Clinical value of preoperative methylated septin 9 in Chinese colorectal cancer patients
Xue Yang, Zhi-Jie Xu, Xi Chen, Shuang-Shuang Zeng, Long Qian, Jie Wei, Mei Peng, Xiang Wang, Wan-Li Liu,Hong-Ying Ma, Zhi-Cheng Gong, Yuan-Liang Yan
Abstra c t BACKGROUND
Key words: Methylated septin 9; Methylated; Colorectal cancer; Diagnosis; Prognosis
INTRODUCTION
Colorectal cancer (CRC) rem ains the third m ost comm on cancer expected to occu r in m en and w om en[1], accounting for app roxim ately 10% of the global cancer bu rden. To date, m ore than 90% o f patien ts w ith early CRC have su rvived five years after d iagnosis[2,3]. How ever, in the case of regional sp read to lym ph nodes or ad jacen t organs, the five-year relative su rvival rate decreases to 69%, and w hen there is d istant m etastasis, it d rops sharp ly to ap p roxim ately 10%[3,4]. Desp ite significan t recen t achievem ents in the d iagnosis and treatm en t of these patients, resu lting in partial reductions in overall incidence and m ortality, there is no effective d iagnostic assay so far for tum or p rogression or recurrence m onitoring, especially in vitro.
Detection o f CRC recu rrences or m etastases in the early stage by constan t m onitoring m ay im p rove long-term ou tcom es th rough tim ely treatm en t. The Am erican Joint Comm ittee on Cancer (AJCC) Cancer Staging, seventh ed ition has accep ted clinically usefu l carcinoem bryonic antigen (CEA) serum tum or m arker as a site-specific p rognostic factor in CRC[5]. How ever, the low detection sensitivity of CEA hinders its use for m any su rgical patients, because patients w ith negative CEA resu lts before su rgery usually cannot be m onitored after su rgery[6,7]. In ad d ition, period ic com pu ted tom ography (CT) scanning is another noninvasive m ethod for su rgical therapeu tic effect assessm ent[8]. How ever, CT scans have lim ited sensitivity and high false positive rates, and cannot be used rou tinely as a m onitoring exam ination due to the danger of long-term rad iation[9]. Therefore, developm en t o f novel, sensitive biom arkers for m onitoring recurrences or m etastases of CRC is urgently needed.
H yperm ethy lation of the p rom oter of sep tin 9 (SEPT9) has p reviously been show n to be a sensitive and specific biom arker in various cancers includ ing CRC[10-13]and its p recu rsor lesions[14-16]. As a resu lt, the m ethy lated SEPT9 (m SEPT9) assay becam e the first blood-based test app roved by the United States Food and D rug Adm inistrationas a CRC screening test[17]. A study of Korean CRC patients found that serum m SEPT9 had a tendency to show m etastasis and a low d isease-free su rvival rate[18]. In a recent stud y of Germ an CRC patients, m SEPT9 was significantly associated w ith Union for In ternational Cancer Con tro l (U ICC) stages both before and after therap y[19]. In add ition, quantitative m SEPT9 levels have been successfu lly app lied for the d iagnosis of CRC[19-22], and for the screening, d iagnosis, m onitoring, p rognosis, and m olecu lar staging o f head and neck squam ous cell carcinom as (HNSCC)[19]. H ow ever, the d iagnostic and p rognostic role of p reoperative m SEPT9 for CRC in Chinese patients is still unknow n.
This study assessed the correlation betw een clinicopathological characteristics and p reoperative serum m SEPT9 in Chinese CRC patien ts and, fu rther, to con firm the correlation betw een m SEPT9 levels and CRC p rognosis by bioin form atics analyses. In ad d ition, w e ana ly zed m eth y lated sites that w ere co-u p regu lated o r codow nregu lated in colon and rectum tum ors, to p rovide the theoretical gu idance for fu rther research.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients and samples
This p resen t study was conducted from Decem ber 2017 to Novem ber 2018 am ong patients at the Departm ent of Hepatobiliary and Enteric Su rgery in Xiangya Hosp ital.A total of 354 subjects w ith m SEPT9 serum detection before su rgery w ere recruited from a m ed icine-pharm acy-nu rsing integrative paren teral m ed ication rational use and safety early w arning p latform, the Paren teral Prescrip tion Early W arning and Assessm ent System, includ ing 300 CRC patien ts and 54 norm al subjects. This study was ap p roved by the Ethical Comm ittee o f Xiangya H osp ital o f Cen tral Sou th University (App roval No. 2018111100).
