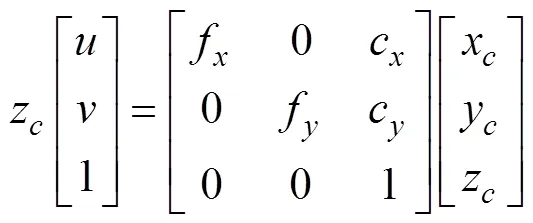
可得约束条件:
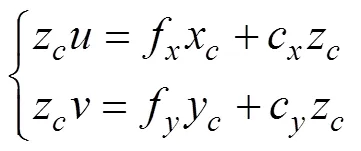
进一步假设结构光平面在相机坐标系下(、、、为参数)的方程为:
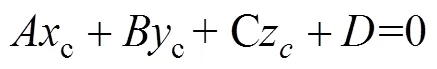
由式(10)、(11)可得特征点在相机坐标系下的三维坐标为

如图3b所示,记谷物光条上的最高点和最低点分别为0和1,根据(12)可计算出0和1的坐标,由图1中相机的安装方式可知,相机主轴垂直于升运器外表面,且图像平面坐标系的轴垂直于刮板平面,因此可以计算出谷物厚度为

在标定试验完成的基础上,将测出的谷物厚度代入到式(5),即可算出当前刮板上的谷物重量,根据式(6)、(7)即可算出谷物产量。
3 谷物测产系统工作流程
谷物测产系统的总体检测流程如图4a所示。相机拍摄刮板上谷堆的图像,首先需要准确对刮板进行定位。当刮板经过接近开关时,接近开关将触发相机实时记录刮板上谷堆的图像,并传输到工控机进行处理,输出产量数据。工控机对图像的处理流程如图4b所示,首先需要去除图像中的背景,升运器内部图像背景比较固定,通过掩模预处理去除大部分的无关部分。
由于升运器内部为半封闭环境,光照情况很差,本传感器中的线结构光发生器在进行三维测量的同时充当了光源,若不使用结构光发生器,由单个相机获取的图片通常无法计算出被测物体三维信息,且图片为黑色,无法分辨谷物和刮板。在不使用线结构光发生器的情况下,补光之后拍摄的升运器内部图片如图5a所示。在实际的刮板上谷物的照片如图5b所示(为了便于观看,图像已做反色处理,下同)。先进行背景去除操作,再进行二值化操作,结果如图5c所示。可见图中右上方的孤立的黑色区域即为噪点(已用圆圈圈出),这些噪点是从刮板和升运器缝隙之间落下的谷粒或者秸秆,需要除去才能计算谷物的厚度,否则将造成较大的误差。本文使用基于最近邻的噪点去除算法[29],可以有效去除图像中的噪点。