Ethnobotanical and traditional uses,phytochemical constituents and biological activities of Eryngium species growing in Iran
Masoumeh Ghajarieh Sepanlou,Mehran Mirabzadeh Ardakani,Mannan Hajimahmoodi, ,Sima Sadrai,Gholam-Reza Amin,Naficeh SadeghiSeyedeh Nargess Sadati Lamardi*
1Department of Traditional Pharmacy,School of Persian Medicine,Tehran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran,Iran.
2Drug and Food Control Department,Faculty of Pharmacy,Tehran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran,Iran.
3Persian Medicine and Pharmacy Research Center,Tehran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran,Iran.
4Pharmaceutical Department,Faculty of Pharmacy,Tehran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran,Iran.
5Pharmacognosy Department,Faculty of Pharmacy,Tehran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran,Iran.
Abstract
Keywords: Eryngium,Iranian species,Pharmacological activities,Phytochemical compositions,Traditional and ethnopharmacological uses
Background
Eryngiumis the largest genus ofApiaceaefamily.It contains 274 accepted species that are distributed all around the world especially in Europe,Africa,America and Australia [1-3].Eryngiumspecies are spiny perennial or biennial herbaceous plants with 30 to 150 cm height with vertical roots,one principal stem main or several stems and elliptic and ovate-oval-shaped spiny fruits.The spiny leaves are often long and wide,may have two or three section;basal leaves have petiole and the stem leaves without petiole with spiny flattened pods.The inflorescence is commonly paniculous or pistil cluster shape.Flowers are most often bisexual,without peduncule;petals are white or nearly greenish,rarely blue sky [4].All parts of these plants produce a pleasant volatile oil.Beside their uses as food ingredients,these plants are utilized as herbal remedies for their renowned medicinal properties [5,6].
Eryngiumspecies have variety of uses in folklore and traditional medicine in different nations.In addition,new research demonstrates that different plant species from this genus are rich sources of various phytochemicals.In vivoandin vitroinvestigations have reported several pharmacological and biological activities fromEryngiumspecies[5-7].
Ten species ofEryngiumhave been identified in Iran includingE.caeruleumM.B.(syn:E.caucasicumTrautv.),E.creticumLam.,E.bungeiBoiss.,E.billardieriF.Delaroche.,(syn:E.kotschyiBoiss.),E.glomeratumLam.(syn:E.parviflorumSm.),E.bornumulleriNab.,E.pyramidaleBoiss.&Husson.,E.noeanumBoiss.,E.wanaturiWoron.(syn:E.woronowiiBordz.),andE.thyrsoideumBoiss.These species are distributed in all regions of Iran and especially are abundant in the northern provinces such as Gilan and Mazandaran [4].Young leaves of these plants which locally called “Chuchagh” are mainly collected in large quantities from the wild by native people and sold in local markets for using in different local foods as a flavoring cooked vegetable[2,8].
Eryngiumgenus is one of the medicinal herbs mentioned in several Persian medicine references by the name of “Qaracaane” and as its description;widespread morphologies are mentioned due to different species and varieties.In Persian medicine,numerous therapeutic properties as well as good nutritional values have been mentioned forEryngiumand the use of its roots is confirmed beside the aerial parts[9].
Given that there is no review on Iranian species ofEryngium,the aim of this study is to pay attention to various prospects of Iranian species ofEryngium,including pharmacological activity and phytochemical constituents as well as ethnopharmacological and traditional uses of these species in Persian medicine and various nations in other regions of the world to provide a scientific document for prospective exploits of natural drugs from these plants for management of various disorders.
Method and search strategy
Electronic databases including PubMed,Scopus,Science Direct (ISI Web of Knowledge) and Embase library were searched for research onEryngium.The search period was from 1966 to October 2018.the search keywords were as follows: “Eryngium”,“E.caeruleum”,“E.caucasicum”,“E.billardieri”,“E.kotschyi”,“E.thyrsoideum”,“E.bungei”,“E.creticum”,“E.glomeratum”,“E.parviflorum”,“E.bornumulleri”,“E.pyramidale”,“E.wanaturi” or “E.noeanum”.