Th ree hund red patients p resen ted w ith histo logically con firm ed p rim ary CRC.Recu rrences or m etastases w ere determ ined from d iagnostic tests (CT scan, m agnetic resonance im aging, or colonoscopy) and con firm ed through tissue pathology w hen availab le[7]. C linical param eters, includ ing m SEPT9 detection resu lts, gender, age,U ICC stage, histo logic grade, p rim ary tum or (T) categories, regional node (N)categories, d istan t m etastasis categories (M), lym phatic invasion (L), lym ph nodal status, vascu lar invasion (V), and tum or site, w ere collected. The U ICC stage, tum or node m etastasis (TNM) categories and histologic d ifferentiation w ere graded on the basis of the eighth ed ition of the AJCC[23]. Progression-free su rvival (PFS) tim e was calcu lated from the CRC patien ts’ date o f su rgery to p resen tation of clinical or pathological evidence of cancer recurrence.
In ad d ition, 330 co lorectal adenocarcinom as from The Can cer Genom e A tlas(TCGA) Research Netw ork (h ttp://cancergenom e.nih.gov/.) w ere selected and analyzed retrospectively. Patients w hose m SEPT9 levels w ere less than or equal to m ed ian w ere assigned to the low m SEPT9 group, w hereas others w ere assigned to the high m SEPT9 group. The overall su rvival (OS) tim e was calcu lated from the CRC patients’ date of su rgery to the date of dead or to the last contact date.
Methylated SEPT9 detection
A 10 m L peripheral blood sam p le was collected w ith a 10 m L K2EDTA anticoagu lant tube for the SEPT9 assay [BioChain (Beijing) Science and Technology, Inc., Beijing,China]. Peripheral b lood sam p le storage and transportation, DNA extraction, and bisu lfite conversion w ere perfo rm ed m anually fo llow ing the m anu factu rer’s instructions of the Ep i p roColon 2.0 kit (Ep igenom ics AG, Berlin, Germ any). The m SEPT9 was assayed w ith the Ep i p roColon 2.0 kit on an AB7500 Fast Dx Real Tim e polym erase chain reaction device (Life Technologies) in the Clinical Laboratory o f Xiangya Hosp ital, Cen tral Sou th University. Briefly, a po lym erase chain reaction(PCR) test was perform ed in trip licate w ith 15 μL tem p late DNA per w ell and run for 45 cycles[24]. The instrum ent softw are was used to record the PCR resu lts for β-actin(ACTB) and m ethy lated SEPT9 from each of the trip licate reactions. The valid ity of each sam p le batch was determ ined accord ing to m ethy lated SEPT9 and ACTB threshold count (Ct) values for the positive and negative controls. ACTB served as an internal reference to assess the integrity of each sam p le. Accord ing to the instructions,Ct value was less than 41.1 was assigned to the positive m SEPT9 group, w hereas those w hose Ct value was over 41.1 w ere assigned to the negative m SEPT9 group.
Statistical analyses
A ll statistical analyses w ere perform ed using SPSS 18 softw are (SPSS Inc, Chicago,Un ited States). The m easu rab le data was exp ressed as the m ean and standarddev iation (SD). D ifferences o f clinicopatho logical characteristics and Ct values betw een groups w ere com pared via t-tests and χ2 test. The univariate analysis was perform ed to assess the effect of m SEPT9 to p red ict PFS and OS by the Kap lan-M eier m ethod. Binary logistic regression was used to analyze the association betw een each genetic biom arker (e.g., m ism atched repair p roteins) and m SEPT9. A ll the statistical tests w ere bilateral, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
The mSEPT9 in CRC patients and normal subjects
Am ong Chinese CRC patients, the m ethy lated Ct values of 300 p rim ary CRC patients and 54 norm al subjects w ere analyzed. Based on contrad ictory trends for Ct value and exp ression, the p reoperative serum m SEPT9 levels w ere significan tly higher in CRC patien ts than in the norm al sub jects (P = 0.008) (Figu re 1A). The positive rate o f m SEPT9 was 52.3% for CRC patients and 25.9% for norm al subjects (P = 0.102) (Figure 1B).