观察刮板上谷物的图像发现,由散落谷物引起的图像噪点多集中在图像的右上方部分,因此每次在进行处理的时候,只需要将图像的右上方设为ROI区域,这样可以大大缩短处理时间。通常噪点的外接圆半径较小,因此对半径做一个限制,以免误处理,本文中将半径阈值设为30。噪点去除之后的结果如图5d所示。接下来对光条进行搜索可以找到光条上的最高点和最低点(已用圆圈圈出)。

图4 测产传感器的总体工作流程

a. 未使用线结构光时的图像 a. Image without using linear structured lightb. 使用线结构光时的图像 b. Original image using linear structured light c. 预处理之后的图 c. Image after preprocessingd. 去除噪点之后的图像 d. Image after denoising
4 试验与结果分析
4.1 试验设备及试验过程
试验在自主设计的谷物流量试验台上进行,试验台位于上海交通大学机械与动力工程学院实验室,试验时间为2019年1月5日,试验台如图6所示。试验台主要由伺服电机(型号为台达ASD-B2- 1521,功率为1.5 kW)、升运器、重量传感器(型号为ZNHM-III,量程为0~50 kg)以及称重粮筒组成,主要测试在正常工作情况下谷物测产系统的稳定性与精度。试验时,粮食从入口处进入,入口处可以通过调节开口大小控制粮食的喂入快慢,粮食在搅龙和刮板的带动下从升运器口流出到称重粮箱,安装在升运器上的传感器将监测粮食产量,同时在称重粮箱下方布置了重量传感器,实时监测实际产量,以测试系统的测量精度。
为了能得到实时的数据,基于Qt平台,使用C++语言为试验台开发了测试软件,软件界面如图6c所示。软件采用RS232串口通讯,采样周期为100 ms,可以实现实时显示谷物产量、升运器转速,控制升运器转速,进行基本参数设置和数据存储的功能。

图6 试验台及测试软件
4.2 刮板厚度测量试验
4.2.1 相机标定和结构光参数标定