Inclusion criteria werein vitro,in vivoor phytochemical evaluations as well as traditional and ethnobotany uses of ten IranianEryngiumspecies as well as papers with available English full texts.Exclusion criteria were review articles and papers with non-English full-texts.
Results
A total of 57 papers were enrolled in analyses,in which there 14 reports ofE.caucasicum,5 ofE.caeruleum,7 ofE.billardieri,6 ofE.kotschyi,5 ofE.bungei,1 ofE.glomeratum,21 ofE.creticum,1 ofE.pyramidale.Data from the final included articles were summarized in Tables 1 and Appendix.
Traditional and ethnobotany uses
In different Persian medicine references,various therapeutic effects and pharmacological actions ofEryngiumhave been mentioned including antidote(antitoxin),diuretic,emmenagogue,aphrodisiac,galactagogue,digestive,anti-flatulent,antiinflammatory and analgesic properties.Other applications of this plant in Persian medicine are for pulmonary disease,halitosis,snakebite and insect bites,cramps and gripes and early stages of lymphatic filariasis(elephantiasis)[9,10].
In various regions of Iran specially the northern provinces,E.caeruleumleaves are used as flavoring vegetable in different local foods [8,11].In southwest of Iran,E.billardieriis used orally for treatment of constipation [12].It is also reported thatE.caeruleumis used as enforcing generative power,diuretic,lenitive and appetizer [13].In southeastern of Turkey,roots decoction and crushed leaves ofE.billardierihave been used for toothache and wound healing,respectively.Also young fresh shoots are eaten after peeling [14].In JordanE.creticumroots are used for scorpion and snakes bite[15].