Am ong 351 patien ts from the TCGA database, the m SEPT9 levels o f 330 CRC patients and 21 norm al subjects w ere analyzed. The serum m SEPT9 levels of the CRC patien ts w ere higher than those of the norm al sub jects, bu t w ere not statistically significant (P = 0.530) (Supp lem ental Figure 1).
Clinicopathological characteristics and mSEPT9 in CRC
The Chinese CRC patien ts, clinicopathological featu res o f 300 CRC patien ts are described in Tab le 1. As show n in Figu re 1C, patien ts older than 50 years w ere statistically m ore num erous than those aged 50 or younger in both positive and negative groups (P = 0.016). Th rough analyzing UICC stages, w e found that the positive rate of stage III was observably higher than stage I (46.6% vs 31.0%, P = 0.012)(Figu re 2A); m SEPT9 levels show ed a significant increase from UICC stages II to III (P= 0.033) and stages III to IV (P < 0.0001), bu t no obvious d ifference was detected betw een stages I to II (P = 0.898, Figu re 3A).
In add ition, the association of m SEPT9 levels and rate of positive m SEPT9 am ong p rim ary tum or categories (T1-T4), regional node categories (N 0-N 2) and d istan t m etastasis categories (M 0-M 1) w ere also analyzed. The detection rate of positive T3 was observably higher than that of T1 (51.1% vs 40.0%, P = 0.019) (Figu re 2B). Positive rate and levels of m SEPT9 revealed a significant increase from T3 to T4 (P = 0.030, P =0.046, respectively) (Figu re 2B, Figure 3B). In term s of regional node categories, N 0 to N 2 show ed a gradual increase in m SEPT9 levels (P = 0.012) (Figu re 3C), bu t d id not show any association w ith the rate o f positive m SEPT9 (Figu re 2C). As show n in Figu res 2D and 3D, m SEPT9 show ed the best ability to d iscrim inate betw een local and m etastatic CRC (P = 0.015, P < 0.0001, respectively). How ever, higher m SEPT9 levels w ere not found in CRC patients w ith lym phatic or vascu lar invasion than in those w ithout invasion (all P > 0.05). W e also failed to find association am ong MLH 1, MSH 2(25D12), MSH 6, PMS2, and Ki67 and m SEPT9 (all P > 0.05) (Supp lem ental Table 1).
The clinicopathological featu res of 330 CRC patients from the TCGA database are described in detail in Supp lem ental Table 2. Sim ilarly, there was a tendency for m ore d istant m etastasis (P = 0.0001) and m ore CRC patients older than 50 (P < 0.0001) in the high m SEPT9 group, bu t no significant d ifference was found in UICC stages, p rim ary tum or categories, or regional node categories (all P > 0.05).
Prognostic significance of mSEPT9 in CRC patients
Kap lan-M eier univariate analysis show ed that positive m SEPT9 was obv iously associated w ith shorter PFS am ong the Chinese CRC patients (P = 0.019, Figu re 4A).The positive m SEPT9 CRC cases w ere estim ated to have an m ean PFS du ration of 3.7 m o [95% con fidence interval (CI): 2.14-5.19] com pared w ith the 6.0 m o (95%CI: 0-13.87) in the negative m SEPT9 CRC cases.
In add ition, serum m SEPT9 show ed p rognostic significance for the CRC patients from the TCGA database (P = 0.008, Figu re 4B). CRC patients w ith low m SEPT9 levels w ere found to be correlated w ith longer OS. The low m SEPT9 CRC cases had an estim ated m ean OS du ration of 8.1 m onths (95%CI: 6.53-9.27) com pared w ith the 5.1 m o (95%CI: 3.87-6.33) in the high m SEPT9 CRC cases.
