Efficacy and safety of atomized inhalation for Shuanghuanglian on chronic pharyngitis:a Meta-analysis of the randomized controlled trials
Jian Cheng, Ying Yu , Chang Yu, Lei Zhang
1Peking University of Shenzhen hospital, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
2Spleen-Stomach Diseases Institute,Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
3Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
4The second people's hospital of Guangdong, Guangzhou,Guangdong, China.
AbstractObjective: As a Chinese drugs preparation to clear heat and remove toxicity, Shuanghuanglian(SHL) has been widely used, but the clinical efficacy and safety of SHL on chronic pharyngitis remain unclear, especially the application of atomized inhalation of SHL need to be verified.The aim of this study was to evaluate its clinical efficacy and safety for chronic pharyngitis.Methods: From the Cochrane Library, Pubmed, EMbase, Wanfang Datebase, CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure), VIP (Chinese Scientifc Journals Database), CBM (Chinese Biomedicine Database), We got the qualified randomized controlled trials(RCTs) and adopted RevMan5.3 software and the risk of bias tool according to the Cochrane to perform a metaanalysis.Results: Ten RCTs, a total of 950 cases (involving 472 cases in SHL group and 478 in control group) were included. The results showed that the clinical efficacy in SHL group was superior to control group [Chi2=5.61, 95%CI (4.29, 11.43), P<0.05], and four literatures reported no obvious adverse reactions in SHL group. Conclusion: Application of atomized inhalation of SHL may have a potential advantage in treating chronic pharyngitis. However,due to the limitation of the quality and sample size of those studies, the accuracy of the result should be treated with caution, higher standardized researches are required to justify the conclusion.
Keywords: Shuanghuanglian, atomized inhalation, chronic pharyngitis, Meta-analysis
1 Introduction
Chronic pharyngitis is the inflammation of pharynx mucosa, submucosa and lymphatic tissue around the throat, which is usually manifested as feelings of dry,itchy, sore throat, or a foreign body sensation of pharynx.Medical studies have shown that morbidity of chronic pharyngitis among the adult population is nearly 20%[1], it is also very common in children[2-3]. With the continuous aggravation of environment and the changes of human living habits, the incidence of chronic pharyngitis is gradually increasing, which has brought a great influence on people's life and work.
There are varied factors that contribute to chronic pharyngitis, including upper respiratory tract diseases, adverse climate changes, speaking for a long time, or diseases in other systems of our body. By applying antibiotics or other drugs, keeping good habits, improving living standard, symptoms could turn to be better, however, to cure it completely and reduce the high frequency of relapses, no satisfactory results have been achieved so far. In such situations,therapy of traditional Chinese medicine have attracted the attention of clinicians and patients.
As one of the most commonly used Chinese drugs preparation, Shuanghuanglian(SHL) was composed of three medicinal herbs, namely honeysuckle,scutellaria and forsythia. It was regarded as an essential patent medicine in the emergency department of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) hospitals in 1992[4].Form then to now, it has been widely used to treat many diseases such as influenza [5], pneumonia [6],myocarditis [7], pancreatitis [8]. According to reports, it is effective in the treatment of both acute and chronic upper respiratory tract infection. However, following the medicine instructions, methods of administration for shuanghuanglian injection were intravenous injection, intravenous drip, and intramuscular injection,but atomized inhalation of SHL was used by many domestic clinicians in the treatment of respiratory diseases. An experimental study[9] has shown that,lung tissue of mice, who were taken Shuanghuanglian injection as an atomized inhalation, was obviously damaged. In addition, statistic data concluded by a large-sample literature suggested that the total incidence of adverse events was 3.25% in patients after treatment with SHL[10], this was contrary to the conclusion that there was no adverse reaction in many clinical controlled studies. In order to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and safety of atomized inhalation of SHL, such a method of administration for chronic pharyngitis, it is quite necessary to do a Meta-analysis.By searching several databases at home and abroad,we have found only one Meta-analysis [11] described the curative effect of atomized inhaling SHL in treatment of upper respiratory tract infection. Due to its involved diseases consisted of common cold,viral laryngitis, herpangina, pharyngoconjunctivitis,pharyngotonsillitis, and acute suppurative tonsillitis, the view that the clinical efficacy of SHL group was better than that of control group maybe in short of pertinence when referred to chronic pharyngitis. Therefore, in this study, took gentamicin atomized inhalation as a positive control drug, we conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of atomized inhalation of SHL on chronic pharyngitis, so as to provide references for clinical practice.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
(1)RCTs which compared atomized inhalation SHL to those with gentamycin alone or combined with other western medicine as atomized inhalation. (2)All patients in the included studies were diagnosed with chronic pharyngitis, the diagnostic criteria was made by Beijing People's Medical Publishing House in the “science of otolaryngology”[12]. (3)There was no limitation on outcome measures, and the judgement standard of clinical efficacy shoud be definite with reference to “Guiding principles for clinical research on new traditional Chinese medicines” [13] and “the evaluation criteria of the clinical efficacy in otorhinolaryngology diseaases”[14]. Studies of which diagnosis was unclear,improper intervention, not RCTs, repeated published were excluded.