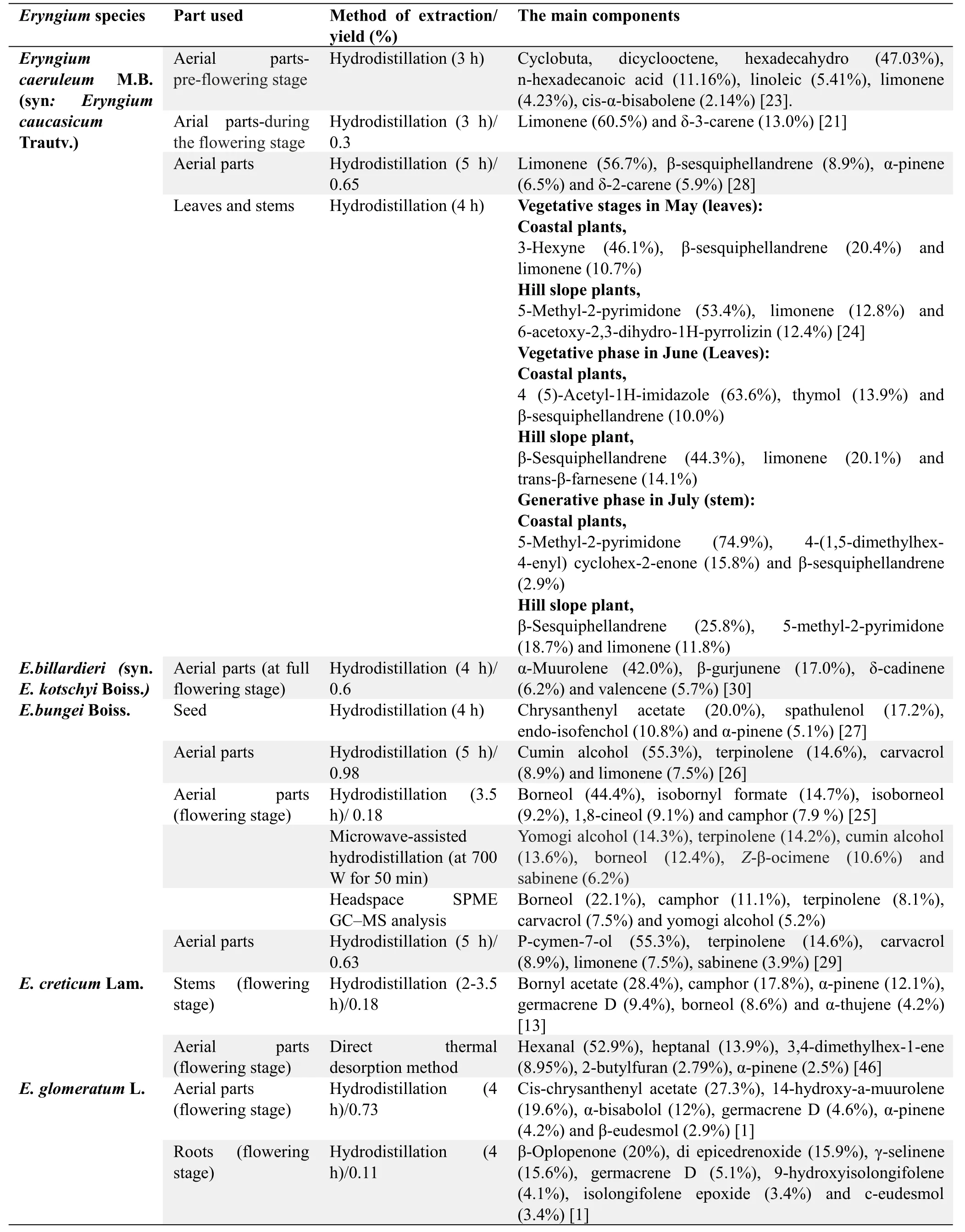
Table1 Essential oil analysis of Eryngium species growing in Iran
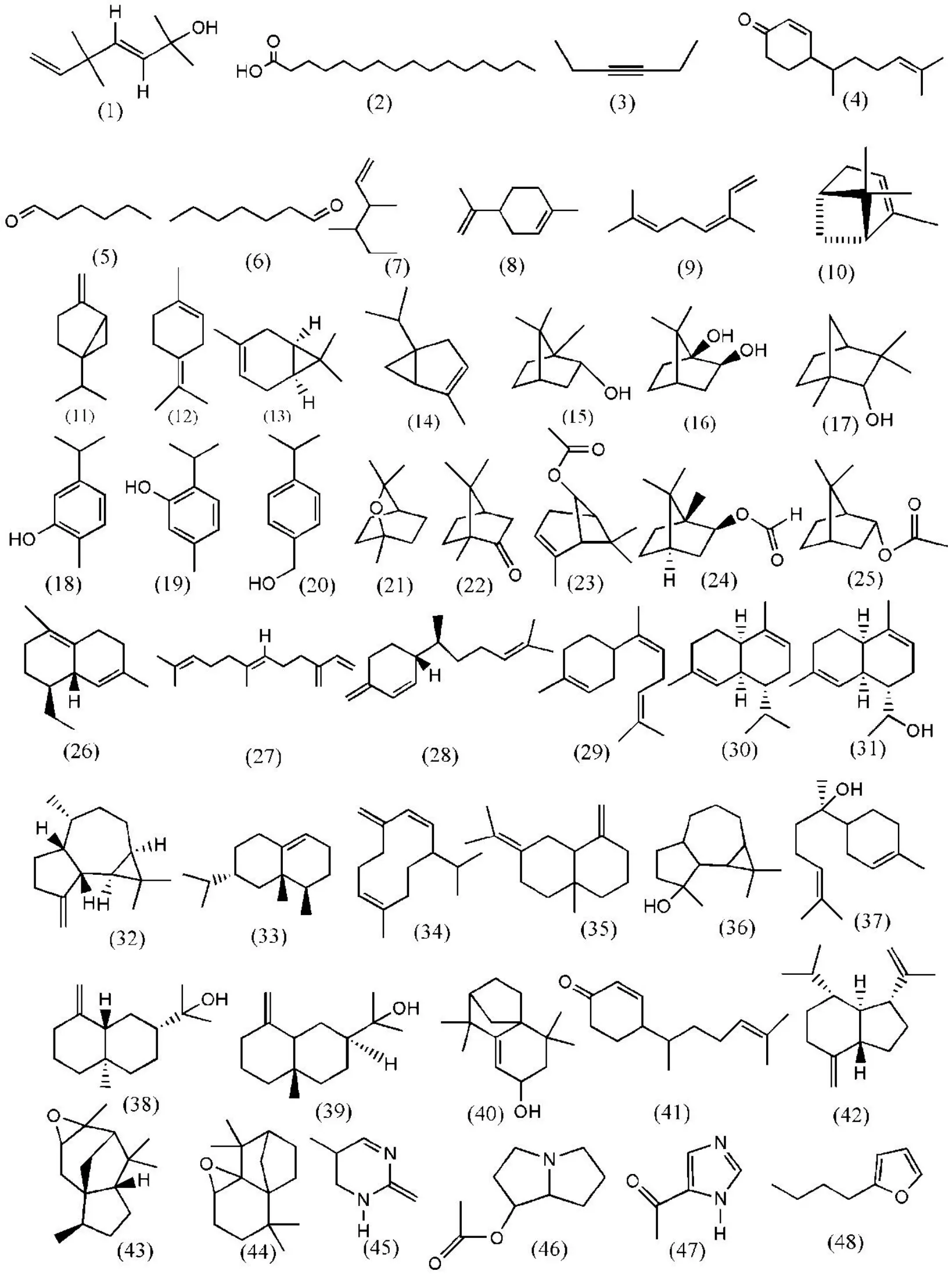
Figure1 Chemical structures of essential oil analysis reported from Eryngium species growing in Iran
In Israel,whole plant decoction ofE.creticumhas been used for the treatment of anaemia,infertility problems,poisonings and liver diseases.Also decoction of fresh leaves has been used for treatment of snake bites or applied on wounds directly.Leaves decoction also is used for diabetes treatment[16,17].E.creticumleaves and stalk or aerial parts are used for hypoglycemic effects,anti-poisonous property and blood properties in Lebanon [18].Also it has been reported thatE.creticumaerial parts,roots and seeds are used traditionally as laxative,diuretic,antidote and treatment of snakebites,poisoning,liver diseases,tumors,kidney stone,infections,skin diseases,infertility and anemia in different countries[19,20].
Phytochemical composition
Table1 and Figure 1 show the chemical structure and phytochemical category of compounds from different parts of IranianEryngiumspecies.