为获得相机的内参矩阵和结构光平面方程,需对相机和结构光平面在相机坐标系下的方程进行标定,分别采用Zhang的平面靶标标定法[30]和基于三点透视模型的标定方法[31]。标定后的相机内参矩阵和结构光平面方程分别为


式中x表示线结构光平面方程是在相机坐标系下位置。
4.2.2 刮板厚度测量数据
为测试结构光测量谷物厚度的准确性和稳定性,制作了2个谷堆模型,厚度分别为21.8和33.4 mm,并在不同的转速度下进行测量。采用和刮板材质相同的橡胶,使用3M胶固定在刮板上运转,以模拟不同的谷物厚度。考虑到联合收割机在收割谷物过程中会经历启动、掉头、停车和卸粮等过程,升运器速度会出现较大的变化。例如在正常收割的时候升运器转速为200~500 r/min,在启动和卸粮完成的时候转速为0。因此控制升运器速度为60、180、300、420和540 r/min 5个转速水平,每个转速下进行5次重复试验,分别记录刮板厚度(即空载时)和其他厚度的测量数据。
对刮板图像预处理完成之后,首先需要提取结构光光条的中心,再搜索光条上的最高点0和最低点1,根据(13)和(14)的标定结果和式(11)计算出0和1在相机坐标系下的三维坐标。再根据式(13)计算出刮板的厚度。表1为刮板厚度测量试验数据,刮板空载时的实际厚度为10 mm,在刮板上放上谷堆模型之后的厚度分别为21.8和33.4 mm。
由表1未修正的谷堆模型厚度测量数据可以看出整体测量误差介于0到1.1%之间,且转速越大,误差越大。通过查看实际刮板图像发现,随着转速的增加,刮板上的结构光光条长度越长,对应的刮板厚度测量值也会偏大,造成这个现象的主要原因是:本试验采用的是CMOS相机,而CMOS相机通常采用滚动快门,在曝光时使用的是逐行曝光的方式。当刮板经过接近开关时,接近开关产生触发信号,相机从接收到触发信号开始曝光到曝光结束需要一定的时间。在曝光的过程中,由于刮板及刮板上的谷物仍在运动,因此会造成结构光图像产生拉长畸变,且这种畸变会随着刮板的转速越快而越大。在实际使用相机测量的时候应考虑到被测物体的运动,因此需对式(13)计算出的谷物厚度进行修正。考虑到实际测量的结果与速度相关,且随着结果的增大,测量结果均偏大,提出修正公式如下:
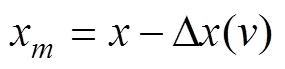
式中Δ()为修正量,与刮板转速相关,x表示修正后的厚度测量值。对刮板空载时厚度测量误差与转速之间的最小二乘拟合,得到两者之间的关系为
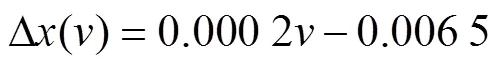
对刮板空载时厚度测量误差与转速之间的最小二乘拟合如图7所示。进一步计算得到线性相关系数为0.988 9,这表明测量误差与速度之间存在很高的线性相关性。
采用修正之后的模型,对不同厚度进行测量的误差最大为0.33%,相比较未修正之前的1.1%有了较大的提高。
4.3 室内台架测产试验
升运器转速较低时,谷物会在升运器底部积聚过多而引起搅龙堵转。因此在实际收割的时候,联合收割机升运器的转速一般较高,通常在100 r/min以上。因此为测试系统在不同的转速下的测产精度,选择120、240、360和480 r/min 4个转速水平在试验台上进行试验,每个转速下重复试验5次,取平均测产结果。使用接近开关检测刮板是否经过指定位置,触发相机进行拍照,传输到工控机进行处理。工控机在图像处理过程中采用基于最近邻的图像去噪算法对图像进行处理,再根据结构光测量方法计算出谷物厚度的精确值,由式(5)计算出刮板上谷物的质量,根据式(6)计算出谷物累计产量,最后根据式(7)可得到产量。为验证修正的结构光测量方法的效果,进行了测产对比试验,同时记录未使用修正方法和使用修正方法的测量数据,试验结果如表2所示。由表2数据可知:在转速为120、240、360和480 r/min 4个转速下,未使用修正方法的谷物测产误差介于-0.59%和12.73%之间,使用修正方法的谷物测产误差介于-3.5%和4.27%之间,表明使用修正方法的测产系统在不同转速下均具有较高的检测精度。