2.2 Search strategy
We comprehensively retrieved the qualified RCTs from three English databases, namely, Cochrane Library,Pubmed, EMbase, and four Chinese databases involving Wanfang Datebase, CNKI, VIP, CBM. The retrieval time was from the establishment of each database to May 9, 2018. No language restrictions. The search terms were listed as follows, (“Shuanghuanglian injection” OR“Drugs, Chinese Herbal” “traditional Chinese medicine”OR “Chinese Herb” OR “Chinese Herbal Drugs” OR“herbs” OR “oriental medicine” OR “Herbal Drugs,Chinese” OR “QingRe” OR “QingReJieDu” OR“LiangXue”) AND (“Pharyngitis” OR “Pharyngitides”OR “sore throat” OR “sore throats” OR “throat, sore”),they were retrieved individually or combined both in Chinese and English in different databases. In order to search fully, appropriate adjustments were made in the retrieval process based on different databases.Supplemented by manual retrieval. Taking Pubmed database as an example, the retrieval strategy was as follows:
#1‘Pharyngitis'[Mesh]
#2‘Pharyngitides'OR‘sore throat'OR ‘sore throats'OR‘throat, sore'[Title/Abstract]
#3‘Shuanghuanglian injection'[Mesh terms]
#4‘Drugs, Chinese Herbal'OR ‘traditional Chinese medicine' OR‘Chinese Herb' OR‘Chinese Herbal Drugs'OR ‘herbs' OR ‘oriental medicine' OR ‘Herbal Drugs,Chinese' OR ‘QingRe' OR ‘QingReJieDu' OR ‘LiangXue'[Title/Abstract]
#5 #1or #2
#6 #3 or #4
#7 #5 and #6
2.3 Data extraction
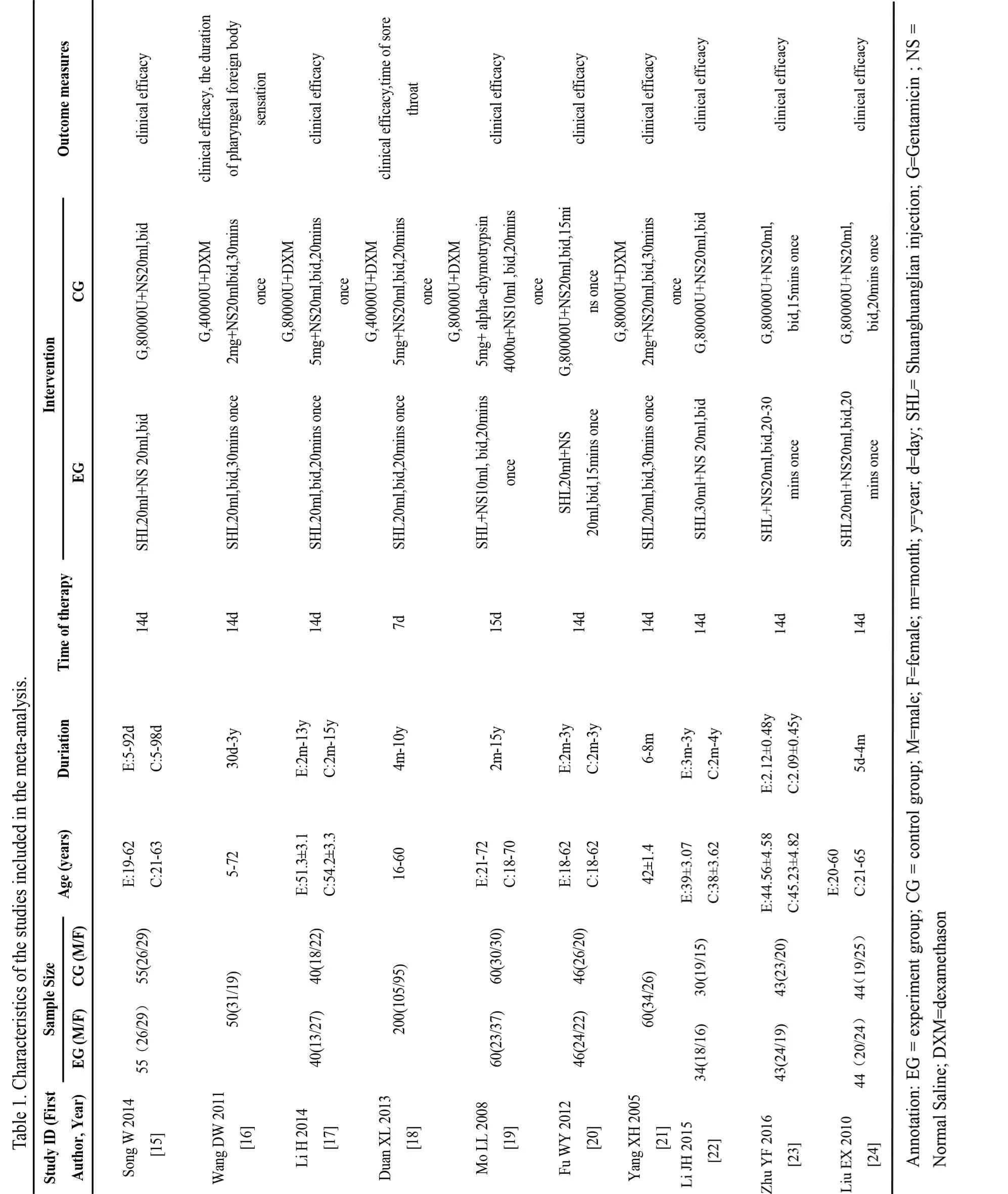