Essential oil.Studies have shown that the yield of the essential oil extracted from the aerial parts,seeds and roots ofEryngiumspp.,collected in different growth conditions of Iran were 0.05-0.98% (v/w).The essential oil of this plant was found to be a yellowish liquid.According to the reports,monoterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids are the major components ofEryngiumspp.oil.Figure 1 shows the structures of some major active components in the essential oil ofEryngiumspp.
Alcohols and hydrocarbons.Yomogi alcohol (1),and some hydrocarbons were reported from the essential oil ofEryngiumspecies collected in Iran such as:n-hexadecanoic acid (2),3-hexyne (3),4-(1,5-dimethylhex-4-enyl) cyclohex-2-enone (4),hexanal (5),heptanal (6),and 3,4-dimethylhex-1-ene(7)[21-24].
Monoterpenes.Several monoterpenes including:monoterpene hydrocarbons,monoterpene alcohols,and oxygenated monoterpens have been reported as major components of essential oils fromEryngiumspp.It has been presented that the essential oil of IranianEryngiumspp.contains a high amount of monoterpens hydrocarbons,such as: limonene (8),terpinolene (12),δ-3-carene (13),(Z)-β-ocimene (9),α-Pinene (10),sabinene (11) and α-thujene (14).Borneol (15),isoborneol (16),endo-isofenchol (17),carvacrol (18),thymol (19),and cumin alcohol (ρ-Cymen-7-ol) (20)have been reported as the major monoterpen alcohol while oxygenated monoterpens such as: 1,8-Cineole(21),camphor (22),chrysanthenyl acetate (23),isobornyl formate (24),and bornyl acetate (25) have been reported[1,13,21-30].