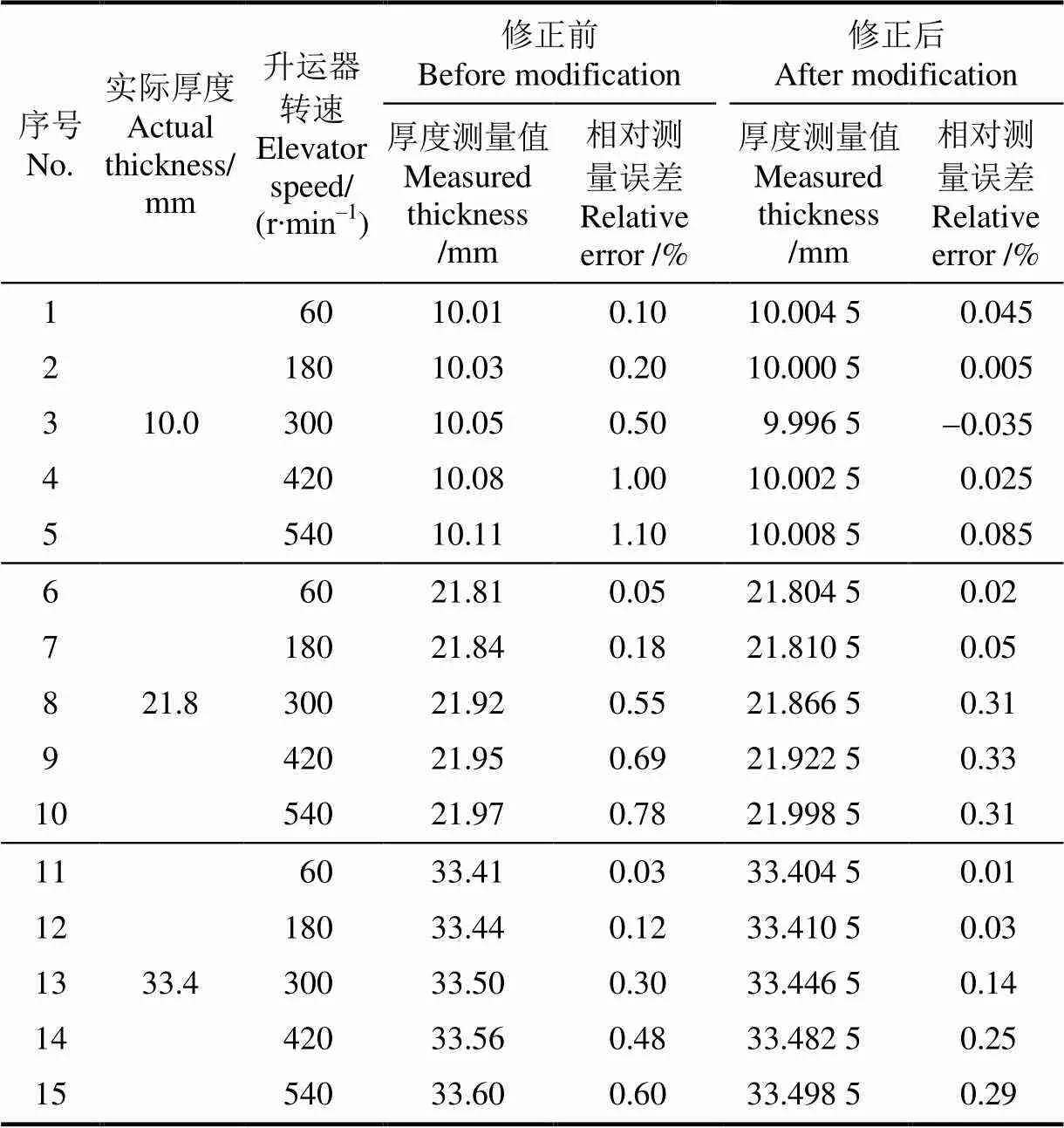
表1 刮板厚度测量试验数据
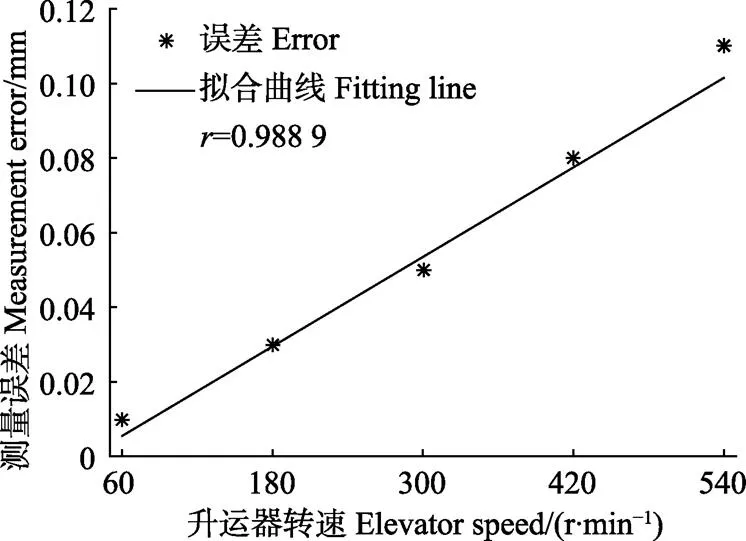
图7 刮板厚度测量误差与升运器转速最小二乘拟合曲线
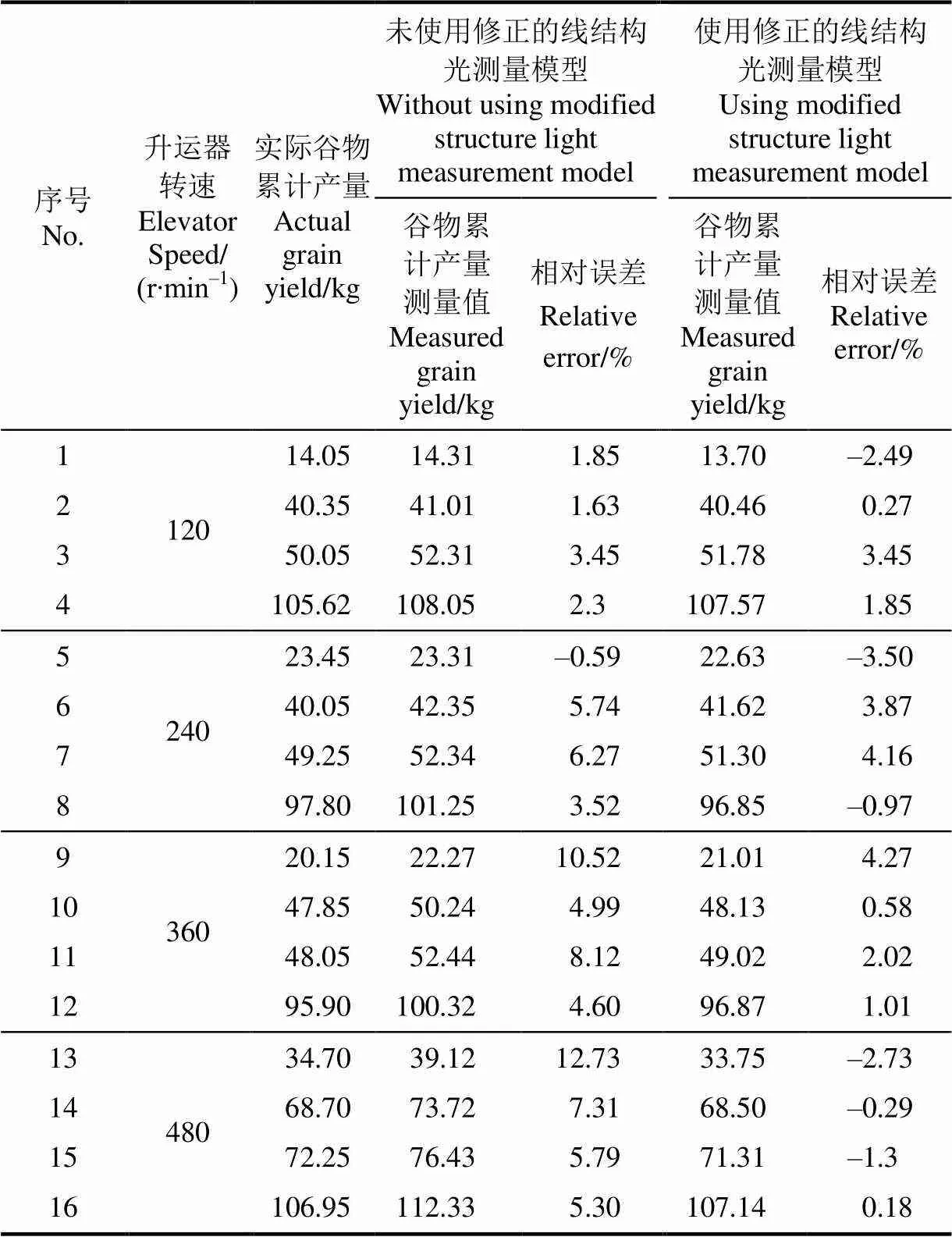
表2 测产试验数据表
4.4 讨 论
通过试验结果可知,未作修正之前的测产误差超过了10%,修正之后的误差只有4.27%,这说明影响本测产系统的主要因素为刮板上谷物厚度的测量精度。试验中发现,图像噪点处理的不完全有可能造成谷物厚度测量值偏大,从而导致谷物质量测量值偏大,需要进一步提高噪点处理算法的稳定性来消除这一影响。由于刮板与升运器之间有缝隙,会有少部分谷粒受到振动影响从缝隙之间掉落,导致实际测量结果偏小,这是由于升运器内部结构引起的,可通过将传感器安装在离出口较近的位置来减小这一影响。若使用光电式传感器,掉落的谷粒会造成传感器的误触发,因而造成传感器出现测量误差,测产误差通常超过10%,且误差波动较大。由于容重是事先测定的,刮板上谷物的容重有可能不等于测量容重,结果是产量测量值与产量实际值之间相差一个比例系数,但这一影响在标定之后会消除。
5 结 论
本文使用接近开关检测刮板的运动,触发相机进行拍照,使用基于最近邻的噪点去除算法进行图像处理,使用修正的线结构光测量模型得到精确的谷堆厚度,根据谷物几何模型和容重计算出谷物的质量。根据上述方案的传感器在自主设计的试验台上分别在120、240、360、480 r/min 4个转速下进行了测产试验,使用修正方法的测产误差介于–3.50%和4.27%之间,表明传感器具有较高的检测精度,满足实际测产需要。
[1] Reyns P, Missotten B, Ramon H. et al. A review of combine sensors for precision farming[J]. Precision Agriculture, 2002, 3(2):169-182.