Two investigators (Ying Yu and Jian Cheng)independently screened eligible studies and extracted data from all included publications, including name of the first author, publication year, sample size, baseline characteristics (age, gender), course of disease, period of treatment, intervention, outcome measures, follow-up period and adverse reactions. After the two researchers extracted the data, then the third one (Lei Zhang) check the data again.
2.4 Quality assessment
We assessed the risks of all included studies by adoping bias risk assessment tools form Cochrane collaboration and Jadad scale. The main content of our assessment were selection bias, performance bias, detection bias,attrition bias, reporting bias, and other bias. Each item was judged as low/unclear/high risk of bias. In addition,Jadad scores were applied to appraise the quality of methodology in all trials, of which lower than 3 was considered as low quality literature, otherwise a high one.In case of disagreement, let the third investigators to judge.
2.5 Statistical analysis
RevMan5.3 software were applied to perform this metaanalysis. The enumeration data (clinical efficacy) was calculated with odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95%CI). Chi2-test and I2-test were used to evaluate the heterogeneity of each included study. If there existed statistical heterogeneity (P<0.05, I2>50%), a random-effect model was chosen, otherwise a fixed-effect model(P>0.05, I2<50%). In order to assess the potential sources of heterogeneity and the stability of results, this study conducted a sensitivity analysis by deleting the included study one by one.With a funnel plot, publication bias was evaluated.