Sesquiterpenes.Several major sesquiterpene hydrocarbons identified in the essential oil from IranianEryngiumspp.including: δ-Cadinene (26),trans-β-farnesene (27),β-sesquiphellandrene (28),cis-α-bisabolene (29),α-muurolene (30),14-hydroxy-α-muurolene (31),β-gurjunene (32),valencene(33),germacrene D(34)and γ-Selinene(35).Moreover,spathulenol (36),α-bisabolol (37),β-eudesmol (38),γ-eudesmol (39),and 9-hydroxy isolongifolene(40),as sesquiterpene alcohols and 4-(1,5-dimethylhex-4-enyl) cyclohex-2-enone (41),β-oplopenone (42),Di-epi-cedrenoxide (43),Isolongifolene epoxide (44) as oxygenated sesquiterpenes,as well as 5-methyl-2-pyrimidone (45),6-acetoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizin (46),4(5)-acetyl-1H-imidazole (47) and 2-butylfuran (48)have been reported[1,13,21-24,27,28,30].
Other phytochemicals.GenusEryngiumis known for it’s secondary metabolites like triterpenoid saponins,triterpenoids,flavonoids,coumarins,and steroids [7].AmongEryngiumspp.growing in Iran,Erdemet al.reported five new oleanane-type saponins from the roots ofEryngiumkotschyiincluding 3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-dglucuronopyranosyl-22-O-β,β-dimethylacryloylA1-barrigenol,3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-dglucuronopyranosyl-22-O-angeloylA1-barrigenol,3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-[β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-d-glucopyranosyl-21,22,28-O-triacetyl-(3β,21β,2 2α)-olean-12-en-16-one,3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-glucopyranosyl-22-O-β-d-glucopyranosylstegano genin,3-O-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→2)-[α-larabinopyranosyl-(1→3)]-β-d-glucuronopyranosyl-22-O-angeloylA1-barrigenol and 3-O-α-lrhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-glucuronopyranosylolean olic acid [31].In addition,Ur Rehmanet al.identified two flavonol glycosides,kaempferol 3-O-[6-O-E-p-coumaroyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside and kaempferol 3-O-(2",6"-di-O-E-p-coumaroyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside fromE.caeruleum[32].Three sesquiterpenes with an unusual carbon skeleton,1-n-propyl-perhydronaphthaline,and a methyl ketone eicos-8,11-dien-18-ol-2-one were isolated from the fresh aerial parts ofE.creticumcollected from Sinai(Egypt)[33].
Pharmacological effects
All biological and pharmacological activities of IranianEryngiumincludingin vitroandin vivostudies were summarized in Appendix.Various investigations demonstrated a broad range of pharmacological and biological activities from different parts and extracts of these plants are explained below.
Antioxidant activities.As evident oxidative stress condition is an important cause in the pathogenesis of different human diseases.Therefore,discovering natural antioxidants which have positive biological potentials can lead to developing of new multifunctional natural drugs to prevent or treat various human disorders [11,34].Variousin vitrostudies confirmed remarkable antioxidant potential of IranianEryngiumspecies.Severalin vitroinvestigations reported that n_hexane,ethyl acetate,acetone,aqueous fractions,ethanolic and methanolic extracts of E.caeruleum aerial parts,leaves and inflorescence,had remarkable antioxidant properties by various methods [35-40].Yurdakok and Gencay reported that lyophilized extracts from the aerial parts and roots of E.kotschyi possessed significant antioxidant properties in three different methods[41].
In vitro investigation revealed that volatile oil obtained from the seeds of Eryngium bungei demonstrated antioxidant activity [27].Ethanol extract from aerial parts of E.billardieri showed antioxidant properties by different methods [42].Methanolic and aqueous extract from aerial parts of E.creticum showed remarkable antioxidant activities through various in vitro methods[19,20,43].
Antimicrobial effects.The antibacterial activity from leaves and aerial parts of E.caeruleum have been confirmed by several in vitro investigations.Sadiq et al.reported that methanolic extract and its different fractions of E.caeruleum aerial parts demonstrated remarkable antibacterial and antifungal activities against six bacterial strains and three fungal strains[44].Essential oil obtained from the aerial parts of E.caeruleum showed high antibacterial activity against six bacterial strains that are important pathogens in plants and human [23].Ethanol extract of leaves of E.caeruleum and E.bungei demonstrated antibacterial effect against four strains of bacteria that are oral and skin pathogens[45].