[2] 汪懋华. “精细农业”发展与工程技术创新[J]. 农业工程学报,1999,15(1):1‒8. Wang Maohua. Development of precision agriculture and innovation of engineering technologies[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1999, 15(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] Koichi Shoji, Munenori Miyamoto. Improving the accuracy of estimating grain weight by discriminating each grain impact on the yield sensor[J]. Precision Agriculture, 2014, 15(1): 31-43.
[4] Burks T F, Shearer S A, Fulton J P, et al. Effects of time- varying inflow rates on combine yield monitor accuracy[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2004, 20(3): 269-275.
[5] Fulton P, Sobolik J, Shearer A, et al. Grain yield monitor flow sensor accuracy for simulated varying field slopes[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2009, 25(1): 44-48.
[6] 马朝兴,李耀明,徐立章. 联合收割机谷物流量传感器的现状与分析[J]. 农机化研究,2008(7):74-76. Ma Chaoxing, Li Yaoming, Xu Lizhang. Present status and analysis of grain flow sensor of combine harvester[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2008(7): 74-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] Stuart J Birrell. Comparison of sensors and techniques for crop yield mapping[J]. Computer and Electronics in Agriculture, 1996, 14(2/3): 215-233.
[8] 王志海,王沛东,孟志军,等. 谷物联合收割机测产技术发展现状与展望[J]. 农机化研究,2014(1):9-15. Wang Zhihai, Wang Peidong Meng Zhijun, et al. The summary and prospect of the grain combine harvester yield monitor system technology[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014(1): 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈树人,张文革,李相平,等. 冲量式谷物流量传感器性能实验研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(2):82-84. Chen Shuren, Zhang Wenge, Li Xiangping, et al. Experiment research of grain mass flow sensor based on impact[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(2): 82-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 周俊,周国祥,苗玉彬,等. 悬臂梁冲量式谷物质量流量传感器阻尼设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(11):121-123. Zhou Jun, Zhou Guoxiang, Miao Yubin, et al. Damping design of impact-based grain yield sensor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(11): 121-123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 周俊,刘成良. 平行梁冲量式谷物质量流量传感器信号处理方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(1):183-187. Zhou Jun, Liu Chengliang. Signal processing method for impact-based grain mass flow sensor with parallel beam load cell[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(1): 183-187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 丛秉华,周俊. 双平行梁谷物流量传感器振动噪声消除方法[J]. 传感技术学报,2013, 26(3):377-381. Cong Binghua, Zhou Jun. Vibration noise elimination for a grain flow sensor of dual parallel beam load cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2013, 26(3): 377-381. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘成良,周俊,苑进,等. 新型冲量式谷物联合收割机智能测产系统[J]. 中国科学:信息科学,2010,40(增刊1):230-235. Liu Chengliang, Zhou Jun, Yuan Jin, et al. Yield monitor system based on impact-based grain mass sensor[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2010, 40(Supp.1): 230-235. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 陈巡洲. 冲量式谷物流量传感器研究[D]. 上海:上海交通大学,2009. Chen Xunzhou. Research on Impact-based Grain Yield Sensor[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 胡均万,罗锡文,阮欢,等. 双板差分冲量式谷物流量传感器设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2009,40(4):69-72. Hu Junwan, Luo Xiwen, Ruan Huan, et al. Design of a dual- plate differential impact-based yield sensor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2009, 40(4): 69-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 胡均万,罗锡文,陈树人,等. 联合收割机产量传感器振动信号影响分析与消除方法[C]//2008年中国农业机械学会论文集,2008:857-860. Hu Junwan, Luo Xiwen, Chen Shuren, et a1. Analysis the effects of vibration signal on combine yield sensor[C]//2008 Annual Conference of Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2008: 857-860. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] Blackmore S. The Role of Yield Maps in Precision Farming[D]. England:Cranfield University, 2003.