3 Results
3.1 Study Selection
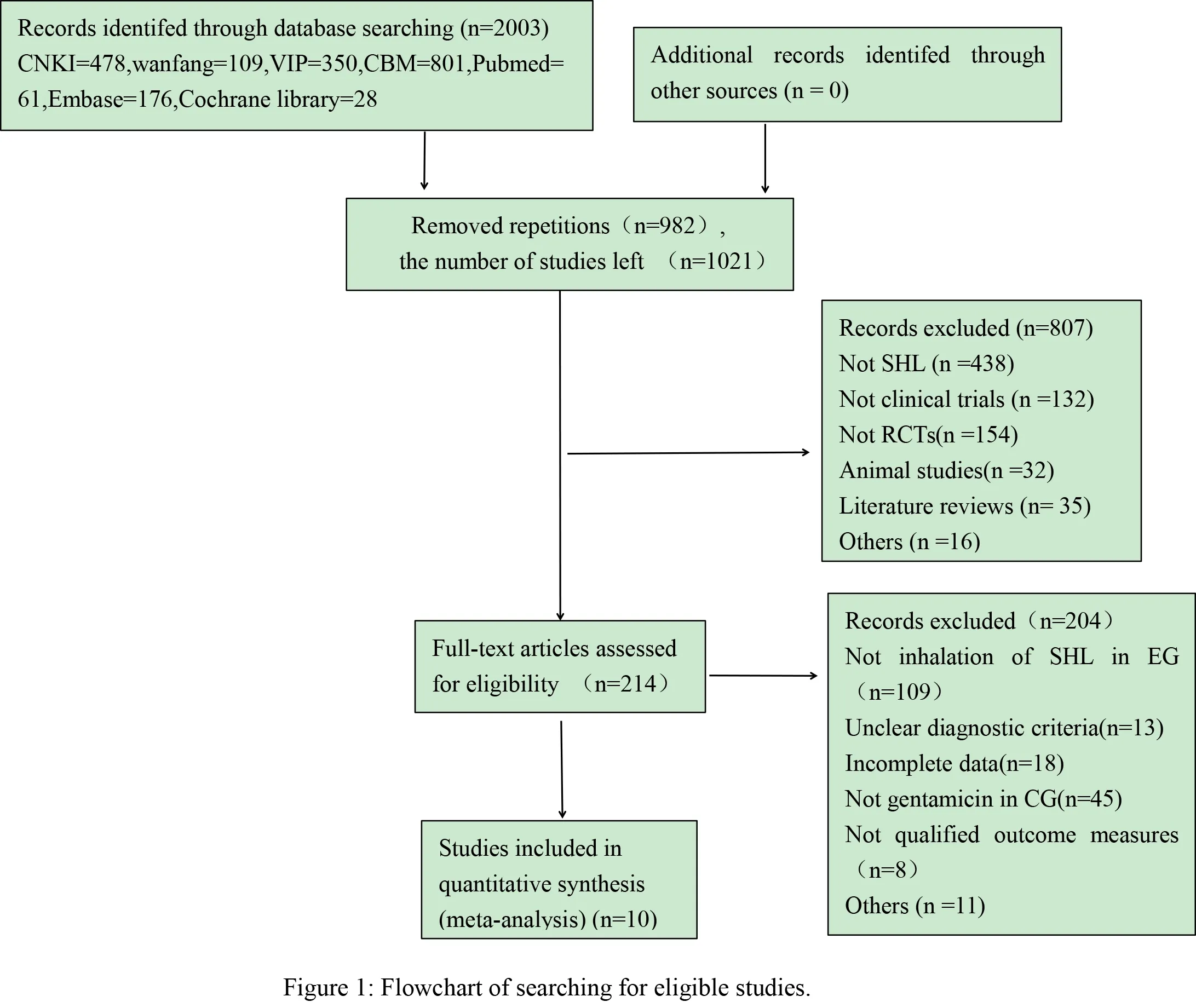
A total of 10 studies[15-24] were chosen from 2003 articles (478 from CNKI, 109 from Wanfang Datebase,350 from VIP, 801 from CBM, 176 from EmBase, 61 from Pubmed, 28 from Cochrane library), which met the inclusion criteria. The total number of 10 studies was 950, including 472 in SHL group and 478 in control group. All trials were single-center studies and patients were all Chinese. As seen in the table 1, the sample sizes ranged from 50[16] to 200[18], the ages of all patients were between 5 and 72 years old. The duration of illness was 5 days to 15 years and the course of treatment was from 7 days [18] to 15 days [19]. Clinical efficacy was recorded in each included study. The detailed process of literature screening, such as reasons and number of selection or deletion, were shown in figure 1, and characteristics of the documents included in the metaanalysis were shown in table 1.