Aqueous extracts obtained from aerial parts and roots of E.kotschyi possessed antibacterial properties[41].E.creticum essential oil possessed antimicrobial activity against seven methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains [46].Also,methanolic extract from the leaves of E.creticum showed antimicrobial activity [47].Another study demonstrated that petroleum ether and methanolic extract from the leaves of E.creticum demonstrated antifungal activity against 4 fungi species,although petroleum ether extract showed higher activities [48].Essential oil from aerial parts of E.glomeratum showed antimicrobial activity against 15 microbial strains [1].Volatile oil obtained from the seeds of E.bungei demonstrated notable antifungal effect comparing with amphotericin B[27].
Anti-inflammatory,analgesic and antinociceptive effects.Erdem et al.reported that methanolic extract from whole plant of E.billardieri demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity in mice.This study also evaluated anti-inflammatory effect of various fractions from the aerial parts and roots of E.billardieri.The results showed that the precipitated portion of butanol extract of the roots demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory activity.This anti-inflamatory effect of the roots can be related to its saponin contents[49].
Küpeli et al.investigated anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of eight Eryngium species including E.kotschyi and E.creticum.The aqueous and ethanolic extracts from roots and aerial parts of both Eryngium species presented apparent antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities [50].It has been demonstrated that various fractions of methanolic extract from the roots of E.kotschyi,showed remarkably antinociceptive activity in mice[51].Petals essential oil of E.pyramidale demonstrated significant anti-nociceptive,analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities in rats[52].
Antidiabetic activity.Rehman and Hashmi reported two new flavone glycosides obtained from the aerial parts of E.caeruleum.These two components demonstrated remarkable antidiabetic activities via in vitro experimental investigations[32].
It has been reported that n-hexane,ethyl acetate and methanolic extracts of aerial parts of E.caeruleum possesses antidiabetic effect.Methanolic extract showed higher inhibitory effect followed by ethyl acetate and n-hexane extracts[11].
Aqueous extract from aerial parts and roots of E.creticum demonstrated notable acute antihyperglycemic activities in rats [53,54].Also methanolic extract of E.creticum illustrated in vitro anti-lipase activity.As evident,enhanced levels of fatty acids and triglycerides had important role in development of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance[55].
Cytotoxic,antimutagenic and anticancer activities.Aqueous extracts of aerial parts and roots from E.kotschyi possesses cytotoxic activity.Root parts showed more toxicity activity than aerial parts [56].Esmaeili et al.evaluated cytotoxic activity of 26 species grown in south-west of Iran.Among these 26 species,only four species were toxic and two out of these four species containing E.billardieri have shown cytotoxic effects on all tested cell lines with lower IC50values[57].
In an in vitro assessment,methanolic extracts of 35 species from southwest of Iran were examined for prophage induction ability in Escherichia coli K-12(λ).E.billardieri aerial parts was one of five species that demonstrated the potency to interact with DNA and might have cytotoxic effects [12].Among 15 tested plant species,aqueous extract of E.creticum showed the highest antitumor effect by 84.30%inhibition[58].In vitro assesments demonstrated that methanolic extracts from both leaves and stems of E.creticum exerted cytotoxicity effect [20].Ethanolic extract from the inflorescences of E.creticum demonstrated inhibitory effect on mutagenicity in rats[59].
Phytotoxic activity.Seeds volatile oil of E.bungei was evaluated for phytotoxic activity on six plants.It demonstrated noticeable effect on germination of the seeds and epicotyl and radicle growth of these plants with IC50values ranging from 1.32 to 2.1 μg/mL[27].
Anti-scorpion,snake and venoms activities.Aqueous and ethanolic extracts of fresh and dried leaves and roots of E.creticum demonstrated inhibition effects on hemolytic activities of Leiurusquinquesteiartusscorpion venoms.The extract of fresh leaf showed higher inhibition of hemolytic activity of the scorpion venom compared with the extract of dried leaf.Both fresh and dried roots extracts illustrated 100% inhibition of the snake and scorpion venoms,although ethanolic extracts from the leaves and roots increased hemolysis of RBC (red blood cells) rather than inhibition activity of venom effects on RBC[60].