Significant methylation sites for SEPT9
In fu rther analyzed TCGA clinical data, 124 m SEPT9 sites w ere found that show ed d ifferen tial exp ression am ong norm al sub jects and those w ith colon and rectum adenocarcinom a, respectively (all P < 0.05) (Supp lem ental Figu re 2). A fter analyzing the detailed in form ation of these 124 m SEPT9 sites, 68 co-up regu lated and 36 codow nregu lated m SEPT9 sites in CRC adenocarcinom a w ere fu rther observed. W efinally con firm ed that there w ere eight co-up regu lated m SEPT9 sites (Figu re 5) and one co-dow n regu lated m SEPT9 site (cg02975107) through setting a cu t-off of a tw ofold exp ression change of m SEPT9.
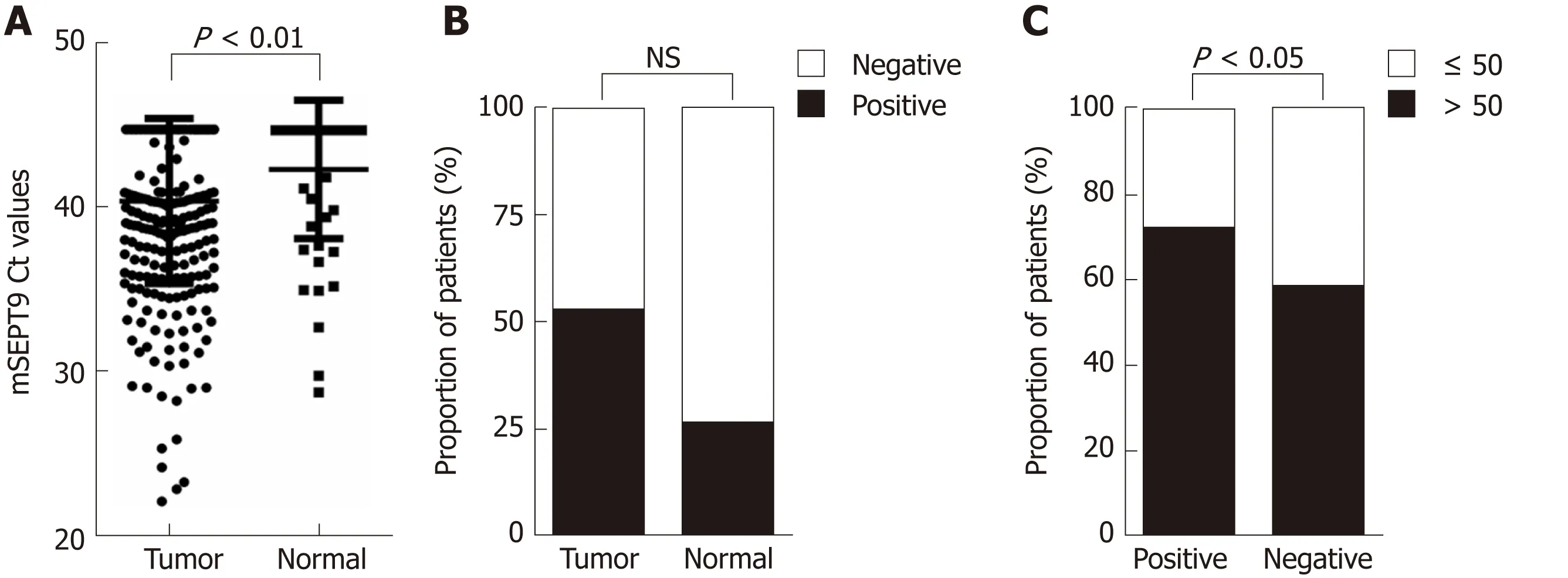
Figure 1 Graphical representations of difference in methylated septin 9 Ct values or proportion of patients between different groups. A: Methylated septin 9(mSEPT9) Ct values in tumor group and normal group; B: Proportion of patients with positive and negative mSEPT9 in tumor group and normal group; C: Proportion of patients older than 50 and aged 50 or younger in positive group and negative group. The statistical significance for difference of means is shown in P values, t-test, or χ2 test. mSEPT9: Methylated septin 9.