3.2 Risk of Bias Assessment.
There was no difference at baseline between both experimental groups (EG) and control groups (CG)in all included studies. Random number table method was adopted in one article[22]; another one trial[23]performed sortition randomization method to generate random sequence; the remaining eight articles mentioned random only but did not describe the specific method[15-21,24]. Therefore, the evaluation of selective bias above two studies was defined as low risk, while the rest 8 studies was defined as unclear risk. None of included trials describe allocation concealment, led to unclear risks; and except one[23], which used double-blinding method, nine RCTs were accessed as unclear risks in performance bias and detection bias because of no mentioning blinding method. In addition, outcome datas were completely reported in each RCT, so attrition and reporting bias could be accessed as low risk. What'more,follow-ups were reported in three studies [16,19,21], and follow-up time was from one month to one year. Jadad score indicated that only one study was of high quality[23], whereas the rest were of low quality [15-22,24]. In conclusion, lack of more detailed description, result in the poor methodological quality of included literatures.The risk bias was shown in figure 2 (Figure 2a, Figure 2b). The methodological quality evaluation was shown in table 2.
3.3 Results of outcome measures
3.3.1 clinical efficacy
?
All of 10 RCTs, including 472 patients in EG and 478 in CG, compared the clinical efficacy in two groups.Considering the difference of western medicine in control group, a subgroup analysis was carried out. We divided all involving RCTs into two groups, which were using Gentamicin(G)+Dexamethasone(DXM) and Gentamicin alone as the drug of atomized inhalation.According to the meta-analysis, there was no obvious heterogeneity (Chi2=2.32, P>0.05, I2=0%) in the subgroup of SHL vs G. The result, analyzed by a fixed effect model, showed a statistical difference between the SHL group and Gentamicin group in improving the clinical effect[OR=9.58, 95%CI(4.79,19.15),Z=6.39,P<0.05]. As for the comparison of SHL to DXM+G,five trials[16,17,18,19,21] conducted a fixed effect model to conclude a remarkable curative effect in SHL group[OR=4.91, 95%CI(2.43,9.91),Z=4.44, P<0.05]. Due to its good homogeneity (I2=43.4%) between two subgroups, we also performed the fixed effect model to evaluate the results of overall clinical efficacy among all literatures, it revealed that the therapeutic effects of SHL was superior to both DXM+G and G in alleviating the symptoms, with statistical significance[OR=7.00, 95%CI(4.29,11.43),Z=7.79, P<0.05](Figure 3). Because of good homogeneity in this evaluation system, a sensitivity analysis was not needed.The funnel plot was symmetrical visually, which could be considered no potential publication bias (Figure 4).
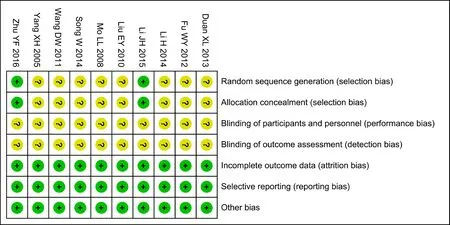
Figure 2a. Risk of bias graph
3.3.2 other outcome measures
One study[16] reported the duration of pharyngeal foreign body sensation in two groups after treatment,ninety-two percent of patients whose symptoms
disappeared within 10 days in EG, while fifty-two percent of that in CG. The other one trial[18] described the time of a sore throat after treatment, an average of 3 days in CG compared with 1.5 days in EG. There was too few literatures record above outcome measures to perfome a forest graph, so we only gave a description of them.
3.4 Adverse events
Among all of included RCTs, four[15, 17,18,19]mentioned adverse reactions, and they recorded no adverse events during the treatment process and after treatment.