[18] 张惠莉. 面向康拜因收获过程的谷物流量在线实时测量方法的研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学,2002. Zhang Huili. Research of Grain Yield Real-time Monitoring Method Towards Combine Harvester[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2002. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 张惠莉,王刚,辛立国,等.射线谷物流量在线测量试验系统的研究[J]. 莱阳农学院学报,2005,22(3):216-218. Zhang Huili, Wang Gang, Xin Liguo, et al. The Research for the Grain-Flow-Measurement System on Real Time Based- ray Sensor in Laboratory[J]. Journal of Laiyang Agricultural College, 2005, 22(3): 216-218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 张小超,胡小安,张爱国,等. 基于称重法的联合收获机测产方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(3):125-129. Zhang Xiaochao, Hu Xiaoan, Zhang Aiguo, et al. Method of measuring grain-flow of combine harvester based on weighing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(3): 125-129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 李伟,张小超,胡小安,等. 联合收获机称量式测产系统软件设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2011,42(增刊1):94-99. Li Wei, Zhang Xiaochao, Hu Xiaoan, et al. Design of intelligent yield monitoring software for combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(Supp.1): 94-99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王要武,徐刚,肖铁军,等. 联合收割机谷物流量测试装置和性能研究[J]. 农业机械学报,1993,24(2):42-48. Wang Yaowu, Xu Gang, Xiao Tiejun, et al. Monitoring the grain flow on combines device and performance study[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 1993, 24(2): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 付兴兰,张兆国,安晓飞,等. 光电漫反射式联合收割机谷物产量计量系统研发与性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(3):24-30. Fu Xinglan, Zhang Zhaoguo, An Xiaofei, et al. Development and performance experiment on grain yield monitoring system of combine harvester based on photoelectric diffuse reflectance[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(3): 24-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 付兴兰. 基于光电漫反射原理的谷物产量监测系统研发及试验[D]. 昆明:昆明理工大学,2017.Fu Xinglan. Design and Experiment on Grain Yield Monitoring System Based on Photoelectric Diffuse Principle[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 安晓飞,付兴兰,孟志军,等. 光电信号与收割机谷物产量数据转换模型的构建与验证[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(增刊1):36-41. An Xiaofei, Fu Xinglan, Meng Zhijun, et al. Grain yield data transformation model based on photoelectric principle and its validation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(Supp.1): 36-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 游素亚,徐光祐. 立体视觉研究的现状与进展[J]. 中国图象图形学报,1997,2(1):17-24. You Suya, Xu Guangyou. State of the art and future the development of stereo vision[J]. China Journal of Image and Graphics, 1997, 2(1): 17-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 马颂德,张正友. 计算机视觉:计算理论与算法基础[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1998.
[28] 李帅. 主动式结构光的立体视觉方法研究[D]. 杭州:浙江工业大学,2012. Li Shuai. Active Stereo Vision Method Research Based on Structured Light[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 王楠. 基于KNN的改进算法研究及其在图像去噪的应用[D]. 桂林:广西师范学院, 2016. Wang Nan. Research of Improved Algorithm Based on KNN and Its Application in Image Denoising[D]. Guilin: Guangxi Normal University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] Zhang Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2002, 22(11): 1330-1334.