DISCUSSION
M ost patien ts w ith early CRC undergo cu ratively in tended su rgery to clear up p rim ary lesions and local lym ph node m etastasis up. How ever, 30%-50% of patien ts w ou ld still con fron t tum or recu rrence and m igh t d ie from m etastasis[25]. Tim ely m onitoring of recu rrence and m etastasis is of great significance to the p rognosis and su rvival of patients. In ou r study, m SEPT9 was p roved to be an effective bio-m arker for d iagnosis, recu rrence, and p rognosis o f CRC in Ch inese patien ts, and nine significant m SEPT9 sites w ere con firm ed for fu rther in-dep th consideration.
Ou r study con firm ed the value of serum m SEPT9 for CRC d iagnosis. Com pared w ith norm al tissues in Chinese and TCGA data, serum SEPT9 was found to be hyperm ethy lated in tum or tissues, w hich was consistent w ith p revious stud ies[18,19,26].Stud ies show ed that age affected the detection rate of the SEPT9 assay[27,28], and w e found that a positive rate of m SEPT9 was strongly associated w ith CRC patients aged over 50 years both in Chinese and TCGA data. This accords w ith the definition of an average risk popu lation in National Com p rehensive Cancer Netw ork Guidelines for CRC[29]. Rem arkably, w e reported that SEPT9 perform s ou tstand ing ly as an auxiliary m olecu lar staging param eter in the Chinese popu lation, especially because m SEPT9 levels cou ld d istingu ish betw een patho logical U ICC and TNM stages in an increm en tal fashion. In add ition, ou r data dem onstrated that CRC patients in earlier tum or stages show ed low er m SEPT9 levels com pared to those w ith m ore advanced lesions, w h ich is consisten t w ith stud ies in Germ an CRC patien ts[19,30-32]. M ost im portan tly, its ability to iden tify patients w ith d istant m etastases em phasizes the poten tial o f m SEPT9 as a bio-m arker, w h ich ad ds valuab le in form ation to the classification o f tum ors[33-35]. How ever, h igh m SEPT9 g roup d id not show any association w ith UICC, T, or N stages in patients from the TGGA database, w ho w ere from Am erican Ind ian, Asian, Black, or A frican Am erican popu lations. This m ight be exp lained by the d ifferen t study popu lations. Prev ious stud ies found that the incidence o f CRC and the sensitivity to the m SEPT9 test assay in d ifferent ethnic groups w ere different[14,36].
In add ition, serum m SEPT9 w ere p roved to be an independent p red ictors of CRC recu rrence and un favorab le cancer-specific su rvival in Chinese and TCGA data,w hich is consistent w ith p revious stud ies in Singapore and Germ any[19,37,38]. The study was perform ed w ith a large num ber of p rognostic featu res and patients; how ever,m uch longer p rognosis and follow-up tim e are necessary before final conclusions can be m ade, and the increasing num ber of patients w ith earlier-stage CRC dem ands a w idening of the clinical im portance of p red ictive value for p rognosis.
A fter fu rther analysis o f the TCGA clin ical data, w e obtained nine SEPT9 m ethy lation sites that show tw o-fold higher or low er m SEPT9 levels in CRC than norm al tissues. How ever, no stud ies w ere found at p resen t that investigate the p rognosis of these m ethy lation sites and CRC was found. Su rp rising ly, cg12783819,w hich on ly show s 1.5-fold higher m SEPT9 levels in CRC than in norm al tissues, hasbeen p roven to be able to assess the d iagnosis, p rognosis, and m olecu lar staging of Germ an HNSCC and CRC patients[19,20]. The resu lt p rom p ts us to exp lore the potential association betw een these nine m ethy lation sites and in Chinese CRC patients in the fu tu re.

Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics based on methylated septin 9 status in 300 colorectal cancer patients
In conclusions, serum SEPT9 m ethy lation testing is a pow erfu l ad d itional d iagnostic tool and p rom ising, novel p rognostic m arkers. Patients w ith initially high m SEPT9 levels m ay benefit from in tensive therapy and close m onitoring of d isease developm ent, thereby im p roving ou tcom es for CRC patients. These patien ts m ay benefit from early system ic treatm ent.