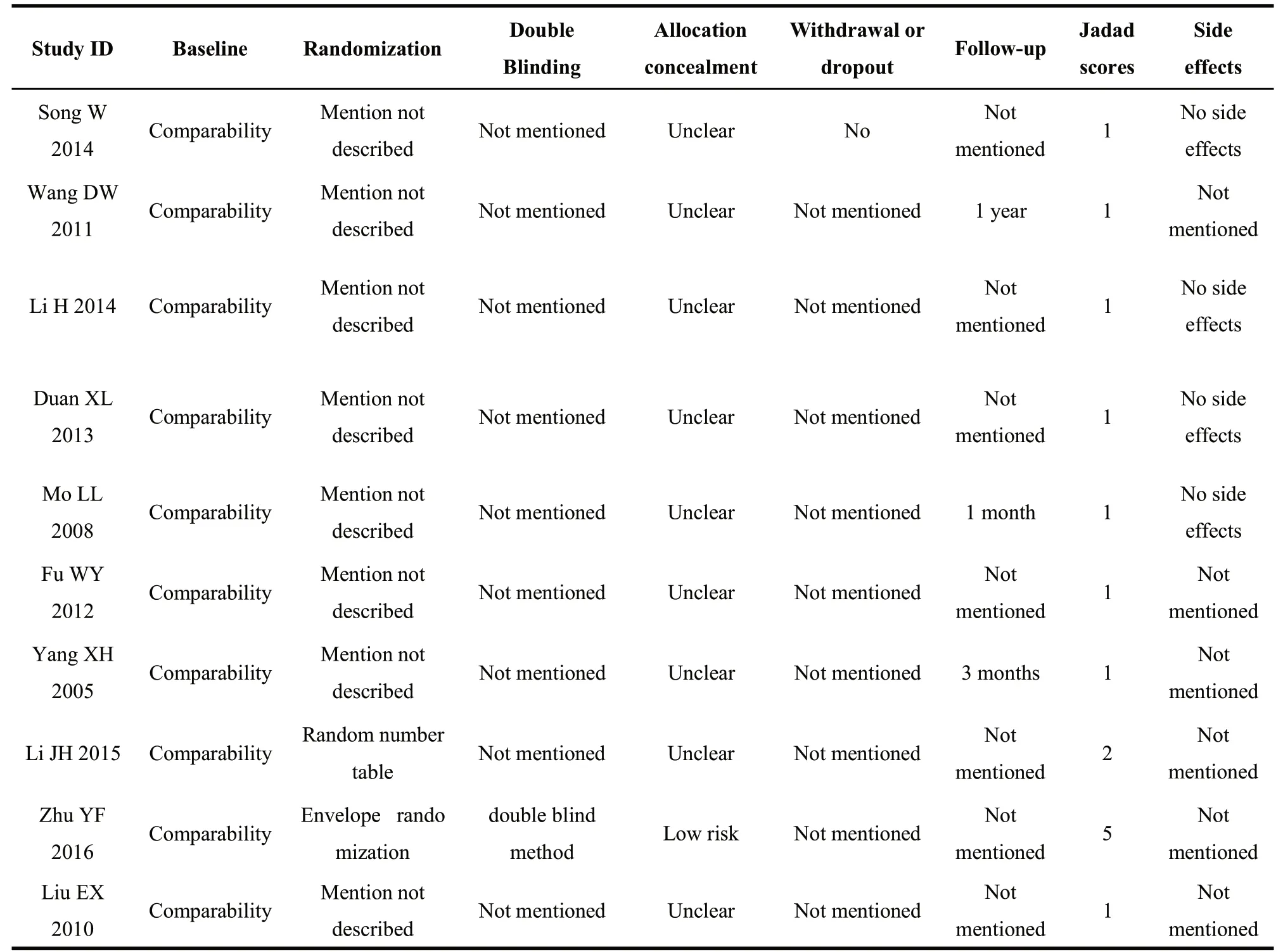
Table2. Assessment of methodological quality of the qualified studies
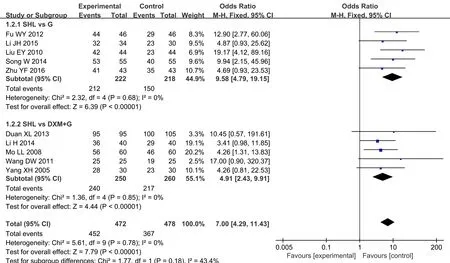
Figure 3. Forest plot of clinical efficacy (a fixed effect model)
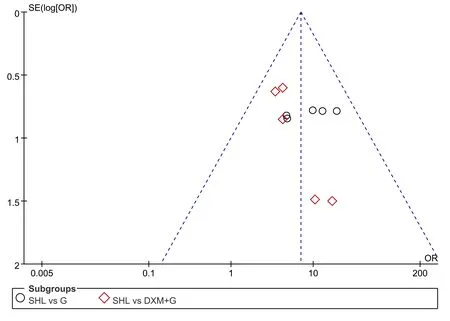
Figure4. Funnel plot of clinical efficacy
4 Discussion
Compared with atomized inhalation of both Gentamicin+Dexamethasone group and Gentamicin group, the results of this meta-analysis indicated that the overall clinical curative effect of atomized inhalation Shuanghuanglian is more significant[OR=7.00,95%CI(4.29,11.43),Z=7.79, P<0.05]. Specifically,the clinical manifestations, such as swelling, pain, dryness and foreign body sensation in throat, were improved statistically. What's more, symptoms of lymphoid follicles, congestion, herpes in the wall of the throat were relieved. No obvious adverse reactions were reported in four articles[15, 17-19], but in view of the small number of literatures, the safety of of atomized inhalation of ShuangHuangLian remains to be confirmed.
The causes of chronic pharyngitis are complex and varied. Recurrent attacks of acute pharyngitis is a major facter, other reasons involves environmental factors(temperature, humidity, dust and harmful gas, etc.),dietary factors (alcohol, tobacco, spicy foods, etc.),occupational factors (teachers, radio announcer, singers,etc.), physical factors (heredity, allergic constitution,etc.), systemic disorder (anemia, immune dysfunction,indigestion, gastroesophageal reflux, heart disease,etc.). Those complicated causes of chronic pharyngitis resulted in difficulties of clinical treatment. In addition to improving symptoms, doctors still need to control multiple kinds of pathogenic factors. Antibiotics are the effective drugs for controling acute episodes of chronic pharyngitis, but it can't solve the problem of its high relapses rate. More seriously, the side effects of antibiotics are unavoidable in many cases. Gentamycin,a kind of aminoglycoside antibiotic drug to bacterial infection, is a very common antibiotics used for treating