Roots aqueous extract ofE.creticumshowed antagonistic effect againstLeiurus quinquestriatusscorpion venom.The results showed that the extract inhibited 40-50% of the maximum tracheal muscles contraction induced by the venom in both guinea pigs and rabbits.Also,the extract partially inhibited contraction of rabbit and guinea pig jejunum before and after exposure to the venom[61].
Anticonvulsant activity.Different doses of methanolic and polyphenolic extracts ofE.caucasicuminflorescence showed antiepileptic activity in mice.Polyphenolic extract showed more protection effect against seizures[62].
Antihypoxic activity.Various disorders such as heart diseases,hemorrhage,stroke,etc.can be the cause of hypoxia followed by deleterious effects and tissue destruction and possible death.Also,hypoxia can produce nitric oxide and other free radicals [63].Various doses of methanolic extract and polyphenol fraction obtain fromE.caeruleuminflorescence demonstrated significant protective effects against asphyctic,hemic and circulatory models of hypoxia in mice.The hypoxia effects of extracts were dose dependent[64].
Renoprotective effect.Renoprotective activity of methanol extract from the aerial parts ofE.caeruleumwas demonstrated in mice.The results of this study demonstrated thatE.caeruleumextract reduced blood urea nitrogen serum creatinine,and urea in nephrotoxic mice blood serum.This reduction was significant at the dose of 200,400 mg/kg/day from the extract[65].
Antihemolytic activity.Different fractions of acetone extract obtained from the leaves ofE.caeruleumshowed antihemolytic effects on rat erythrocyte[38].
Contractile effect.Contraction induction ofE.kotschyiaerial parts and roots was illustrated on isolated ileum and detrussor muscle of rat.The results showed that aqueous extracts of both the aerial parts and roots had contractile effects in detrusor and ileum muscle in different doses and various protocols[66].
Food preservative.Raeisiet al.demonstrated thatE.caeruleumleaves extract had good potential for use as natural preservatives for the extension of fish products shelf-life.
Two concentrations of ethanolic extracts (2% and 4%) obtained from the leaves ofE.caeruleumwere evaluated for effects on the quality deterioration indices,sensory and microbiological characteristics and lipid oxidation in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets within refrigerated storage at 40C ± 1.Both concentrations of the leaf extracts illustrated significant retardation on oxidative deterioration,bacterial growth and had positive efficacy on sensory quality[39].
Percutaneouspenetrationenhancingeffect.Different concentrations of methanol extract and essential oil from the aerial parts ofE.bungeishowed significant enhancing effect on transport of piroxicam in rat skin.The results showed that both of the essential oil and methanol extract in various concentration enhanced piroxicam absorption.The highest permeation rate was due to the highest concentration of the essential oil.It illustrated 9.17-fold increase in permeability coefficient of piroxicam [29].Another similar study demonstrated that essential oil fromE.caeruleumaerial parts enhanced permeation of piroxicam significantly through rat skin.The plant essential oil in 5 % w/v,showed 8.56-fold increase in permeability coefficient of piroxicam[28].
Nutrition values.Atomic absorption spectrometer analysis showed that theE.caeruleumleaf was a good source of various elements.The amount of iron was remarkably higher than other minerals (Fe >Zn >Mn >Cr >Cu) [36].Metinet al.analyzed the mineral content of 26 species of edible plant leaves in eastern Anatolia.Among themE.billardierihad the highest content of potassium.This study concluded that most of these plants had significant quantities of essential nutrients.Micro and macro mineral contents ofE.billardieriwere approximately in the middle of the rang contents of these 26 plants and also was higher than mineral content of eight selected cultivated vegetables[67].
Discussion
More than half of the 57 articles that were selected for this review,are related to recent years (2013-2018).It can show ever increasingly attention to medicinal plants for treatment or prevention of diseases in recent years.Enormous traditional and ethnobotanical uses ofEryngiumspecies have been reported in Persian medicine and other regions that require to be evaluated by clinical trials in humans and more new research.