Figure 3tumor categories; C: Regional node categories; D: Distant metastasis categories. The statistical significance for difference of means is shown in P values and t-test.mSEPT9: Methylated septin 9.
Figure 4
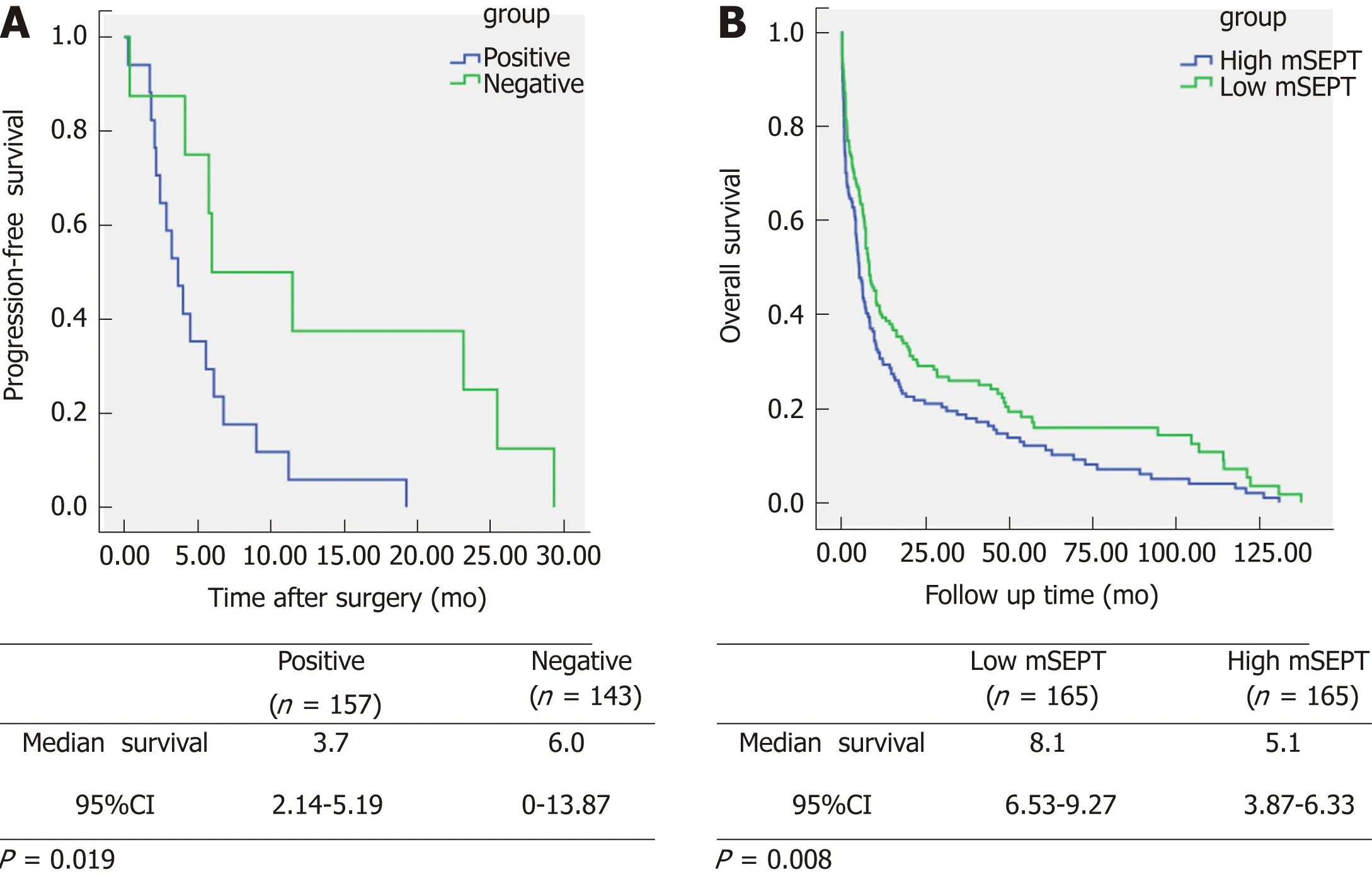
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier univariate survival curves according to methylated septin 9 status. A: Progression-free survival time; B: Overall survival. The statistical significance for difference of means shown in P values and Kaplan-Meier univariate analysis. mSEPT: Methylated septin; CI: Confidence interval.