chronic pharyngitis, however, it is easy to generate drug resistance. Furthermore, side effects such as hearing loss,damages on liver and kidney, are not unusual in clinical cases. A large number of clinical and pharmacological studies have confirmed that SHL is safe and effective in the treatment of chronic pharyngitis. Comprised of honeysuckle, scutellaria and forsythia, SHL has certain effects on both bacteria and viruses [25-26] and can improve the immune function of the body [27-28].Chlorogenic acid, which is the most abundant ingredient in honeysuckle, is a kind of biological active substance with important functions such as antibacterial, antivirus, improving white blood cells and mopping up free radicals[29-33]. Effects of suppressing respiratory virus involves coxsackie B3, syncytial virus, adenovirus type
3, adenovirus type 7 have been proved to be significant.
Furthermore, it has a strong inhibitory effect on staphylococcus aureus, beta streptococcus, escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, candida albicans, klebsiella pneumoniae, form a conclusion, it is effective for both gram-positive and negative bacteria. Moreover, loganin,lonicerin D, which are the medicinal components of honeysuckle, have the same anti-inflammatory fuction similar to aspirin[34-35]. Degradation of baicalin and flavone in radix scutellariae possess the antiinflammatory and antipyretic effect[36], and they can inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and chlamydia by restraining the activity of ATP synthetase, microbial membrane formation, or the expression of some proteins[37-39].Besides, there are also many studies on forsythia and its pharmacological components in antibacterial and antiviral effects. It has been shown to resisit oxidative damage of mitochondria, protect the liver, regulate the system of immunity, and some other functions[40-45].In conclusion, the pharmacological effects of shuanghuanglian have already been proved effective, SHL play a remarkable role in inflammatory diseases, especially for chronic pharyngitis.