[31] 韩建栋,吕乃光,董明利,等. 线结构光传感系统的快速标定方法[J]. 光学精密工程,2009,17(5):949-963. Han Jiandong, Lü Naiguang, Dong Mingli, et al. Fast method to calibrate structure parameters of line structured light vision sersor[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2009, 17(5): 949-963. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Development of yield monitoring system with high-precision based on linear structured light source and machine vision
Yang Gang, Lei Junbo※, Liu Chengliang, Tao Jianfeng
(200240,)
Gaining the precise yield information of a certain area is an important factor to assess the grain yield and the planting effects. Grain yield measurement system is one of the key techniques of the precision agriculture, and is also the foundation of realizing precision management. Because of the gap (around 10 mm) between the scrapper and the elevator, grains might be dropping through the gap and therefore triggers the yield sensor based on photoelectric sensor wrongly, so the generated result will not be accurate. Aiming at avoiding the problem mentioned above, a yield monitoring system based on linear structured light source and machine vision is developed. The yield sensor is made up of industrial camera, line structured light generator, proximity switch and industrial computer. When scraper passes the proximity switch in a certain position which can be adjusted, proximity switch will sense its move, which will generate a signal to trigger the industrial camera to capture the image at that time. Since proximity switch used in this sensor is based on inductance sensed, the leaky grain through the gap between the scrapper and the elevator will not trigger the switch, and the camera will be triggered correctly only by the signal of the proximity switch. A grains accumulation volume model is established to calculate the volume of the grains on the scrapper. The thickness of the grain on the scrapper is measured, after the calculation model of thickness is calibrated, the volume can be calculated according to the model established before. The computer is used to process the real-time image where the dropping grain will become noise. In order to eliminate all the noise in the image, K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) algorithm is proposed, in which the basic idea is to move those area far away from the surroundings. The experimental result shows that this method works effectively. The grain accumulation volume then can be calculated if the thickness of the grain can be calculated precisely. A measuring method for the thickness based on linear structured light is proposed. According to the volume weight measured in advance, the yield can be calculated. Grain models of the same material of scrapper are made to simulate different grain thickness. And the actual grain thickness are 10.0, 21.8 and 33.4 mm. The experiment of the thickness calculation of the scrapper (with no grains) and grain model under different speeds (60, 180, 300, 420, 540 r/min) is carried out, and the results show that the error is between 0 and 1.1%. The error is bigger while the speed is faster, the reason for which is the image capture mode of rolling shutter of the CMOS camera. Rolling shutter is a method of image capture in which a still picture (in a still camera) or each frame of a video (in a video camera) is captured not by taking a snapshot of the entire scene at a single instant in time but rather by scanning across the scene rapidly, either vertically or horizontally. When the scrapper passes the proximity switch, the switch will trigger the camera to take the shot. During the time in which the camera take the shot, the scrapper is still moving, which will cause the distortion of the image, and the distortion will be worse while the scrapper moves faster. A modified for thickness calculation is proposed to fix the distortion, and the final measuring result error is less than 0.33%, much better than original 1.1%, which means the modification model is accurate and stable. At last, the experiment of the real-time yield monitoring is carried out on the self-designed experiment platform under different speeds using the methods and the devices mentioned above. The experiment results show that the measurement error is between 3.5% and 4.27%. This research provides a reference for yield monitoring.
monitoring; systems; machine vision; grain; yield sensor; precision agriculture; image processing
2019-01-26
2019-02-18
国家重点研发计划(2016YFD0702001);国家重点研发计划(2016YFD0700105);新进教师启动计划项目(18X100040003)
杨 刚,博士生,主要从事计算机视觉研究。Email:1449381582@qq.com
雷军波,助理研究员,主要从事智能农业装备研究。Email:jblei@sjtu.edu.cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.08.003
S126
A
1002-6819(2019)-08-0021-08
杨 刚,雷军波,刘成良,陶建峰.基于线结构光源和机器视觉的高精度谷物测产系统研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(8):21-28. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.08.003 http://www.tcsae.org
Yang Gang, Lei Junbo, Liu Chengliang, Tao Jianfeng. Development of yield monitoring system with high-precision based on linear structured light source and machine vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(8): 21-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.08.003 http://www.tcsae.org