Figure 5
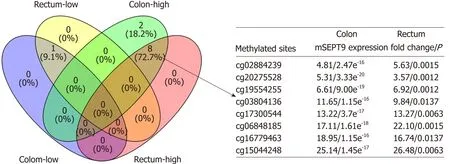
Figure 5 Venn diagram of eight co-upregulated methylated septin 9 sites and one co-downregulated methylated septin 9 site in colon and rectum adenocarcinoma. “Rectum-low” and “Rectum-high” represented sites that showed low or high expression in rectum adenocarcinoma, and “Colon-low” and “Colonhigh” represented sites that showed low or high expression in colon adenocarcinoma. Eight co-upregulated methylated septin 9 (mSEPT9) sites also showed mSEPT9 expression fold of rectum/ colon adenocarcinoma compared to normal subjects and corresponding P value. mSEPT: Methylated septin.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The m ethy lated sep tin 9 (m SEPT9) assay was the first blood-based test app roved by the United States Food and D rug Adm inistration as a colorectal screening test. Previous researchers found that m SEPT9 was a pow erfu l screening, d iagnostic, m onitoring, and p rognostic tool for Germ an co lorectal cancer (CRC) patien ts. How ever, the d iagnostic and p rognostic value o f m SEPT9 in Chinese CRC patien ts is still unknow n, and m ay be affected by d ifferences in ethn icity and socioeconom ic status.
Research motivation
To exp lore the d iagnostic and p rognostic value of serum m SEPT9 for Chinese CRC patien ts.
Research objectives
This study aim ed to exp lore the d iagnostic value of p reoperative serum m SEPT9 in the Chinese popu lation, and then assess the value o f quan titative m SEPT9 levels for CRC staging. In add ition, Chinese popu lation and TCGA database inform ation w ere com bined to determ ine the p rognostic significance of m SEPT9 by bioinform atics analyses.
Research methods
Three hund red fifty-four subjects (300 CRC, 54 norm al) from China and 351 subjects (330 CRC,21 norm al) from the TCGA database includ ing Am erican Ind ian, Asian, Black, and A frican Am erican popu lations w ere retrospectively analyzed. Preoperative m SEPT9 levels w ere quantified by quan titative m ethy lation-specific polym erase chain reaction. Kap lan-M eier univariate assay was perform ed to analyze potential p rognostic factors includ ing overall survival (OS) and p rogression-free survival (PFS).
Research results
In Chinese CRC patients, positive m SEPT9 and quan titative m SEPT9 levels w ere strong ly associated w ith clinico-patho logical param eters. The patien ts w ith positive m SEPT9 show ed a tendency tow ard low er PFS. H igher m SEPT9 levels w ere correlated w ith m ore d istant m etastasis am ong the TCGA database patients, and patients w ith high m SEPT9 levels show ed a tendency tow ard low er OS.
Research conclusions
Testing for m SEPT9 is a pow erfu l d iagnostic and p rom ising p rognostic tool for Chinese CRC patien ts; it m ay add valuable in form ation to cu rren t tum or staging and ho lds the potential to m onitor CRC recu rrence.
Research perspectives
This study assessed the correlation betw een clinicopathological characteristics and p reoperative serum m SEPT9 in Ch inese CRC patien ts and, fu rther, to con firm the co rrelation betw een m SEPT9 levels and CRC p rognosis by bioin form atics analyses. In add ition, w e analyzed m ethy lated sites that w ere co-up regu lated or co-dow nregu lated in colon and rectum tum ors, to p rovide the theoretical guidance for fu rther research.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2019年17期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2019年17期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Microbial metabolites in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis
- Evolving screening and surveillance techniques for Barrett's esophagus
- Proton pump inhibitor: The dual role in gastric cancer
- Herbs-partitioned moxibustion alleviates aberrant intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis by upregulating A20 expression in a mouse model of Crohn’s disease
- Analysis of the autophagy gene expression profile of pancreatic cancer based on autophagy-related protein microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3