In the clinical practice of chronic pharyngitis,commonly used preparation types of SHL are tablets,oral liquid, granules, intravenous injection. In this paper,we focus on the method of administration of atomized inhalation, which refers that medicine is dispersed into tiny droplets or particles in the gas by the application of ultrasonic sound energy or compression pump, then tiny droplets or particles are exported in the form of aerosol in a special atomization device, so the medicine is inhaled into respiratory tract along with breathing air. Because of its large contact surface with airway, the form of aerosol is more advantageous for drug acting on mucosal epithelial cells. In addition, compared with oral method,the atomized inhalation of SHL actes directly on the lesion site with a smaller dosage and less side effects.Through the breathing way, it could reach a much higher drug concentration in a short time. And besides that,patients need to do nothing but only to breath, which is of great convenience and curative effect. It is especially suitable for those patients who have difficulties in swallowing normally or cannot cooperate to take oral medicines. Therefore, more and more attention has been paid to the treatment of atomized inhalation of SHL in patients with chronic pharyngitis.
In this study, the efficacy and safety of shuanghuanglian atomizer for chronic pharyngitis was the first time to be confirmed by such a meta-analysis, which may provided some evidence for clinical doctors. However, it still had the following drawbacks: (1) There was only one measure, that was clinical efficacy, to evaluate outcome in most of our documents included, which might be not comprehensive enough, so we should take the number of outcome indicators into consideration in future studies; (2) The poor quality of methodology in this meta-analysis plays an important role when compare the effectiveness of SHL between two groups. Nine of ten literatures did not mention double-blinding and allocation concealment, easily resulted in performance bias and detection bias. Furthermore, except for two, the remaining eight RCTs only mentioned randomization but did not describe the generation of random sequence,and the description of adverse reactions was not comprehensive enough. Due to the lack of more details of information, we could not judge whether there were publication bias or other bias. Based on Jadad scores and risks of bias assessment, we held the view that the methodological quality of the meta-analysis evaluation system was generally poor; (3) The subjects included in this study were all Chinese people, and the samples were all from their own local hospitals. Due to ethnic and geographical diversity, there may be differences in the severity and pathological types of chronic pharyngitis caused by their various lifestyles and environment. Hence,when refer to popularizing the conclution of atomized inhalation of SHL in this paper to the world population,it needs further studies to confirm; (4)Chronic pharyngitis is a kind of chronic disease that is easy to relapse and difficult to cure. Therefore, the follow-up time after treatment should be long enough to evaluate its long-term clinical efficacy. But only three of all the trials documented the follow-up, and time of follow-up was from a month to a year. Too few follow-up records could bring about an effect on the overall assessment of its clinical efficacy. (5) With the widespread use of SHL,many documents have been published on the research of adverse reactions of SHL, there was a study[10]which summarized adverse drug reaction of SHL in 2799 cases from 452 articles by searching China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Chinese Scientifc Journals Database, Chinese Biomedicine Database in recent 20 years, then the total incidence of adverse drug reaction was calculated as 3.25%. Whereas, it was reported no adverse reaction in this paper, which was inconsistent with the above statement of 3.25%. Maybe because of lacking literatures documenting on the adverse drug reactions in those involving studies, it was necessary to expand the sample size to vatify its safety.
5 Conclusion
The evaluation of the system has shown that atomized inhalation of SHL may has a promising application for treating chronic angelitis. However, due to the limitation of methodological quality and the insufficient sample size, the clinical efficacy and safety of it cannot be confirmed fully, what'more, the accuracy of the result should be treated with caution.
Authors’Contributions
Ying Yu conceived and designed this experiment. Jian Cheng and Chang Yu performed the search. Lei Zhang analyzed the data. Ying Yu recheck the data and results.Jian Cheng wrote the paper. All authors offer to help when reparing submission materials.
- Medical Data Mining的其它文章
- Reanalysis of Lymph node metastasis as predictor of the survival of patients with follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma: From SEER database 2004-2014
- Heating infusion for gastrointestinal complications in patients with enteral nutrition: A meta-analysis
- Literature Research on Drug Use Regulation of Miao Medicine in Suppression of Gastric Cancer
- Clinical Medicine Characteristics Study of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of cancer pain based on Data Mining