Although several of these ethnobotanical and traditional properties have been confirmed with newin vivoandin vitrostudies such as anti-inflammatory,analgesic and antinociceptive activities,anti-scorpion,snake and venoms activities and antidiabetic effects.Some other reported traditional and ethnobotany activities could be related to proven compounds and activities of these plants including: 1.Antidote activities,treatment of liver diseases and poisonings that can be related to high antioxidant properties.2.Chop and break up calculus property and tissue sclerosis discutient activity that can be related to anticancer and cytotoxic effects.3.Elimination of spasmodic pain in the bowels and removing gripes and cramps,flatus discutient property,beneficial in pulmonary disease and halitosis that can be related to antibacterial and antifungal activities.4.Hormonal and sexual effects such as aphrodisiac and erectile activity,emmenogogue and galactogogue and treatment of infertility problems that can be related to phytosterols compositions.5.Treatment of anaemia that can be related to high nutritional value of theseEryngiumspecies.
According to presence of triterpen saponins especially olean-type saponins inEryngiumspecies,it can be concluded that several medicinal properties of this genus can be related to these components.It has been proven that,olean-type saponins which are glycosides of oleanolic acid found in food and medicinal plants have several biological and pharmacological importance.Recently,it was confirmed that oleanolic acid had antimicrobial and hepatoprotective power,anti-inflammatory and antipruritic activities,spasmolytic effect,anti-angiogenic property,antiallergic,antiviral,anti-tumor and cytotoxic effects,antihyperlipidemic,antioxidant,and anti-diabetic activities.These compounds also can increase the bioavailability of the active component of some pharmaceuticals.In addition to these compounds,the presence of flavonoid derivatives as well as essential oils in these plants are involved in their biological effects[68].
Although,up to date only a few studies have been done on the toxicity of the plants belonging to the genusEryngium,which can be cytotoxic especially at high doses.So it is necessary to carry out more toxicity studies before clinical trials assessments.Also,there is no clinical information about these beneficial effects.Investigation about the molecular mechanisms of chemicals isolated from theseEryngiumspecies that are responsible for various pharmacological effects such as cytotoxicity,anticancer activity,etc.,can lead to prospective drug development.
Therefore,recommend future studies which should be performed are: finding the exact mechanism of pharmacological effects ofEryngiumspecies that have been confirmed within vitrostudies,toxicity evaluation of the plant belonging to genusEryngium,clinical studies of the safety and efficacy ofEryngiumspecies,discovering safe doses that are most effective for clinical studies and ascertaining the possible interactions of the genusEryngiumwith foods.
Conclusion
Eryngiumgenus is one of the medicinal herbs mentioned in several Persian medicine references which its roots and aerial parts has various therapeutic properties as well as good nutritional values.Results acquired from the present review revealed thatEryngiumspecies were nutritional plants that were used worldwide as ethnobotanical remedies to manage a broad range of diseases and several of the various traditional and ethnobotany properties ofEryngiumgenus had been confirmed with newin vivoandin vitrostudies.
Considering enormous diversity of pharmacological effects of IranianEryngiumspecies as well as their large variety of phytochemical compounds,it can be concluded that these plants have immense potential for prospective preparation of herbal medicinal products and are good candidates for discovering new drugs in future.Especially considering notable anticancer and antioxidant properties ofEryngiumspecies,it can lead to further investigations for development of new anticancer drugs.
 Traditional Medicine Research2019年3期
Traditional Medicine Research2019年3期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Unveiling the book of Persian medicine-the official document of Persian medicine in Iran and delivering it to the WHO representative
- Annual advances of traditional medicine toxicity in 2018
- Leech therapy indications:a scoping review
- The potential role of grape (Vitis vinifera L.) in prevention of threatened abortion via immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory abilities:a hypothesis
- Digestion process and causes of indigestion based on Avicenna's view and modern medicine
- Application of herbal rectal suppositories beyond intestinal disorders in Persian medicine
